当前位置:网站首页>INT 104_ LEC 06
INT 104_ LEC 06
2022-06-23 08:00:00 【NONE_ WHY】
1. Support Vector Machine【 Support vector machine 】
1.1. Hyperplane【 hyperplane 】
1.1.1. describe
- Hyperplanes are n Linear subspace with codimension equal to one in dimensional Euclidean space , Its dimension must be (n-1)
- Codimension is a measure of subspace ( Sub cluster, etc ) A numerical quantity of size . hypothesis X Is an algebraic family ,Y yes X A sub cluster in .X The dimension of is n,Y The dimension of is m, Then we call Y stay X The codimension in is n-m, Specially , If X and Y It's all linear spaces , that Y stay X The codimension in is Y The dimension of the complement space of
1.1.2. Definition
- mathematics
- set up
 Is the domain ( It can be considered as
Is the domain ( It can be considered as  ),
), Dimensional space
Dimensional space  The hyperplane of is determined by the equation :
The hyperplane of is determined by the equation : Defined subset , among
Defined subset , among  Is a constant that is not all zero
Is a constant that is not all zero
- set up
- linear algebra
 Vector space
Vector space  A hyperplane in is a plane shaped like :
A hyperplane in is a plane shaped like : The subspace of , among
The subspace of , among  Is any nonzero linear mapping
Is any nonzero linear mapping
- Projective geometry
- In homogeneous coordinates
 Next , Projective space
Next , Projective space  The hyperplane of is determined by the equation :
The hyperplane of is determined by the equation : Definition , among
Definition , among  Is a constant that is not all zero
Is a constant that is not all zero
- In homogeneous coordinates
1.1.3. Some special types
Affine hyperplane
Affine hyperplane is an algebra in affine space 1 In Cartesian coordinates , The equation can be used :
 describe , among
describe , among  Is a constant that is not all zero
Is a constant that is not all zero In the case of real affine space , let me put it another way , When the coordinates are real numbers , The affine space divides the space into two half spaces , They are the connecting components of the complement of the hyperplane , By inequality
 and
and  give
give Affine hyperplane is used to define the decision boundary in many machine learning algorithms , For example, linear combination ( tilt ) Decision tree and perceptron
Vector hyperplane
In vector space , Vector hyperplane is algebra 1 The subspace of , You can only shift from the origin by a vector , under these circumstances , It is called a plane . Such a hyperplane is the solution of a single linear equation
Projection hyperplane
The shadow casting space is a set of points with attributes , For any two points in the set , All points on the line determined by two points are included in the set . Projective geometry can be seen as adding vanishing points ( Infinity ) Affine geometry of . Affine hyperplane and infinitely related points form a projective hyperplane . A special case of a projected hyperplane is an infinite or ideal hyperplane , It is defined as the set of all points at infinity
In projection space , A hyperplane does not divide a space into two parts : contrary , It requires two hyperplanes to separate points and divide the space . The reason is that space is basically “ Surround ", So that the two sides of a single hyperplane are connected to each other
1.1.4. PPT
- A hyper plane could be used to split samples belonging to different classes
- The hyperplane can be written as WX + b = 0 hence
- Positive class will be taken as WX + b > +1
- Negative class will be taken as WX + b < -1
1.2. Support Vector【 Support vector 】
1.2.1. INFO
- Support vector machine (SVM) It's a kind of press Supervised learning (Supervised Learning) The method of binary classification of data Generalized linear classifier (Generalized Linear Classifier), The decision boundary is to solve the learning sample Maximum margin hyperplane (Maxmum Margin Hyperplane)
- SVM Use the hinge loss function (Hinge Loss) Calculate empirical risk (Empirical Risk) The regularization term is added to the solution system to optimize the structural risk (Structural Risk), It is a classifier with sparsity and robustness
- SVM You can use and methods (Kernel Method) Non linear classification , Is a common nuclear learning (Kernel Learning) One method
1.2.2. What do we want?
- The maximum distance between the hyperplane and the support vector
-

