当前位置:网站首页>R语言手写数字识别
R语言手写数字识别
2022-07-24 07:07:00 【huiyiiiiii】
目录
1.训练集数据的选择
原数据文件中有60000个个体,要求选择1000个个体进行模型的训练(为了提高训练难度),其余的个体丢弃。有0~9共10种标签,为保证标签的平衡,防止某一种标签的训练集过少而造成训练结果较差,对10种标签进行相同数量的选择,即每种标签选择100个个体作为训练集。具体操作是按照标签将个体分成10类,每一类随机选择100个个体,将选择结果进行合并组成训练集。
若要求使用全部的训练集,则忽略此步。
2.模型的构建
利用keras的模型,是一个多个网络层的线性堆迭,通过向Sequential模型传递一个layer的列表构造。模型有一个784节点的输入层,一个784节点的全连接层,10个节点的输出层。激活函数选择为relu与exponential,损失函数选择为categorical_crossentropy,优化器选择为Nadam。评估标准选择为accuracy。
3.模型训练
每次神经网络的升级是使用了100个样本,这100个样本来自于对1000个样本的抽样。每个epoch包含了10次iteration,一共100个epoch。
4.结果
模型训练结果:
- 没有噪声:测试集上的准确率91.57%。



噪声方差0.1:测试集上的准确率82.41%

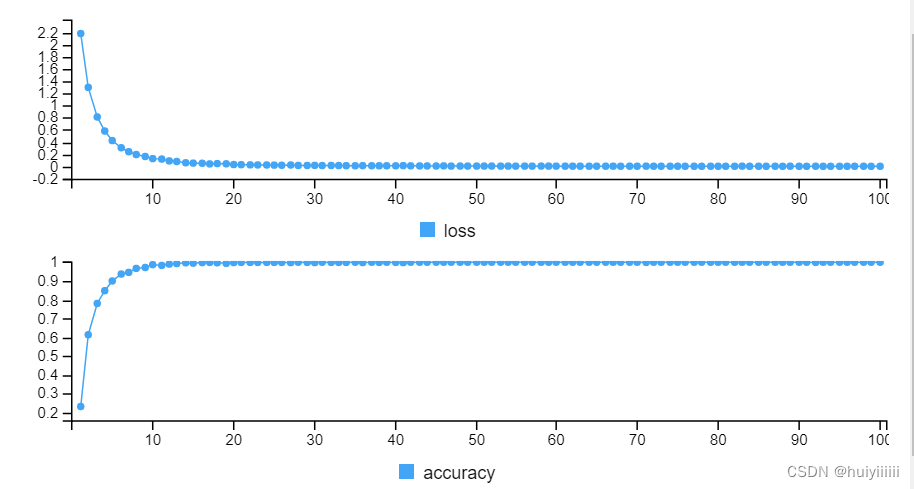

噪声方差0.25:测试集上的准确率75.91%。



噪声方差0.5:测试集上的准确率67.37%。



5.代码
rm(list=ls())
##读取图片数据的函数,返回一个数据列表
read_image<-function(filename){
read.filename <- file(filename, "rb")
test<-list()
length(test)<-7
names(test)<-c("magic_number1","magic_number2","number_of_images",
"number_of_rows","number_of_columns","data","label")
test$magic_number1<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=4,n=1,endian="big")
test$number_of_images<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=4,n=1,endian="big")
test$number_of_rows<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=4,n=1,endian="big")
test$number_of_columns<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=4,n=1,endian="big")
data<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=1,n=test$number_of_images*test$number_of_rows*test$number_of_columns,signed=F,endian="big")
data<-data/255
data<-matrix(data,byrow=T,test$number_of_images,test$number_of_rows*test$number_of_columns)
data<-as.data.frame(data)
test$data<-data
close(read.filename)
return (test)
}
##读取图片标签的函数,返回数据列表
read_label<-function(filename,test){
read.filename <- file(filename, "rb")
test$magic_number2<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=4,n=1,endian="big")
readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=4,n=1,endian="big")
data<-readBin(read.filename,integer(),size=1,n=test$number_of_images,signed=F,endian="big")
test$label<- as.factor(data)
close(read.filename)
return (test)
}
##选取训练数据集函数
Randomlychoose<-function(test,r){
d0<-test$data[which(test$label=="0"),]
d1<-test$data[which(test$label=="1"),]
d2<-test$data[which(test$label=="2"),]
d3<-test$data[which(test$label=="3"),]
d4<-test$data[which(test$label=="4"),]
d5<-test$data[which(test$label=="5"),]
d6<-test$data[which(test$label=="6"),]
d7<-test$data[which(test$label=="7"),]
d8<-test$data[which(test$label=="8"),]
d9<-test$data[which(test$label=="9"),]
t0<-sample(nrow(d0),r/10)
t1<-sample(nrow(d1),r/10)
t2<-sample(nrow(d2),r/10)
t3<-sample(nrow(d3),r/10)
t4<-sample(nrow(d4),r/10)
t5<-sample(nrow(d5),r/10)
t6<-sample(nrow(d6),r/10)
t7<-sample(nrow(d7),r/10)
t8<-sample(nrow(d8),r/10)
t9<-sample(nrow(d9),r/10)
test$data<-rbind(d0[t0,],d1[t1,],d2[t2,],d3[t3,],d4[t4,],d5[t5,],d6[t6,],
d7[t7,],d8[t8,],d9[t9,])
test$label<-as.factor(rep(0:9,each=r/10))
test$number_of_images<-r
return (test)
}
##显示图片的函数
show_picture<-function(test){
layout(matrix(1:100,10,10),rep(1,10),rep(1,10))
