当前位置:网站首页>Add and multiply two polynomials using linked list
Add and multiply two polynomials using linked list
2022-06-23 05:58:00 【Octopus bro】
The design function calculates the product and sum of two univariate polynomials .
Input format :
Enter the score 2 That's ok , Each line gives the number of nonzero terms of the polynomial , Then input a non-zero coefficient and index of polynomial in exponential descending way ( The absolute values are not more than 1000 The integer of ). Numbers are separated by spaces .
Output format :
Output points 2 That's ok , The product polynomials and the coefficients and exponents of nonzero terms of the sum polynomials are output in exponential descending mode respectively . Numbers are separated by spaces , But no extra space at the end . Zero polynomials should output 0 0.
sample input :
4 3 4 -5 2 6 1 -2 0
3 5 20 -7 4 3 1
sample output :
15 24 -25 22 30 21 -10 20 -21 8 35 6 -33 5 14 4 -15 3 18 2 -6 1
5 20 -4 4 -5 2 9 1 -2 0
To implement this program , Here are a few steps :
1. Read in polynomials 1
2. Read in polynomials 2
3. Do addition calculation
4. Realize multiplication calculation
5. Output the multiplication result
6. Output the addition calculation result
1. Consider how to read polynomials
Before that, we need to determine the structure of the linked list nodes
Need to have coef Store the coefficients of a polynomial
Need to have expon Store the exponent of a polynomial
Need to have link Store the address of the next node
Therefore, the data type is constructed
typedef struct PolyNode * Polynomial;
struct PolyNode{
int coef;
int expon;
Polynomial link;
};
Based on this data structure , Construct a linked list , Use the tail insertion method , So you need a tail pointer , If there is no tail pointer , Each time a node is added to the linked list , All need to traverse from scratch .
At the same time, consider another question , When inserting a node to the end of the linked list , If the list is empty , Then apply for a new node to be inserted into the current location , At the same time, let the tail pointer point to the node ;
If the list is not empty , You need to apply for a node to be inserted behind the current location , Therefore, you need to determine whether it is empty when inserting .
For unified operation , We can apply for a leading node linked list , In this way, the tail node is inserted every time when inserting , Unified operation , Of course , After reading the linked list, you need free U-turn node .
Here is the insert node Attach Functions and read polynomials ReadPoly function :
void Attach(int c, int e, Polynomial * rear)// Insert node operation
{
Polynomial input = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
// Apply for a new node and assign an initial value
input->coef = c;
input->expon = e;
input->link = NULL;
(*rear)->link = input;
*rear = input; // Modify the end pointer , Because it is to modify the pointer , Therefore, the pointer of the pointer is used here
}
Polynomial ReadPoly()
{
Polynomial P1, rear, t;
int N;// Number of polynomial terms
int c,e;// Used to temporarily store coefficients and indices
P1 = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));// Application header node
// The application header node is for convenience Attach Function time , Don't differentiate rear Is it empty or not , With the header, all nodes are non empty , Easy to insert
P1->link = NULL;
rear = P1;// The tail pointer points to the head node
scanf("%d",&N);
while(N--)
{
scanf("%d %d",&c, &e);
Attach(c, e, &rear);
}
t = P1;
P1 = P1->link;
free(t);// Mission completion for easy insertion of header node , Release the head node
return P1;
}First, pass in two polynomial linked lists , Apply for a linked list to store the result of addition , Take out the nodes of two polynomials in turn
If the exponents are equal, they are added , The result is zero , Release the node , If it is not zero, the application node stores the addition result in the node , And insert the nodes into the sum polynomial ;
If it's not equal , Then insert the node with large exponent into the sum polynomial .
After a linked list is calculated, if another linked list has nodes , Then all the remaining nodes are inserted into the sum polynomial
The following is the addition function :
Polynomial AddPoly(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2)
{
Polynomial t1,t2,rear,t;
t1 = P1;
t2 = P2;
Polynomial P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
rear = P;
while(t1 && t2)
{
if(t1->expon == t2->expon)// If the exponents are the same, add them
{
if(t1->coef + t2->coef)// If the coefficients do not add up to zero , Then add the calculation results to P in
{
Attach(t1->coef + t2->coef, t1->expon, &rear);
}
t1 = t1->link;
t2 = t2->link;
}
else if(t1->expon > t2->expon)// Find the one with a large index and add it to P in
{
Attach(t1->coef, t1->expon, &rear);
t1 = t1->link;
}
else
{
Attach(t2->coef, t2->expon, &rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
}
while(t1)// If t1 There are also redundant nodes , Then continue to join
{
Attach(t1->coef, t1->expon, &rear);
t1 = t1->link;
}
while(t2)// If t2 There are also redundant nodes , Then continue to join
{
Attach(t2->coef, t2->expon, &rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
t = P;
P = P->link;
free(t);// Release the head node
return P;
}3. Consider how to multiply polynomials
There are two ways to multiply :
1. Multiply the first term of the first polynomial by the second polynomial , Generate a polynomial , Take this generated polynomial as the basic , Then multiply the second term of the first polynomial by each term of the second polynomial , For each item generated , Insert the result into the previously generated polynomial .( Equivalent to insert item )
2. Multiply each term of the first polynomial by the second polynomial , Generate one polynomial at a time , Add these polynomials together to get the result .( It is equivalent to the sum of several polynomials )
The first method is used here :
First, multiply the first term of the first polynomial by the second polynomial to generate a basic polynomial , Because every item generated in the future will be inserted , The insertion operation needs to know the node before the insertion position , So every time we judge
" Tail pointer ->link" Whether it is related to the product term obtained :
First, move the tail pointer to the previous term that is not greater than the product term exponent
if “ Tail pointer ->link-> Index ” Same as product term index , Then add , If zero , Delete node ; Otherwise, modify the node .
Otherwise, it would be “ Tail pointer ->link-> Index ” < Product term exponent , Then insert the product term after the tail pointer .
The following is the multiplication function :
Polynomial MultyPoly(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2)
{
Polynomial P, t1, t2, t, rear;
int c, e;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
t1 = P1;
t2 = P2;
rear = P;
