当前位置:网站首页>使用Keras和LSTM实现对于长期趋势记忆的时间序列预测-LSTNet
使用Keras和LSTM实现对于长期趋势记忆的时间序列预测-LSTNet
2022-07-24 05:21:00 【一只小EZ】
各位好,好久不见。我终于忙完论文和答辩啦。
今天我们来实现长期趋势的多维度时间序列预测
同时会提供一个完整的预测流程以及相关的评价指标,用于评价预测精确度。
算法来源于一篇经典的论文LSTNet,相关的介绍可以见 LSTNet详解-知乎
开源代码来源于 LSTNet_keras ,做了替换数据集和简化处理。’
LSTNet是一个专门为多变量时间序列预测所建立的模型,在交通流量,电力消耗和汇率等数据上进行了实验,取得了不错的结果。发表于2018年的ACM SIGIR会议上。
数据介绍
该数据集是一个污染数据集,我们需要用该多维时间序列去预测pollution这个维度,采用80%作为训练集,20%作为测试集。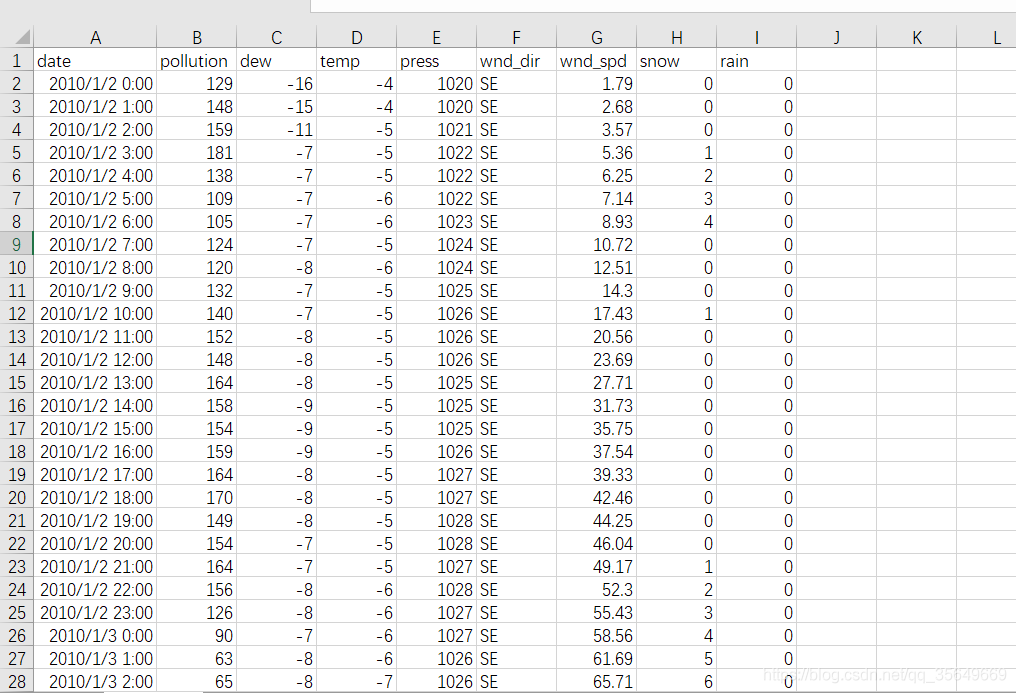
pollution数据趋势如下: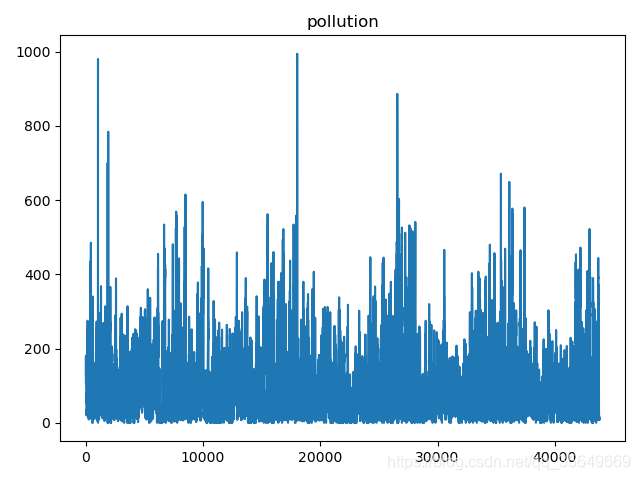
模型介绍
LSTNet的网络结构如图所示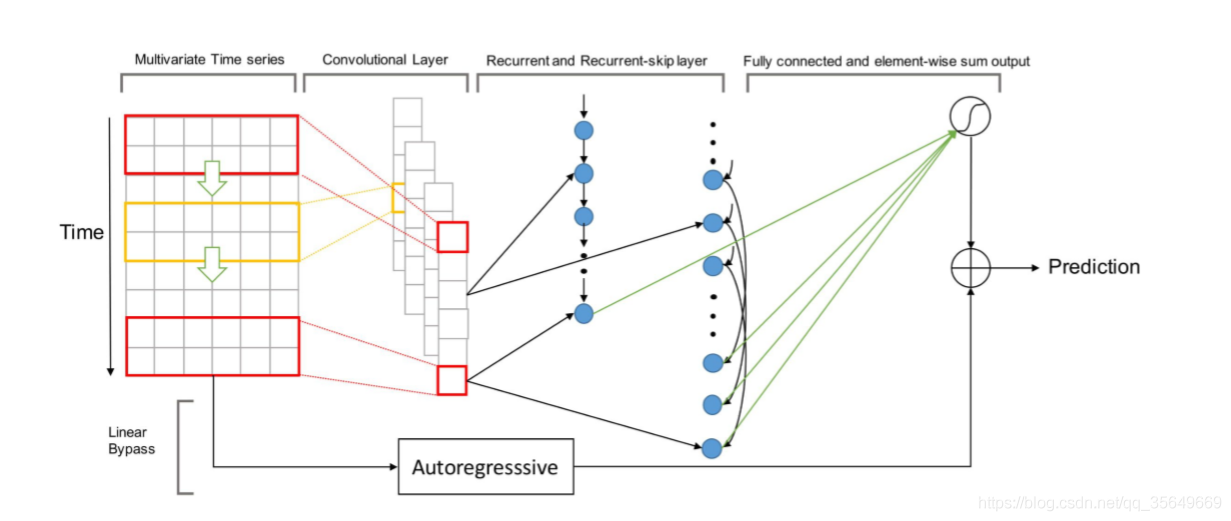
我们可以看到使用了一个卷积层 两层循环神经网络(论文中使用了RNN或GRU,本文中使用了LSTM),可以看到第二层图上实现了一个称为"跳过层"的结构,用于实现对于非常长期趋势的记忆。但是其实是进行了数据变换而非LSTM结构的更改。
对于跳过层,例如输入数据[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12],会进行一系列的数据变换变换为
[[1,7] , [2,8] , [3,9] , [4,10] , [5,11] , [6,12]],然后输入到LSTM之中,实现对于长期趋势的记忆。之后综合两层LSTM的结果,输入到全连接层之中。
对于Autogressive,是使用了全连接层模拟的自回归机制,会截取进几个时间步的数据,输入到全连接层的机制。得到结果。论文中称为"为模型添加了线性成分",实际在预测某些峰值时有很好的效果。
模型实现
对于原模型而言 对于第二个跳过层的实现需要大量的数据切片,会非常耗时
但是本文参考了LSTNet_keras 将输入分解为(1)短期时间序列,如(t-3, t-2, t-1, t)和(2)长期跳跃时间序列,如(t-2xskip, t-skip, t)。结果和原来的一样好,但是快得多。
数据构造
数据构造采用了如下的代码,具体如何使用见文末的github源代码
def create_dataset(dataset, look_back,skip):
''' 对数据进行处理 '''
dataX,dataX2,dataY = [],[],[]
#len(dataset)-1 不必要 但是可以避免某些状况下的bug
for i in range(look_back*skip,len(dataset)-1):
dataX.append(dataset[(i-look_back):i,:])
dataY.append(dataset[i, :])
temp=[]
for j in range(i-look_back*skip,i,skip):
temp.append(dataset[j,:])
dataX2.append(temp)
TrainX = np.array(dataX)
TrainX2 = np.array(dataX2)
TrainY = np.array(dataY)
return TrainX, TrainX2 , TrainY
模型代码
对于初始的LSTNet而言,只使用单个一维卷积对于数据进行处理,之后再进行数据变换。但是对于本简化版而言,在构造数据时进行了数据变换。所以需要两个一维卷积,然后对他们赋予了相同的权重。
模型中的z指的是AR模型的实现
def LSTNet(trainX1,trainX2,trainY,config):
input1 = Input(shape=(trainX1.shape[1], trainX1.shape[2]))
conv1 = Conv1D(filters=48, kernel_size=6, strides=1, activation='relu') # for input1
# It's a probelm that I can't find any way to use the same Conv1D layer to train the two inputs,
conv2 = Conv1D(filters=48, kernel_size=6 , strides=1, activation='relu') # for input2
conv2.set_weights(conv1.get_weights()) # at least use same weight
conv1out = conv1(input1)
lstm1out = CuDNNLSTM(64)(conv1out)
lstm1out = Dropout(config.dropout)(lstm1out)
input2 = Input(shape=(trainX2.shape[1], trainX2.shape[2]))
conv2out = conv2(input2)
lstm2out = CuDNNLSTM(64)(conv2out)
lstm2out = Dropout(config.dropout)(lstm2out)
lstm_out = concatenate([lstm1out,lstm2out])
output = Dense(trainY.shape[1])(lstm_out)
#highway 使用Dense模拟AR自回归过程,为预测添加线性成份,同时使输出可以响应输入的尺度变化。
highway_window = config.highway_window
#截取近3个窗口的时间维 保留了所有的输入维度
z = Lambda(lambda k: k[:, -highway_window:, :])(input1)
z = Lambda(lambda k: K.permute_dimensions(k, (0, 2, 1)))(z)
z = Lambda(lambda k: K.reshape(k, (-1, highway_window*trainX1.shape[2])))(z)
z = Dense(trainY.shape[1])(z)
output = add([output,z])
output = Activation('sigmoid')(output)
model = Model(inputs=[input1,input2], outputs=output)
return model
模型结构如图,
进行预测
我们选取前80%的数据进行训练,后20%的数据进行预测,预测下一时刻的pollution数据。
data = pd.read_csv("./pollution.csv")
#注:为了演示方便故不使用wnd_dir,其实可以通过代码将其转换为数字序列
data = data.drop(['wnd_dir'], axis = 1)
data = data.iloc[:int(0.8*data.shape[0]),:]
print("长度为",data.shape[0])
评价指标
选取的评价指标为RMSE,MAE,MAPE
import numpy as np
from sklearn import metrics
def GetRMSE(y_hat,y_test):
sum = np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_hat))
return sum
def GetMAE(y_hat,y_test):
sum = metrics.mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_hat)
return sum
def GetMAPE(y_hat,y_test):
sum = np.mean(np.abs((y_hat - y_test) / y_test)) * 100
return sum
预测结果:

