当前位置:网站首页>Redis cache
Redis cache
2022-06-22 23:37:00 【Old saying】
1. Why cache ?
Life story
Xiao Ming is a chef in a restaurant , In the early days of hotel development , Because there are not many customers, Xiao Ming lives a leisurely life , Clock in at work and play with mobile phones , Punch in and go to the nightclub after work , Life is very pleasant , But with the development of hotels , There are more and more customers , As a result, customers have been waiting for a long time during the peak period , Satisfaction has also dropped significantly .
So the boss found Xiao Ming , Asked about the relevant information , Xiao Ming says he has to wash vegetables during the rush hour 、 Cut and stir fry , Everyone has a lot of work to do, so they are busy , So the service is slow .
So the smart boss came up with a good idea , He asked the chef to prepare the long order in advance when he was not busy , Then keep it properly , Just take it out and heat it up during the rush hour , thus , As expected, the work efficiency has been greatly improved , It is easy to cope with the rush hour .
Cache definition
Caching is a High speed data exchange memory , It can be used to quickly access and manipulate data .
Cache in program
For the program , When cache is not used , The calling process of the program is like this :
But as the business grows , The framework of the company has gradually become the case that multiple programs call one database :
After this transformation , All programs do not call the database directly , Instead, the cache will be called first , When there is data in the cache, it will directly return , Query the database only when there is no data in the cache , This greatly reduces the pressure on the database , And accelerate the response speed of the program .
Cache advantages
Compared to databases , Cache operation performance is higher , The main reasons for high cache performance are as follows :
- Caches are generally key-value Query data , Because unlike databases, there are also factors such as query conditions , So the performance of query is generally higher than that of database ;
- The cached data is stored in memory , The data of the database is stored in the disk , Because the operating performance of memory is much better than that of disk , Therefore, the query efficiency of the cache will be much higher ;
- Caching makes distributed deployment easier ( When a server becomes a cluster of connected servers ), The database is generally difficult to realize distributed deployment , Therefore, the load and performance of the cache can be expanded and increased in parallel .
2. Cache classification
Cache can be roughly divided into two categories :
- Local cache
- Distributed cache
Local cache
Local cache Also called stand-alone cache , That is to say, it can be applied to caching in a stand-alone environment . The so-called stand-alone environment refers to , Deploy the service to a server , As shown in the figure below :

for instance
The local cache is equivalent to the corporate regulations of every enterprise , Different company regulations are also different , Like working hours , Different companies have different working hours , For enterprises and institutions, the general requirements are 9:00-17:00 Go to work , And for bars , This time is completely inappropriate .
therefore , The characteristic of local caching is that it only applies to the current system .
Distributed cache
Distributed cache It refers to the cache that can be applied in the distributed system . The so-called distributed system refers to the deployment of a set of servers to multiple servers , And the user's requests are distributed to different servers according to certain rules through load distribution , As shown in the figure below :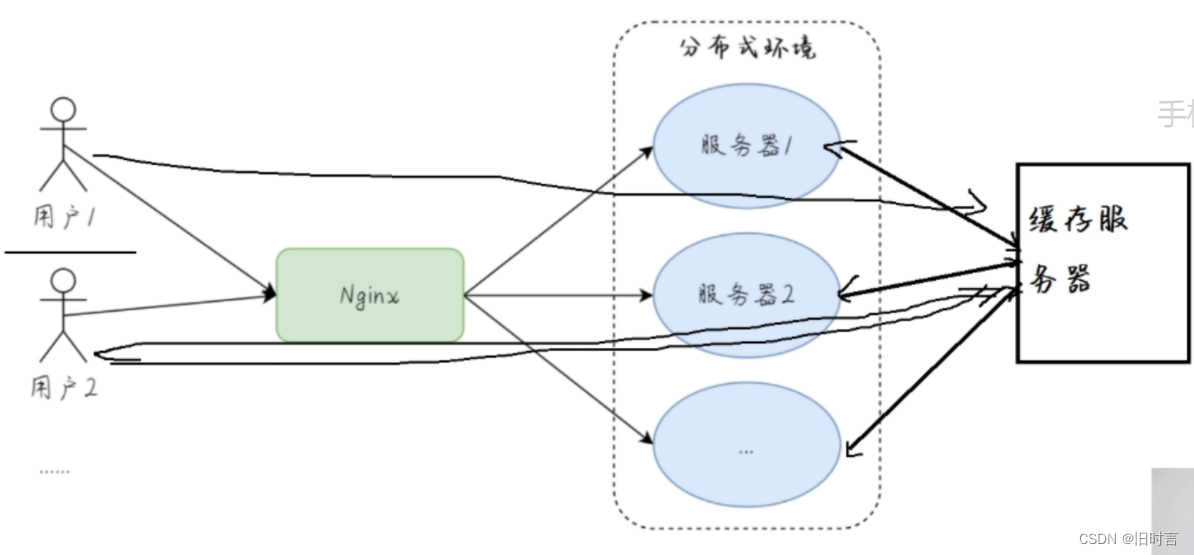
for instance
Distributed caching is equivalent to the rules that apply to all companies , For example, no company can evade taxes , Don't do anything against the law , This situation is similar to distributed caching , For all systems .
For example, our servers in distributed systems A A cache is stored in key=laowang, So on the server B You can also read key=laowang The data of , This is the role of distributed caching .
3. Common cache usage
Common uses of local caching : Spring Cache、MyBatis And so on .
Common uses of distributed caching : Redis and Memcached.
Local cache : Spring Cache
stay Spring Boot project , You can use it directly Spring The built-in Cache( Local cache ), You only need to complete the following three steps to be able to use it normally :
- Open the cache
- Operating the cache
- Call cache
Open the cache
stay Spring Boot Add the following code to the startup class of , Open the cache :
@SpringBootApplication
@Enablecaching # Enable caching
public class BiteApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BiteApplication.class,args );
}
}
Operating the cache
@service
public class UserService {
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "user" ,key = "#id" )
public string getUser(int id){
// Pseudo code
System.out.println(" I'm in getUser Method ");
return "ID: "+id;
}
}
Use the cache
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
Userservice userService;
@RequestMapping("/get")
public string getUser(int id) {
return userService.getUser(id);
}
}
Use Postman To test 

