当前位置:网站首页>What are the problems with traditional IO? Why is zero copy introduced?
What are the problems with traditional IO? Why is zero copy introduced?
2022-06-25 07:49:00 【Zhan sir (open source byte)】
Conventional IO What are the problems ? Why zero copy ?
If the server wants to provide the function of file transfer , The simplest way we can think of is : Read out the files on the disk , And then send it to the client through the network protocol .
Tradition I/O The way we work is , Data read and write are copied back and forth from user space to kernel space , And the kernel space data is through the operating system level I/O Interface to read or write from disk .
The code is usually as follows , Generally, two system calls are required :
read(file, tmp_buf, len); write(socket, tmp_buf, len);
The code is simple , Although only two lines of code , But there's a lot going on here .

First , A total of 4 Context switch between secondary user mode and kernel mode , Because there were two system calls , Once it was read() , Once it was write(), Every system call must first switch from user mode to kernel mode , After the kernel completes its task , Then switch from kernel mode to user mode .
The cost of context switching is not small , A switch takes tens of nanoseconds to microseconds , Although the time seems short , But in a high concurrency scenario , This kind of time is easy to accumulate and amplify , This will affect the performance of the system .
secondly , It also happened 4 Secondary data copy , among Twice DMA A copy of the , in addition Twice through CPU Copy Of , Let's talk about the process :
- The first copy , Copy the data on the disk into the buffer of the operating system kernel , The process of copying is through DMA Carrying .
- Second copy , Copy the data from the kernel buffer to the user's buffer , So our application can use this data , This copy to process is done by CPU Accomplished .
- The third copy , Just copy the data to the user's buffer , And then copy it to the kernel socket In the buffer of , The process is still by CPU Carrying .
- The fourth copy , Put the kernel of socket Data in the buffer , Copy to the network card buffer , This process is again caused by DMA Carrying .
Let's go back to the file transfer process , We're just carrying a piece of data , It turned out to be carrying 4 Time , Too many copies of data will no doubt consume CPU resources , Greatly reduces system performance .
This simple and traditional way of file transfer , There are redundant handoffs and data copies , It's very bad in a highly concurrent system , A lot of unnecessary expenses , Will seriously affect system performance .
therefore , To improve the performance of file transfer , You need to reduce 「 Context switch between user mode and kernel mode 」 and 「 Memory copy 」 The number of times .
If you reprint , Please indicate the source : Open source byte https://sourcebyte.cn/article/169.html
边栏推荐
- Four software 2021-10-14 suitable for beginners to draw PCB
- PCB board design - automatic layout 2021-10-15
- AttributeError: ‘Upsample‘ object has no attribute ‘recompute_ scale_ factor‘
- Understand the reasons for impedance matching of PCB circuit board 2021-10-07
- Insert and sort the linked list [dummy unified operation + broken chain core - passive node]
- Different paths ii[dynamic planning improvement for DFS]
- 神经网络与深度学习-3- 机器学习简单示例-PyTorch
- [QT] shortcut key
- 单位转换-毫米转像素-像素转毫米
- Usememo simulation usecallback
猜你喜欢

Fairmot yolov5s to onnx

饮食干预减轻癌症治疗相关症状和毒性

消息中间件之ActiveMQ的基本使用

微信小程序开通客服消息功能开发

Manufacturing process of PCB 2021-10-11

差点被这波Handler 面试连环炮带走~

How to use ad wiring for PCB design?
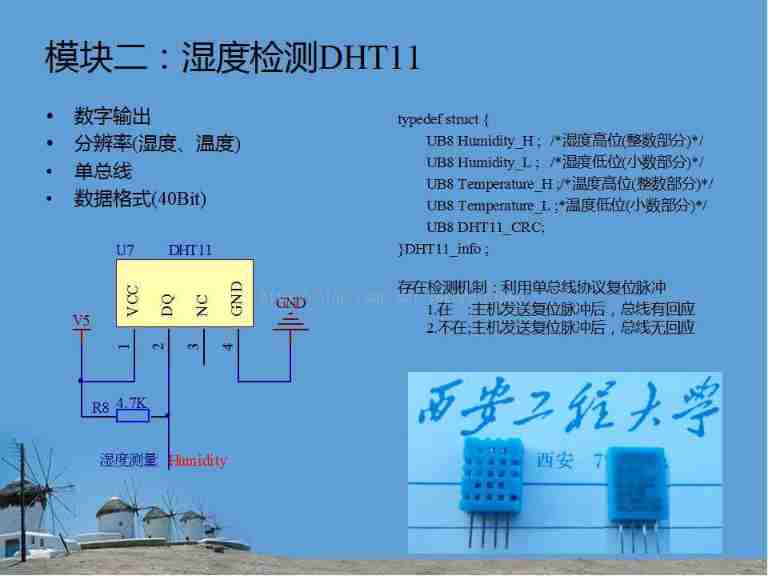
Home environment monitoring system design (PC version) (mobile app version to be determined)

SCM Project Training

OpenCV每日函数 结构分析和形状描述符(8) fitLine函数 拟合直线
随机推荐
Find out what informatization is, and let enterprises embark on the right path of transformation and upgrading
【蒸馏】PointDistiller: Structured Knowledge DistillationTowards Efficient and Compact 3D Detection
NPM install reports an error: gyp err! configure error
SSL证书免费获取教程
Summary of small problems in smartbugs installation
Requirements for Power PCB circuit board design 2021-11-09
Chuantu microelectronics ca-if1051 can-fd transceiver
test
Collection of common terms and meanings in forestry investigation based on lidar
CPDA | how to start the growth path of data analysts?
Microsoft Office Word 远程命令执行漏洞(CVE-2022-30190)分析与利用
基于STM32MP157调试MIPI-DSI屏幕
PCB board design - automatic layout 2021-10-15
对链表进行插入排序[dummy统一操作+断链核心--被动节点]
基于激光雷达的林业调查常用术语及含义锦集
C#中如何调整图像大小
C reads XML on the web
Mysql面试-执行sql响应比较慢,排查思路。
Construction of occupancy grid map
Sichuan earth microelectronics ca-is1300 isolated operational amplifier for current detection is on the market