当前位置:网站首页>Pytorch deep learning practice lesson 10 / assignment (basic CNN)
Pytorch deep learning practice lesson 10 / assignment (basic CNN)
2022-07-24 07:11:00 【m0_ fifty-six million two hundred and forty-seven thousand and 】
One 、1. Model structures,

import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F # use Relu function
import torch.optim as optim # Optimizer optimization
batch_size = 64
# transform Preprocessing , Transform image into image tensor
'''ToTensor: Will a ’PIL Image‘or‘numpy.ndarray’ Turn into tensor Format ,PIL Image or numpy.ndarray Of shape by (H x W x C), The scope is [0, 255]
Turn into shape by (C x H x W) The scope is [0.0, 1.0]'''
'''Normalize: Standardized functions , Use the mean and standard deviation to tensor Standardize
output[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]
'''
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])
# mnist The data set is 1*28*28 A single channel image of
# ./ Represents the current directory ../ Represents the parent directory / Represents the root directory
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transform) # Training data set
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset,
shuffle=True,
batch_size=batch_size)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=batch_size)
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.pooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(320, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pooling(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pooling(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
# here x The dimension is 4 Of tensor, namely (batchsize,C,H,W),x.size(0) finger batchsize Value
# Flatten Layer is used to input “ Flatten ”, That is, the multidimensional input is unidimensional , It is often used in the transition from convolution layer to fully connected layer .
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # -1 It's automatic calculation , by C*H*W
x = self.fc(x) # x Apply fully connected network
return x
model = Net()
# Migrate the model to GPU On
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
# Because the network model is already a little big , Therefore, a better optimization algorithm should be used in gradient descent , For example, with impulse (momentum), To optimize the training process
# Encapsulate a loop into a function
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0.0
# By function enumerate Return each batch of data data, And index index(batch_idx), because start=0 therefore index from 0 Start
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
inputs, targets = data # Divide the data into images and corresponding labels
inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device) # Migrate to GPU On
optimizer.zero_grad() # Clear the historical loss gradient
# forward
y_pred = model(inputs) # Input the training pictures into the network and get the output
# backward
loss = criterion(y_pred, targets)
loss.backward()
# update
optimizer.step() # Parameters are updated
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 300 == 299: # Every time 300 individual mini-batches Print once
print('[%d,%5d] loss:%.3f' % (epoch + 1, batch_idx + 1, running_loss / 300))
running_loss = 0.0
def test():
correct = 0 # How much is correct
total = 0 # How much is the total
with torch.no_grad(): # The test doesn't count as a gradient
for data in test_loader: # from test_loader Get data
images, labels = data # Divide the data into images and corresponding labels
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device) # Migrate to GPU On
outputs = model(images) # Get the data and make predictions
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1) # Find the subscript of the maximum value along the first dimension , There are two return values , the reason being that 10 Come on , Return value
# The return value is the maximum value of each row , The other is the subscript of the maximum ( Each sample is a line , Every line has 10 Quantity )( Line No 0 Dimensions , Column is number 1 Dimensions )
total += labels.size(0) # take size The first of a tuple 0 Elements (N,1), After accumulation, the total number of test samples can be obtained
# Inferred classification and label Whether it is equal or not , It's just 1, Fake is 0, After summing, take out the scalar , After the cycle is completed, the correct number of samples can be predicted
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print("accuracy on test set:%d %% [%d/%d]" % (100 * correct / total, correct, total))
# Training
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(10):
train(epoch)
test() # A round of training , Test round
2. Result display

Two 、1. Model structures, ( deepen )

