当前位置:网站首页>Distributed transaction solutions and code implementation
Distributed transaction solutions and code implementation
2022-06-25 02:27:00 【Dr. Lao】
I'm learning Spring cloud alibaba Seata Before , Let's take a look at the common solutions and code implementations of distributed transactions , After going out for an interview, you will encounter the problem of distributed transactions , invincible . The article includes 2PC,3PC Rigid business ;TCC, Local message table , Reliability message , Double write reconciliation , Best effort notification ,sage Flexible transactions such as transactions , And most of them have code references .
1. What is distributed transaction
Completing a business function may need to span multiple services , Working with multiple databases , This is the time , Our local transactions cannot guarantee that each service's operations on the database will succeed or fail at the same time , At this time, we need to understand distributed transactions .
1.1 Distributed transaction scenario
1. Cross-database transaction
Cross database transactions refer to , A certain function of an application needs to operate multiple libraries .
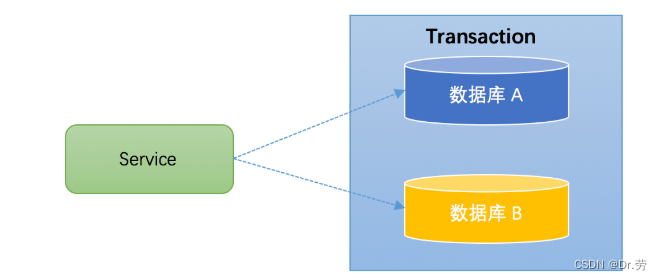
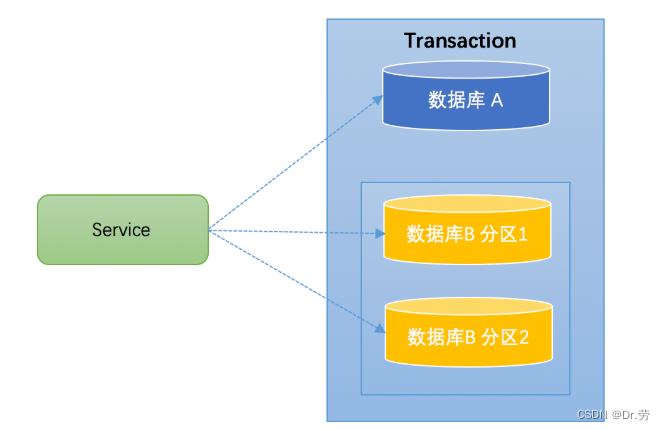
2. Sub database and sub table
Generally, a database has a large amount of data, or it is expected that there will be a large amount of data in the future , Will be split horizontally , That is, sub database and sub table . Here's the picture , Will database B Split into 2 Databases :
For the case of sub database and sub table , General developers will use some database middleware to reduce sql Complexity of operation . Such as , about sql:insert into user(id,name) values (1," Zhang San "),(2," Li Si "). This article sql Is the syntax of the operation list Library , In case of single warehouse , Can guarantee the consistency of transactions .
But now because of the sub database and sub table , Developers want to 1 No. record insertion branch 1,2 No. record insertion branch 2. So database middleware should rewrite it as 2 strip sql, Insert two different sub databases , At this time, we need to ensure the success of both libraries , Or they all fail , So basically all database middleware are faced with the problem of distributed transaction .
3. As a service
In our microservices , Services and services through Rpc The remote invocation , If ServiceA It's called in B And then call C, call B succeed ,C failed , But service B Can't roll back . perhaps ServiceA A successful call BC, But when I was about to commit a local transaction, I went down , This is the time B and C Has submitted . At this time, the data will be inconsistent .

1.2.CAP Principles and BASE theory
Previous articles have covered a lot , If you are interested, please take a look at my previous blog .
2. Distributed transaction solutions ( Rigid business -- Strong consistency )
2.1 Two-phase commit 2PC
2.1.1 DTP(Distributed Transaction Processing) Model
If one system operates multiple databases , There must be a problem with distributed transactions across multiple libraries , Many years ago, the world , Americans have already discovered this problem , A whole set of solutions have been defined long ago to deal with the problem of distributed transactions There is one called X/Open Our organization defines the model of distributed transactions (DTP).
There are several roles in it , Namely
AP(Application, Applications )
TM(Transaction Manager, Transaction manager ),
RM(Resource Manager, Explorer ),
CRM(Communication Resource Manager, Communication resource manager )
Then a very important concept is defined here , Namely Global transaction , This gadget is simply a transaction that spans multiple databases , It's a business , Involving multiple database operations , Then make sure that there are multiple databases , Any one of the operations failed , All other library operations are rolled back , This is called a distributed transaction .
2.1.2 XA standard
The above set of things is called X/Open A distributed transaction model developed by the organization , that XA What is? ? To put it bluntly , It's the defined one TM And RM Interface specifications between , It is an interface between the component managing the distributed transaction and each database .
For example, components that manage distributed transactions ,TM Will be based on XA Defined interface specification , Swipe communicates and interacts with various databases , Tell everyone that , Let's roll back the database , Or submit a transaction together , About that
This XA It's just a norm , The specific implementation is provided by the database manufacturer , for instance MySQL Will provide XA Standardized interface functions and class library implementation , wait
2.1.3 Two phase submission agreement
X/Open A set of distributed transaction models defined by the organization , It's still empty , Can't land yet , and XA The interface specification is also a relatively modest thing , I can't just say these things Basically , You got it XA That's why I understand 2PC 了 ,2PC To put it bluntly, it is based on XA A set of theory of distributed transaction , It can also be called a set of specifications , Or an agreement .
Two-Phase-Commitment-Protocol, Two phase submission agreement 2PC, It's based on XA standard , So that distributed transactions can be implemented , It defines many details in the process of implementing distributed transactions .
2.1.4 Life cases


2.1.5 Two stage submission code implementation
- 1. Generate user Kuhe account Library connection object
- 2. Generate global transactions id And branch business id( These two will be explained later Id The role of ) And bind ,user Library a branch transaction Id,account Library a branch data id.
- 3.TM towards user library (RM) Initiate the request and execute it in sequence xa.start, executable sql,xa.end.
- 4.TM towards account library (RM) Initiate the request and execute it in sequence xa.start, executable sql,xa.end.
- 5.TM inquiry user Kuhe account Is the library ready ?
- 6. Two RM All answers Ok, Commit transaction
- 7. If there is an exception or the reply is not Ok, Roll back the transaction .
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//true Means to print XA sentence ,, For debugging
boolean logXaCommands = true;
// Get resource manager operation interface instance RM1
Connection conn1 = DriverManager.getConnection
("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_user", "root", "root");
XAConnection xaConn1 = new MysqlXAConnection(
(com.mysql.jdbc.Connection) conn1, logXaCommands);
XAResource rm1 = xaConn1.getXAResource();
// Get resource manager operation interface instance RM2
Connection conn2 = DriverManager.getConnection
("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_account", "root", "root");
XAConnection xaConn2 = new MysqlXAConnection(
(com.mysql.jdbc.Connection) conn2, logXaCommands);
XAResource rm2 = xaConn2.getXAResource();
// AP request TM Execute a distributed transaction ,TM Generate global transactions id
byte[] gtrid = "g12345".getBytes();
int formatId = 1;
try {
// ============== Separately RM1 and RM2 Transaction branch on ====================
// TM Generate rm1 Transaction branch on id
byte[] bqual1 = "b00001".getBytes();
Xid xid1 = new MysqlXid(gtrid, bqual1, formatId);
// perform rm1 Transaction branch on
rm1.start(xid1, XAResource.TMNOFLAGS);//One of TMNOFLAGS, TMJOIN, or TMRESUME.
PreparedStatement ps1 = conn1.prepareStatement(
"INSERT into user(name) VALUES ('test')");
ps1.execute();
rm1.end(xid1, XAResource.TMSUCCESS);
// TM Generate rm2 Transaction branch on id
byte[] bqual2 = "b00002".getBytes();
Xid xid2 = new MysqlXid(gtrid, bqual2, formatId);
// perform rm2 Transaction branch on
rm2.start(xid2, XAResource.TMNOFLAGS);
PreparedStatement ps2 = conn2.prepareStatement(
"INSERT into account(user_id,money) VALUES (1,10000000)");
ps2.execute();
rm2.end(xid2, XAResource.TMSUCCESS);
// =================== Two-phase commit ================================
// phase1: Ask all RM Ready to commit transaction branch
int rm1_prepare = rm1.prepare(xid1);
int rm2_prepare = rm2.prepare(xid2);
// phase2: Commit all transaction branches
boolean onePhase = false;
//TM There is a judgment 2 Transaction branches , Therefore, it cannot be optimized for one-stage submission
if (rm1_prepare == XAResource.XA_OK
&& rm2_prepare == XAResource.XA_OK) {
// All transaction branches are prepare success , Commit all transaction branches
rm1.commit(xid1, onePhase);
rm2.commit(xid2, onePhase);
} else {
// If a transaction branch fails , Then roll back
rm1.rollback(xid1);
rm2.rollback(xid2);
}
} catch (XAException e) {
// If there is an anomaly , Also roll back
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Execution results : hinder byte For global and branch transactions id

