当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of cache (for the postgraduate entrance examination of XD)
Detailed explanation of cache (for the postgraduate entrance examination of XD)
2022-06-25 02:30:00 【Solitary meow】
Western Electric Meter group Postgraduate entrance examination notes
The content is more Recommended collection
Continuous updating Welcome to your attention
List of articles
Cache Cache Detailed explanation
One .Cache Overview and introduction background
because CPU The speed increase of has been higher than that of the memory , And CPU High speed memory with matching speed is expensive , So that the contradiction is : If you use low-cost slow memory as main memory , Unable to make CPU The speed of ; And if you use expensive high-speed memory as main memory , The price is unacceptable . Cache Cache Is used to solve such contradictions .
Locality principle :
Cache memory Cache Our work is based on the principle of locality of program and data , That is, within a short time interval , The assembly executes on a small main memory address space , Similarly, there is a local phenomenon in the access to data .
Cache The concept of :
Based on the locality principle of program and data , stay CPU And main memory ( Try to get as close as possible to CPU The place of ) Set up a high-speed memory with small capacity , Put the program currently executing and the data being accessed into it . When the program is running , There is no need to fetch instructions and data from slow main memory , But directly access this kind of high-speed and small capacity memory , So as to improve CPU Program execution speed , This kind of memory is called cache memory , abbreviation Cache.
- Cache It's usually by SRAM Realized .( Access by address )
- The address mapping table is usually implemented by the associated memory .( By content / Address access )
- Cache Most of the management work needs to be realized by hardware
Two . Address mapping and transformation
Main memory address to Cache Address mapping of addresses :
stay Cache In the course of work , You need to copy the main memory information to Cache in , This requires the establishment of the main memory address and Cache Mapping between addresses , And store the relationship in the address mapping table .
If the address of the main memory information to be read and written is retrieved in Cache Address mapping table , It is called a ” hit “; If it is not in the address mapping table , It is called a ” Not hit “.
Address change :
When the program is executed , If hit , be CPU You can start from Cache Access information in , At this point, you need to convert the main memory address to Cache Address can be correct Cache Visit . Convert the main memory address to Cache Addresses are called address transformations .
Be careful :
Division of main memory address ( Area code , Block number , Block address ) It is an artificial logical division , It doesn't actually change the original form of the main memory address , The division of main memory address is still determined by the addressing space .
There are three basic ways of address mapping and address transformation :
1. Fully associative address mapping
Cache Block with main memory
take Cache And main memory is divided into several storage blocks with the same capacity . For example, main memory capacity 64MB,Cache Capacity 32KB, With 4KB Size block . be Cache Divided into 8 block , Block number 0~7, You can use 3 Bit binary encoding represents . The main memory is divided into 16K Block , Block number 0 ~16383, You can use 14 Bit binary encoding represents .
Fully associative mapping rules :
Any piece of main memory can be loaded ( Copy ) To Cache Any piece of .
Cache The block number is used as the entry address of the address mapping table ( That is, the unit address of the associated memory ), The loaded... Is then recorded in the storage unit of the associated memory Cache The block number of the main memory block of ( That is, the mark ).
Working process of full associative mapping mode :
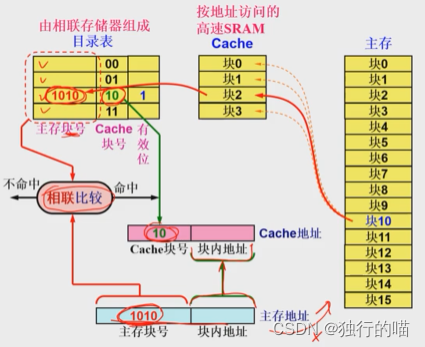
A brief description of fully associative address mapping Cache Working process of :
If CPU The address to be accessed is given through the address bus in the 10 block , At this time, the main memory address is loaded into the main memory and is also loaded into Cache Address mapping and transformation module . Main memory number... Was not retrieved in the address mapping table 10 Block content ( There is nothing in the mapping table in the figure , Set all significant bits 0), It means a miss . At this point, you need to access the main memory and transfer the main memory to 10 The stored contents of the block are loaded Cache In any piece of the , If... Is loaded at this time Cache Of the 2 block .
In the main memory of 10 Block loading Cache The first 2 The contents of the address mapping table need to be established at the same time of the block :
- In the address mapping table 2 Table items (Cache The block number is 2) Effective location of 1
- Set the main memory block number 10 namely 1010 Save in this table item
The next time you access main memory 10 The contents of the block , It will hit , Then remove access to main memory , The address mapping table is used to know the corresponding... Of the main memory block number Cache After the block number , Direct access Cache No 2 Block to access content .
Advantages and disadvantages of fully associative address mapping
Advantages of fully associative address mapping : Main memory load Cache flexible , Any piece can be loaded . Only when Cache It needs to be replaced after it is fully filled .
Disadvantages of fully associative address mapping : Fully associative mapping is the most expensive , The maximum capacity of the associated memory is required , It is necessary to retrieve all units of the associated memory to obtain Cache Block number of , The address translation mechanism is the most complicated .
2. Direct address mapping
Partition of main memory
In the direct address mapping mode , Logically partition main memory . The size of each zone is Cache Capacity size of . give an example : hypothesis Cache The capacity of is 32KB, The size of main memory is 64MB, Then the size of each partition should be the same as Cache Of the same size , by 32KB, Main memory can be divided into 64 M / 32 K = 2 K 64M/32K=2K 64M/32K=2K Districts , The area code is from 0 To 2047. then Cache And each area of main memory 4KB Block .
Direct mapping rules :
Memory blocks with the same block number in each main memory area can only be loaded Cache In a storage block with the same block number in