由于y_test有为0的元素,所以我们将其删除再求MAPE
得到结果如下:
RMSE为 26.184022062997542
MAE为 13.882745963353731
MAPE为 22.928112428670353
总结
在本博客中,提供了一套完整的建模-预测-评价方法,是现成可用的
实现了一种对于长期趋势记忆的方法
预测精度仍然有进步空间(有许多原因,笔者在大量数据上使用该方法预测效果很好)
注:
环境: Keras 2.2 & Tensorflow 1.13.1
代码已上传到我的github
如果觉得不错的话可以去github点个星星(看在我租服务器跑实验的份上)
参考:
LSTNet_keras
LSTNet
边栏推荐
- 世界坐标系、相机坐标系和图像坐标系的转换
- Chapter III summary of linear model
- [MYCAT] MYCAT configuration file
- [activiti] gateway
- In GCC__ attribute__ ((constructor) and__ attribute__ ((destructor)).
- Openwrt quick configuration Samba
- JDBC初级学习 ------(师承尚硅谷)
- Machine learning (Zhou Zhihua) Chapter 4 notes on learning experience of decision tree
- Statistical learning methods (2nd Edition) Li Hang Chapter 22 summary of unsupervised learning methods mind mapping notes
- Qt新手入门级 计算器加、减、乘、除、应用
猜你喜欢
![[MYCAT] MYCAT installation](/img/52/2f77ed64b2ed4e9297acaa8362e194.png)
[MYCAT] MYCAT installation