2.1.6 Two phase commit principle (Seata Of AT Pattern is also this kind of model )
(1) Preparation stage (Prepare phase): The transaction manager sends... To each participant prepare news , Each database participant performs transactions locally , And write the local Undo/Redo, The transaction is not committed at this time .
(Undo Log is to record the data before modification , User database rollback ,Redo Log is to record the modified data , Used to write data after committing a transaction .)
(2) Submission phase (Commit phase): If the transaction manager receives a participant execution failure or timeout message , Send a rollback message directly to each participant , Otherwise, send a submit message ; The participant performs commit or rollback operations according to the instructions of the transaction manager , And release the lock resources used in transaction processing .
2.1.7 Defects in two-stage submission
1. Lock resource ( Low efficiency ): The first stage of preparation for a two-stage commit agreement is more than answering YES or NO, We still need to perform transaction operations , It's just the end of the transaction , It didn't go on commit perhaps rollback. in other words , Once the transaction is executed , No execution at commit perhaps rollback Before , Resources are locked in . This can cause obstruction , If sql If it is a row lock, lock the row , A watch lock locks a watch .
2. limitations : If the database does not have its own pair of XA You can't use the implementation of , what redis None of that can be used .
3. A single point of failure : Because of the importance of the coordinator , Once the coordinator TM failure . participants RM It will keep blocking . Especially in the second stage , Coordinator failed , Then all participants are still in the state of locking transaction resources , Cannot continue to complete the transaction .
4. Data inconsistency : In phase II of phase II submission , When the coordinator sends commit After the request , There is a local network exception or sending commit The coordinator failed during the request , This will result in only a few participants receiving commit request , And in this part of the participants received commit The request is then executed commit operation , But the rest didn't receive commit The requested machine is unable to perform a transaction commit . So the whole distributed system appears the phenomenon of data inconsistency .
2.1.8 Two phase commit protocol transaction suspension and solution
If we are in the process of execution , What to do if the machine goes down , perhaps commit,rollback When the network broke down , The whole transaction process has not been completed , I believe many students will have this idea , At this time, resources will be locked , Where is the business still hanging , Do how? ?
Solution : Global transaction id And branch business id The role of this time comes , We must record which process each branch transaction goes to , What is the status of the transaction , Has it been completed , When is the time . Then timing task compensation , Call the above mentioned XA.RECOVER, He can find out all the information about Prepare( Hang ) Global of transaction id And branch business id, According to these id Information , The query log suspended transactions for several minutes , Then based on the status of all branch transactions , We can decide whether to commit or rollback . For example, some open source distributed transaction frameworks Atomikos,hmily, Has helped us achieve .
Of course , If the transaction cannot be committed in the end , It has to be handled manually .
2.1.9 Two stage submission summary
Two stages , We seldom use , Generally speaking, if there is such an operation across multiple libraries in a certain system , It is not in compliance , And the performance is not very good . Now microservices , A large system is divided into dozens of services . Generally speaking , Our rules and regulations , Each service can only operate its own database . If you want to operate the library corresponding to other services , It is not allowed to directly connect to the library of other services , Violating the specification of microservice Architecture , You make random cross visits , Such a set of services can't be managed , It's not manageable , Data is often corrected by others , Their own library has been written by others . If you want to operate someone else's Library of services , You have to do this by calling the interface of another service , You are absolutely not allowed to cross access other people's databases .
There are still some on the market 2PC The implementation framework of , for example Atomikos, In fact, the bottom layer is through the dynamic proxy data source , Intercept sql perform , And then execute xa.start Other methods . And they are very good at helping us solve the two-phase commit transaction suspension problem , You don't need to do it yourself .
2.2. Three stage commit 3PC(three-phase-commitment)
2.2.1 What is? 3PC
Three stage commit (3PC), It's a two-stage submission (2PC) Improved version .
Different from the two-stage submission is , There are two changes in the three-phase submission :
1、 Introduce timeout mechanism . At the same time, the timeout mechanism is introduced in both the coordinator and the participants .
2、 Insert a preparation stage in the first and second stages . It ensures that the states of participating nodes are consistent before the final submission stage . in other words , In addition to introducing a timeout mechanism ,3PC hold 2PC Once again, the preparation phase of the project is divided into two parts , In this way, there are three stages of submission CanCommit、PreCommit、DoCommit Three stages .

2.2.2 3PC Three stages of
- CanCommit Stage
3PC Of CanCommit The stage is actually the same as 2PC The preparation stage of is very similar to . The coordinator sends... To the participants commit request , Participants return if they can submit Yes Respond to , Otherwise return to No Respond to .
1. Business inquiry The coordinator sends... To the participants CanCommit request . Ask if the transaction commit operation can be performed . Then start waiting for the response from the participants .
2. Respond to feedback The participants received CanCommit After the request , Under normal circumstances , If it thinks it can execute the transaction smoothly , Then return to Yes Respond to , And get ready . Otherwise feedback No
- PreCommit Stage
The coordinator decides whether the transaction can be remembered according to the response of the participants PreCommit operation . According to the response , There are two possibilities .
If the coordinator's feedback from all participants is Yes Respond to , Then the pre execution of the transaction will be executed .
1. Send pre submit request The coordinator sends... To the participants PreCommit request , And enter Prepared Stage .
2. Transaction pre commit Participant received PreCommit After the request , Will perform transaction operations , And will undo and redo Information is recorded in the transaction log .
3. Respond to feedback If the participant successfully performs the transaction operation , Then return to ACK Respond to , And start waiting for the final order .
If any of the participants sent No Respond to , Or wait for the timeout , None of the coordinators received a response from the participants , Then the interruption of the execution of the transaction .
1. Send interrupt request The coordinator sends... To all participants abort request .
2. Interrupt the business The participants received... From the coordinator abort After the request ( Or after the timeout , The request of the coordinator has not yet been received ), The interruption of the execution of a transaction .
- doCommit Stage
In this phase, the real transaction commit , It can also be divided into the following two situations .
Case 1: Execute commit
- 1. Send submit request Coordinate to receive... Sent by participants ACK Respond to , Then he will go from pre submission to submission . And send it to all participants doCommit request .
- 2. Transaction submission Participant received doCommit After the request , Perform formal transaction submission . And release all transaction resources after transaction commit .
- 3. Respond to feedback After the transaction is committed , Send... To the coordinator Ack Respond to .
- 4. Complete the business The coordinator receives... From all participants ack After responding , Complete the business .
Case 2: Interrupt the business The coordinator did not receive the ACK Respond to ( It may be that the recipient sent it not ACK Respond to , It's also possible that the response timed out ), Then the interrupt transaction will be executed .
- 1. Send interrupt request The coordinator sends... To all participants abort request
- 2. Transaction rollback Participant received abort After the request , Take advantage of the undo Information to perform the rollback operation of the transaction , And release all transaction resources after rollback .
- 3. Feedback results After the participant completes the transaction rollback , Send... To the coordinator ACK news
- 4. Interrupt the business The coordinator received feedback from the participants ACK After message , The interruption of the execution of a transaction .
stay doCommit Stage , If the participant cannot receive the... From the coordinator in time doCommit perhaps abort When asked , After the timeout , Transaction commit will continue .( In fact, this should be based on probability , When entering the third stage , Indicate that participants have received... In the second phase PreCommit request , Then the coordinator produces PreCommit The premise of the request is that he is , Received... From all participants CanCommit The responses are all Yes.( Once the participants have received PreCommit, It means that he knows that everyone actually agrees to modify ) therefore , In a word, it is , When entering the third stage , Due to network timeout and other reasons , Although participants did not receive commit perhaps abort Respond to , But he has reason to believe : The chances of a successful submission are great . )
2.2.3 3PC The shortcomings of
be relative to 2PC,3PC The main single point of failure to solve , And reduce congestion , Because once the participants can't receive the information from the coordinator in time , He will default to commit. Instead of holding transaction resources and blocking them all the time . But this mechanism also leads to data consistency problems , because , Because of the Internet , Sent by the coordinator abort The response was not received by the participants in time , Then the participant executes after the timeout commit operation . In this way, we will receive abort There is data inconsistency between the participants who command and perform the rollback .
2.2.4 2PC,3PC summary
2pc and 3pc Are all rigid transactions , Performance will have an impact , because prapare The phase will lock resources , And we found that , This pattern is mostly used for a single project with multiple data sources , It is not suitable for our distributed environment RPC call .2PC Only TM The timeout mechanism of ,3PC Added participants (RM) The timeout mechanism of ,3PC More CanCommit Stage , This is the biggest difference .
3. Distributed transaction solutions ( Flexible business -- Final agreement )
3.1 tcc Distributed transactions
TCC yes Try,Confirm,Cancel Abbreviations of three words ,TCC Each branch transaction is required to implement three operations : Preprocessing Try, Confirmation stage Confirm, revoke Cancel.
Try Do sth Business inspection and Reserve resources ,confirm do Business confirmation ,Cancel To achieve a relationship with Try The opposite operation is Rollback operation . In fact, it is a compensation .
TM( Transaction manager , This is just a concept ) Initiate all branch transactions first try operation , Of any branch transaction try Operation execution failed ,TM Will initiate all branch transactions cancel operation ; if try success ,TM Will initiate all branch transactions confirm operation , among confirm/cancel If the operation fails ,TM Will try again .
use TCC Think Confirm There is no mistake in the stage . namely : as long as Try success ,Confirm It will succeed . if Confirm The stage really went wrong , Need to introduce retry mechanism or manual processing .
Cancel Phase is when the business execution error needs to be rolled back Cancellation of branch transaction , Reserve resource release . Usually , use TCC Think Cancel Stage is sure to be successful . if Cancel The stage is really wrong , Need to introduce retry mechanism or manual processing .
Try Operation can be empty , Do nothing . for example A turn 20 Block to B( Two users have different libraries ),Try When A buckle 20,B You can do nothing ,comfirm Only when B increase 20 block .

