当前位置:网站首页>postgresql之List
postgresql之List
2022-06-24 13:04:00 【happytree001】
一、简介
postgresql中实现了一套功能强大的List库,List分为两部分,head+body。
- body可以是任意对象,使用方便
- 使用数组方式实现,存储紧凑、随即访问、访问方便
- 使用0长数组,扩展方便
- 预分配空间,减少扩容次数,提升写入速度
- 可以将head和body分离,扩容后,可以减少缓存实效
- 功能强大,交、并、差集,头插、尾插、任意位置插入,头删、尾删、任意位置删除 …
二、 List结构
src/include/nodes/pg_list.h
2.1 定义
typedef union ListCell
{
void *ptr_value;
int int_value;
Oid oid_value;
} ListCell;
typedef struct List
{
NodeTag type; /* T_List, T_IntList, or T_OidList */
int length; /* number of elements currently present */
int max_length; /* allocated length of elements[] */
ListCell *elements; /* re-allocatable array of cells */
/* We may allocate some cells along with the List header: */
ListCell initial_elements[FLEXIBLE_ARRAY_MEMBER];
/* If elements == initial_elements, it's not a separate allocation */
} List;
NodeTag标识当前List的类型,同时也确定了List中存储的数据类型,是指针还是整数等。虽然List中可以存储任意的ListCell,但是ListCell中没有表示存储的类型,不方便读取,所以每个List都是存储的同一类数据。
2.2 结构图

三、 List API
src/include/nodes/pg_list.h
src/backend/nodes/list.c
3.1 创建list
创建一个新的list, 初始大小将进行2的幂次方对齐,这样将会产生多余的空间(即预分配空间)
static List *
new_list(NodeTag type, int min_size)
{
List *newlist;
int max_size;
...
max_size = pg_nextpower2_32(Max(8, min_size + LIST_HEADER_OVERHEAD));
max_size -= LIST_HEADER_OVERHEAD;
...
newlist = (List *) palloc(offsetof(List, initial_elements) +
max_size * sizeof(ListCell));
newlist->type = type;
newlist->length = min_size;
newlist->max_length = max_size;
newlist->elements = newlist->initial_elements;
return newlist;
}
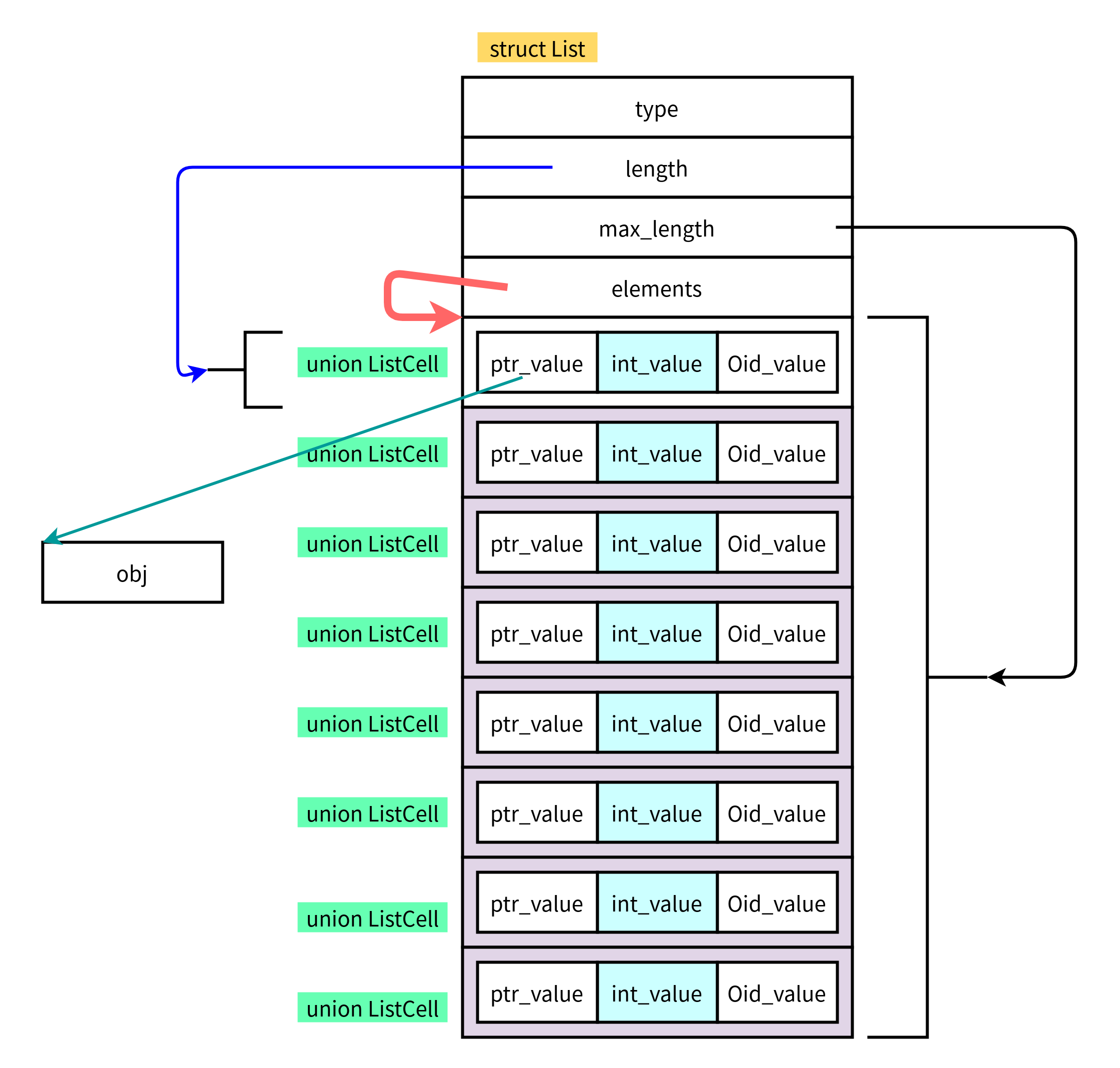
- head 和 body是一体的
- length表示当前已经使用的元素个数
- max_length表示当前已经分配的元素个数
- 一般max_length >= length, 这样预分配有多余的空间,后续使用可以减少扩容次数
- 获取元素个数时间复杂度O(1)
- 因为是数组实现,所以除了尾部插入元素,其他位置都需要移动数据,建议都尾插入和尾删
3.2 扩容list
static void
enlarge_list(List *list, int min_size)
{
int new_max_len;
...
/* * As above, we prefer power-of-two total allocations; but here we need * not account for list header overhead. */
/* clamp the minimum value to 16, a semi-arbitrary small power of 2 */
new_max_len = pg_nextpower2_32(Max(16, min_size));
...
if (list->elements == list->initial_elements)
{
/* * Replace original in-line allocation with a separate palloc block. * Ensure it is in the same memory context as the List header. (The * previous List implementation did not offer any guarantees about * keeping all list cells in the same context, but it seems reasonable * to create such a guarantee now.) */
list->elements = (ListCell *)
MemoryContextAlloc(GetMemoryChunkContext(list),
new_max_len * sizeof(ListCell));
memcpy(list->elements, list->initial_elements,
list->length * sizeof(ListCell));
...
}
else
{
...
/* Normally, let repalloc deal with enlargement */
list->elements = (ListCell *) repalloc(list->elements,
new_max_len * sizeof(ListCell));
...
}
list->max_length = new_max_len;
}
当数组填满后,将进行扩容,但是扩容又和普通的List扩容不同 ,这里只扩容body, head保持不变,这样可以减少缓存失效。
- 第一次扩容时,head 和body分离
- 第二次扩容开始,只扩容body

注意
原始body还指向相同的对象,不要再访问, 原代码中做了处理,这里粘贴的代码删除了。
3.3 返回已有元素的个数
/* Fetch list's length */
static inline int
list_length(const List *l)
{
return l ? l->length : 0;
}
3.4 返回元素