Jestson installs IBus input method

Sequential stack C language stack entry and exit traversal
![[MYCAT] Introduction to MYCAT](/img/26/8911fe9e1fb104d7185dda0881804b.png)
[MYCAT] Introduction to MYCAT

JVM系统学习
![[activiti] gateway](/img/8c/c89ec6c4c5871a32218ddadfd8beba.png)
[activiti] gateway

Answers and analysis of some after-school exercises in signals and systems (Wujing)

‘Results do not correspond to current coco set‘
MySql下载,及安装环境设置
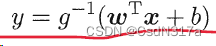
Chapter III summary of linear model
随机推荐
day4-jvm
day3-jvm+排序总结
[USB host] stm32h7 cubemx porting USB host with FreeRTOS to read USB disk, usbh_ Process_ The OS is stuck. There is a value of 0xa5a5a5
Qt 使用纯代码画图异常
头歌 平台作业
day2-WebSocket+排序
The kernel apps to have died. it will restart automatically
JVM系统学习
C语言链表(创建、遍历、释放、查找、删除、插入一个节点、排序,逆序)
Qt新建工程简介
Search of two-dimensional array of "sword finger offer" C language version
Typora installation package in November 2021, the last free version of the installation package to download v13.6.1
Accurate calculation of time delay detailed explanation of VxWorks timestamp
How to solve the problem of large distribution gap between training set and test set
day6-jvm
"Statistical learning methods (2nd Edition)" Li Hang Chapter 14 clustering method mind map notes and after-school exercise answers (detailed steps) K-means hierarchical clustering Chapter 14
[principles of database system] Chapter 5 algebra and logic query language: package, extension operator, relational logic, relational algebra and datalog
【深度学习】手写神经网络模型保存
Common features of ES6
Common methods of array