For example, in all areas 0 Block No. can only be loaded into Cache Medium 0 In block , In main memory 1 Block No. can only be loaded into Cache Medium 1 In block , And so on . This mapping method makes the main memory block number and Cache Keep the block number consistent .
Direct mapping address translation
Main memory addresses are logically divided into : Area code , Block number in the area , Block address Three parts
With the above example as the background , namely :
- Divide the main memory into 2K Districts ,
- Each zone is divided into 8 Block ,
- Each block size bit 4KB
When CPU The main memory address given for access is :28B57A4H when , The logical division of the address is as follows :
| Area code (11 position ) | Block number in the area (3 position ) | Block address (12 position ) |
|---|---|---|
| 10100010110 | 101 | 011110100100 |
Make a brief analysis of the above division :
- The number of partitions is 2K, So the area code needs 11 Bit binary number means , So high 11 Bit is area code
- Each zone is divided into 8 block , Therefore, the block number needs 3 Bit binary number means , So next 3 Bit is block number
- The size of each block is 4KB, Memory is addressed in bytes , The size of a storage unit is 1B, So there is... In a block 4K Storage unit , Yes 4K Addressing storage units requires 12 Bit binary number means , So low 12 Bit is the address within the block .
Direct mapping mode work process
CPU The main memory address given by the address bus is first transmitted to the main memory and the Cache Address transformation and mapping module , Then through address mapping and transformation : Just use the main memory block number as the address of the address mapping table to retrieve whether the area code stored in the unit is the main memory address of the block , That is, only one storage unit in the address mapping table needs to be detected .( mapping ) If you hit , It is directly obtained from the main memory address Cache Address .( Transformation )
If the main memory address is Cache Hit in the middle , Access to main memory is revoked , Directly from Cache Access the content to be accessed in the corresponding block in the .
If the main memory address is Cache Miss in , You need to continue to access the main memory , And load the blocks accessed in main memory Cache In the corresponding block .
Advantages of direct address mapping
The address transformation in the direct mapping mode is simple , And the retrieval speed of the address mapping table is fast , You only need to retrieve one table item . The address mapping table may consist of static memory , The hardware implementation is simple .
Disadvantages of direct address mapping
The disadvantage of direct address mapping is low efficiency , When Cahce When a block is in use and a block with the same block number in other areas of main memory needs to be loaded , Only those in use Cache Block to replace , Even if Cache Other blocks in the are currently idle .
If blocks with the same block number in different areas of main memory are frequently accessed alternately , These blocks are frequently loaded and replaced , Will greatly affect Cache shooting , Therefore, direct address mapping is suitable for large capacity Cache( Those with many block numbers Cache)
3. Group associated address mapping mode ( important )
Fully associative address mapping and direct address mapping have their own advantages and disadvantages , The group associated address mapping method is to combine the advantages of both and minimize the disadvantages of both .
Group partition and block partition
The storage structure of group associated address mapping is take Cache Group first , In group regrouping .
The main memory structure is Start with Cache Capacity partition , Press... In the area Cache Method grouping , In group regrouping .
Group associated address mapping rules
The group associated address mapping rule is : Main memory and Cache Inter group address mapping is a direct mapping between groups and a fully associative mapping within groups , In other words, blocks in a group of main memory can only be loaded Cache In the same number group of , But you can load Cache In any block of the same number group . The main memory area number and the block number in the group should be recorded in the associated mapping table .
The group association address mapping method reduces the range of association comparison to a certain range , While providing a certain flexibility, it effectively reduces the size of the associated memory .
Group associated address mapping workflow
The working process of group associated address mapping differs from the above two in that :
Address mapping is different : The process of group associative address mapping is simpler than that of full associative address mapping , But it is more complicated than direct address mapping . Due to the group associated address mapping , Blocks in a group in main memory can only be stored in Cache In the corresponding group with the same number , So when retrieving the address mapping table , We only need to detect the entries within the corresponding group number range in the address mapping table . The following is an example , If we need to access main memory : The first 2 District No 1 Group No 0 block , Then we only need to narrow the search scope to the last two rows of the directory table , That is, No. in the table of contents 1 Within the storage range of the group . Then the area code and the block number in the group of each table item in the range are compared in parallel , If there is a line with the same area code and block number as the main memory address , shows Cache hit .
At this time, the address transformation is also relatively simple , If you hit , The corresponding in the table item will be Cache Take out the block number in the group , We know that the main memory block is in Cache The corresponding block number in , Then it is spliced with the group number and the address in the block to get Cache The address in .
If it misses , You need to try to save the contents of the main memory block you are accessing Cache, You also need to retrieve the address mapping table to see if there is a block conflict , When retrieving, you still only need to retrieve the catalog table within the same group number range , The search scope is small . If there are free blocks in the same group, the main memory block can be stored in the Cache In the free block . The probability of collision is much lower than that of direct address mapping .