- Optimal hyperplane 【 Optimal hyperplane 】
- Optimal Margin 【 Optimal interval 】
- Dashed Line 【 Support vector 】
1.3. Kernel Function【 Kernel function 】
1.3.1. Definition
- Support vector machine through some nonlinear transformation
 , Map the input space to the high-dimensional feature space . If only the inner product calculation is used to solve the support vector , And there is a function in the lower input space
, Map the input space to the high-dimensional feature space . If only the inner product calculation is used to solve the support vector , And there is a function in the lower input space  , It happens to be equal to the inner product in the higher dimensional space , namely
, It happens to be equal to the inner product in the higher dimensional space , namely  , Then support vector machines do not need to compute complex nonlinear transformations , And by this function
, Then support vector machines do not need to compute complex nonlinear transformations , And by this function  The inner product of the nonlinear transformation is obtained directly , It greatly simplifies the calculation . A function like this
The inner product of the nonlinear transformation is obtained directly , It greatly simplifies the calculation . A function like this  It's called kernel function
It's called kernel function
1.3.2. classification
- The choice of kernel function should satisfy Mercer's Theorem, That is, any of the kernel functions in the sample space Gram Matrix【 Gram matrix 】 Is a positive semidefinite matrix
- frequently-used :
- Linear kernel function
- Polynomial kernel function
- Radial basis function
- Sigmoid Kernel function
- Composite kernel function
- Fourier series kernel function
- B Spline kernel function
- Tensor product kernel function
- ......
1.3.3. theory
- According to pattern recognition theory , Low dimensional space is linearly nonseparable The pattern of is non linearly mapped to High dimensional feature space may be linearly separable
- The kernel function technique can effectively avoid the problems in the operation of high-dimensional feature space “ Dimension disaster ”
- set up
 Belong to
Belong to  Space , Nonlinear functions
Space , Nonlinear functions  Implement input space
Implement input space  To feature space
To feature space  Mapping , among
Mapping , among  Belong to
Belong to  ,
, , According to kernel technique, there are
, According to kernel technique, there are  , among
, among  Is inner product ,
Is inner product , It's a kernel function
It's a kernel function
- Kernel function will m The inner product operation of high dimensional space is transformed into n Calculation of kernel function in low dimensional input space , Thus, the problem of calculating in high-dimensional feature space is ingeniously solved “ Dimension disaster ” Other questions , Thus, it lays a theoretical foundation for solving complex classification or regression problems in high-dimensional feature space
- set up
1.3.4. nature
- Avoided “ Dimension disaster ”, It greatly reduces the amount of calculation , Effectively handle high-dimensional input
- There is no need to know the nonlinear transformation function
 Form and parameters of
Form and parameters of - The change of the form and parameters of the kernel function will implicitly change the mapping from the input space to the feature space , Then it has an impact on the properties of feature space , Finally, the performance of various kernel methods is changed
- Kernel function method can be combined with different algorithms , Form a variety of different methods based on kernel function technology , And the design of these two parts can be carried out separately , Different kernel functions and algorithms can be selected for different applications
1.3.5. PPT
1.4. Multiple Classes【 Multiple classification problem 】
1.4.1. OvO---One Vernus One
- Figure
- thought
- take N Pairing two categories , Each use 2 Data training classifiers of categories
- Provide samples to all classifiers , The final result is produced by voting
- Number of classifiers
- characteristic
- There are many classifiers , And each classifier only uses 2 Sample data of categories
1.4.2. OvM---One Vernus Many
- thought
- Use one class at a time as a positive example of the sample , All others are counterexamples
- Each classifier can recognize a fixed category
- When using , If a classifier is a positive class , Then it is the category ; If more than one classifier is a positive class , Then select the category recognized by the classifier with the highest confidence
- Number of classifiers
- characteristic
- comparison OvO Fewer classifiers , And each classifier uses all the sample data in training
1.4.3. MvM---Many Vernus Many
- thought
- Take several classes as positive examples at a time 、 Several classes as counterexamples
- The common technique is ECOC【 Error correcting output code 】
- Encoding phase
- Yes N A class to do M Sub division , Each partition treats a part as a positive class , Part of the division is anti class
- There are two forms of coding matrix : Binary code and ternary code
- Binary code : It is divided into positive and negative classes
- Ternary code : It is divided into positive class, negative class and inactive class
- A total of M Training set , Training out M A classifier
- Decoding phase
- M Two classifiers predict the test samples respectively , These predictive markers make up a code , Compare this prediction code with the code of each class , Return the category with the smallest distance as the final result
- Number of classifiers
- M individual
- characteristic
- ECOC Coding length is positively correlated with error correction capability
- The longer the code, the more classifiers need to be trained , Computing storage overhead will increase ; On the other hand, it is meaningless for the finite class code length to exceed a certain range . For codes of the same length , In theory , The farther the coding distance between the two categories of the task is , The stronger the error correction ability
- example
- ECOC In the coding diagram ,“+1” and “-1” They are positive 、 Counter example , In ternary code “0” Indicates that this type of sample is not used
- Black and white are positive respectively 、 Counter example , Grey in ternary code means that such samples are not used
binary ECOC code 




