当前位置:网站首页>SQL advanced
SQL advanced
2022-06-25 09:09:00 【Fairy wants carry】
Catalog
stay linux In the installation mysql5.7
Check the oldest person in each institution
The difference between caching and buffering :
Underlying logical architecture
MyISAM And InnoDB The difference between :
Then I will talk about the differences between the two storage engines (InnoDB and MyISAM):
Index introduction , structure
Officially ,mysql Index structure
About the time complexity of data structure :
2. Which indexes need to be created , Which don't need
Introduction and naming rules

Sub database and sub table , Two different machines , Most tables 500w data , The library is the most 5000w data
Table naming rules



stay linux In the installation mysql5.7
To uninstall first mysql
1 View the version information of the database
rpm -qa | grep mariadb
2. unload data base ( Strong delete )
rpm -e --nodeps mariadb-libs3. After uninstalling , see mysql Does the class library have (libaio)
rpm -qa | grep libaio
![]()
4. Check whether the network tools have
rpm -qa | grep net-tools
5. see tmp File permissions are not 777


5.7 Version does not initialize automatically , I have to write it myself according to the order
6. Check the database version
mysqladmin --version
7. initialization mysql
mysqld --initialize --user=mysql
8. Check the password ( Use the log to view )
cat /var/log/mysqld.log

oJdkEa:3HWEj9. To start the
systemctl start mysqld.service 10. Check the status ( Just read the log )
systemctl status mysqldcat /var/log/mysqld.log

11. Sign in
mysql -uroot -poJdkEa:3HWEj
12. Change Password , Get access to
mysql -uroot -p2002514wyh11quit sign out mysql
The specific database operation can be realized as usual
![]()

13. see mysql Whether it is self starting
systemctl list-unit-files | grep mysqld 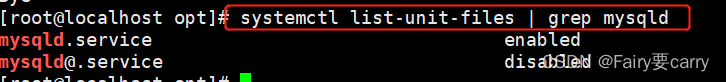
Where data is stored


Character set problem
Configuration file in /etc/my.cnf Inside
Add configuration information and restart
character_set_server=utf8
And then restart
systemctl restart mysqld
Log in again
mysql -uroot -pnew_password
Then let's look at the character sets of databases and tables
It is found that we need to modify it manually ( You can't just modify the configuration file )

Modify character sets in databases and tables
alter table mytbl character set 'utf8';
alter table mytbl convert to character set 'utf8';
Then insert and find Chinese again

Remote connection
First, let's take a look at user surface
Switch to mysql Library View user surface
select * from user\G;
View permissions

see host,user And authority
select host,user,authentication_string from user;

Create a custom user
create user Fairy identified by '2002514wyh11';
It is found that by default, all users can access

Then we test on the client

How to authorize users

1. Create a new one root The user authorizes , all ip All support , All permissions for all library tables
grant all privileges on *.* to root @'%' identified by '123456';2. Then log in remotely , Access to all libraries

Remote password modification (mysql In local library )
Whether it's changing the password or changing the permissions , The change is the data in the hard disk , Need to be synchronized , So we need to flush once

The problem of grouping
CREATE TABLE mytbl2(
id INT,
NAME VARCHAR(200),
age INT,
dept INT
);
INSERT INTO mytbl2 VALUES(1,'zhangsan1',33,101);
INSERT INTO mytbl2 VALUES(2,'lisi2',31,101);
INSERT INTO mytbl2 VALUES(3,'san1',35,102);
INSERT INTO mytbl2 VALUES(1,'ffu',37,102);Check the oldest person in each institution
![]() Will report a mistake
Will report a mistake

reason :
5.5 Of mysql Medium sql_mode It's empty , So direct select The corresponding fields can be displayed , But there will be miscellaneous ;
5.7 Yes sql_mode To configure , The aim is to strictly configure
show variables like 'sql_mode'
solve :
We sq according to deptl Execute grouped select Field , There can be no dept Of the field
SELECT * FROM mytbl2 m INNER JOIN(SELECT dept,MAX(age)maxage FROM mytbl2 GROUP BY dept
)ab ON ab.dept=m.`dept` AND m.`age`=ab.maxage;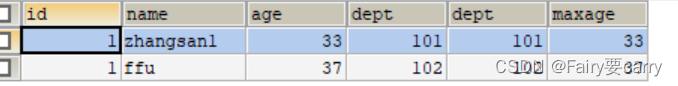
The difference between caching and buffering :
One is the reading of data , One is to write data ;
Underlying logical architecture
Sql interface:sql Implementation interface of
parser:sql The parser , Analytical complexity sql
optimizer: Optimizer , Be similar to JVM A function of the optimization of , about sql Play an optimization role
It produces a storage engine , There is a role similar to that of a military division , Be able to give sql Execute the corresponding situation , Get the result and return it to your client , Of course , Will first put a copy to our cache , You won't have to operate on the database next time ;