1. 返回首元素
/* Fetch address of list's first cell; NULL if empty list */
static inline ListCell *
list_head(const List *l)
{
return l ? &l->elements[0] : NULL;
}
2.返回尾元素
/* Fetch address of list's last cell; NULL if empty list */
static inline ListCell *
list_tail(const List *l)
{
return l ? &l->elements[l->length - 1] : NULL;
}
使用场景不同,list_tail不知道list是否为空,而list_last_cell使用时list必须非空。
/* * Return the last cell in a non-NIL List. */
static inline ListCell *
list_last_cell(const List *list)
{
Assert(list != NIL);
return &list->elements[list->length - 1];
}
3. 返回某个位置的元素
/* * Locate the n'th cell (counting from 0) of the list. * It is an assertion failure if there is no such cell. */
static inline ListCell *
list_nth_cell(const List *list, int n)
{
Assert(list != NIL);
Assert(n >= 0 && n < list->length);
return &list->elements[n];
}
4. 返回当前元素的下一个元素
/* * Get the address of the next cell after "c" within list "l", or NULL if none. */
static inline ListCell *
lnext(const List *l, const ListCell *c)
{
Assert(c >= &l->elements[0] && c < &l->elements[l->length]);
c++;
if (c < &l->elements[l->length])
return (ListCell *) c;
else
return NULL;
}
3.5 返回元素值
1. 获取索引0-3及最后位置元素值
由函数list_nth_cell构成了一些列的宏函数, 获取索引0-3以及last的位置的元素的值。
#define lfirst(lc) ((lc)->ptr_value)
#define lfirst_int(lc) ((lc)->int_value)
#define lfirst_oid(lc) ((lc)->oid_value)
#define lfirst_node(type,lc) castNode(type, lfirst(lc))
#define linitial(l) lfirst(list_nth_cell(l, 0))
#define linitial_int(l) lfirst_int(list_nth_cell(l, 0))
#define linitial_oid(l) lfirst_oid(list_nth_cell(l, 0))
#define linitial_node(type,l) castNode(type, linitial(l))
#define lsecond(l) lfirst(list_nth_cell(l, 1))
#define lsecond_int(l) lfirst_int(list_nth_cell(l, 1))
#define lsecond_oid(l) lfirst_oid(list_nth_cell(l, 1))
#define lsecond_node(type,l) castNode(type, lsecond(l))
#define lthird(l) lfirst(list_nth_cell(l, 2))
#define lthird_int(l) lfirst_int(list_nth_cell(l, 2))
#define lthird_oid(l) lfirst_oid(list_nth_cell(l, 2))
#define lthird_node(type,l) castNode(type, lthird(l))
#define lfourth(l) lfirst(list_nth_cell(l, 3))
#define lfourth_int(l) lfirst_int(list_nth_cell(l, 3))
#define lfourth_oid(l) lfirst_oid(list_nth_cell(l, 3))
#define lfourth_node(type,l) castNode(type, lfourth(l))
#define llast(l) lfirst(list_last_cell(l))
#define llast_int(l) lfirst_int(list_last_cell(l))
#define llast_oid(l) lfirst_oid(list_last_cell(l))
#define llast_node(type,l) castNode(type, llast(l))
并且 caseNode宏将元素值转换为对应的数据类型,用于 void* 类型的类型转换。
src/include/nodes/nodes.h
#define castNode(_type_, nodeptr) ((_type_ *) (nodeptr))
2. 返回某个位置元素值
/* * Return the pointer value contained in the n'th element of the * specified list. (List elements begin at 0.) */
static inline void *
list_nth(const List *list, int n)
{
Assert(IsA(list, List));
return lfirst(list_nth_cell(list, n));
}
/* * Return the integer value contained in the n'th element of the * specified list. */
static inline int
list_nth_int(const List *list, int n)
{
Assert(IsA(list, IntList));
return lfirst_int(list_nth_cell(list, n));
}
/* * Return the OID value contained in the n'th element of the specified * list. */