Result analysis : On the first call , Call pseudo code to enter Dao layer , The console will print “ I'm in getUser Method ”. The second time 、 After the third call, it will not enter Dao layer , Instead, it reads data from the cache , Will not print “ I'm in getUser Method ”.
Distributed cache : Redis
stay Spring We can also operate directly in the framework Redis cache , Its operation flow is shown in the figure below :
Redis and Memcached What's the difference? ?
- Different storage methods : memcache Store all the data in memory , It hangs when the power goes out , Data cannot exceed memory size ; Redis Some of it is stored on the hard drive , This ensures data persistence ;
- Data support type :memcache Support for data types is relatively simple ;Redis There are complex data types ;
- The stored values differ in size : Redis Maximum attainable 512mb,memcache Only 1mb.
summary : Usually , If it's a single machine Spring project , Can use directly Spring Cache As a local cache , If it is a distributed environment, it will generally use Redis.
4. Redis Data type and usage
Redis Yes 5 Big basic data types :
- String—— String type
- Hash—— Dictionary type
- List—— List the type
- Set—— Collection types
- zSet—— Ordered set type
The most commonly used are string and dictionary types .
String type
String type (Simple Dynamic Strings abbreviation SDS), Translated into : Simple dynamic string , It is based on key value pairs key-value In the form of storage , according to key To store and retrieve value value , Its use is relatively simple , But it is widely used in practical projects .
The use of strings is as follows :
1 127.e.0.1:6379> set k1 v1# Add data
2 OK
3 127.0.0.1:6379>get k1 # Query data
4 "v1"
5 127.8.8.1:6379> strlen k1 # The length of the query string
6 (Integer) 5
We can also use ex (expires) Parameter to set the expiration time of the string , As shown in the following code :
1 127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 v1 ex 1000 # Set up k1 1000s After expired ( Delete )
2 OK
Common usage scenarios for Strings :
- Store users ( Sign in ) Information ;
- Store Article Details and list information ;
- Store and accumulate web page Statistics .
…
Dictionary type
Dictionary type (Hash) It is also called hash type or hash table type , It is a key value (key) And a special “ Hashtable ” Connect , This “ Hashtable ” The table contains two columns of data : Fields and values , It's equivalent to Java Medium Map<String,Map<String,String>> structure .
Suppose we use a dictionary type to store the details of an article , The storage structure is shown in the figure below :
Similarly, we can also use dictionary types to store user information , And using dictionary types to store such information eliminates the need to manually serialize and deserialize data , So it is more convenient and efficient to use .
The use of dictionary types is as follows :
1 127.0.0.1:6379> hset myhash key1 value1 # Add data
2 (integer) 1
3 127.e.0.1:6379> hget myhash key1 # Query data
4 "value1"
Dictionary type data structure , As shown in the figure below :
List the type
List the type (List) Is an ordered structure stored in a linked list structure , Its element insertion will be stored in the linked list structure in order , So its element operation ( Insert and delete ) The time complexity is O(1), So the speed is relatively fast , But its query time complexity is O(n), Therefore, the query may be slow .
The use of list types is as follows :
1 127.e.e.1:6379> lpush list 1 2 3# Add data
2 (integer) 3
3 127.e.0.1:6379> lpop list # Get and delete the first element of the list
4 1
The typical usage scenarios of the list are as follows :
- Message queue : List types can use rpush Realize the function of first in first out , At the same time, you can use lpop Easily pop up ( Query and delete ) First element , So the list type can be used to implement message queuing ;
- The article lists : For blog sites , When there are more and more users and articles , In order to speed up the response speed of the program , We can store the user's own articles in List in , because List It's an orderly structure , So this can perfectly realize the paging function , Thus, the response speed of the program is accelerated .
Collection types
Collection types (Set) Is an unordered and unique set of key values .
The use of collection types is as follows :
1 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset v1 v2 v3# Add data
2 (integer) 3
3 127.8.0.1:6379> smembers myset # Query all data in the collection
4 1) "v1"
5 2) "v3"
6 3) "v2"
The classic usage scenarios of collection types are as follows :
- People who follow me on Weibo and those I follow are suitable for collective storage , It can ensure that personnel will not repeat ;
- The winner information is also suitable to be stored in collection type , This ensures that a person will not win the prize repeatedly .
Collection types (Set) And list type (List) The difference is as follows :
- Lists can store duplicate elements , Collections can only store non repeating elements ;
- The list stores the elements in their order , Collections store elements in an unordered way .
Ordered set type
Ordered set type (Sorted Set) One more sort attribute than the set type score ( The score is ), For ordered sets ZSet Come on , Each storage element is equivalent to having two values , One is the ordered combination of element values , One is the sort value . The storage element values of an ordered set cannot be repeated , But the score can be repeated .