Hamming distance Euclidean distance 































The test sample 




Three yuan ECOC code 






Hamming distance Euclidean distance 







































The test sample 






2. Naive Bayes【 Naive Bayes 】
2.1. Baye's Rule
2.1.1. Definition
- States the relationship between prior probability distribution【 A priori probability distribution 】 and posterior probability distribution【 A posteriori probability distribution 】
2.1.2. Formula
2.1.3. Application
- Parameter estimation
- Classification
- Model selection
2.2. Baye's Rule for Classification
2.2.1. How can we make use of Bayes’ Rule for Classification?
- We want to maximise the posterior probability of observations
- This method is named MAP estimation (Maximum A Posteriori)
2.2.2. How to use?
- Presume that
 means that a sample
means that a sample  belongs to class
belongs to class  where all samples belong to class
where all samples belong to class  from dataset
from dataset 
- Recall Bayes' Rule
- As the observation is same(the same training dataset), we have
- So we need to find the CCP and the prior probability
- According to Law of Large Numbers, the prior probability can be taken as the probability resulted from the frequency of observations
- So we only care about the term
2.3. Naïve Bayes Classifier【 Naive Bayes 】
2.3.1. Calculate
- Calculate the term
 is never an easy task
is never an easy task - A way to simplify the process is to assume the conditions / features of
 are independent to each other
are independent to each other - Assume that
 , we have
, we have
2.3.2. Example 01
- Will you play on the day of Mild?
Original Dataset Outlook Temprature Humidity Windy Play Overcast Hot High False Yes Overcast Cool Normal True Yes Overcast Mild High True Yes Overcast Hot Normal False Yes Rainy Mild High False Yes Rainy Cool Normal False Yes Rainy Cool Normal True No Rainy Mild Normal False Yes Rainy Mild High True No Sunny Hot High True No Sunny Hot High False No Sunny Mild High False No Sunny Cool Normal False Yes Sunny Mild Normal True Yes
- Solution
Temprature Yes No p Hot 2 2 0.28 Mild 4 2 0.43 Cool 3 1 0.28 p 0.64 0.36 




2.3.3. Example 02
- Will you play on the day of Rainy, Cool , Normal and Windy?
Original Dataset Outlook Temprature Humidity Windy Play Overcast Hot High False Yes Overcast Cool Normal True Yes Overcast Mild High True Yes Overcast Hot Normal False Yes Rainy Mild High False Yes Rainy Cool Normal False Yes Rainy Cool Normal True No Rainy Mild Normal False Yes Rainy Mild High True No Sunny Hot High True No Sunny Hot High False No Sunny Mild High False No Sunny Cool Normal False Yes Sunny Mild Normal True Yes
- Solution
Outlook Yes No p Overcast 4 0 0.28 Rainy 3 2 0.36 Sunny 2 3 0.36 p 0.64 0.36 Temprature Yes No p Hot 2 2 0.28 Mild 4 2 0.43 Cool 3 1 0.28 p 0.64 0.36 Humidity Yes No p High 3 4 0.50 Normal 6 1 0.50 p 0.64 0.36 Windy Yes No p T 3 3 0.43 F 6 2 0.57 p 0.64 0.36 
-