if(!t1 || !t2)// If a polynomial is empty , Then the multiplication result is null
return NULL;
while(t2)// First use P1 The first term of times P2 Generate a polynomial to insert
{
c = t1->coef * t2->coef;
e = t1->expon + t2->expon;
Attach(c, e, &rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
t1 = t1->link;//t1 Point to the second item
while(t1)
{
t2 = P2;// Re point the pointer to P2 The beginning of
rear = P;// Used to find a suitable insertion position
while(t2)
{
c = t1->coef * t2->coef;
e = t1->expon + t2->expon;
while(rear->link && rear->link->expon > e)// take rear Point to the index and e Equal or ratio e A position before a small node
rear = rear->link;
if(rear->link && rear->link->expon == e)// If rear And is not null rear Then the node index and e equal , Then add
{
if(c + rear->link->coef)// If the sum is not 0
{
rear->link->coef += c;
rear = rear->link;
}
else// The sum is 0 , Delete rear After node
{
t = rear->link;
rear->link = t->link;
free(t);
}
}
else // Construct a new node to insert into rear after
{
t = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
t->coef = c;
t->expon = e;
t->link = rear->link;
rear->link = t;
rear = rear->link;
}
t2 = t2->link;
}
t1 = t1->link;
}
t = P;
P = P->link;
free(t);// Release the U-turn node
return P;
} 4. How to output
The output is easy :
void PrintPoly(Polynomial P)
{
int flag = 0;
if(!P)
{
printf("0 0\n");
return;
}
while(P)
{
if(!flag)
flag = 1;
else
printf(" ");
printf("%d %d",P->coef, P->expon);
P = P->link;
}
printf("\n");
}
Finally, the complete code is given :
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
/*
1. First, read the polynomial , Constructors ReadPoly()
2. Add polynomials , Constructors AddPoly()
3. Do polynomial multiplication , Constructors MultyPoly()
4. Output the polynomial , fear 、PrintPoly()
*/
typedef struct PolyNode * Polynomial;
struct PolyNode{
int coef;
int expon;
Polynomial link;
};
void Attach(int c, int e, Polynomial * rear);// Add the newly read coefficients and exponents to the end of the polynomial
Polynomial ReadPoly();// Read in polynomials
Polynomial AddPoly(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2);// Calculate the sum of two polynomials
Polynomial MultyPoly(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2);// Calculate the product of two polynomials
void PrintPoly(Polynomial P);
int main()
{
Polynomial P1 = ReadPoly();
Polynomial P2 = ReadPoly();
Polynomial PA = AddPoly(P1, P2);
Polynomial PP = MultyPoly(P1, P2);
PrintPoly(PP);
PrintPoly(PA);
}
void Attach(int c, int e, Polynomial * rear)
{
Polynomial input = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
// Apply for a new node and assign an initial value
input->coef = c;
input->expon = e;
input->link = NULL;
(*rear)->link = input;
*rear = input; // Modify the end pointer , Because it is to modify the pointer , Therefore, the pointer of the pointer is used here
}
Polynomial ReadPoly()
{
Polynomial P1, rear, t;
int N;// Number of polynomial terms
int c,e;// Used to temporarily store coefficients and indices
P1 = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));// Application header node
// The application header node is for convenience Attach Function time , Don't differentiate rear Is it empty or not , With the header, all nodes are non empty , Easy to insert
P1->link = NULL;
rear = P1;// The tail pointer points to the head node
scanf("%d",&N);
while(N--)
{
scanf("%d %d",&c, &e);
Attach(c, e, &rear);
}
t = P1;
P1 = P1->link;
free(t);// Mission completion for easy insertion of header node , Release the head node
return P1;
}
Polynomial AddPoly(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2)
{
Polynomial t1,t2,rear,t;
t1 = P1;
t2 = P2;
Polynomial P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
rear = P;
while(t1 && t2)
{
if(t1->expon == t2->expon)// If the exponents are the same, add them
{
if(t1->coef + t2->coef)// If the coefficients do not add up to zero , Then add the calculation results to P in
{
Attach(t1->coef + t2->coef, t1->expon, &rear);
}
t1 = t1->link;
t2 = t2->link;
}
else if(t1->expon > t2->expon)// Find the one with a large index and add it to P in
{
Attach(t1->coef, t1->expon, &rear);
t1 = t1->link;
}
else
{
Attach(t2->coef, t2->expon, &rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
}
while(t1)// If t1 There are also redundant nodes , Then continue to join
{
Attach(t1->coef, t1->expon, &rear);
t1 = t1->link;
}
while(t2)// If t2 There are also redundant nodes , Then continue to join
{
Attach(t2->coef, t2->expon, &rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
t = P;
P = P->link;
free(t);// Release the head node
return P;
}
Polynomial MultyPoly(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2)
{
Polynomial P, t1, t2, t, rear;
int c, e;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
t1 = P1;
t2 = P2;
rear = P;
if(!t1 || !t2)// If a polynomial is empty , Then the multiplication result is null
return NULL;
while(t2)// First use P1 The first term of times P2 Generate a polynomial to insert
{
c = t1->coef * t2->coef;
e = t1->expon + t2->expon;
Attach(c, e, &rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
t1 = t1->link;//t1 Point to the second item
while(t1)
{
t2 = P2;// Re point the pointer to P2 The beginning of
rear = P;// Used to find a suitable insertion position
while(t2)
{
c = t1->coef * t2->coef;
e = t1->expon + t2->expon;
while(rear->link && rear->link->expon > e)// take rear Point to the index and e Equal or ratio e A position before a small node
rear = rear->link;
if(rear->link && rear->link->expon == e)// If rear And is not null rear Then the node index and e equal , Then add
{
if(c + rear->link->coef)// If the sum is not 0
{
rear->link->coef += c;
rear = rear->link;
}
else// The sum is 0 , Delete rear After node
{
t = rear->link;
rear->link = t->link;
free(t);
}
}
else // Construct a new node to insert into rear after
{
t = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
t->coef = c;
t->expon = e;
t->link = rear->link;
rear->link = t;
rear = rear->link;
}
t2 = t2->link;
}
t1 = t1->link;
}
t = P;
P = P->link;
free(t);// Release the U-turn node
return P;
}
void PrintPoly(Polynomial P)
{
int flag = 0;
if(!P)
{
printf("0 0\n");
return;
}
while(P)
{
if(!flag)
flag = 1;
else
printf(" ");
printf("%d %d",P->coef, P->expon);
P = P->link;
}
printf("\n");
}边栏推荐
- June 22, 2022: golang multiple choice question, what does the following golang code output? A:3; B:1; C:4; D: Compilation failed. package main import ( “fmt“ ) func mai
- 新课上线 | 每次 5 分钟,轻松玩转阿里云容器服务!
- Use of visdom
- AHA C language Chapter 8 game time is up (lesson 29)
- Leetcode topic resolution divide two integers
- 技能自检 | 想当测试Leader,这6项技能你会吗?
- Opportunities and challenges of digital collections from the perspective of technology development team
- Work accumulation - judge whether GPS is on
- Jvm: when a method is overloaded, the specific method to call is determined by the static type of the incoming parameter rather than the actual type of the parameter
- Pat class B 1012 C language
猜你喜欢

