当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to GUI programming to game practice (I)
Introduction to GUI programming to game practice (I)
2022-06-26 05:16:00 【Air transport Alliance】
GUI Introduction to programming to game practice ( One )
GUI It's the graphical user interface , It's a graphical interface ,windows Is a graphical user interface operating system , and DOS Is a command prompt based operating system ,GUI Programming is Program a graphical user interface software .
Components :
- window
- Popup
- panel
- The text box
- List box
- Button
- picture
- Monitoring events
- mouse
- Keyboard events
- Crack tools
1. brief introduction
GUI Two core programming techniques of :Swing AWT
- The interface is not beautiful
- need jre Environmental Science
therefore , It didn't catch on .
Why study ?
- You can write about the small public actions you want
- Maintenance may be required during operation swing Interface ( The probability is small )
- understand MVC framework , Learn about monitoring
AWT It's the ground floor ,Swing It's encapsulated
2.AWT
2.1AWT Introduce
1) Contains many classes and interfaces , be used for GUI( Graphical user interface ) Programming
2) Elements : window 、 Button 、 The text box
3)java.awt

2.2 Components and containers
1.Frame window
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
//GUI The first interface of
public class TestFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Frame JDK Look at the source code
Frame frame = new Frame(" My first one Java Image interface window ");
// You need to set visibility
frame.setVisible(true);
// Set window size
frame.setSize(400,400);
// Set the background color Color
//frame.setBackground(Color.black);// Direct use
frame.setBackground(new Color(85,150,68));// own new One , Set up RGB Value
// The initial position of the pop-up
frame.setLocation(200,200);// Screen coordinates (0,0) spot , In the upper left corner
// Set the size fixed
frame.setResizable(false);// Can't change
}
}
Operation result diagram :

Try to encapsulate :
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFrame2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Show multiple windows
// Make a package inheritance
MyFrame myFrame01 = new MyFrame(100, 100, 200, 200, Color.blue);
MyFrame myFrame02 = new MyFrame(300, 100, 200, 200, Color.yellow);
MyFrame myFrame03 = new MyFrame(100, 300, 200, 200, Color.pink);
MyFrame myFrame04 = new MyFrame(300, 300, 200, 200, Color.green);
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame {
static int id = 0;// There may be multiple windows , A counter is required to distinguish title
public MyFrame(int x, int y, int w, int h, Color color) {
super("MyFrame" + (++id));// Call the parent constructor
// You need to set visibility
setVisible(true);// Inherit , Just call the parent method directly
// Set window size
setSize(w, h);
// The initial position of the pop-up
setLocation(x, y);// Screen coordinates (0,0) spot , In the upper left corner
//setBounds(x,y,w,h);// Equivalent to the above two , Set the position and size directly
// Set the background color Color
setBackground(color);
// Set the size fixed
setResizable(false);// Can't change
}
}
Running results :

2.Panel panel
Frame A panel is added in the , After that, all components are added in the panel
meanwhile , Solved the problem of closing the window
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowListener;
// The panel can be seen as a space , But it can't exist alone
public class TestPanel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
// The concept of layout
Panel panel = new Panel();
// Setting up layout
frame.setLayout(null);
// coordinate 、 background
frame.setBounds(300, 300, 500, 500);
frame.setBackground(new Color(40, 161, 35));
//panel Set coordinates , be relative to frame—— Relative coordinates
panel.setBounds(50, 50, 400, 400);
panel.setBackground(new Color(157, 115, 24));
// Add panels to frame in
frame.add(panel);
// Set visibility
frame.setVisible(true);
// Monitoring events : Listen for window closing events
/* direct new One WindowListener, Many methods need to be rewritten ; Therefore, consider the adapter mode , Write only the methods you need */
// Adapter pattern , Just choose the method you want
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
// Click on what to do when the window closes
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
// End procedure
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
Running results :

2.3 Layout manager
- Fluid layout
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
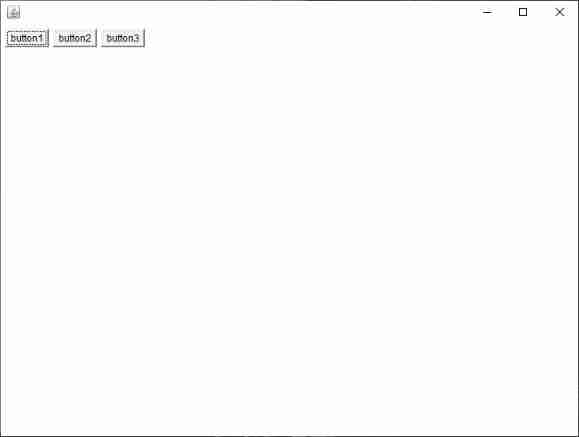
public class TestFlowLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
// Components -- Button
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
// Set to flow layout
//frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
frame.setSize(200, 200);
// Add the button
frame.add(button1);
frame.add(button2);
frame.add(button3);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
- Southeast northwest middle
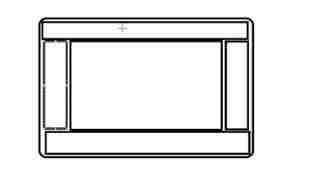
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestBorderLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button1 = new Button("East");
Button button2 = new Button("West");
Button button3 = new Button("South");
Button button4 = new Button("North");
Button button5 = new Button("Center");
frame.add(button1, BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(button2, BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(button3, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(button4, BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(button5, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(200, 200);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

- Table layout
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestGridLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button1 = new Button("1");
Button button2 = new Button("2");
Button button3 = new Button("3");
Button button4 = new Button("4");
Button button5 = new Button("5");
Button button6 = new Button("6");
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2));//3 That's ok 2 Column
frame.add(button1);
frame.add(button2);
frame.add(button3);
frame.add(button4);
frame.add(button5);
frame.add(button6);
frame.pack();//Java function , Auto fill
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

practice

1.frame
2.4 Panels
border
Left :button
in : panel
Right :button
package com.song.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// General layout Frame
Frame frame = new Frame();
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));//2 That's ok 1 Column , Separate the upper and lower structures
frame.setSize(400, 300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setBackground(Color.pink);
//4 Panels
Panel panel1 = new Panel(new BorderLayout());// Divide the above into East, West, north, South and middle , Isolate 2 The side button
Panel panel2 = new Panel(new GridLayout(2, 1));// In the middle is 2 That's ok 1 Column
Panel panel3 = new Panel(new BorderLayout());
Panel panel4 = new Panel(new GridLayout(2, 2));
// above
panel1.add(new Button("East-1"), BorderLayout.EAST);
panel1.add(new Button("West-1"), BorderLayout.WEST);
panel2.add(new Button("p2-btn-1"));
panel2.add(new Button("p2-btn-2"));
panel1.add(panel2, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// below
panel3.add(new Button("East-2"), BorderLayout.EAST);
panel3.add(new Button("West-2"), BorderLayout.WEST);
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
panel4.add(new Button("p4-btn-" + i));
}
panel3.add(panel4, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(panel1);
frame.add(panel3);
}
}

summary
1.Frame It's a top-level window
2.Panel You can't show it alone , Must be placed in a container (Frame) in
3. Layout manager
- Fluid layout
- Southeast northwest middle
- Table layout
4. size 、 location 、 The background color 、 visibility 、 monitor
2.4 Event monitoring
package com.song.lesson02;
import com.sun.javafx.logging.JFRInputEvent;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestActionEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Press the button , Trigger an event
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button = new Button("button");
// Because of the need addActionListener() