当前位置:网站首页>JUC并发编程基础(4)--线程组和线程优先级
JUC并发编程基础(4)--线程组和线程优先级
2022-07-24 05:21:00 【aMythhhhh】
线程组
线程组就是一系列线程的集合,线程一定存在于某一个线程组里,不能独立存在,如果在创建线程的时候没有显式指定线程组名称,那么默认加到父线程的线程组中。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread testThread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("testThread当前线程组名字:" +
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName());
System.out.println("testThread线程名字:" +
Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
testThread.start();
System.out.println("执行main所在线程的线程组名字: " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName());
System.out.println("执行main方法线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
执行main所在线程的线程组名字: main
执行main方法线程名字:main
testThread当前线程组名字:main
testThread线程名字:Thread-0
ThreadGroup管理着它下面的Thread,ThreadGroup是一个标准的向下引用的树状结构。
线程的优先级
线程优先级可以指定,Java中的范围是1-10,默认优先级是5,可以通过setPriority方法设置线程优先级。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread a = new Thread();
System.out.println("我是默认线程优先级:"+a.getPriority());
Thread b = new Thread();
b.setPriority(10);
System.out.println("我是设置过的线程优先级:"+b.getPriority());
}
}
我是默认线程优先级:5
我是设置过的线程优先级:10
但要注意的是,线程优先级并不是说越高操作系统就先执行你,具体执行哪个线程还是根据线程调度算法来决定的,优先级只是给操作系统一个小小的建议!
public class Demo {
public static class T1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
System.out.println(String.format("当前执行的线程是:%s,优先级:%d",
Thread.currentThread().getName(),
Thread.currentThread().getPriority()));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntStream.range(1, 10).forEach(i -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(new T1());
thread.setPriority(i);
thread.start();
});
}
}
//很明显不是按线程优先级排序
当前执行的线程是:Thread-17,优先级:9
当前执行的线程是:Thread-1,优先级:1
当前执行的线程是:Thread-13,优先级:7
当前执行的线程是:Thread-11,优先级:6
当前执行的线程是:Thread-15,优先级:8
当前执行的线程是:Thread-7,优先级:4
当前执行的线程是:Thread-9,优先级:5
当前执行的线程是:Thread-3,优先级:2
当前执行的线程是:Thread-5,优先级:3
Java提供一个线程调度器来监视和控制处于RUNNABLE状态的线程。线程的调度策略采用抢占式,优先级高的线程比优先级低的线程会有更大的几率优先执行。在优先级相同的情况下,按照“先到先得”的原则。每个Java程序都有一个默认的主线程,就是通过JVM启动的第一个线程main线程。
还有一种线程称为守护线程(Daemon),守护线程默认的优先级比较低。
如果某线程是守护线程,那如果所有的非守护线程都结束了,这个守护线程也会自动结束。
应用场景是:当所有非守护线程结束时,结束其余的子线程(守护线程)自动关闭,就免去了还要继续关闭子线程的麻烦。
一个线程默认是非守护线程,可以通过Thread类的setDaemon(boolean on)来设置。
一个线程必然存在于一个线程组中,那么当线程和线程组的优先级不一致的时候将会怎样?
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("t1");
threadGroup.setMaxPriority(6);
Thread thread = new Thread(threadGroup,"thread");
thread.setPriority(9);
System.out.println("我是线程组的优先级"+threadGroup.getMaxPriority());
System.out.println("我是线程的优先级"+thread.getPriority());
}
我是线程组的优先级6
我是线程的优先级6
所以,如果某个线程优先级大于线程所在线程组的最大优先级,那么该线程的优先级将会失效,取而代之的是线程组的最大优先级。小于最大优先级就不会变。
线程组常用方法
//获取当前的线程组名字
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()
// 获取当前的线程组
ThreadGroup threadGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
// 复制一个线程组到一个线程数组(获取Thread信息)
Thread[] threads = new Thread[threadGroup.activeCount()];
threadGroup.enumerate(threads);
//线程组统一异常处理
package com.func.axc.threadgroup;
