当前位置:网站首页>Lua-- use of data types, variables, loops, functions and operators
Lua-- use of data types, variables, loops, functions and operators
2022-06-22 22:33:00 【aruba】
lua It's a lightweight scripting language , from c Language writing , Design lua My original intention is to : Embedded in the application , Provide flexible expansion and customization functions lua Official website :https://www.lua.org/ You can download and install lua
One 、 first lua Program
lua There are two ways to program : Interactive and scripted . Scripted is to write a script file and execute it , Interactive is to enter lua The console is programmed , Interactive is not used in actual development , The following will be programmed using scripting
1. Create script file
lua The script does not require a suffix , But generally we all take lua For the suffix , To differentiate
vi hello.luaThe content is :
print("hello world")2. perform lua Script
lua Script execution , Use lua command
lua ./hello.lua result :
Two 、 data type
Before using data types , So let's see lua Notes
lua Middle single line comments use :
-- Single-line comments Multiline comments use :
--[[
Multiline comment
]]--Here is lua Use of data types
1. number
number Type is used to represent lua The number type in , Including integers and floating-point numbers , The precision is double
i = 1
print(i)
i = 9.99999
print(i)
print(type(i))Running results :
2. nil
and Java Medium null similar ,nil Represents an invalid value , You can also leave a variable blank
i = 1
print(i)
i = nil
print(i)Running results :
3. string
3.1 Define the way
There are three ways to define string types :
Define the way | describe |
|---|---|
Single quotation marks :' Content ' | Represents a single line string |
Double quotes :" Content " | Same as single quotation marks |
square brackets :[[ Content ]] | Represents a multiline string |
s = "abc"
print(s)
s = 'def'
print(s)
s = [[
gh,
Multi line content ,
123
]]
print(s)Running results :
3.2 Get string length
Use # Get string length
print("-----")
s = 'abcedf'
print(#s)Running results :
3.3 String usage +
lua Use... In a string + Time of signal , Convert string to number first
print("-----")
print('1' + 2)
print('1' + '2')Running results :
3.4 String splicing
So how to splice strings ? Use .. Connection string
print("-----")
print("1".."2".."abc")Running results :
4. table
table It can be used as a hash table , It can also be used as a list 、 Array .tab Is more like map
Definition table Use :{}
4.1 table Use as an array
tb = {'a','b','c'}
-- Traverse the output
for k,v in pairs(tb) do
print(k..":"..v)
endRunning results :
You can see ,table If you don't specify key, The default from the 1 Start indexing as key
4.2 table As map Use
tb = {k1 = '1',k2 = '2',k3 = '3'}
for k,v in pairs(tb) do
print(k..":"..v)
endRunning results :
4.3 obtain table The elements in
Two ways :
Access method | Example |
|---|---|
adopt table['key'], If it's an array, you don't need quotation marks | tb["k1"] |
adopt table.key, If it is an array, it does not support | tb.k1 |
test :
tb = {k1 = '1',k2 = '2',k3 = '3'}
print(tb['k1'])
print(tb.k2)Running results :
4.4 Modify and add table Elements
Use obtain table The way the elements in the Modification and addition can be realized by assigning values table Elements
tb = {k1 = '1',k2 = '2',k3 = '3'}
tb["k1"] = 4
tb['k4'] = 8
tb.k5 = 10
for k,v in pairs(tb) do
print(k..":"..v)
endRunning results :
4.5 Delete table Elements
Assign an element to nil that will do
tb.k2 = nil5. function
There are two ways to define function types :
- Defined function , Assign a function method name to a variable
- Anonymous functions , Directly assign a function to a variable
5.1 How to define functions
-- Define a function
function sum(a,b)
return a + b
end
-- Assign a function to a variable
f1 = sum
print(f1(1,6))Running results :
5.2 Anonymous functions
function sumAndPrint(a,b,printFunc)
ret = a + b
-- Call the incoming function
printFunc(ret)
return ret
end
-- The third argument is a function
sumAndPrint(10,20,
function(result)
print(result)
end
)Running results :
3、 ... and 、 Variable
1. Scope
lua Variables in are divided into local variables and global variables , Default to global variable , Local variables use local Keyword declaration
function scope()
a = 0
local b = 1
end
scope()
print(a)