3.1.1 Take the user's balance payment order as an example to demonstrate tcc
1. Deduct commodity inventory
2. Generate order
3. Bonus points
4. Deduct the balance
Under the micro service , this 4 Operations correspond to different microservices , Each microservice connects to a different library , Therefore, the problem of distributed transactions will arise , Let's take a look at TCC Here is how to deal with .
1.try operation
The inventory service modifies the corresponding goods ( Original inventory 100) Inventory is 99, Frozen inventory is 1
The order service adds a record order A, Status to be paid
Points service adds a new record points record , The status is to be generated
User service modifies user balance ( Original balance 100) by 99, The frozen balance is 1
2.comfirm operation
When all try Execute after success comfirm
The inventory service modifies the corresponding commodity inventory to 99, Frozen inventory is 0
The order service adds a record order A, The status is paid
Points service adds a new record points record , The status is unused
The user service modifies the user balance to 99, The frozen balance is 0
3.cancel operation
When you have one try The operation has abnormal execution cancel
The inventory service modifies the corresponding commodity inventory to 100, Frozen inventory is 0
The order service modifies the record order A, The status is canceled
Points service adds a new record points record , The status is canceled
The user service modifies the user balance to 100, The frozen balance is 0
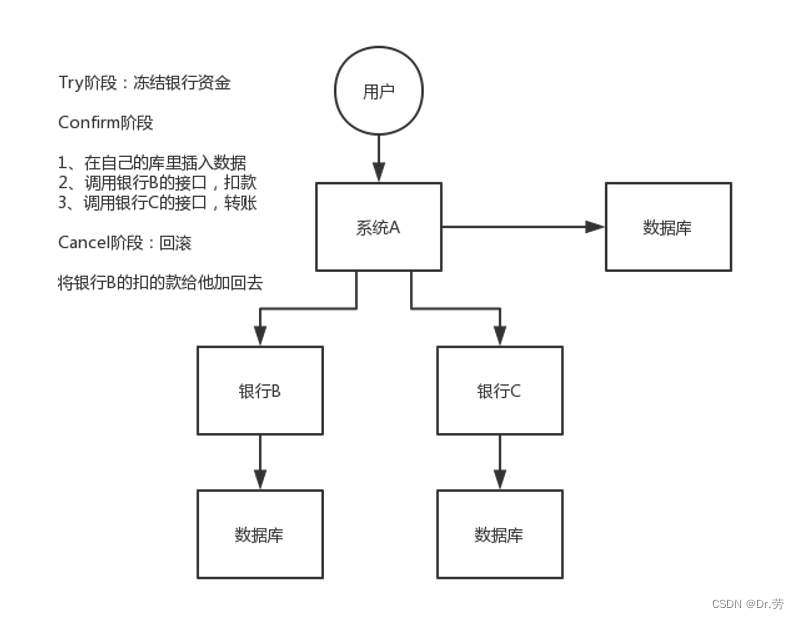
3.1.2 What is reserved resources (try)?
stay try During operation, we usually add an additional field to record the reserved resources , Record the status before and after modification .
For example, to perform try operation
newly added :
Add a new record and we will have a status field , We will insert a piece of data and change the status to be added , Just reserve resources for
Delete :
When deleting records, we change the status to be deleted , The status is reserved resources .
modify :
When modifying, this field is in the status to be modified , for example A to B( There are 100 block ) turn 20 block , First A The balance becomes 80, The frozen balance is -20,B The balance of is 100, The frozen balance is 20,A and B The frozen fields are reserved resources . Why can't we just give B turn 20, Instead, add a frozen field , Because you give it directly to B Add ,B It was used 120 block , Well, then , cold . So sometimes we need to reserve a field to record some data before and after modification .
3.1.3 TCC Code demonstration
The open source framework I use here is byteTcc As an example , We just need to see how to split an interface into try,comfirm,cancel, Even if you use seata It's the same process , The framework will automatically help you call the corresponding... Of each microservice try,comfirm,cancel, There is no need for us to operate manually . And they will help you record Transaction log , If you don't use a frame , Which microservice has executed try,confirm,cancel All need to be saved in our transaction log table , Save logs and business operations in the same transaction commit .
Code logic :
We simulate UserClient2 Transfer to UserClient1, Called UserClient1#transfer, Two client All marked @Compensable, Prove that this is a method that needs to start distributed transactions , There is an interface in this annotation , The methods in this interface correspond to Try, for example client1 yes transfer ,client2 yes decreaseAmount .
UserClient1:
try:#transfer hypothesis B Transfer to A Of 10 element , user A Frozen funds field of +10
confirm:#confirmTransfer user A Real fund field of +10, Freeze funds -10, It's recovery 0, Indicates that the transfer has been completed
cancel:#cancelTransfer user A Frozen funds field of -10
UserClient2:( Here we freeze the fields -10 It's fine too , There is no need to tangled up. )
try:#decreaseAmount user B Add... To your own frozen funds field +10, And real money -10
confirm:#decreaseAmountConfirm user B Freeze funds -10, It's recovery 0, Indicates that the transfer has been completed
cancel:#decreaseAmountCancel user B Of frozen funds -10, Real money +10
First UserClient1#transfer, This method will pass through Feign To deduct UserClient2 The money , also UserClient2 The method of deduction is also Try Method , then Client1 Local affairs for their own money Try Method , Transaction submission , The framework will help us automatically call client1 and client2 Of comfirm Method , If there are exceptions, the framework will automatically call them for us cancel Method . Remember not to catch exceptions yourself .
As you can see from here ,TCC Distributed transaction is that we manually write frozen resources , Submit , Compensation interface , Will split an interface into 3 individual , It increases the complexity of the system , But it does not lock resources , And the degree of control is very high .
UserClient1:
public interface ITransferService {
public void transfer(String sourceAcctId, String targetAcctId, double amount);
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Compensable(interfaceClass = ITransferService.class, simplified = true)
@RestController
public class SimplifiedController implements ITransferService {
@Autowired
private TransferDao transferDao;
@Autowired
private IAccountService acctServiceFeign;
/**
*ITransferService Realized transfer This method , Default byteTcc Would think he was Try Method
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/simplified/transfer", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@Transactional
public void transfer(@RequestParam String sourceAcctId, @RequestParam String targetAcctId, @RequestParam double amount) {
this.acctServiceFeign.decreaseAmount(sourceAcctId, amount);
this.increaseAmount(targetAcctId, amount);
}
private void increaseAmount(String acctId, double amount) {
System.out.println("update tb_account_two set frozen = frozen + #{amount} where acct_id = #{acctId}");
int value = this.transferDao.increaseAmount(acctId, amount);
if (value != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR!");
}
System.out.printf("exec increase: acct= %s, amount= %7.2f%n", acctId, amount);
}
@CompensableConfirm
@Transactional
public void confirmTransfer(String sourceAcctId, String targetAcctId, double amount) {
System.out.println("update tb_account_two set amount = amount + #{amount}, frozen = frozen - #{amount} where acct_id = #{acctId}");
int value = this.transferDao.confirmIncrease(targetAcctId, amount);
if (value != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR!");
}
System.out.printf("done increase: acct= %s, amount= %7.2f%n", targetAcctId, amount);
}
@CompensableCancel
@Transactional
public void cancelTransfer(String sourceAcctId, String targetAcctId, double amount) {
System.out.println("update tb_account_two set frozen = frozen - #{amount} where acct_id = #{acctId}");
int value = this.transferDao.cancelIncrease(targetAcctId, amount);
if (value != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR!");
}
System.out.printf("exec decrease: acct= %s, amount= %7.2f%n", targetAcctId, amount);
}
}UserClient2:
public interface IAccountService {
public void decreaseAmount(String accountId, double amount);
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Compensable(interfaceClass = IAccountService.class, confirmableKey = "accountServiceConfirm", cancellableKey = "accountServiceCancel")
@RestController
public class AccountController implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
*IAccountService Realized decreaseAmount This method , Default byteTcc Would think he was Try Method
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/decrease", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@Transactional
public void decreaseAmount(@RequestParam("acctId") String acctId, @RequestParam("amount") double amount) {
int value = this.jdbcTemplate.update(
"update tb_account_one set amount = amount - ?, frozen = frozen + ? where acct_id = ?", amount, amount, acctId);
if (value != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR!");
}
System.out.printf("exec decrease: acct= %s, amount= %7.2f%n", acctId, amount);
// throw new IllegalStateException("error");
}
@CompensableConfirm
@Transactional
public void decreaseAmountComfirm(String acctId, double amount) {
int value = this.jdbcTemplate.update("update tb_account_one set frozen = frozen - ? where acct_id = ?", amount, acctId);
if (value != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR!");
}
System.out.printf("done decrease: acct= %s, amount= %7.2f%n", acctId, amount);
}
@CompensableCancel
@Transactional
public void decreaseAmountCancel(String acctId, double amount) {
int value = this.jdbcTemplate.update(
"update tb_account_one set amount = amount + ?, frozen = frozen - ? where acct_id = ?", amount, amount, acctId);
if (value != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR!");
}
System.out.printf("undo decrease: acct= %s, amount= %7.2f%n", acctId, amount);
}
}3.1.4 TCC The problem that a transaction can produce is : Idempotency
Idempotency problems will occur in our confirm and cancel Stage ,try Yes, but rarely , When all our services call try When the interface succeeds , We will call the corresponding service confirm perhaps cancel, At this time, due to network reasons, the timeout occurred , There will be one. retry Retry operation for , Network timeout means we don't know confirm perhaps cancel Executive conclusion , If you try again , If idempotency is not guaranteed, data errors will occur , So we have to guarantee idempotency .