When we store students' grades in an ordered set , Its storage structure is shown in the figure below :
The use of ordered collection types is as follows :
1 127.0.0.1:6379> zadd zset1 3 golang 4 sql 1 redis # Add data
2 (integer) 3
3 127.0.0.1:6379> zrange zset 0 -1 # Query all the data
4 1) "redis"
5 2) "mysql"
6 3) "java"
The classic usage scenarios for ordered collections are as follows :
- Student performance ranking
- Fans list , Sort according to the priority of attention
5. Persistence
Persistence is Save data from memory to disk The process of , its The purpose is to prevent data loss . Because the data in memory will be lost after the server restarts , The data on the disk will not , So for the sake of system stability , We need to persist the data . At the same time, the persistence function is Redis and Memcached One of the main differences , because Redis Support persistence and Memcached I won't support it .
Redis Persistence can be done in the following ways 3 Kind of :
- Snapshot mode (RDB,Redis DataBase) Put the memory data of a certain time , Write to disk in binary mode ;
- How to add documents (AOF,Append Only File), Record all operation commands , And in the form of text appended to the file ;
- Mixed persistence ,Redis 4.0 And then the new way , Blending persistence is a combination of RDB and AOF The advantages of , At the time of writing , First, put the current data into RDB Write to the beginning of the file , And then follow up the operation command with AOF The format is stored in the file , This will ensure Redis Speed at restart , And reduce the risk of data loss .
Persistence policy settings
Can be in redis-cli Execute... On the command line config set aof-use-rdb-preamble yes To turn on hybrid persistence , When mixed persistence is turned on Redis Take the mixed persistence method as the persistence strategy ; When mixed persistence is not enabled , Use config set appendonly yes To open AOF Persistent strategy , When AOF When both and mixed persistence are not enabled, the default will be RDB The way of persistence .
RDB advantage
- RDB The content of is binary data , Smaller footprint , More compact , More suitable as backup files ;
- RDB Very useful for disaster recovery , It's a compact file , It can be transmitted to the remote server faster Redis Service recovery ;
- RDB Can be improved to a greater extent Redis
Running speed of , Because every time you persist Redis The main process will fork() A subprocess , Persist data to disk ,Redis The main process does not execute the disk I/○ Wait for the operation ; - And AOF File format compared to ,RDB Files can be restarted faster .
RDB shortcoming
- because RDB Only data of a certain time interval can be saved , If midway through Redis The service was unexpectedly terminated , Will lose... For a while Redis data ;
- RDB Need to often fork() To use subprocesses to persist it on disk . If the data set is large ,fork() It can be time consuming , And if the data set is large and CPU Poor performance , May lead to Redis Stop serving clients for milliseconds or even - Second .
AOF advantage
- AOF Persistence saves more complete data ,AOF Three preservation strategies are provided : Save every operation 、 Save every second 、 Follow the persistence policy of the system , Once a second , It is a good choice to consider both data security and performance , It's also
AOF Default policy , Even if something unexpected happens , At most, it will only be lost 1s Clock data ; - AOF It adopts the write mode of command appending , So there is no problem of file corruption , Even for some unexpected reason , The persistent data that caused the last operation was written in half , It can also be done through redis-check-aof Tools for easy repair ;
- AOF Persistent files , Very easy to understand and parse , It is to put all Redis Key operation command , Saved to disk as a file . Even if you don't use
flushallThe command deletes all key information , Just use AOF file , Delete the lastflushallcommand , restart Redis It can recover the data deleted by mistake .
AOF shortcoming
- For the same dataset ,AOF The file is larger than RDB file ;
- stay Redis When the load is high ,RDB Than AOF Better performance ;
- RDB Use snapshots to persist the entire Redis, data , and AOF Just append every command executed to AOF In file , So in theory ,RDB Than AOF More robust .
Hybrid persistence benefits
- Mixed persistence combines RDB and AOF The advantages of persistence , Beginning with RDB The format of , bring Redis Can start faster , At the same time combined with AOF The advantages of , It reduces the risk of massive data loss .
Disadvantages of mixed persistence
- AOF Added... To the file RDB Content of format , bring AOF The readability of the file becomes very poor ;
- Compatibility is poor , If you turn on mix persistence , So this hybrid persistence AOF file , Can't be used in Redis 4.0 Previous version .
6. Frequently asked questions
Cache avalanche
Cache avalanche means that in a short time , A large number of caches expire at the same time , Resulting in a large number of requests to query the database directly , This has caused great pressure on the database , In severe cases, the situation that may lead to database downtime is called cache avalanche .
Let's first look at the execution flow chart of the program under normal conditions and cache avalanche , The execution process of the system under normal conditions is shown in the following figure :
Cache the execution process of avalanche , As shown in the figure below :