static inline Oid
list_nth_oid(const List *list, int n)
{
Assert(IsA(list, OidList));
return lfirst_oid(list_nth_cell(list, n));
}
3.6 返回当前元素在list中的索引值
/* * Get the given ListCell's index (from 0) in the given List. */
static inline int
list_cell_number(const List *l, const ListCell *c)
{
Assert(c >= &l->elements[0] && c < &l->elements[l->length]);
return c - l->elements;
}
3.7 迭代循环整个list
根据同时遍历不同个数的list, 使用不同的ForXxxState的迭代器进行记录中间状态。最大能同时遍历5个list。
/* * State structs for various looping macros below. */
typedef struct ForEachState
{
const List *l; /* list we're looping through */
int i; /* current element index */
} ForEachState;
typedef struct ForBothState
{
const List *l1; /* lists we're looping through */
const List *l2;
int i; /* common element index */
} ForBothState;
typedef struct ForBothCellState
{
const List *l1; /* lists we're looping through */
const List *l2;
int i1; /* current element indexes */
int i2;
} ForBothCellState;
typedef struct ForThreeState
{
const List *l1; /* lists we're looping through */
const List *l2;
const List *l3;
int i; /* common element index */
} ForThreeState;
typedef struct ForFourState
{
const List *l1; /* lists we're looping through */
const List *l2;
const List *l3;
const List *l4;
int i; /* common element index */
} ForFourState;
typedef struct ForFiveState
{
const List *l1; /* lists we're looping through */
const List *l2;
const List *l3;
const List *l4;
const List *l5;
int i; /* common element index */
} ForFiveState;
使用foreach宏过程中,不能随意删除元素
#define foreach(cell, lst) \ for (ForEachState cell##__state = {
(lst), 0}; \ (cell##__state.l != NIL && \ cell##__state.i < cell##__state.l->length) ? \ (cell = &cell##__state.l->elements[cell##__state.i], true) : \ (cell = NULL, false); \ cell##__state.i++)
只能使用 foreach_delete_current 在遍历过程中删除当前元素
#define foreach_delete_current(lst, cell) \ (cell##__state.i--, \ (List *) (cell##__state.l = list_delete_cell(lst, cell)))
还可以指定从某个位置开始遍历, 使用for_each_from宏。
#define for_each_from(cell, lst, N) \ for (ForEachState cell##__state = for_each_from_setup(lst, N); \ (cell##__state.l != NIL && \ cell##__state.i < cell##__state.l->length) ? \ (cell = &cell##__state.l->elements[cell##__state.i], true) : \ (cell = NULL, false); \ cell##__state.i++)
static inline ForEachState
for_each_from_setup(const List *lst, int N)
{
ForEachState r = {
lst, N};
Assert(N >= 0);
return r;
}
3.8 插入
1. 尾插元素
/* * Make room for a new tail cell in the given (non-NIL) list. * * The data in the new tail cell is undefined; the caller should be * sure to fill it in */
static void
new_tail_cell(List *list)
{
/* Enlarge array if necessary */
if (list->length >= list->max_length)
enlarge_list(list, list->length + 1);
list->length++;
}
/* * Append a pointer to the list. A pointer to the modified list is * returned. Note that this function may or may not destructively * modify the list; callers should always use this function's return * value, rather than continuing to use the pointer passed as the * first argument. */
List *
lappend(List *list, void *datum)
{