-

-


-


-



- Yes
3. Methods
3.1. Parametric Methods【 Parametric methods 】
- We presume that there exists a model, either a Bayesian model (e.g. Naïve Bayes) or a mathematical model (e.g. Linear Regression)
- We seldom obtain a “true” model due to the lack of prior knowledge
- For the same reason, we never know which model should be used
3.2. Non-parametric Methods【 Nonparametric methods 】
- Non-parametric models can be used with arbitrary distributions and without the assumption that the forms of the underlying densities are known.
- Moreover, they can be used with multimodal distributions which are much more common in practice than unimodal distributions.
- With enough samples, convergence to an arbitrarily complicated target density can be obtained.
- The number of samples needed may be very large (number grows exponentially with the dimensionality of the feature space).
- These methods are very sensitive to the choice of window size (if too small, most of the volume will be empty, if too large, important variations may be lost).
- There may be severe requirements for computation time and storage.
- Two major methods
- Decision tree
- k-nearest neighbour
4. Decision Tree【 Decision tree 】
4.1. Steps
4.1.1. Provide
- Suppose we have a training dataset
 whose labels are
whose labels are  respectively, where
respectively, where 
4.1.2. Step
- Given a node as root node
- Determine whether the node is a leaf note by
- Whether the node contains no samples
- Whether the samples belong to the node is from a universal class
- Whether a common attribute is shared
- Whether attributes are yet to be further analysed
- The decision of leaf is determined by voting
- Select attribute
 in
in  to build a new branch for each value of the selected branch then determine the mode of nodes by the previous procedure
to build a new branch for each value of the selected branch then determine the mode of nodes by the previous procedure - Entropy gain【Do not consider the size of dataset】
- Ratio gain (C4.5)【Prefer small size】
- Gini index (CART)【R: Regression】
-


-
- Entropy gain【Do not consider the size of dataset】
4.2. Example
4.1.1. Dataset
Original Dataset Outlook Temprature Humidity Windy Play Overcast Hot High False Yes Overcast Cool Normal True Yes Overcast Mild High True Yes Overcast Hot Normal False Yes Rainy Mild High False Yes Rainy Cool Normal False Yes Rainy Cool Normal True No Rainy Mild Normal False Yes Rainy Mild High True No Sunny Hot High True No Sunny Hot High False No Sunny Mild High False No Sunny Cool Normal False Yes Sunny Mild Normal True Yes
4.1.2. Analysis
- Outlook
Outlook Yes No Overcast 4 0 4 Rainy 3 2 5 Sunny 2 3 5 - Entropy of Outllook




- Entropy of Overcast




- Entropy of Rainy




- Entropy of Sunny





- Entropy Gain
- Build the decision tree
- Select the attribute with highest entropy gain to build up
- e.g.
- Suppose Entropy Gain of Outlook is the highest
- The 1st level of decision tree will look like

4.3. Overfitting【 Over fitting 】
4.3.1. Too good to be true
- Sometimes, the decision tree has fit the sample distribution too well such that unobserved samples cannot be predicted in a sensible way
- We could prune(remove) the branches that cannot introduce system performance
4.4. Random Forest → Typical Example of Boosting【 Random forests 】
- Another way to improve the system is to have multiple decision tree and vote for the final results
- Attributes for each decision tree is random selected
- Each decision tree is only trained by a part set of attributes of samples
- e.g.
- For attribute {A,B,C,D}
- Tree 1 ={A,B,C}
- Tree 2 ={B,C,D}
- Tree 3 = {C,D}
- Trained
- Tree 1 ={A,B,C} → Yes
- Tree 2 ={B,C,D} → Yes
- Tree 3 = {C,D} → No
- For attribute {A,B,C,D}
- e.g.
5. KNN
5.1. PPT
- As in the general problem of classification, we have a set of data points for which we know the correct class labels
- When we get a new data point, we compare it to each of our existing data points and find similarity
- Take the most similar k data points (k nearest neighbours)
- From these k data points, take the majority vote of their labels. The winning label is the label / class of the new data point
5.2. Extra
5.2.1. The core idea
If a sample is in the feature space K Most of the closest samples belong to a certain category , Then the sample also belongs to this category , And have the characteristics of samples in this category
5.2.2. Algorithm flow
Preprocess the data
Calculate test sample points ( That is, the points to be classified ) Distance to each other sample point 【 Usually use European distance 】
Sort each distance , Then choose the one with the smallest distance K A little bit
Yes K Compare the categories of points , According to the principle that the minority is subordinate to the majority , The test sample points are classified in K The one with the highest percentage of points
5.2.3. Advantages and disadvantages
- advantage
- Simple thinking , Easy to understand , Easy to implement , There is no need to estimate parameters
- shortcoming
- When the sample is unbalanced , For example, a class has a large sample size , And the sample size of other classes is very small , It is possible to cause when entering a new sample , The sample K Most of the samples of large capacity classes in neighbors
- The amount of calculation is large , Because for each text to be classified, the distance from it to all known samples should be calculated , To get it K Nearest neighbors
5.2.4. Improvement strategy
- Seek a distance function that is closer to the actual distance to replace the standard Euclidean distance 【WAKNN、VDM】
- Search for more reasonable K Value in place of the specified size K value 【SNNB、DKNAW】
- Using a more accurate probability estimation method to replace the simple voting mechanism 【KNNDW、LWNB、ICLNB】
- Build efficient indexes , In order to improve the KNN The efficiency of the algorithm 【KDTree、NBTree】
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Hcip Road