The above comparison chart shows the impact of cache avalanche on the system , How to solve the cache avalanche problem ? Cache avalanche Common solutions There are the following .
Line up with locks
Locking queue can play a buffer role , Prevent a large number of requests from operating the database at the same time , But its disadvantage is that it increases the response time of the system , Reduce the throughput of the system , Sacrificing part of the user experience .
Randomize expiration time
To avoid simultaneous cache expiration , Random time can be added when setting the cache , This can greatly avoid a large number of cache failures at the same time .
The sample code is as follows :
1 l/ Cache original expiration time
2 int exTime = 10 * 60;
3 // Random number generating class
4 Random random = new Random( );
5 / Cache Settings
6 jedis.setex(cacheKey,exTime+random.nextInt(1000) , value) ;
Set the secondary cache
L2 cache refers to anything other than Redis Its own cache , Set another layer of cache , When Redis After failure , First query the L2 cache .
For example, you can set up a local cache , stay Redis When the cache fails, first query the local cache instead of the database . After adding the L2 cache, the program execution process , As shown in the figure below :
Cache penetration
Cache penetration means that there is no data in the query database and cache , Because the database query has no data , For fault tolerance , The results will not be saved to the cache , Therefore, every request will query the database , This is called cache penetration .
The cache penetration execution process is shown in the following figure :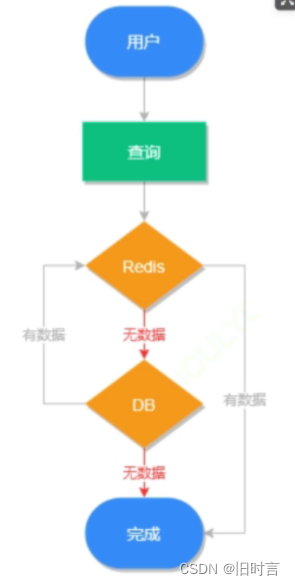
The red path indicates the execution path of cache penetration , It can be seen that cache penetration will put a lot of pressure on the database . There are several solutions for cache penetration .
Cache empty results
Another way is that we can save the data queried from the database to the cache every time , In order to improve the use experience of foreground users ( Solve the situation that no information can be queried for a long time ), We can set the cache time of empty results to be shorter , for example 3-5 minute .
Cache breakdown
The execution process of cache breakdown is shown in the following figure :
Its solutions are as follows 2 individual .
Line up with locks
This processing method is similar to the cache avalanche lock queuing method , Are locked and queued when querying the database , Buffer operation requests to reduce the running pressure of the server .
Settings never expire
For some hotspot caches , We can set it to never expire , This ensures the stability of the cache , But it should be noted that after the data changes , To update this hotspot cache in time , Otherwise, it will cause the error of query results .
Cache preheating
First of all , Cache warm-up is not a problem , It's an optimization scheme when using cache , It can improve the use experience of front-end users .
Cache warm-up refers to when the system starts , First, the query results are pre stored in the cache , So that users can directly read from the cache when querying later , To save users' waiting time .
Cache warm-up execution process , As shown in the figure below :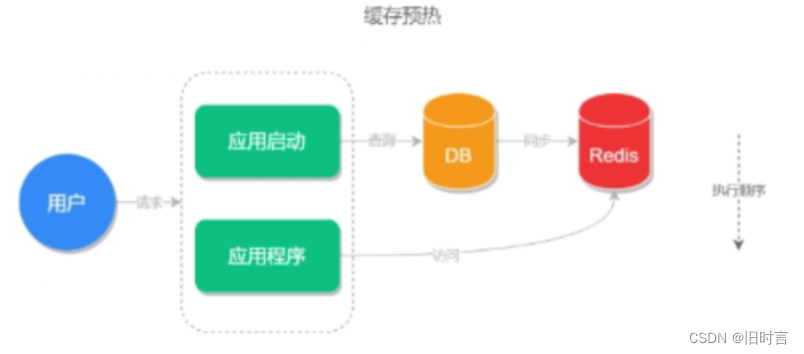
There are three ways to realize cache preheating :
- Write the method to be cached in the system initialization method , In this way, the system will automatically load data and cache data when starting up ;
- Mount the method to be cached to a page or back-end interface , Manually trigger cache warm-up ;
- Set timing task , Automatic cache warm-up at regular intervals .
边栏推荐
- 2020-12-20
- Safe and reliable! Tianyi cloud data security management platform passed the evaluation
- OJ每日一练——单词的长度
- SSH method 2 for adding node nodes in Jenkins
- ArcGIS application (20) the ArcGIS grid image symbol system prompts "this dataset does not have valid histogram required for classificati..."
- 在Word中自定义多级列表样式
- 1. class inheritance (point)
- Spark SQL Generic Load/Save Functions(2.4.3)
- Freshman girls' nonsense programming is popular! Those who understand programming are tied with Q after reading
- Digital data was invited to participate in Nantong enterprise digital transformation Seminar
猜你喜欢