par(mar=c(0,0,0,0))
for(i in 1:100){
pic<-matrix(unlist(test$data[i,][-785])*255,test$number_of_rows,test$number_of_columns,byrow=F)
image(pic,col=grey.colors(255),axes=F)
}
}
##添加高斯白噪声的函数
add_noise<-function(test,m,s){
d<-mapply(rnorm,n=test$number_of_images,mean=rep(m,28*28),sd=rep(sqrt(s)/255,28*28))
test$data[1:784]<-test$data[1:784]+d
return (test)
}
##读取训练集与测试集的数据与标签
library("keras")
test<-read_image("t10k-images.idx3-ubyte")
test<-read_label("t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte",test)
train<-read_image("train-images.idx3-ubyte")
train<-read_label("train-labels.idx1-ubyte",train)
train<-Randomlychoose(train,1000)
##查看图片
show_picture(test)
show_picture(train)
dev.off()
##添加高斯白噪声,方差分别为0.1,0.25,0.5。
test<-add_noise(test,0,0.5)
train<-add_noise(train,0,0.5)
test<-add_noise(test,0,0.1)
train<-add_noise(train,0,0.1)
test<-add_noise(test,0,0.25)
train<-add_noise(train,0,0.25)
##提取训练集与测试集的数据与标签
train_x<-as.matrix(train$data[,1:784],1000,784)
test_x<-as.matrix(test$data[,1:784],10000,784)
test_y<-to_categorical(test$label,10)
train_y<-to_categorical(train$label,10)
##定义网络参数
model<-keras_model_sequential()
model %>%
layer_dense(units=784,input_shape = 784) %>%
layer_dropout(rate=0.7)%>%
layer_activation(activation = 'relu') %>%
layer_dense(units=10) %>%
layer_activation(activation = 'exponential')
model %>% compile(
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='Nadam',
metrics=c('accuracy')
)
##训练模型
model %>% fit(train_x,train_y,epochs=100,batch_size=100)
##评估模型表现
loss_and_metrics<-model%>% evaluate(test_x,test_y,batch_size=1000)
result<-model%>%predict(test_x)
result<-apply(result,1,which.max)-1
err <- sum(result != test$label)/test$number_of_images
err
6.数据来源
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

In the era of e-commerce, what should enterprises do in the transformation of social e-commerce?

Take you step by step to learn C (one)

Redis persistence

C language from entry to Earth - array

项目中数据库插入大批量数据遇到的问题

传统电商红利消失,怎么进军新型社交电商?

论文阅读:HarDNet: A Low Memory Traffic Network

STM32H750VBT6驱动程控增益放大模块PGA113——基于CubeMX的Hal库
![[sequential logic circuit] - register](/img/a5/c92e0404c6a970a62595bc7a3b68cd.gif)
[sequential logic circuit] - register

Redis sentinel mechanism
随机推荐
Empty cup mentality, start again
Basic syntax of MySQL DDL and DML and DQL
C language from entry to soil (I)
Oauth2==SSO三种协议。Oauth2四种模式
C language from entry to soil (III)
Prompt for garbled code when CHM file is opened
第二部分—C语言提高篇_1. C语言概述
GIMP自定义截图
Feature Selective Anchor-Free Module for Single-Shot Object Detection
Aggregated new ecological model - sharing purchase, membership and reward system
Raspberry pie change source
Pytorch deep learning practice lesson 10 / assignment (basic CNN)
What kind of mode can make platform users self-help fission- Chain 2+1
Flow control statement of avascript
yocs_ velocity_ Smooth source code compilation
GDB debug core/dump
[tips] a simple method to create a version control project
[sequential logic circuit] - register
JMeter笔记2 | JMeter原理及测试计划要素
深度学习二三事-回顾那些经典卷积神经网络