Qt工程报错:-1: error: Cannot run compiler ‘clang++‘. Output:mingw32-make.exe

openvino系列 19. OpenVINO 与 PaddleOCR 实现视频实时OCR处理

Test APK exception control nettraffic attacker development

Apache Solr 任意文件读取复现

The eighth experiment of hcip Road
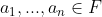
INT 104_LEC 06

Commonly used bypass methods for SQL injection -ctf

MIT CMS.300 Session 12 – IDENTITY CONSTRUCTION 虚拟世界中身份认同的建立 part 2

Detailed explanation of redis persistence, master-slave and sentry architecture
随机推荐
Location of firewalld configuration file
SQL注入常用到的绕过方式-ctf
Mathematical knowledge: Euler function - Euler function
一篇文章学会er图绘制
Eureka服务注册与发现
数学知识:欧拉函数—欧拉函数
Socket programming -- select model
unity 音频可视化方案
Tensorboard的使用
MySQL gets the system time period
浅谈ThreadLocal和InheritableThreadLocal,源码解析
深度学习------不同方法实现lenet-5模型
C# richTextBox控制最大行数
1. probability theory - combination analysis
Create an orderly sequence table and perform the following operations: 1 Insert element x into the table and keep it in order; 2. find the element with the value of X, and delete it if found; 3. outpu
Tri rapide + Tri par bulle + Tri par insertion + Tri par sélection
Take you to tiktok. That's it
Commonly used bypass methods for SQL injection -ctf
记一次高校学生账户的“从无到有”
Acwing第 56 场周赛【完结】
 Is the domain ( It can be considered as
Is the domain ( It can be considered as  ),
), Dimensional space
Dimensional space  The hyperplane of is determined by the equation :
The hyperplane of is determined by the equation : Defined subset , among
Defined subset , among  Is a constant that is not all zero
Is a constant that is not all zero  Vector space
Vector space  A hyperplane in is a plane shaped like :
A hyperplane in is a plane shaped like : The subspace of , among
The subspace of , among  Is any nonzero linear mapping
Is any nonzero linear mapping  Next , Projective space
Next , Projective space  The hyperplane of is determined by the equation :
The hyperplane of is determined by the equation : Definition , among
Definition , among  Is a constant that is not all zero
Is a constant that is not all zero  and
and  give
give  , Map the input space to the high-dimensional feature space . If only the inner product calculation is used to solve the support vector , And there is a function in the lower input space
, Map the input space to the high-dimensional feature space . If only the inner product calculation is used to solve the support vector , And there is a function in the lower input space  , It happens to be equal to the inner product in the higher dimensional space , namely
, It happens to be equal to the inner product in the higher dimensional space , namely  , Then support vector machines do not need to compute complex nonlinear transformations , And by this function
, Then support vector machines do not need to compute complex nonlinear transformations , And by this function  Belong to
Belong to  Space , Nonlinear functions
Space , Nonlinear functions  Implement input space
Implement input space  To feature space
To feature space  ,
, , According to kernel technique, there are
, According to kernel technique, there are  , among
, among  Is inner product ,
Is inner product , It's a kernel function
It's a kernel function 































 means that a sample
means that a sample  belongs to class
belongs to class  where all samples belong to class
where all samples belong to class 



 is never an easy task
is never an easy task are independent to each other
are independent to each other , we have
, we have 














 whose labels are
whose labels are  respectively, where
respectively, where 
 in
in  to build a new branch for each value of the selected branch then determine the mode of nodes by the previous procedure
to build a new branch for each value of the selected branch then determine the mode of nodes by the previous procedure 
