Assert(IsPointerList(list));
if (list == NIL)
list = new_list(T_List, 1);
else
new_tail_cell(list);
llast(list) = datum;
check_list_invariants(list);
return list;
}
/* * Append an integer to the specified list. See lappend() */
List *
lappend_int(List *list, int datum)
{
Assert(IsIntegerList(list));
if (list == NIL)
list = new_list(T_IntList, 1);
else
new_tail_cell(list);
llast_int(list) = datum;
check_list_invariants(list);
return list;
}
/* * Append an OID to the specified list. See lappend() */
List *
lappend_oid(List *list, Oid datum)
{
Assert(IsOidList(list));
if (list == NIL)
list = new_list(T_OidList, 1);
else
new_tail_cell(list);
llast_oid(list) = datum;
check_list_invariants(list);
return list;
}
2. 唯一性尾插
当插入的值已经存在,则直接返回,不进行操作, 否则插入新元素。
/* * Append datum to list, but only if it isn't already in the list. * * Whether an element is already a member of the list is determined * via equal(). */
List *
list_append_unique(List *list, void *datum)
{
if (list_member(list, datum))
return list;
else
return lappend(list, datum);
}
/* * This variant of list_append_unique() determines list membership via * simple pointer equality. */
List *
list_append_unique_ptr(List *list, void *datum)
{
if (list_member_ptr(list, datum))
return list;
else
return lappend(list, datum);
}
/* * This variant of list_append_unique() operates upon lists of integers. */
List *
list_append_unique_int(List *list, int datum)
{
if (list_member_int(list, datum))
return list;
else
return lappend_int(list, datum);
}
/* * This variant of list_append_unique() operates upon lists of OIDs. */
List *
list_append_unique_oid(List *list, Oid datum)
{
if (list_member_oid(list, datum))
return list;
else
return lappend_oid(list, datum);
}
3. 头插元素
/* * Make room for a new head cell in the given (non-NIL) list. * * The data in the new head cell is undefined; the caller should be * sure to fill it in */
static void
new_head_cell(List *list)
{
/* Enlarge array if necessary */
if (list->length >= list->max_length)
enlarge_list(list, list->length + 1);
/* Now shove the existing data over */
memmove(&list->elements[1], &list->elements[0],
list->length * sizeof(ListCell));
list->length++;
}
List *
lcons(void *datum, List *list)
{
Assert(IsPointerList(list));
if (list == NIL)
list = new_list(T_List, 1);
else
new_head_cell(list);
linitial(list) = datum;
check_list_invariants(list);
return list;
}
/* * Prepend an integer to the list. See lcons() */
List *
lcons_int(int datum, List *list)
{
Assert(IsIntegerList(list));
if (list == NIL)
list = new_list(T_IntList, 1);
else
new_head_cell(list);
linitial_int(list) = datum;
check_list_invariants(list);
return list;
}
/* * Prepend an OID to the list. See lcons() */
List *
lcons_oid(Oid datum, List *list)
{
Assert(IsOidList(list));
if (list == NIL)
list = new_list(T_OidList, 1);
else
new_head_cell(list);
linitial_oid(list) = datum;
check_list_invariants(list);
return list;
}
3.9 删除
1. 删除某个位置的元素
/* * Delete the n'th cell (counting from 0) in list. * * The List is pfree'd if this was the last member. */
List *
list_delete_nth_cell(List *list, int n)
{
...