public class ThreadGroupDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup threadGroup1 = new ThreadGroup("group1") {
// 继承ThreadGroup并重新定义以下方法
// 在线程成员抛出unchecked exception
// 会执行此方法
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage());
}
};
// 这个线程是threadGroup1的一员
Thread thread1 = new Thread(threadGroup1, new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 抛出unchecked异常
throw new RuntimeException("测试异常");
}
});
thread1.start();
}
}
线程组数据结构
线程组还可以包含其他的线程组,不仅仅是线程。
首先看看 ThreadGroup源码中的成员变量
public class ThreadGroup implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
private final ThreadGroup parent; // 父亲ThreadGroup
String name; // ThreadGroupr 的名称
int maxPriority; // 线程最大优先级
boolean destroyed; // 是否被销毁
boolean daemon; // 是否守护线程
boolean vmAllowSuspension; // 是否可以中断
int nUnstartedThreads = 0; // 还未启动的线程
int nthreads; // ThreadGroup中线程数目
Thread threads[]; // ThreadGroup中的线程
int ngroups; // 线程组数目
ThreadGroup groups[]; // 线程组数组
}
然后看看构造函数:
// 私有构造函数
private ThreadGroup() {
this.name = "system";
this.maxPriority = Thread.MAX_PRIORITY;
this.parent = null;
}
// 默认是以当前ThreadGroup传入作为parent ThreadGroup,新线程组的父线程组是目前正在运行线程的线程组。
public ThreadGroup(String name) {
this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);
}
// 构造函数
public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);
}
// 私有构造函数,主要的构造函数
private ThreadGroup(Void unused, ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
this.name = name;
this.maxPriority = parent.maxPriority;
this.daemon = parent.daemon;
this.vmAllowSuspension = parent.vmAllowSuspension;
this.parent = parent;
parent.add(this);
}
第三个构造函数里调用了checkParentAccess方法,这里看看这个方法的源码:
// 检查parent ThreadGroup
private static Void checkParentAccess(ThreadGroup parent) {
parent.checkAccess();
return null;
}
// 判断当前运行的线程是否具有修改线程组的权限
public final void checkAccess() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkAccess(this);
}
}
这里涉及到
SecurityManager这个类,它是Java的安全管理器,它允许应用程序在执行一个可能不安全或敏感的操作前确定该操作是什么,以及是否是在允许执行该操作的安全上下文中执行它。应用程序可以允许或不允许该操作。比如引入了第三方类库,但是并不能保证它的安全性。
其实Thread类也有一个checkAccess()方法,不过是用来当前运行的线程是否有权限修改被调用的这个线程实例。(Determines if the currently running thread has permission to modify this thread.)
总结来说,线程组是一个树状的结构,每个线程组下面可以有多个线程或者线程组。线程组可以起到统一控制线程的优先级和检查线程的权限的作用。
边栏推荐
- Vscode multiline comments always expand automatically
- "Statistical learning methods (2nd Edition)" Li Hang Chapter 14 clustering method mind map notes and after-school exercise answers (detailed steps) K-means hierarchical clustering Chapter 14
- Could not load library cudnn_ cnn_ infer64_ 8.dll. Error code 126Please make sure cudnn_ cnn_ infer64_ eight
- [activiti] group task
- day1-jvm+leetcode
- Signals and systems: Hilbert transform
- Thymeleaf快速入门学习
- 【USB Host】STM32H7 CubeMX移植带FreeRTOS的USB Host读取U盘,USBH_Process_OS卡死问题,有个值为0xA5A5A5A5
- [activiti] personal task
- [deep learning] handwritten neural network model preservation
猜你喜欢