Advantages and disadvantages of group associative mapping
advantage :
- The probability of block collision is relatively low
- The utilization of blocks is greatly improved
- The failure rate of the block is significantly reduced
shortcoming :
- Implementation difficulty and cost are higher than direct mapping
4. Example analysis



3、 ... and .Cache Replacement algorithm
1. Random replacement algorithm (RAND)
The algorithm uses a random function generator to generate a replacement Cache Block number , Replace it . This approach does not take into account the history and use of information , May reduce the hit rate , But the implementation is simple , And when the Cache When the capacity is large ,RAND The actual performance of the algorithm is good .
2. Fifo algorithm (FIFO)
The algorithm is to load... First Cache Replace the main memory block of . This method only considers the history of the information and does not consider its use , Perhaps the first piece loaded is being used frequently .
3. The least frequently used algorithm (LFU)
The algorithm is to minimize the number of visits in a period of time Cache Block replace out . For each Cache Block to set a counter , And set at the beginning 0,Cache Every time a block is accessed , The counter is incremented 1. When a replacement is needed , The block with the lowest count value is replaced , At the same time, all counters are cleared 0. This method limits the counting period to two replacement intervals , It can not fully reflect the recent visit .
4. The longest unused algorithm (LRU)
This algorithm will be the least used in the near future Cache Block replace out . This algorithm needs to be applied to every Cache Block to set a counter , Every time a piece hits , Clear the counter 0 The counters of the other blocks are incremented 1, Record Cache Usage of the middle block . When a replacement is needed , Replace the block with the largest count value . The algorithm utilizes the locality principle .
5. Optimal replacement algorithm (OPT)
According to the information after the execution , according to Cache The best strategy of replacement is known from the use of blocks .
This method can't be realized , It can only be used as a standard to measure the advantages and disadvantages of other algorithms