print(b)Running results :
2. Multivariable assignment
except 1:1( One variable corresponds to one assignment ) Perform variable assignment ,lua And support n:n 、(m < n):n、n:(m < n) Variable assignment
The way | describe |
|---|---|
n : n | Assign values to variables in order |
(m < n) : n | Assign values to variables in order , Extra values are discarded |
n : (m < n) | Assign values to variables in order , Low value , The assignment is nil |
a1,b1 = 1,2
print('a1:'..a1..',b1:'..b1)
a1,b1 = 5,3,4
print('a1:'..a1..',b1:'..b1)
a1,b1 = 9
print('a1:'..a1)
print(b1)Running results :
Four 、 loop
1. while
a = 0
while(a < 10) do
a = a + 1
print(a)
endRunning results :
2. for
for The syntax of loops has slightly different advantages , The first value represents the initial value , The second value represents the value at the end of the condition , The third value represents the step size , Step size can be omitted without writing , The default is 1
for i = 0,10,2 do
print(i)
endRunning results :
3. repeat until
repeat repeat After the code , Until you meet until Conditions
j = 0
repeat
j = j+1
print(j)
until(j > 4)Running results :
5、 ... and 、 Condition and jump out of loop
1. if
if Judge to execute some code that meets the conditions
n = nil
if(n == nil) then
print('n It's empty ')
endRunning results :
2. break
break Used to force a loop out
k = 0
while(k < 10) do
k = k+1
if(k == 5) then
break;
end
print(k)
endRunning results :
6、 ... and 、 function
From the above data types, we know , Function can also be used as a variable , Define function use function keyword , Functions are divided into named functions and anonymous functions , Named functions can be called by function names , Anonymous functions can only be called through the assigned functional variables , In addition to the above use , The function also contains the following
1. Multiple value return
lua Function can return multiple values
-- The parameter a,b,a+b Return as return value
function moreReturn(a,b)
return a,b,a+b
end
i,j,k = moreReturn(1,2)
print(i)
print(j)
print(k)Running results :
2. Variable parameters
Use ... Passing variable parameters
-- Add all the parameters
function sum(...)
local sum = 0
for k,v in pairs({...}) do
sum = sum + v
end
return sum
end
print(sum(1,2,3,4,5))Running results :
2.1 With fixed parameters
There are both fixed and variable parameters , Fixed parameters are written in the front
-- Format output
function fmtPrint(fmt,...)
io.write(string.format(fmt,...))
end
fmtPrint("%d,%s,%d\n",12,'asd',66)Running results :
2.2 select function
lua in select Function can handle variable parameters , For example, obtain variable parameter length , Intercept variable parameters
-- averaging
function avg(...)
local avg = 0
for k,v in pairs({...}) do
avg = avg + v
end
return avg / select("#",...)
--return avg / #{...}
end
print(avg(2,4,6,8))Running results :
-- Intercept variable parameters
function limit(limit,...)
return select(limit,...)
end
a,b,c = limit(2,"a","b","c","d","e")
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)Running results :
7、 ... and 、 Operator
Operators are common , Some we have used before
1. Arithmetic operator
Symbol | describe |
|---|---|
+ | Add |
- | reduce |
* | ride |
/ | except |
% | Remainder |
^ | Power |
- | Minus sign |
2. Relational operator
Symbol | describe |
|---|---|
== | be equal to |
~= | It's not equal to |
> | Greater than |
< | Less than |
>= | Greater than or equal to |
<= | Less than or equal to |
3. Logical operators
Symbol | describe |
|---|---|
and | also |
or | perhaps |
not | Not |
4. Other operators
Symbol | describe |
|---|---|
.. | String connector |
# | Length calculator |
边栏推荐
- Cvpr2022 𞓜 feature decoupling learning and dynamic fusion for re captured images
- For an unforgettable memory: special topic of Sun Jian
- RealNetworks vs. Microsoft: the battle in the early streaming media industry
- Self service library system Tkinter interface and openpyxl form comprehensive design case
- How much do you know about the cause of amplifier distortion?
- Kdd'22 | Ali: fine tuning CTR estimation based on EE exploration
- Implementation of depth traversal adjacency table in Figure 6-7
- redis 报错解决与常用配置
- There are 15 necessary knowledge points for the second level cost engineer before the exam! I wish you success!
- 自监督表征预训练之掩码图像建模:CAE 及其与 MAE、BEiT 的联系
猜你喜欢