Explicability of counter attack based on optimal transmission theory

Real MySQL interview question (23) -- pinduoduo ball game analysis

Wechat applet: unfashionable love talk

True question of MySQL interview (29) -- case - finding favorite movies

runc 符号链接挂载与容器逃逸漏洞预警(CVE-2021-30465)
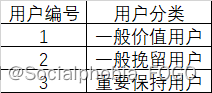
MySQL面试真题(二十七)——RFM分析法对用户进行分类

最优传输理论下对抗攻击可解释性

Deploy docker and install MySQL in centos7
Visdom draws multiple dynamic loss curves

数字藏品如何赋能经济实体?
随机推荐
【owt】owt-client-native-p2p-e2e-test vs2017构建 6:修改脚本自动生成vs工程
雷达图canvas
Activity startup mode and life cycle measurement results
C primer plus学习笔记 —— 2、常量与格式化IO(输入/输出)
AHA C language Chapter 8 game time is up (lesson 29)
MySQL面试真题(二十六)——滴滴2020年笔试题
PAT 乙等 1015 C语言
阿里云 ACK One、ACK 云原生 AI 套件新发布,解决算力时代下场景化需求
Jvm: when a method is overloaded, the specific method to call is determined by the static type of the incoming parameter rather than the actual type of the parameter
android Handler内存泄露 kotlin内存泄露处理
Arctime makes Chinese and English subtitle video
The performance of nonstandard sprintf code in different platforms
C prime plus notes d'apprentissage - 2, constantes et formatage io (I / o)
MySQL面试真题(二十八)——案例-通讯运营商指标分析
PAT 乙等 1023 组个最小数
Basic calculator for leetcode topic analysis
Wireshark TS | video app cannot play
Pat class B 1010 C language
True MySQL interview question (21) - Finance - overdue loan
Genetic engineering of AI art? Use # artbreeder to change any shape of the image