Open cache , utilize show profile see sql Execution cycle ( Whether the time is reduced due to cache hits )
1. First, add a cache message to the configuration file
vi /etc/my.cnf
query_cache-type=1 # Open the cache 2. then restart once , restart mysql
systemctl restart mysqld
3. View status found successfully

4. Switch on cache ( You can find profiling It's off ), Set up later
show variables like '%profiling%';

5. Then set the profiling, Start the execution plan ( Our storage engine will execute the corresponding... According to the execution plan sql)
set profiling=1;

6. Query the data in the table , Then look at its implementation plan , Look at the cache

7. View one of its execution plans
show profilesYou can see the execution sql And time consuming

8. Detailed plan :
show profile cpu,block io for query 2;
Start off and finish , Start with caching , Then the end
1. First wait for the cache lock and then Start execution , Query in the cache
2.checking permission View permissions
3. Open the table , Then initialize
4. Then wait for the cache lock , then optimizing To optimize , Generate execution lies and then transform execute perform sql
5. Then send the data sending data
6. After query , Close table , Wait for cache lock
7. Write data to the cache , then clear up Remove all

Query again and find the hit cache

Be careful : Only sql To hit the cache , Just follow map Of kv Key value pairs are similar to ;
principle :
disnect: duplicate removal
having: Screen again
group by: grouping , Execute function
Specific case specific analysis , Because according to the optimizer optimizer Conduct sql Optimize

Storage engine
See all the storage engines
show engines;

MyISAM And InnoDB The difference between :

notes : In fact, our projects generally do not use foreign keys , Because you use foreign keys to constrain the relationship between tables
1. Resulting in high coupling , And the performance is very low , For example, the class student list ( The student list has class foreign keys ), When inserting data into the student table , Will scan for class table , See if there is a suitable class , This will lead to low efficiency ;
2. And when inserting data , Slow speed , A wrong place , All have to be changed ( When there are too many watches, it is a nightmare , The rings are connected in series );
3. And when performing the delete operation , The data in a single table cannot be deleted because of foreign keys , For example, class students , Class is a foreign key among students , Want to delete the class without deleting the students , This is no good
So we usually make our own logical judgments ;
Then I will talk about the differences between the two storage engines (InnoDB and MyISAM):
MylSAM Watch lock used , A lock is the whole watch , Not suitable for high concurrency
InnoDB It uses a row lock , Lock a single piece of data , Suitable for high concurrent operation , There will be deadlock ;
Cache :MyISAM Only cache the index , No cache of real data ; and InnoDB, It's all cached , However, it will have an impact on the performance ;
Business :MyISAM Unsupported transaction , and InnoDB Support transactions
Another important difference :
1. and MyISAM Index file and data file are separated , The index file only holds the address of the data record ;

2. and InnoDB in Table data file itself According to B+ An index structure organized by a tree

( chart inndb primary key ) yes InnoDB Main index ( It's also a data file ) Schematic diagram , You can see that the leaf node contains the complete data record . This kind of index is called clustered index . because InnoDB The data files themselves should be aggregated by primary key , therefore InnoDB Table must have primary key (MyISAM There can be no ), If not explicitly specified , be MySQL The system will automatically select a column that can uniquely identify the data record as the primary key , If there is no such column , be MySQL Automatically for InnoDB Table generates an implicit field as the primary key , The length of this field is 6 Bytes , The type is long plastic .
What's the use of MyISAM?
Our system table uses MyISAM, Reduce resources , Relatively simple business , But the data cannot be recovered after the system crashes ;
Archive engine
Generally used for log and data collection

csv engine
It's a storage format , Each column is separated by commas , One line is in newline format
scene : Generally used to store data , As Mysql The table to deal with ——> Sure As a way of data exchange
For example, e-commerce platform , You pay for the order , But the money doesn't have to be deducted , There is a delay when messages in our message queue are processed by the message sender , Then we can store the data in csv In file , Then make daily reconciliation ;
(26 Bar message ) First time to know MQ-01_Fairy want carry The blog of -CSDN Blog _mq Full name
(26 Bar message ) RabbitMQ_Fairy want carry The blog of -CSDN Blog
Update every time csv file
Other engines
Memory engine
It's cache. , Restart will not lose , Faster
Federated engine
Federated The engine is accessing other Mysql A proxy for the server

sql preheating


In real development, the left outer connection is generally used left join Get data