Assert(n >= 0 && n < list->length);
/* * If we're about to delete the last node from the list, free the whole * list instead and return NIL, which is the only valid representation of * a zero-length list. */
if (list->length == 1)
{
list_free(list);
return NIL;
}
...
memmove(&list->elements[n], &list->elements[n + 1],
(list->length - 1 - n) * sizeof(ListCell));
list->length--;
...
return list;
}
2. 删除某个元素
将元素转换为索引进行删除。
/* * Delete 'cell' from 'list'. * * The List is pfree'd if this was the last member. However, we do not * touch any data the cell might've been pointing to. */
List *
list_delete_cell(List *list, ListCell *cell)
{
return list_delete_nth_cell(list, cell - list->elements);
}
3. 删除某个值
/* * Delete the first cell in list that matches datum, if any. * Equality is determined via equal(). */
List *
list_delete(List *list, void *datum)
{
ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (equal(lfirst(cell), datum))
return list_delete_cell(list, cell);
}
/* Didn't find a match: return the list unmodified */
return list;
}
/* As above, but use simple pointer equality */
List *
list_delete_ptr(List *list, void *datum)
{
ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (lfirst(cell) == datum)
return list_delete_cell(list, cell);
}
/* Didn't find a match: return the list unmodified */
return list;
}
/* As above, but for integers */
List *
list_delete_int(List *list, int datum)
{
ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (lfirst_int(cell) == datum)
return list_delete_cell(list, cell);
}
/* Didn't find a match: return the list unmodified */
return list;
}
/* As above, but for OIDs */
List *
list_delete_oid(List *list, Oid datum)
{
ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (lfirst_oid(cell) == datum)
return list_delete_cell(list, cell);
}
/* Didn't find a match: return the list unmodified */
return list;
}
4. 删除第一个元素
/* * Delete the first element of the list. * * This is useful to replace the Lisp-y code "list = lnext(list);" in cases * where the intent is to alter the list rather than just traverse it. * Beware that the list is modified, whereas the Lisp-y coding leaves * the original list head intact in case there's another pointer to it. */
List *
list_delete_first(List *list)
{
check_list_invariants(list);
if (list == NIL)
return NIL; /* would an error be better? */
return list_delete_nth_cell(list, 0);
}
5. 删除最后一个元素
当长度大于1时,只需要将length减1即可,不需要数据的移动,速度很快。
/* * Delete the last element of the list. * * This is the opposite of list_delete_first(), but is noticeably cheaper * with a long list, since no data need be moved. */
List *
list_delete_last(List *list)
{
check_list_invariants(list);
if (list == NIL)
return NIL; /* would an error be better? */
/* list_truncate won't free list if it goes to empty, but this should */
if (list_length(list) <= 1)
{
list_free(list);
return NIL;
}
return list_truncate(list, list_length(list) - 1);
}
6. 删除开头N个元素
/* * Delete the first N cells of the list. * * The List is pfree'd if the request causes all cells to be deleted. */
List *
list_delete_first_n(List *list, int n)
{
check_list_invariants(list);
/* No-op request? */
if (n <= 0)
return list;
/* Delete whole list? */
if (n >= list_length(list))
{
list_free(list);
return NIL;
}
...
memmove(&list->elements[0], &list->elements[n],
(list->length - n) * sizeof(ListCell));
list->length -= n;
...