Four .Cache Update strategy
1. Write back
The writeback method is when CPU Write Cache Hit, , Only write data to Cache Write to main memory without self-interest . Only if CPU Rewritten Cache When a block is replaced, the block is written back to main memory .
If CPU Write Cache Not hit , First, transfer the corresponding main memory block into Cache in , And then Cache Write operation in . Changes to main memory are still made when the block is replaced .
The implementation of the writeback method needs to Cache Each piece of is added 1 Bit modification flag , So that when the block is replaced, it can be discarded or written back to main memory . The writeback method is faster , But it may cause main memory and Cache Inconsistent content .
2. Write direct (RAND)
Direct writing is also called full writing , When CPU Write Cache Hit, , Writing data to Cache Also write to main memory , Thus, the main memory and Cache Consistency of content .
When CPU Write Cache Not hit, , Write and modify the main memory directly , Then you can transfer the modified main memory block in or out Cache.
There is no need to add a modification flag for the direct writing method , The speed is slow, but the main memory and Cache The content is consistent .
The following figure shows several different computer structures , Write Cache when Cache The problem of consistency with main memory content :
5、 ... and .Cache Performance analysis
1.Cache Performance metrics for
1). shooting
shooting h For the definition of : h = N c N × 100 % h=\frac{N_c}{N}\times100\% h=NNc×100%
- among Nc To hit Cache The number of times ,N For the visit Cache- The total number of times the main memory system
2). Average visit time
Cache The visit time is T c T_c Tc, The access time of main memory is T M T_M TM,Cache Hit rate is h
Then the two-layer structure Cache- Average access time of main memory system T Can be expressed as :
T = h × T c + ( 1 − h ) × ( T c + T M ) = T c + ( 1 − h ) × T M T=h\times{T_c}+(1-h)\times(T_c+T_M)=T_c+(1-h)\times{T_M} T=h×Tc+(1−h)×(Tc+TM)=Tc+(1−h)×TM
3). Speedup ratio
Cache- The speedup ratio of the main memory system Sp Defined as :
S p = T M T = T M T c + ( 1 − h ) T M = 1 1 − h + 1 r S_p=\frac{T_M}{T}=\frac{T_M}{T_c+(1-h)T_M}=\frac{1}{1-h+\frac{1}{r}} Sp=TTM=Tc+(1−h)TMTM=1−h+r11
- among r=TM/Tc From main memory to Cache Multiple of speed increase .
- Speedup ratio Sp The limit value of is r=TM/Tc
2.Cache Performance improvement of
1) multistage Cache
In two levels Cache For example , take L1Cache( Get closer to CPU) The capacity is small , But the speed is very high , And CPU Match ; take L2Cache Large capacity , But the speed is between L1Cache And main memory . When L1Cache Not hit, , Then to L2Cache Middle search , because L2Cache Large capacity , The hit rate will be very high .
two level C a c h e Of total Lack of loss rate = L 1 Lack of loss rate × L 2 Lack of loss rate Level two Cache Total deletion rate of =L1 Absence rate \times L2 Absence rate two level Cache Of total Lack of loss rate =L1 Lack of loss rate ×L2 Lack of loss rate 
2) Reduce Cache The missing rate of
- Reasonable design Cache Block size
- Increase reasonably Cache Capacity
- Reasonably set the connection degree
- Hardware prefetching
- Compile optimization
3) Reduce Cache expenses
3. Example analysis