Typora installation package in November 2021, the last free version of the installation package to download v13.6.1

Machine learning (zhouzhihua) Chapter 2 model selection and evaluation notes learning experience

Typora 安装包2021年11月最后一次免费版本的安装包下载V13.6.1

Thymeleaf快速入门学习

JVM系统学习
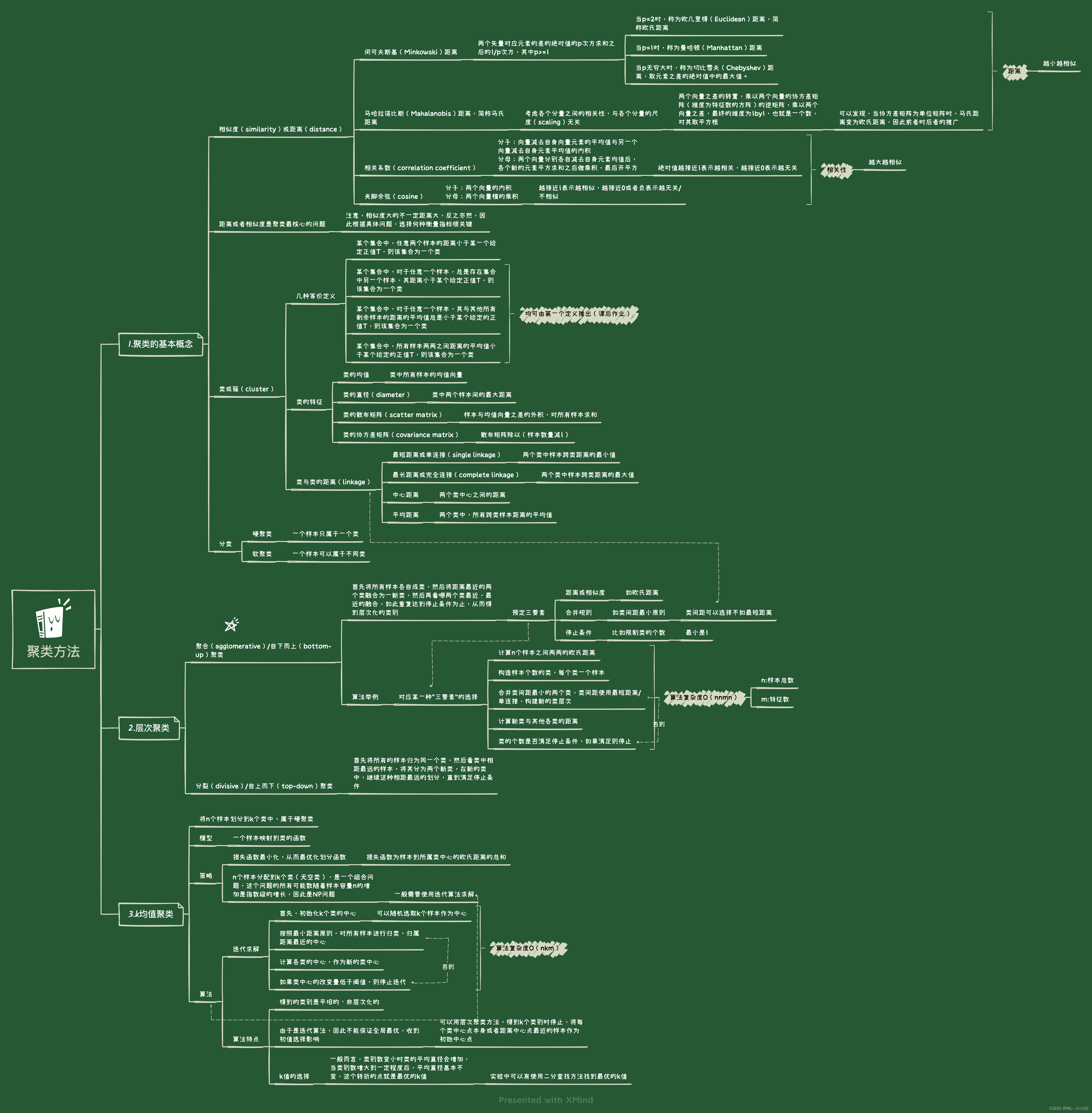
《统计学习方法(第2版)》李航 第14章 聚类方法 思维导图笔记 及 课后习题答案(步骤详细) k-均值 层次聚类 第十四章

day-7 jvm完结

【深度学习】手把手教你写“手写数字识别神经网络“,不使用任何框架,纯Numpy
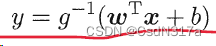
Chapter III summary of linear model

Delete the weight of the head part of the classification network pre training weight and modify the weight name
随机推荐
[activiti] activiti introduction
Chapter 5 neural network
删除分类网络预训练权重的的head部分的权重以及修改权重名称
Openwrt quick configuration Samba
STM32 DSP library MDK vc5\vc6 compilation error: 256, (const float64_t *) twiddlecoeff64_ 256, armBitRevIndexTableF64_ 256,
[activiti] activiti system table description
bat批处理脚本、同时运行多个文件、按照顺序执行的批处理命令及xshell脚本。
systemctl + journalctl
如何在网页上下载视频
Machine learning (zhouzhihua) Chapter 2 model selection and evaluation notes learning experience
测试数据增强后标签和数据集是否对应
传统的k-means实现
精确计算时间延迟VxWorks 时间戳 详解
MySql下载,及安装环境设置
PDF文本合并
IoTP2PGate 两台物联网设备点对点通信快速实现方案
Deepsort summary
day-7 jvm完结
第三章 线性模型总结
MySql与Qt连接、将数据输出到QT的窗口tableWidget详细过程。