Solution : Actually tcc Transaction execution , There will be a throughout the overall transaction Global transaction id And each branch transaction will have a branch transaction id, We Every microservice A branch is required locally Local transaction log table , There are some fields , Global transaction id, Branch business id, Branch transaction execution status (1.try Successful implementation ,2.confirm Successful implementation ,3cancel Successful implementation ), So when we try again , First, branch transactions id As a lock key, Then go to query the local transaction table , Have I ever performed this step , If it has been executed, it will not be executed , This ensures idempotency . Therefore, we need to record the current branch transaction status in the local transaction table at each step of the business operation , Commit the transaction with the business code , This allows you to trace whether the branch transaction is completed .
Example :
Start global transaction : Generate global transactions id=123
Branch business =1, Global transaction id=123. Deduct commodity inventory
Branch business =2, Global transaction id=123. Generate order
Branch business =3, Global transaction id=123. Bonus points
Branch business =4, Global transaction id=123. Deduct the balance
End global transaction : Delete the corresponding transaction asynchronously id
3.1.5 TCC The second problem caused by transaction is : Transactions hang
Or the problem caused by the network , Suppose we set the request timeout to 3 second , When we are about service B perform try During operation , A timeout occurred , At this time, we will call B Corresponding cancel Interface , That's it , our try Not yet implemented , And then we did cancel, At this time, dirty data may be generated . Service at this time B perform try The thread of comes back when it is free , And then we did try operation , Then it's over , This is me. try The operation is always suspended here , Bobbi Q, Because I have already executed cancel.
Solution : Global transaction id, Branch business id, Branch Local transaction log table , In our execution try Before the operation , Lock , Then go to the local transaction table to find out whether it has been executed cancel operation , If there is one, it will not be implemented .
3.1.6 TCC The third problem caused by transactions : Empty rollback
Take the following order placing process as an example , Suppose the steps 1 perform try succeed , Then step 2 failed , At this time, the framework will help us call the steps automatically 1,2,3,4 Of cancel Method , However 2,3,4 Of try Methods haven't been implemented yet , Prove that they haven't started reserving resources yet , You just rolled me back , I try The balance has not been deducted yet , you cancel Instead, he gave me the balance , Win twice . This is the empty rollback problem .
Solution : Global transaction id, Branch business id, Branch Local transaction log table , In our execution cancel Before the operation , Lock , Then go to the local transaction table to find out whether it has been executed try operation , If there is one, carry it out , No, No , And record the status of the local transaction log table .
1. Deduct commodity inventory
2. Generate order
3. Bonus points
4. Deduct the balance
3.1.7 TCC The third problem caused by transactions :cancel perhaps confirm Failure
There are many curious children to ask , Suppose I have all try It's all done , Or some have failed , need cancel and confirm I failed because of network problems , What about swelling . Don't panic , There will be a local scheduled task , Go regularly Local transaction table log Scan outstanding transactions , Suppose this firm has try They all succeeded , Part of it confirm failed , Regular tasks will continue to help you perform confirm operation , conversely cancel. At this time, we still need to rely on Global transaction id, Branch business id, Local transaction log table .
If the last multiple retries fail, it must be compensated manually , Early warning .
3.1.8 TCC The fourth problem caused by transactions : Downtime recovery
There are many curious children to ask , What should I do if I go down in the middle of a transaction , Don't panic . When the project starts, go to the local transaction log table to scan the unfinished transactions , Then ask if all the branch transactions try It's all done , If it is , Regular tasks will continue to help you perform confirm operation , conversely cancel. At this time, we still need to rely on Global transaction id, Branch business id, Local transaction log table .
If the last multiple retries fail, it must be compensated manually , Early warning .
3.1.9 TCC Simple principle of equal framework
Local transaction log table , Global transaction id, Branch business id about TCC Distributed transactions are very important , But the general framework helps us realize this function , Including idempotency , Empty rollback , Failure to retry , Downtime starts , Including the whole try after confirm perhaps cancel Automatic call of , If we implement it ourselves, we need to solve this problem .
The general principle of this framework is dynamic proxy data source , Rewrote commit Other methods , Generate a global transaction when a distributed transaction is started id, adopt feign When called , adopt feign Interceptor , The global transaction id Ask the head to take it , If the invoked service is also in a distributed transaction , Generate branch transactions id, And then in commit The status of the current branch transaction is also recorded during the local transaction , Because it is in a library, atomicity can be guaranteed . Each microservice local transaction commit after try End of the stage , The framework will automatically help us to call the... Associated with our service call chain confirm perhaps cancel.
3.2.0 TCC Distributed transaction summary
advantage : High concurrency , Do not lock resources (2PC Database resources will be locked ), The local transaction can be committed , It is generally applicable to the scenario where there is no mistake in funds .
shortcoming : complex , A business interface needs to be disassembled 3 individual , The business is very intrusive , The old system makes you doubt your life , If you implement it yourself, you have to record the local transaction log , retry , General teams will not use this without strength , Because it's too coquettish .
3.2 Local message table
- A The system operates in its own local transaction at the same time , Insert a piece of data into the message table ( Atomicity of the same database )
- next A The system sends this message to MQ In the middle
- B After the system receives the message , In a business , Go to your local message list ( Idempotency ) Insert a piece of data , Perform other business operations at the same time , If the message has been processed , At this time, the transaction will roll back , This ensures that messages are not processed repeatedly
- B After the successful execution of the system , It will update the status of its local message table and A Status of the system message table
- If B System processing failed , Then the message table status will not be updated , So at this time A The system will scan its message table regularly , If there is a message that hasn't been processed , It will be sent again to MQ In the middle , Give Way B Deal with... Again
- This scheme guarantees final consistency , Even if the B The transaction failed , however A I'll keep sending messages back , until B Until we succeed there , Reach final agreement
- The message we sent , You must bring the data associated with the business , For example, adding new users , Send to increase points mq news , our mq The message body of the message must be accompanied by the new user's id, In order to find the problem in the future .
- Simple understanding : Message localization , Timed task timed message sending middleware .
3.2.1 Local message table examples
The user has registered to give points as an example
1. User service inserts user data
2. In the same transaction , Insert a piece of data giving points into the local message table , The status is not sent .
3. Transaction submission
4. Scheduled tasks go to the local message table regularly , Find data whose status is unsent , send out mq, Then the status changes to sent .
5.mq Persistent message .
6. The score service monitors the corresponding topic, When consuming messages, you must pay attention to idempotency , Because of the steps 4 It is possible to send messages repeatedly , Possible network problems , This causes messages to be sent repeatedly ,mq In the absence of ack It will also be sent repeatedly , Our scheduled task does not change the status of the message , Then the scheduled task will be sent repeatedly . What we need to do is to consume the news first id Insert local message table , To guarantee idempotence , And then deal with our business . Idempotency can be guaranteed by many methods , It is not necessary to record the consumption messages . For example, add distributed locks when consuming , Check whether the business is completed in the lock , If the next message comes after completion , Don't spend . After consuming the news, remember ack, Otherwise mq It will also be delivered repeatedly .
7.( Optional ). The credit service has been consumed , Tell the user the local message table of the service , Change the corresponding message to completed .
8.( Optional ) Scheduled tasks go to the local message table regularly , Find data whose status is sent , Repeat delivery .
9.( The bottom line ) If a message fails to be delivered multiple times , Or if you fail to consume for many times, you will not deliver or consume again , At this time, we have to make an early warning , Handle by hand .
10.( improvement ) We can send immediately after the local transaction is committed mq, Then modify the status of the local message , In this way, the real-time performance will be better , The rest remains the same , Timed tasks are used to reveal and resend .
11.( improvement ) We can add another query interface , The consumer can query the status of our business .