mysql There is no full connection , But we can achieve it , The left outer join + The right outside is not empty
select xx from T A left join T B on A.key=B.keyselect xx from T A right join T B on A.key=B.key where A.key is null;practice
union Contrast with union all: Splicing sql The former will lose weight , The latter will not be repeated -> Stack data
scene : Use if there is duplicate data union To filter , No duplicate data union all
CREATE TABLE t_dept(
id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
deptName VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
address VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
)ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE t_emp(
id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
age INT(3) DEFAULT NULL,
deptld INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
empno INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id),
KEY idx_dept_id(deptld)
#constraint fk_dept_id foreign key(deptld) references t_dept(id)
)ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
SELECT * FROM t_dept;
SELECT * FROM t_emp;
# Internal connection serial data (ab All require )
SELECT * FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`;
# List all users , And display dept Information ( Left lateral )
SELECT * FROM t_emp a LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`;
# All those who don't belong to the sect (a Table exclusive )
SELECT * FROM t_emp a LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id` WHERE b.`id` IS NULL;
# All sects where no one goes (b Table exclusive )
SELECT * FROM t_dept b LEFT JOIN t_emp a ON a.`deptld`=b.`id` WHERE a.`id` IS NULL;
# The complete
SELECT a.*,b.* FROM t_emp a LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`
UNION
SELECT a.*,b.* FROM t_dept b LEFT JOIN t_emp a ON a.`deptld`=b.`id` WHERE a.`id` IS NULL;
Then we added one to the sect table CEO Field
ALTER TABLE `t_dept` ADD CEO INT(11);
UPDATE t_dept SET CEO=2 WHERE id=1;
UPDATE t_dept SET CEO=4 WHERE id=2;
UPDATE t_dept SET CEO=6 WHERE id=3;
UPDATE t_dept SET CEO=8 WHERE id=4;
UPDATE t_dept SET CEO=9 WHERE id=5;
# utilize b Tabular ceo Of id And a The character of the table id Related to ( Characters and ceo)
SELECT * FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON b.`CEO`=a.`id`;
# Based on the above requirements, headmaster CEO Average age
SELECT AVG(a.`age`) FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON b.`CEO`=a.`id`;
# Please all dept Corresponding CEO name
#1.
SELECT c.`name`,ab.name ceoname FROM t_emp c LEFT JOIN
(SELECT b.`id`,a.`name` FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`)ab
ON c.`deptld`=ab.id;
# obtain dept The leader of
SELECT b.`id`,a.`name` FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`
#2. First, check the name and CEO
SELECT ab.name,c.`name` ceoname FROM
(SELECT a.`name`,b.`CEO` FROM t_emp a LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`) ab
LEFT JOIN t_emp c ON ab.ceo=c.`id`;
#3. You can get the sect leader through two external connections at one time ( Get the user's information for the first time , The second is based on CEO Screening )
SELECT a.`name`,c.`name` ceoname FROM t_emp a
LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`
LEFT JOIN t_emp c ON b.`CEO`=c.`id`;
Index introduction , structure
ask :100w Data , If you want to insert , How to ensure execution efficiency ?
effect :
In short , An index is a data structure that can help to arrange and find data quickly

Find the data structure of the algorithm :
Reference data in some way ——> Binary tree used , Search speed increases , Space for time ( When But not a binary tree , Just relevant )
mysql Data and indexes are stored in different files , The index is saved on the hard disk
advantage :
1. Fast query speed ,2. Sorting speed is also fast
shortcoming :
1. Large space consumption ,2. The speed of adding, deleting and modifying is slow , Because binary tree ,n Nodes , The time complexity may be log2n

Disadvantage scenario :
Sometimes, a linked table is generated ( The situation is rubbish ), Query speed becomes chained , Very slowly
our mysql An index is actually a balanced tree ( When unbalanced , It will help you become balanced )
Officially ,mysql Index structure

B The tree contains : data 、 The downward pointer 、 Pointer to current data

B+ Trees : data 、 The downward pointer
mysql The choice is B+ Trees , Because our memory is limited , We B+ A tree has no downward pointer or pointer to data ; And the same memory B+ The tree can load more data than B Count more 1/3( in other words B+ The data that can be loaded at one time is more than B many 1/3), If you don't read the data ,( Send missing pages ) Will read again , Send again IO, This will waste a lot of memory , Excessive performance consumption ;

About the time complexity of data structure :
Array inserts directly a[n]= that will do