return list;
}
将数据元素往前移动N个位置,这样就相当于删除了。
3.10 拼接两个list
/* * Concatenate list2 to the end of list1, and return list1. * * This is equivalent to lappend'ing each element of list2, in order, to list1. * list1 is destructively changed, list2 is not. (However, in the case of * pointer lists, list1 and list2 will point to the same structures.) * * Callers should be sure to use the return value as the new pointer to the * concatenated list: the 'list1' input pointer may or may not be the same * as the returned pointer. */
List *
list_concat(List *list1, const List *list2)
{
int new_len;
if (list1 == NIL)
return list_copy(list2);
if (list2 == NIL)
return list1;
Assert(list1->type == list2->type);
new_len = list1->length + list2->length;
/* Enlarge array if necessary */
if (new_len > list1->max_length)
enlarge_list(list1, new_len);
/* Even if list1 == list2, using memcpy should be safe here */
memcpy(&list1->elements[list1->length], &list2->elements[0],
list2->length * sizeof(ListCell));
list1->length = new_len;
check_list_invariants(list1);
return list1;
}
/* * Form a new list by concatenating the elements of list1 and list2. * * Neither input list is modified. (However, if they are pointer lists, * the output list will point to the same structures.) * * This is equivalent to, but more efficient than, * list_concat(list_copy(list1), list2). * Note that some pre-v13 code might list_copy list2 as well, but that's * pointless now. */
List *
list_concat_copy(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
int new_len;
if (list1 == NIL)
return list_copy(list2);
if (list2 == NIL)
return list_copy(list1);
Assert(list1->type == list2->type);
new_len = list1->length + list2->length;
result = new_list(list1->type, new_len);
memcpy(result->elements, list1->elements,
list1->length * sizeof(ListCell));
memcpy(result->elements + list1->length, list2->elements,
list2->length * sizeof(ListCell));
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
3.11 截断list到指定长度
对于截断长度大于当前长度,不进行扩容。
/* * Truncate 'list' to contain no more than 'new_size' elements. This * modifies the list in-place! Despite this, callers should use the * pointer returned by this function to refer to the newly truncated * list -- it may or may not be the same as the pointer that was * passed. * * Note that any cells removed by list_truncate() are NOT pfree'd. */
List *
list_truncate(List *list, int new_size)
{
if (new_size <= 0)
return NIL; /* truncate to zero length */
/* If asked to effectively extend the list, do nothing */
if (new_size < list_length(list))
list->length = new_size;
...
return list;
}
3.12 判断当前值是否是list成员
/* * Return true iff 'datum' is a member of the list. Equality is * determined via equal(), so callers should ensure that they pass a * Node as 'datum'. */
bool
list_member(const List *list, const void *datum)
{
const ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (equal(lfirst(cell), datum))
return true;
}
return false;
}
/* * Return true iff 'datum' is a member of the list. Equality is * determined by using simple pointer comparison. */
bool
list_member_ptr(const List *list, const void *datum)
{
const ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (lfirst(cell) == datum)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/* * Return true iff the integer 'datum' is a member of the list. */
bool
list_member_int(const List *list, int datum)
{
const ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (lfirst_int(cell) == datum)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/* * Return true iff the OID 'datum' is a member of the list. */
bool
list_member_oid(const List *list, Oid datum)
{
const ListCell *cell;
...
foreach(cell, list)
{
if (lfirst_oid(cell) == datum)
return true;
}
return false;
}
3.13 并集
List *
list_union(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
const ListCell *cell;
Assert(IsPointerList(list1));
Assert(IsPointerList(list2));
result = list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list2)
{
if (!list_member(result, lfirst(cell)))
result = lappend(result, lfirst(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * This variant of list_union() determines duplicates via simple * pointer comparison. */
List *
list_union_ptr(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
const ListCell *cell;
Assert(IsPointerList(list1));
Assert(IsPointerList(list2));
result = list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list2)
{
if (!list_member_ptr(result, lfirst(cell)))