3.2.2 Local message table implementation code
1.UserClient New users , And save the local message to add the integral table , The data of the local integral table must be accompanied by the data of the associated business id etc. , Here we bring users id, In case of subsequent exceptions, we may go to the user service to check whether the user has actually registered .
2. Messages whose scheduled task delivery status is to be sent to mq, And the modification status is sent
3.PointClient Accept processing messages , Insert the message table first , The logo has been processed , And this table has a unique constraint , then , Process business messages .
4. Remember ack, Otherwise mq Will be delivered repeatedly .
5.( Optional ) After the business is processed, we can also tell the caller that the business is processed , The message status changes to completed .
UserClient Customer service
@Component
public class UserClient {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private PointLogMapper pointLogMapper;
// Local transactions , You can optimize the delivery of local transactions as soon as they are committed mq, The real-time performance will be better
@Transactional
public ApiResult save(User user){
// Save the user
userMapper.save(user);
PointLog pointLog=new PointLog();
pointLog.setUserId(user.getid);
pointLog.setPoint(1);
pointLog.setcreateTimeUtc(TimeUtils.getUTCTime());
pointLog.setstate(0);
// Save points log records
pointLogMapper.savePointLog(pointLog);
}
// Local message table not sent mq The news of , send out mq
@Scheduled(cron = "0 1 0 * * ?")
public pushMessage(){
List<PointLog> pointLogList=pointLogMapper.findAllLogUnPush();
for (PointLog pointLog:
pointLogList) {
boolean success=sendMq(JSON.toJsonString(pointLog));
if(success){
pointLog.setstate(1);
pointLogMapper.update(pointLog);
}
}
}
}PointClient Points service
@Component
public class PointClient {
@Autowired
private PonitMessageMapper pointMessageMapper;
@Override
@Transactional
public void onMessage(String message){
PointMessage pointMessage=JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), new TypeReference<PointMessage>(){});
// Insert message table , Unique constraint
pointMessageMapper.insert(pointMessage);
// Processing logic
pointServeice.addPoint(pointMessage);
message.ack();
}
}3.2.3 Local message table summary
advantage :
Simple , Low development cost , Simple
shortcoming :
Binding with business scenarios , High coupling , Not for public use
The local message table and the business data table are in the same library , Occupy business system resources , Large volume may affect database performance
Need to add MQ middleware , In fact, it's ok if you don't need it , We call it ourselves HTTP That's ok .
3.3 Reliable message final consistency scheme
This scheme is actually a variant of our local message table , The implementation principle is basically the same .
We need a Reliable messaging , Let's help us do the functions of local message table and scheduled task , At the beginning of the transaction, we only need to deliver one and a half messages ( Messages that cannot be consumed on the consumer side ), Reliable messaging services persist messages ( It can be seen as a local message table ), Then tell the reliable messaging service , Do I commit or rollback local transactions this time , If it is submitted , I will change the status of this semi message , Become consumable , And if the consumer fails to consume, the scheduled task of our reliable message service will continuously deliver consumable messages to the consumer , The consumer end ack. If the reliable message service fails to receive it for a long time, I should submit or rollback this semi message , It will automatically call the query interface of the sender , Let him tell me that I should change the semi message status to consumable , Or should we delete .
For example, adding new users , Add points
1. My user service first delivers an increase in points ( To bring a new user id) The semi - message to our reliable messaging service , If the transaction fails, the local transaction will not be executed , The delivery is successful, and the consumer of the points service can't see this message .
2. Execute local transactions and add users .
3. Local transaction succeeded , Tell the reliable messaging service , You can turn the previous half message into consumable , In this way, the credit service can consume this message , Note idempotency .
4. Local transaction failed , Tell the reliable messaging service , Please help me delete the half message just now , I failed. .
5. Assume that the reliable messaging service is not informed for network reasons , The reliable messaging service will carry that message , To ask about your user service , Whether my user has generated , If it is generated, you will reply to me. The user generated it , I change the status of the message to consumable , Otherwise delete this message .
6. The consumer consumption is the same as the local message table , To tell reliable information, I have consumed this information , Don't send it to me again , Also keep idempotency .
And this reliable information service , Namely Rocketmq The transaction message function of , He has completed all the above functions .
3.3.1 rocketmq Transaction message
RocketMQ In the design of broker And producter The two-way communication ability of the terminal , bring broker Naturally, it can exist as a transaction coordinator , and RocketMQ The storage mechanism provided by itself provides the persistence capability for transaction messages ,RocketMQ The high-performance mechanism and reliable message mechanism are that the transaction message can still ensure the final consistency of the transaction when the system is abnormal . stay RocketMQ 4.3 After the implementation of the complete transaction message , In fact, it is necessary to encapsulate the local message table , Moved local messages to MQ Inside , solve Producter The atomicity of message sending and local transaction execution at the end .
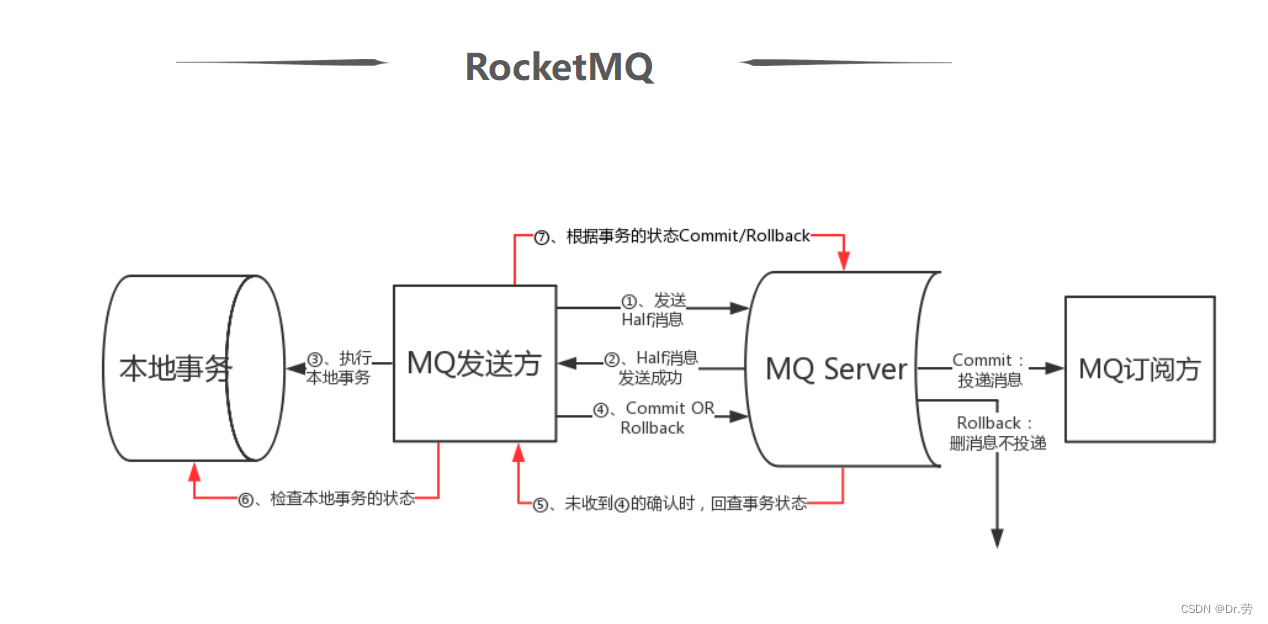
The execution process is as follows :
For the convenience of understanding, we also use the example of registering to send points to describe The whole process .
Producer namely MQ The sender , In this case, the user service , Responsible for new users .MQ The subscriber is the message consumer , In this case, point service , Responsible for adding points .
1、Producer Send transaction message
Producer (MQ The sender ) Send a transaction message to MQ Server,MQ Server Mark the message status as Prepared( Ready state ), notes : At this time, this message consumers (MQ Subscriber ) It can't be consumed .
In this case ,Producer send out ” Add points message “ To MQ Server.
2、MQ Server Response message sent successfully
MQ Server Received Producer The message sent to responds to the message sent successfully MQ Message received .
3、Producer Performing local transactions
Producer End execution business code logic , Through local database transaction control .
In this case ,Producer Perform the add user action .
4、 Message delivery
if Producer If the local transaction is executed successfully, it will automatically send to MQServer send out commit news ,MQ Server Received commit After the news will ” Add points message “ The status is marked as consumable , here MQ Subscriber ( Points service ) Normal consumption message ;
if Producer If the local transaction fails, it will automatically send the MQServer send out rollback news ,MQ Server Received rollback After the news Will delete ” Add points message “ .
MQ Subscriber ( Points service ) News consumption , The success of consumption is to MQ Respond ack, Otherwise, the message will be received repeatedly . here ack Default auto response , That is to say, if the program runs normally, it will automatically respond ack.
5、 Back to business
If you execute Producer In the process of end local transaction , Execution end hangs up , Or a timeout ,MQ Server Will keep asking the rest of the group Producer To get the transaction execution status , This process is called transaction review .MQ Server It will decide whether to post the message or not according to the transaction query result .
The above main process has been completed by RocketMQ Realization , For the user side , The user needs to implement local transaction execution and local transaction callback methods respectively , Therefore, you only need to pay attention to the execution state of the local transaction .
3.3.2 rocketmq Transaction message code landing
Also add new users , Add points as an example .
User service new users , And here's the credit service consumption news , Take care to ensure idempotency .
Notice that we have one Business table , To save the corresponding transaction id Has it been completed , Used for back checking , So we need one Business id Throughout the whole business , It's used below txNo.
AccountClient Customer service
1.accountInfoController#accountCreateMessage
We use UUID It generates a TxNo As a matter of fact id, The user checks back on the transaction , And then call service Send new user message .
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class AccountInfoController {
@Autowired
private AccountInfoService accountInfoService;
@PostMapping(value = "/create")
public String createAccount(@RequestParam("accountNo")String accountNo){
// Create a transaction id, Send as message content to mq
String tx_no = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
AccountChangeEvent accountChangeEvent = new AccountChangeEvent(accountNo,tx_no);
// Send a message
accountInfoService.createAccountMessage(accountChangeEvent);
return " Create user ";
}
}2.accountInfoService#createAccountMessage This method sends rocketmq Transaction messages arrive at producer_group_txmsg, This time is a half message , The consumer cannot see .
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AccountInfoServiceImpl implements AccountInfoService {
@Autowired
AccountInfoDao accountInfoDao;
@Autowired
RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate;
// towards mq Send a new user message
@Override
public void createAccountMessage(AccountChangeEvent accountChangeEvent) {
// take accountChangeEvent Turn into json
JSONObject jsonObject =new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("createAccount",accountChangeEvent);
String jsonString = jsonObject.toJSONString();
// Generate message type
Message<String> message = MessageBuilder.withPayload(jsonString).build();
// Send a transaction message
/**
* String txProducerGroup production team
* String destination topic,
* Message<?> message, The message content
* Object arg Parameters
*/
rocketMQTemplate.sendMessageInTransaction("producer_group_txmsg","topic_txmsg",message,null);
}
// Create user
@Override
@Transactional
public void createAccount(AccountChangeEvent accountChangeEvent) {
// Idempotent judgment
if(accountInfoDao.isExistTx(accountChangeEvent.getTxNo())>0){
return ;
}
// Create user
accountInfoDao.createAccount(accountChangeEvent.getAccountNo());
// Add transaction log
accountInfoDao.addTx(accountChangeEvent.getTxNo());
}
}3. Performing local transactions
When we send half a message , Callbacks ProducerTxmsgListener#executeLocalTransaction, Because I did monitoring @RocketMQTransactionListener
At this time, we can get it and send it out message, Execute the above local transaction accountInfoService#createAccount, Save user data , And save the transaction log ( Insert txNo( Business id)).
4. Back to business
ProducerTxmsgListener#checkLocalTransaction Query whether the local transaction is completed
Because of us Message There's a txNo Business id, When we execute ProducerTxmsgListener#executeLocalTransaction We will tell rocketmq, Whether the local transaction succeeded or failed this time , If successful, the transaction log table will be inserted , If you fail, there will be no such data .
Because the network is not stable , We tell rocketmq He didn't receive the news of ,rocketmq It will call our... Regularly with the message body
ProducerTxmsgListener#checkLocalTransaction, We take it out txNo, Query whether the current transaction is completed , If execution is complete , Just go back to commit, Messages can be visible to consumers .
@Component
@Slf4j
@RocketMQTransactionListener(txProducerGroup = "producer_group_txmsg")
public class ProducerTxmsgListener implements RocketMQLocalTransactionListener {
@Autowired
AccountInfoService accountInfoService;
@Autowired
AccountInfoDao accountInfoDao;
// The callback method after the transaction message is sent , When a message is sent to mq success , This method is called back
@Override
@Transactional
public RocketMQLocalTransactionState executeLocalTransaction(Message message, Object o) {
try {
// analysis message, Turn into AccountChangeEvent
String messageString = new String((byte[]) message.getPayload());
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(messageString);
String accountChangeString = jsonObject.getString("accountChange");
// take accountChange(json) Turn into AccountChangeEvent
AccountChangeEvent accountChangeEvent = JSONObject.parseObject(accountChangeString, AccountChangeEvent.class);
// Performing local transactions , Create user
accountInfoService.createAccount(accountChangeEvent);
// When to return to RocketMQLocalTransactionState.COMMIT, Automatic direction mq send out commit news ,mq Change the status of the message to consumable
return RocketMQLocalTransactionState.COMMIT;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return RocketMQLocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK;
}
}
// Transaction status check , Whether the query was executed successfully
@Override
public RocketMQLocalTransactionState checkLocalTransaction(Message message) {
// analysis message, Turn into AccountChangeEvent
String messageString = new String((byte[]) message.getPayload());
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(messageString);
String accountChangeString = jsonObject.getString("accountChange");
// take accountChange(json) Turn into AccountChangeEvent
AccountChangeEvent accountChangeEvent = JSONObject.parseObject(accountChangeString, AccountChangeEvent.class);
// Business id
String txNo = accountChangeEvent.getTxNo();
int existTx = accountInfoDao.isExistTx(txNo);
if(existTx>0){
return RocketMQLocalTransactionState.COMMIT;
}else{
return RocketMQLocalTransactionState.UNKNOWN;
}
}
}PointClient Points service
No more code here , The code of the consumer side is the same as that of the local message table . Just pay attention to idempotency , Add new points and give mq return ack.
Note that if consumption continues to fail , Need early warning Handle by hand .
3.3.3 Reliable information is finally summarized consistently
benefits :
RocketMQ It mainly solves two functions :
1. Atomicity of local transaction and message sending .
2. Reliability of message received by transaction participants . Finally, reliable message consistent transactions are suitable for scenarios with long execution cycle and low real-time requirements . After introducing the message mechanism , Synchronous transaction operations become asynchronous operations based on message execution , Avoid the impact of synchronous blocking operations in distributed transactions , And realize the decoupling of two services .
3. Performance is better than local message tables , Can withstand higher concurrency
Disadvantage :
If you use rocketmq Transaction message , Strong dependence on rocketmq; We can also follow rocketmq To implement a reliable message service , But it increases the R & D cost and system complexity .
3.4 Best effort notification
We usually access wechat payment , As long as the user pays successfully , Wechat has called back to us at a certain frequency , If we fail to reply to wechat , He will inform you later , At most 15 Time .
15 After that , We can only take the initiative to go to wechat to check whether the order is successful . This service of wechat is the best effort notification