【路径规划】第一周: 大杂烩
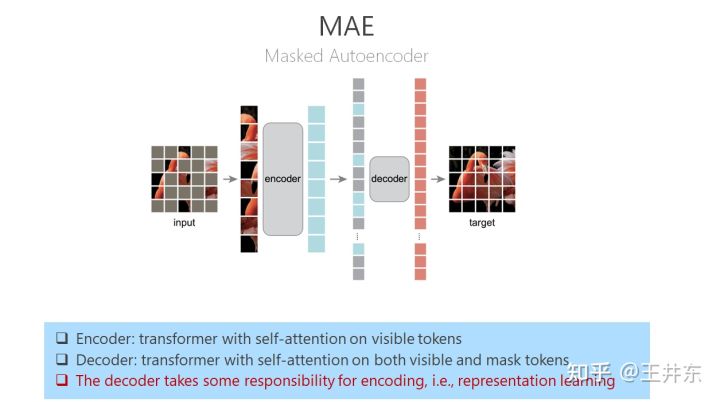
自监督表征预训练之掩码图像建模:CAE 及其与 MAE、BEiT 的联系
NFT can only be viewed from afar, but not blatantly played

大不列颠泰迪熊加入PUBG 手游
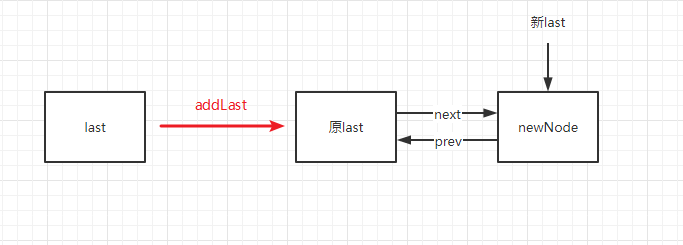
LinkedList source code analysis
General trend wisdom to create inclined model and cut monomer

Optimization solver | gurobi's Mvar class: a sharp tool for matrix modeling and an alternative solution to dual problems (with detailed cases and codes attached)

Uniapp applet mall develops thinkphp6 points mall, group purchase and seckill packaged app

Why do you perform performance tests before the software goes online? How to find a software performance testing organization

【持续更新中...】2021年全国大学生电子设计大赛 (三)匿名四轴拓空者飞控系统设计解读
随机推荐
volume rendering
R language data Table data import practice: data Rename the name of the table data column (rename)
Implementation of depth traversal adjacency table in Figure 6-7
PMP Exam admission ticket problems and precautions in June, which must be read by candidates
【知乎知识主推荐】 无人机中的城堡- 专注于无人机在不同技术领域的应用
为什么感觉中国人月薪过万已经很普遍了?
【李沐】 如何读论文【论文精读】
The method of making videos of knowledge payment system support m3u8 format playback
Mysql8 installation and environment configuration
Database summary: common problems and Optimization in MySQL development
Cryptography series: certificate format representation of PKI X.509
注意|24日截止 2022年广东二级造价工程师准考证打印入口开通
Analysis of open API design specification
【象棋人生】01 人生如棋
Kdd'22 | Ali: fine tuning CTR estimation based on EE exploration
Developing salary management system based on C language course paper + source code and executable EXE file
[path planning] week 1: hodgepodge
The necessary materials for the soft test have been released. All the soft test materials for the whole subject have been prepared for you!
【ROS】ROSmsg cakin_make编译错误
6月PMP考试准考证问题及注意事项,考生必读