It is found that all algorithms are time-based , Space for time
such as : Jump watch , Each of our data has a corresponding pointer , So we need to find this data through the pointer , But the disadvantages are obvious up
Hashtable If there is only one key corresponding value , So the search efficiency is very fast , The bottom layer is based on arrays , So the insertion and deletion are very fast
As for trees ——> It is safer that we can use Balance tree ( Balancing takes time ), It will not appear the extreme case of joint table like binary tree
characteristic :
(1) A non leaf node can have up to two children ;
(2) The non leaf node value is greater than the left child node 、 Smaller than the right child node ;
(3) The difference in the number of levels between the left and right sides of the tree will not be greater than 1;( a key )
(4) There are no nodes with equal duplicate values ;

Cluster index
It is not a separate index type , It's a way of storing data
Specifically by B+ Trees achieve , The primary key of each table constructs one B+ Trees , meanwhile Leaf node Deposit is Record data of the whole subject line
, Leaf nodes can be called data pages . Each table can have only one clustered index ( Because physical storage can only have one order );
And ours InnoDB The data will be aggregated through the primary key , If there is no primary key defined ,InnoDB Instead, a non empty unique index is selected , If still not , An implicit primary key will be defined as the cluster index ;
advantage :
1. Data access is fast , Compare the storage method of clustered index -> Save the index and data in the same B+ In the tree
2. And it is faster to check and find the primary key ;

Nonclustered index
I don't think I understand it very well , My personal feeling is that data and index are separated , The leaf node points to the address of the data , in other words , We find the data by address ( Just look for words in the dictionary , It's the strokes , Clustering index is the order of emphasis , Similar to Pinyin search )
our InnoDB The index structure used is cluster index ,MyISAM The index structure used is a non clustered index
Use of index
1. Create index
# Single value index , An index contains only a single column ( Specify the field name )
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON t_emp(NAME);
# unique index
SELECT * FROM t_emp;
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_empno ON t_emp(empno);
# Create multiple indexes ( Composite index )
CREATE INDEX idx_no_name ON t_emp(id,NAME,deptld);
2. Which indexes need to be created , Which don't need
Those frequently used fields , Creating an index will cause the index to be saved up, Out of memory , performance down

explain
边栏推荐
- Oracle-单行函数大全
- Summary of hardfault problem in RTOS multithreading
- Make a skylearn high-dimensional dataset_ Circles and make_ moons
- [opencv] - Discrete Fourier transform
- Analysis on the bottom calling process of micro service calling component ribbon
- matplotlib matplotlib中axvline()和axhline()函数
- 《乔布斯传》英文原著重点词汇笔记(四)【 chapter two 】
- Mapping mode of cache
- CSV parameterization in JMeter
- compiling stm32f4xx_it.c... “.\Objects\BH-F407.axf“ - 42 Error(s), 1 Warning(s).
猜你喜欢

【OpenCV】—离散傅里叶变换

The first techo day Tencent technology open day, 628 waiting for you!

Close a thread
![[opencv] - Discrete Fourier transform](/img/03/10ce3d7c5d99ead944b2cae8d0cec0.png)
[opencv] - Discrete Fourier transform

4、 Convolution neural networks

(翻译)采用字母间距提高全大写文本可读性的方式

A 35 year old Tencent employee was laid off and sighed: a suite in Beijing, with a deposit of more than 7 million, was anxious about unemployment

Webgl Google prompt memory out of bounds (runtimeerror:memory access out of bounds, Firefox prompt index out of bounds)
![[untitled] * * database course design: complete the student information management system in three days**](/img/69/762819fa1b11085a7e36c95acbe880.png)
[untitled] * * database course design: complete the student information management system in three days**

matplotlib matplotlib中plt.grid()
随机推荐
从别人库里拷贝的游戏如何再自己的库里显示
Unity发布webGL的时候JsonConvert.SerializeObject()转换失败
flutter 多语言的intl: ^0.17.0导不进去
LVS-DR模式单网段案例
使用Navicat对比多环境数据库数据差异和结构差异,以及自动DML和DDL脚本
浅谈Mysql底层索引原理
Flutter multilingual intl: ^0.17.0 cannot be imported
请问在手机上开户股票,还是去证券公司开户安全?
Is the security account opening risky and safe?
第十五周作业
Notes on key words in the original English work biography of jobs (VI) [chapter three]
Socket programming -- poll model
compiling stm32f4xx_it.c... “.\Objects\BH-F407.axf“ - 42 Error(s), 1 Warning(s).
Oracle-单行函数大全
Level 6 easy to mix words
十大券商开户风险大吗,安全靠谱吗?
声纹技术(四):声纹识别的工程部署
Object.defineProperty也能监听数组变化?
atguigu----18-组件
Compile time annotations for custom annotations (retentionpolicy.class)