result = lappend(result, lfirst(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * This variant of list_union() operates upon lists of integers. */
List *
list_union_int(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
const ListCell *cell;
Assert(IsIntegerList(list1));
Assert(IsIntegerList(list2));
result = list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list2)
{
if (!list_member_int(result, lfirst_int(cell)))
result = lappend_int(result, lfirst_int(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * This variant of list_union() operates upon lists of OIDs. */
List *
list_union_oid(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
const ListCell *cell;
Assert(IsOidList(list1));
Assert(IsOidList(list2));
result = list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list2)
{
if (!list_member_oid(result, lfirst_oid(cell)))
result = lappend_oid(result, lfirst_oid(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
3.14 交集
List *
list_intersection(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
const ListCell *cell;
if (list1 == NIL || list2 == NIL)
return NIL;
Assert(IsPointerList(list1));
Assert(IsPointerList(list2));
result = NIL;
foreach(cell, list1)
{
if (list_member(list2, lfirst(cell)))
result = lappend(result, lfirst(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * As list_intersection but operates on lists of integers. */
List *
list_intersection_int(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
List *result;
const ListCell *cell;
if (list1 == NIL || list2 == NIL)
return NIL;
Assert(IsIntegerList(list1));
Assert(IsIntegerList(list2));
result = NIL;
foreach(cell, list1)
{
if (list_member_int(list2, lfirst_int(cell)))
result = lappend_int(result, lfirst_int(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
3.15 差集
List *
list_difference(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
const ListCell *cell;
List *result = NIL;
Assert(IsPointerList(list1));
Assert(IsPointerList(list2));
if (list2 == NIL)
return list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list1)
{
if (!list_member(list2, lfirst(cell)))
result = lappend(result, lfirst(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * This variant of list_difference() determines list membership via * simple pointer equality. */
List *
list_difference_ptr(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
const ListCell *cell;
List *result = NIL;
Assert(IsPointerList(list1));
Assert(IsPointerList(list2));
if (list2 == NIL)
return list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list1)
{
if (!list_member_ptr(list2, lfirst(cell)))
result = lappend(result, lfirst(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * This variant of list_difference() operates upon lists of integers. */
List *
list_difference_int(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
const ListCell *cell;
List *result = NIL;
Assert(IsIntegerList(list1));
Assert(IsIntegerList(list2));
if (list2 == NIL)
return list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list1)
{
if (!list_member_int(list2, lfirst_int(cell)))
result = lappend_int(result, lfirst_int(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
/* * This variant of list_difference() operates upon lists of OIDs. */
List *
list_difference_oid(const List *list1, const List *list2)
{
const ListCell *cell;
List *result = NIL;
Assert(IsOidList(list1));
Assert(IsOidList(list2));
if (list2 == NIL)
return list_copy(list1);
foreach(cell, list1)
{
if (!list_member_oid(list2, lfirst_oid(cell)))
result = lappend_oid(result, lfirst_oid(cell));
}
check_list_invariants(result);
return result;
}
3.16 拷贝list
1. 拷贝
也是一个浅拷贝,对于ptr_value类型的值,只是拷贝了指针值,新旧list都指向相同的对象, 修改会互相影响。
/* * Return a shallow copy of the specified list. */
List *
list_copy(const List *oldlist)
{
List *newlist;
if (oldlist == NIL)
return NIL;
newlist = new_list(oldlist->type, oldlist->length);
memcpy(newlist->elements, oldlist->elements,
newlist->length * sizeof(ListCell));
check_list_invariants(newlist);
return newlist;
}
2. 跳过开头N个元素再拷贝
/* * Return a shallow copy of the specified list, without the first N elements. */
List *
list_copy_tail(const List *oldlist, int nskip)
{
List *newlist;
if (nskip < 0)
nskip = 0; /* would it be better to elog? */
if (oldlist == NIL || nskip >= oldlist->length)
return NIL;
newlist = new_list(oldlist->type, oldlist->length - nskip);
memcpy(newlist->elements, &oldlist->elements[nskip],
newlist->length * sizeof(ListCell));