3.4.1 Try your best to inform the implementation
Because the code here is relatively simple , Is the simplified version of reliable information , I won't do that here , Only the implementation scheme is listed .
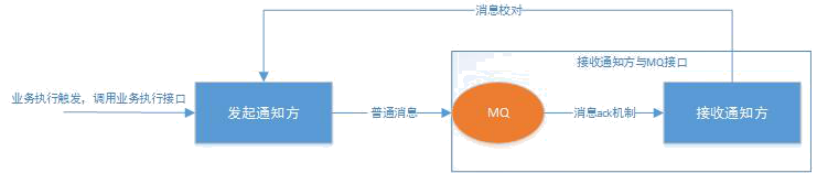
3.4.2 The similarities and differences between best effort notification and reliability messaging
1. Solution ideas are different
-- Reliable message consistency , The initiating notifier needs to ensure that the message is sent , And send the message to the receiving party , The key to the reliability of the message is for the initiator to guarantee .
3.5 Business distributed transaction ( Log plus delay message )
@Transactional
public Result createOrder(Product product){
// Generate order number
String orderNo= RandomUtil.ranDomStr(5);
DeductProduct decute=new DeductProduct();
decute.setCount(product.getCount);
decute.setProductId(product.getId);
decute.setOrderNo(orderNo);
//feign Call inventory service to reduce inventory
boolean success=storeFeignClient.decute(decute);
if(!success){
return "error";
}
//feign Add points to users
Point point=new Point();
point.setPoint(10);
point.setOrderNo(orderNo);
//feign Call inventory service to reduce inventory
boolean success1=pointFeignClient.addPOint(point);
if(!success1){
return "error";
}
// Insert local transaction order
Order order=new Order();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(product,order);
order.setOrderNo(orderNo);
OrderMapper.insert(order);
}Scene two : This feature is also available in our shared power bank orders ( I can lock the power bank , However, the power bank cannot pop up but no order is generated , They are two separate microservices )
1. Go to query which power bank can pop up now
2. Suppose the slot position is 1 Your power bank can pop up , First change his status to To be rented , No one can rent the power bank in this state again , Until his status is changed . A power bank in this state , Whether your order is successfully generated or not , I can change this state through compensation , And ensure that my power bank will not fail to generate orders due to distributed transactions , The power bank pops up .
3. Then generate advance orders , That is, the status is advance order
4. After the order transaction is submitted , Call alicloud asynchronously IOT To issue instructions , Eject the slot 1 The power bank of
5. The eject result returns to the eject slot 1 The power bank of , The status of the power bank is changed to in use , The order is changed to in use , Failed to return to the battery , Then it can be rented , Change order to failed .
6. If there is no feedback , There are two situations ,
The first one is : The order was rolled back , We regularly check the status of the power bank to be leased , See if he has any orders in use , If yes, it will be changed to "on lease" , If not, it can be rented
The second kind : The cabinet was not reported because of network problems , We can take the initiative to query the slot 1 Is your battery still there , It can also be based on the heartbeat reported by the cabinet , Know the slot position 1 Is your power bank still there , So as to change the status of the power bank and the order .
3.5.1 Summary of business distributed transactions
3.6 Synchronous double write ( How to write )+ Asynchronous reconciliation
3.6.2 Synchronous double write transaction code landing
3.6.1 Synchronous double write transaction solution
3.6.2 Synchronous double write ( How to write )+ Asynchronous reconciliation summary
3.7 Alibaba Seata frame