import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F # use Relu function
import torch.optim as optim # Optimizer optimization
batch_size = 64
# transform Preprocessing , Transform image into image tensor
'''ToTensor: Will a ’PIL Image‘or‘numpy.ndarray’ Turn into tensor Format ,PIL Image or numpy.ndarray Of shape by (H x W x C), The scope is [0, 255]
Turn into shape by (C x H x W) The scope is [0.0, 1.0]'''
'''Normalize: Standardized functions , Use the mean and standard deviation to tensor Standardize
output[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]
'''
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])
# mnist The data set is 1*28*28 A single channel image of
# ./ Represents the current directory ../ Represents the parent directory / Represents the root directory
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transform) # Training data set
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset,
shuffle=True,
batch_size=batch_size)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=batch_size)
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=3)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(20, 32, kernel_size=3)
self.pooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(128, 64)
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 32)
self.fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(32, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# batch_size = x.size(0)
x = self.pooling(self.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pooling(self.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pooling(self.relu(self.conv3(x)))
# here x The dimension is 4 Of tensor, namely (batchsize,C,H,W),x.size(0) finger batchsize Value
# Flatten Layer is used to input “ Flatten ”, That is, the multidimensional input is unidimensional , It is often used in the transition from convolution layer to fully connected layer .
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc1(x) # x Apply fully connected network
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
model = Net()
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
# Because the network model is already a little big , Therefore, a better optimization algorithm should be used in gradient descent , For example, with impulse (momentum), To optimize the training process
# Encapsulate a loop into a function
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0.0
# By function enumerate Return each batch of data data, And index index(batch_idx), because start=0 therefore index from 0 Start
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
inputs, targets = data # Divide the data into images and corresponding labels
inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device) # Migrate to GPU On
optimizer.zero_grad() # Clear the historical loss gradient
# forward
y_pred = model(inputs) # Input the training pictures into the network and get the output
# backward
loss = criterion(y_pred, targets)
loss.backward()
# update
optimizer.step() # Parameters are updated
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 300 == 299: # Every time 300 individual mini-batches Print once
print('[%d,%5d] loss:%.3f' % (epoch + 1, batch_idx + 1, running_loss / 300))
running_loss = 0.0
def test():
correct = 0 # How much is correct
total = 0 # How much is the total
with torch.no_grad(): # The test doesn't count as a gradient
for data in test_loader: # from test_loader Get data
images, labels = data # Divide the data into images and corresponding labels
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device) # Migrate to GPU On
outputs = model(images) # Get the data and make predictions
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1) # Find the subscript of the maximum value along the first dimension , There are two return values , the reason being that 10 Come on , Return value
# The return value is the maximum value of each row , The other is the subscript of the maximum ( Each sample is a line , Every line has 10 Quantity )( Line No 0 Dimensions , Column is number 1 Dimensions )
total += labels.size(0) # take size The first of a tuple 0 Elements (N,1), After accumulation, the total number of test samples can be obtained
# Inferred classification and label Whether it is equal or not , It's just 1, Fake is 0, After summing, take out the scalar , After the cycle is completed, the correct number of samples can be predicted
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print("accuracy on test set:%d %% [%d/%d]" % (100 * correct / total, correct, total))
# Training
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(10):
train(epoch)
test() # A round of training , Test round
2. Result display

reference
《PyTorch Deep learning practice 》 Complete the collection _ Bili, Bili _bilibili
边栏推荐
- What kind of mode can make platform users self-help fission- Chain 2+1
- 不要太在意别人对你的看法
- (note sorting is not completed) [graph theory: find the shortest path of single source]
- Camera Hal OEM module ---- CMR_ grab.c
- Prompt for garbled code when CHM file is opened
- Do you really know the judgement sentence?
- In the era of e-commerce, what should enterprises do in the transformation of social e-commerce?
- 第二部分—C语言提高篇_4. 二级指针
- Gangster escape 3
- Use of redis
猜你喜欢
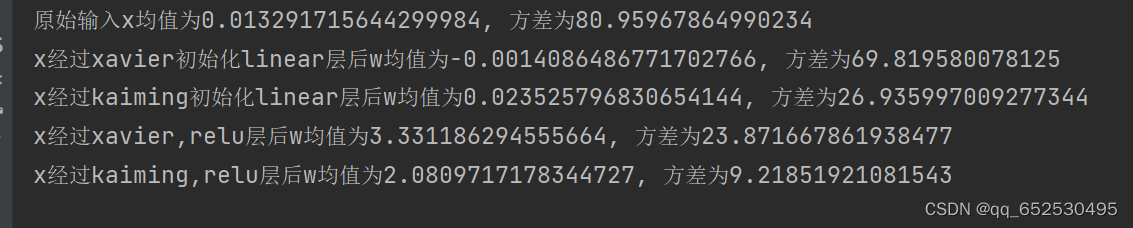
xavier_ normal_ Initialization test

单点登录的三种实现方式

Redis sentinel mechanism
Hackingtool of security tools

记账APP:小哈记账2——注册页面的制作

JMeter笔记2 | JMeter原理及测试计划要素

电子商务时代,企业社交电商转型要做什么?

Introduction to pyqt5 - student management system

What kind of mode can make platform users self-help fission- Chain 2+1
C language from entry to soil (III)
随机推荐
MySQL automatic generation creation time and update time
上传图片base64
聚合型新生态模式-分享购,会员及奖励制度
xavier_ normal_ Initialization test
Don't care too much about others' eyes, it will erase your glory
传统电商红利消失,怎么进军新型社交电商?
C language from entry to soil function
QoS服务质量四QoS边界行为之流量监管
Mongodb application scenario and model selection (massive data storage model selection)
一日一书:机器学习及实践——从零开始通往kaggle竞赛之路
/etc/rc. Local setting UI program startup and self startup
第二部分—C语言提高篇_2. 内存分区
C language from entry to Earth - array
You can't satisfy everyone!
After grouping, return to the last record group in each group_ Use of concat
自己的人生无须浪费在别人的标准中
上传excel文件
tensorflow boolean_ Mask function
Use of redis
Create WPF project