check_list_invariants(newlist);
return newlist;
}
3. 深度拷贝
将元素的值也拷贝一份,这样两个list将完全没有关系,修改互不影响。
List *
list_copy_deep(const List *oldlist)
{
List *newlist;
if (oldlist == NIL)
return NIL;
/* This is only sensible for pointer Lists */
Assert(IsA(oldlist, List));
newlist = new_list(oldlist->type, oldlist->length);
for (int i = 0; i < newlist->length; i++)
lfirst(&newlist->elements[i]) =
copyObjectImpl(lfirst(&oldlist->elements[i]));
check_list_invariants(newlist);
return newlist;
}
3.17 list 排序
使用标准的qsort函数,传递不同的cmp函数进行排序。
void
list_sort(List *list, list_sort_comparator cmp)
{
typedef int (*qsort_comparator) (const void *a, const void *b);
int len;
check_list_invariants(list);
/* Nothing to do if there's less than two elements */
len = list_length(list);
if (len > 1)
qsort(list->elements, len, sizeof(ListCell), (qsort_comparator) cmp);
}
/* * list_sort comparator for sorting a list into ascending int order. */
int
list_int_cmp(const ListCell *p1, const ListCell *p2)
{
int v1 = lfirst_int(p1);
int v2 = lfirst_int(p2);
if (v1 < v2)
return -1;
if (v1 > v2)
return 1;
return 0;
}
/* * list_sort comparator for sorting a list into ascending OID order. */
int
list_oid_cmp(const ListCell *p1, const ListCell *p2)
{
Oid v1 = lfirst_oid(p1);
Oid v2 = lfirst_oid(p2);
if (v1 < v2)
return -1;
if (v1 > v2)
return 1;
return 0;
}
3.18 释放
/* * Free all storage in a list, and optionally the pointed-to elements */
static void
list_free_private(List *list, bool deep)
{
if (list == NIL)
return; /* nothing to do */
check_list_invariants(list);
if (deep)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++)
pfree(lfirst(&list->elements[i]));
}
if (list->elements != list->initial_elements)
pfree(list->elements);
pfree(list);
}
/* * Free all the cells of the list, as well as the list itself. Any * objects that are pointed-to by the cells of the list are NOT * free'd. * * On return, the argument to this function has been freed, so the * caller would be wise to set it to NIL for safety's sake. */
void
list_free(List *list)
{
list_free_private(list, false);
}
void
list_free_deep(List *list)
{
/* * A "deep" free operation only makes sense on a list of pointers. */
Assert(IsPointerList(list));
list_free_private(list, true);
}
总结
- 功能非常丰富
- 使用数组实现,支持随即访问,存储紧凑,但是扩容会有数据的拷贝
- 有预分配空间,减少了扩容次数,提升速度
- head+body形式,但是扩容只对body扩容,减少head的cache失效率
- 对于存储的ptr_value类型的list,大部分的api都是浅拷贝,使用需注意
- 可以通过函数签名判断,其中包含
const的则不会对list进行操作,否则都使用返回值作为list的新值继续使用 - 迭代过程中只能使用特定的宏函数进行删除元素
- 简短、精干的宏+内联函数,提升执行速度
边栏推荐
- 第八章 操作位和位串(四)
- R语言plotly可视化:可视化模型在整个数据空间的分类轮廓线(等高线)、meshgrid创建一个网格,其中每个点之间的距离由mesh_size变量表示、使用不同的形状标签表征、训练、测试及分类标签
- AntD checkbox,限制选中数量
- 日常知识科普
- Second, the examinee must see | consolidate the preferred question bank to help the examinee make the final dash
- Jerry added an input capture channel [chapter]
- Record various sets of and or of mongotemplate once
- Method of establishing unity thermodynamic diagram
- Idea connection MySQL custom generated entity class code
- 10_ Those high-profile personal signatures
猜你喜欢

【比特熊故事汇】6月MVP英雄故事|技术实践碰撞境界思维

港股上市公司公告 API 数据接口
![Jerrys timer0 uses the default pa13 to detect the pulse width [chapter]](/img/4e/de0951c8be5ddd765b15b773c04fa7.png)
Jerrys timer0 uses the default pa13 to detect the pulse width [chapter]

SAP Marketing Cloud 功能概述(四)

MySQL log management, backup and recovery

`Thymeleaf`模板引擎全面解析

Convolution kernel and characteristic graph visualization

Rasa 3. X learning series - it is a great honor to be a source code contributor of Rasa contributors, and to build and share the rasa community with rasa source code contributors all over the world!

How to avoid placing duplicate orders

Télétravail: Camping à la maison gadgets de bureau | rédaction communautaire
随机推荐
leetcode:1504. Count the number of all 1 sub rectangles
高薪程序员&面试题精讲系列115之Redis缓存如何实现?怎么发现热key?缓存时可能存在哪些问题?
How to solve the problem that iterative semi supervised training is difficult to implement in ASR training? RTC dev Meetup
六石管理学:垃圾场效应:工作不管理,就会变成垃圾场
Database considerations
GO语言-goroutine协程的使用
box-sizing
简谈企业Power BI CI /CD 实施框架
Kotlin coordination channel
SAP Marketing Cloud 功能概述(三)
A review of text contrastive learning
Jericho may have some chips with fast music playing speed [chapter]
postgresql 之 ilist
Daily knowledge popularization
六月集训(第24天) —— 线段树
`Thymeleaf`模板引擎全面解析
【Pytorch】量化
Kotlin shared mutable state and concurrency
Jerry added an input capture channel [chapter]
在宇宙的眼眸下,如何正确地关心东数西算?