3.7.1 seataAT Frequently asked questions and XA contrast
1. The global transaction has not been completed yet , Data modified by other transactions
Suppose a request is based on seata A global lock is added to a piece of data , And commit the local branch transaction . At this time, the global transaction is not committed , Another request to come ( This request is simply to update the data , It's not a distributed transaction ) Naturally, there is no need to obtain a global lock , That is, you can directly update . Is there a problem when the global transaction is rolled back ?
you 're right , The scenario described is problematic , This is what we need to consider when developing , When it is possible to operate the same data and cause concurrency problems , Add him to the overall Affairs , To get the global lock .
2. since seata There are also global locks , So with me XA What's the difference? , Everyone locks resources in the first stage .
Architecture level , Tradition 2PC Of the plan RM It's actually in the database layer ,RM Essentially, it's the database itself , adopt XA Protocol implementation , and Seata Of RM In order to jar The package is deployed on the application side as a middleware layer . Two phase submission , Tradition 2PC No matter the resolution of the second stage is commit still rollback, The locks of transactional resources should be kept to Phase2 complete To release . and Seata The way to do this is to Phase1 Commit local transaction , So we can save it Phase2 Time to hold lock , Improve overall efficiency .
Simply speaking , Namely seataAT The schema phase 1 has committed the local transaction , No longer hold database resources , But others want to modify , You must obtain a global lock first ( Data to be modified Id Set ). and XA Mode as long as your transaction is not committed for one day , My database locks these data , Nobody can move , I kiss measuring , stay XA An exception is thrown during execution , You haven't submitted anything in a day , That line of work is locked up , Do not modify , If the modified data has no conditions , Watch lock , It's a watch lock. Just wait for it to explode . therefore seata at Patterns and us 2pc Of XA It's like , It's just seata It is in the first stage that the data is submitted , Follow up on undo_log compensate .
3. What is a global lock
Suppose my users 13 Order operation , Need to lock goods id by 1 and id=5 Inventory of , You need to add points to users , The user's balance needs to be modified , Then we'll put the inventory list id=1 and id=5, User table id=13, Collect it all , use tableName+id As the only index , Insert database , The inventory table is locked 2 individual id Just insert two pieces of data .( The newly added data will not have a global lock )
If other transactions want to modify the corresponding data , You must first obtain the global lock , Look at what I modified this time id Is it in the global lock , If the global lock is obtained circularly for a period of time .
4. Suppose the global transaction is rolled back , He will follow your Undo_log Log to compensate for previous data , If so update He found that ,undo_log The stored data is inconsistent with the current data ( So you need a global lock ), It will be abnormal , Manual compensation is required .
5. It was used seata at Pattern , We can't just update Database fields , Otherwise, he will die miserably .
3.7.2 Code landing ( The next blog post will give a detailed introduction )
actually seata AT Patterns are non intrusive , Just add a comment
1、 Global transactions start using @GlobalTransactional identification .
2、 Each local transaction scheme still uses @Transactional identification .
3、 Every data needs to be created undo_log surface , This watch is seata The key to local transaction consistency .
4、 Whether you are local or distributed , As long as your business needs distributed transactions @GlobalTransactional, Then you have to add this to local transactions @GlobalTransactional, To get the global lock , If my order , Need to lock inventory , Add points , I added... To this process @GlobalTransactional. So if the user refunds , We need to change the order status , This operation does not require distributed transactions , Only local transactions are required , We have to add @GlobalTransactional annotation , He's going to get the global lock , You can only operate without a global lock .
5、@GlobalTransactional This comment is a little heavy , He will http To register global transactions and branch transactions , Then get the global lock , If we only have local transactions, we can use @GlobalLock To get the global lock , He doesn't register global and branch transactions , Only get the global lock .
3.7.3 seata AT Pattern summary
advantage : There is no invasion of business , We just need to add an annotation , The principles are proxy data sources , enhance commit Other methods .
shortcoming : If the global lock is not added properly , Other transactions modify data before the global transaction is completed , Then wait for the explosion in place .
It is suitable for some scenarios where only a few people can modify the data , For example, our backstage service , The corresponding person can only operate his own data . And each step is related to the data modification operation of these tables , You have to get the global lock , Causing performance problems .
3.8 saga Business
In fact, this mode is rarely used , Let's take a look at his brief introduction .
TCC Business , In fact, it is to split an interface into 3 Interface ,try -> confirm -> cancel,try If you succeed confirm,try If you fail cancel. Then if confirm perhaps cancel Failed ?confirm/cancel If you fail, you just keep trying again .
saga Is to connect each interface , Split into 2 Interface , One is the business interface , The other is the compensation interface , It means that tcc Inside try and confirm Merge into one interface , It is to execute the business interface first , Directly try to complete the operation of the whole business logic, and then if it is in the service invocation chain , The execution of the business interface of a service failed , Then directly call the compensation interface for all services that have successfully executed , Rollback the previously executed business logic .
saga This thing , In fact, the core and essence , Each operation is divided into actual business logic and compensation business logic , Under normal circumstances , Just execute the business logic of each service in turn , If a service call fails , Directly execute compensation logic for those services that have been successfully executed before .
saga The idea of affairs , That is, a long distributed transaction , Split into a series of local transactions for each service , Then each service provides two interfaces for each interface , One is the business interface , One is the rollback compensation interface , Normally, it is called in turn .
Under abnormal conditions , Execute the compensation interface for the service that has been successfully executed before , Rollback business logic .
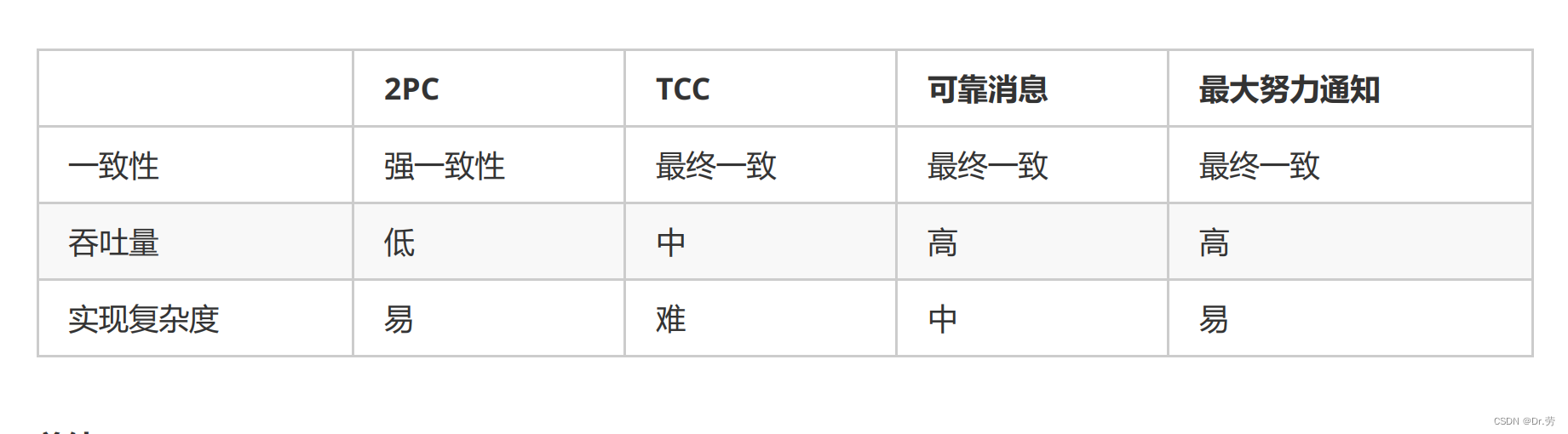
4. Distributed transaction selection
1. Adopt reliable message consistency scheme
Reliable message consistency requires that as long as the message is sent , The transaction participant will execute the transaction successfully after receiving the message , There is no requirement for rollback , Once you've done it, use it with a stiff scalp . It is suitable for scenes with long execution cycle and low real-time requirements . After introducing the message mechanism , Synchronized transaction operations become based on cancellation Asynchronous operations performed by messages , Avoid the impact of synchronous blocking operations in distributed transactions , And realize the decoupling of two services . Typical use scenarios : notes Send points in the book , Log in, send coupons, etc .
2. Use the best effort notification scheme
Best effort notification means that the initiating notifier notifies the transaction participants of the results after executing the local transaction , Even if the transaction participant fails to perform business processing, the initiating notifier will not roll back the transaction , Once you've done it, use it with a stiff scalp . Typical use scenarios : Bank notice 、 Payment result . Notice, etc .
3.TCC
If in a non abnormal state ,TCC It is actually a synchronous process , And if something goes wrong, you can roll back , The application can define the granularity of data operation by itself , Make lock conflict reduction 、 It's possible to increase throughput .
4.seata AT
Some background systems are highly recommended , The same data will not be modified by more than one person , There is no invasion of business .
5. Synchronous double write , Asynchronous reconciliation
That goes without saying , As long as multiple libraries are double written , Basically, this scheme is used .
6. Ultimate solution , Artificial compensation
I don't want to talk about this , Go to the log and write sql Make up for it .
If it is very strongly consistent , It is suggested to use..., which is linked to the capital category TCC,TCC There are too many details , If not a very strong team, it is easy to have problems , The business is very intrusive , An interface has to be changed 3.
Reliable message consistency is commonly used ( Local message table ), Add reconciliation , Generally, it can meet our needs , At most, there is a problem. According to the manual data , I have deeply experienced the pain of manually filling data for many times .
5. summary
Distributed transaction has never been a perfect solution in the industry , Basically, they try again + Log compensation , After understanding this, we found this problem , It's not as terrible as you think , Without distributed transactions , You don't have to , By retry + compensate ( In fact, it is also a flexible transaction ).
If conditions permit , We try to choose the local transaction list data source , Because it reduces the performance loss caused by network interaction , And avoid data Problems caused by weak consistency . If a system uses distributed transactions frequently and unreasonably , We should first observe whether the separation of services is reasonable from the perspective of overall design , High cohesion and low coupling ? Whether the granularity is too small ? Distributed transactions have always been a problem in the industry , Because of the uncertainty of the Internet , And we are used to taking distributed transactions and stand-alone transactions ACID comparing . Whether it's the database layer XA、 Or the application layer TCC、 Reliable information 、 Try your best to inform others , There is no perfect solution to the problem of distributed transactions , They're just performance 、 Uniformity 、 Choose between usability and other aspects , Looking for trade-offs under certain scenario preferences .
Reference resources A detailed explanation of the long essay Shardingsphere Yes XA Distributed transaction support - sea 5 Personal space - OSCHINA - Chinese open source technology exchange community
边栏推荐
- 把 Oracle 数据库从 Windows 系统迁移到 Linux Oracle Rac 集群环境(2)——将数据库转换为集群模式
- Convert string array to list collection
- 【FPGA】串口以命令控制温度采集
- 把 Oracle 数据库从 Windows 系统迁移到 Linux Oracle Rac 集群环境(4)—— 修改 oracle11g rac 集群的 scanIP
- 02 common codes for Epicor secondary development
- 计算机三级(数据库)备考题目知识点总结
- ida中交叉引用的解析
- |遇到bug怎么分析,专业总结分析来了
- When they are in private, they have a sense of propriety
- 会自动化—10K,能做自动化—20K,你搞懂自动化测试没有?
猜你喜欢