Safe and reliable! Tianyi cloud data security management platform passed the evaluation

Introduction to database access tools

C language greedy snake

IPV4的未来替代品!一文读懂IPV6的优势特点和地址类型

c语言---17 函数简介

考过HCIP依然转行失败,职业网工最看重的到底是什么

在Word中自定义多级列表样式

Spark RDD Programming Guide(2.4.3)

Reverse proxy haproxy

【ARM】讯为rk3568开发板lvds屏设置横屏显示
随机推荐
2. interface (calculator)
Enterprise digitalization is not a separate development, but a comprehensive SaaS promotion
获取鼠标移动的方向
2020-12-04
使用Redisson操作分布式队列的注意事项
A spark app demo
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
China Mobile's mobile phone users grow slowly, but strive for high profit 5g package users
Common operations of sourcetree version management
Bubble sort pointer
Smart data won two annual awards at the second isig China Industrial Intelligence Conference
PHP7.3报错undefined function simplexml_load_string()
Digital data was invited to participate in Nantong enterprise digital transformation Seminar
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
c# sqlsugar,hisql,freesql orm框架全方位性能测试对比 sqlserver 性能测试
Stop using system Currenttimemillis() takes too long to count. It's too low. Stopwatch is easy to use!
数据库访问工具简介
2021-01-29
弱电转职业网工难不难?华为售前工程师分享亲身经历
Install the typescript environment and enable vscode to automatically monitor the compiled TS file as a JS file