Program code analysis : The function of this program segment is , stay int integer array a in , From the subscript 0 To 999, this 1000 Array cells , Take one number at a time , And give the value +32 And then write it back to the array cell . Thus, each array cell must be read and written once , That is to say, each cycle requires two operations to access main memory . Every time I access main memory, I will try to access Cache.
consider Cache Blocking of : Cache The size of a block is 16B, And an array cell int The size of the variable is 4B, So a Cache The block can hold 4 Array cells .
consider Cache Address mapping of : In question Cache Direct address mapping is adopted , Direct address mapping may cause frequent block conflicts when repeatedly accessing blocks of the same number in different areas of main memory , But under the logic of the program , Each block can only be loaded once. After the access is completed, the block will not be accessed again , That is, the access to data is performed in a continuous sequence . Therefore, the solution of this problem does not need to consider the conflict caused by direct address mapping .
Now consider the process of program execution Cache Hit and load of :
When the first loop executes , because Cache It's an empty state , So it must miss , At this point, load the block being accessed Cache in , That is to say 4 Consecutive array cells a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3] The content of . After that, the array cells a[0] The write operation of will hit , Then on a[1],a[2],a[3] All read and write access operations will hit , In the operation of this in block unit , All in all 8 Memory accesses ,4 Read access ,4 Write access , Only for the first time a[0] Read access misses for , That is missing . therefore 8 During this visit , The missing rate was 1/8. Then the situation is similar to the above , When the a[4] When a read access miss occurs , It will continue to load the contents 4 Main memory block of units , After that 7 All visits will hit , And so on , So the total deletion rate is still 1/8.
边栏推荐
- 算力服务网络:一场多元融合的系统革命
- When they are in private, they have a sense of propriety
- ida中交叉引用的解析
- Of the seven levels of software testers, it is said that only 1% can achieve level 7
- 目录权限错误导致 Oracle 11g rac 集群数据库无法启动的问题
- 都2022年了,你还不了解什么是性能测试?
- 指南针靠谱吗?开证券账户安全吗?
- File system - basic knowledge of disk and detailed introduction to FAT32 file system
- Multimodal emotion recognition_ Research on emotion recognition based on multimodal fusion
- Use of hashcat
猜你喜欢

What are the reasons for the abnormal playback of the online channel of the channel accessed by easycvr national standard protocol?

Please run IDA with elevated permissons for local debugging.

都2022年了,你还不了解什么是性能测试?

Left hand dreams right hand responsibilities GAC Honda not only pays attention to sales but also children's safety

高速缓存Cache详解(西电考研向)

Experience of epidemic prevention and control, home office and online teaching | community essay solicitation

File system - basic knowledge of disk and detailed introduction to FAT32 file system

入坑机器学习:一,绪论

Please run IDA with elevated permissons for local debugging.

I've been doing software testing for two years. I'd like to give some advice to girls who are still hesitating
随机推荐
当他们在私域里,掌握了分寸感
QT package the EXE file to solve the problem that "the program input point \u zdapvj cannot be located in the dynamic link library qt5cored.dll"
Migrate Oracle database from windows system to Linux Oracle RAC cluster environment (2) -- convert database to cluster mode
Of the seven levels of software testers, it is said that only 1% can achieve level 7
It's 2022, and you still don't know what performance testing is?
Processon producer process (customized)
E - average and median
MCN机构遍地开花:博主和作者要谨慎签约、行业水很深
数据库系统概论必背知识
Distributed transaction solutions and code implementation
中信证券手机开户是靠谱的吗?安全吗
计网 | 【四 网络层】知识点及例题
折叠屏将成国产手机分食苹果市场的重要武器
保险APP适老化服务评测分析2022第06期
业务与技术双向结合构建银行数据安全管理体系
How to monitor the log through the easycvr interface to observe the platform streaming?
The role of software security testing, how to find a software security testing company to issue a report?
Jetson Nano 从入门到实战(案例:Opencv配置、人脸检测、二维码检测)
【直播回顾】战码先锋第七期:三方应用开发者如何为开源做贡献
1-6搭建Win7虚拟机环境