File system - basic knowledge of disk and detailed introduction to FAT32 file system

jwt

【Proteus仿真】Arduino UNO+数码管显示4x4键盘矩阵按键

Is it out of reach to enter Ali as a tester? Here may be the answer you want

What is the reason for the disconnection of video playback due to the EHOME protocol access of easycvr platform?

After reciting the eight part essay, I won the hemp in June

It is said that Yijia will soon update the product line of TWS earplugs, smart watches and bracelets

测试/开发程序员,30而立,你是否觉得迷茫?又当何去何从......

入坑机器学习:一,绪论

1-6搭建Win7虚拟机环境
随机推荐
Processon producer process (customized)
数据库系统概论必背知识
多模态情感识别_多模态融合的情感识别研究「建议收藏」
Dirvish Chinese document of vim
获取图片外链的方法–网易相册[通俗易懂]
How to choose a regular and safe foreign exchange trading platform?
Redis
分布式事务解决方案和代码落地
消息称一加将很快更新TWS耳塞、智能手表和手环产品线
会自动化—10K,能做自动化—20K,你搞懂自动化测试没有?
进入阿里做测试员遥不可及?这里或许有你想要的答案
The role of software security testing, how to find a software security testing company to issue a report?
Using qdomdocument to manipulate XML files in QT
Hashcat 的使用
同花顺是正规平台吗?同花顺开户安全吗
内网学习笔记(7)
当人们用互联网式的思维和视角来看待产业互联网的时候,其实已陷入到了死胡同
Is the compass reliable? Is it safe to open a securities account?
MOS tube related knowledge
Lizuofan, co-founder of nonconvex: Taking quantification as his lifelong career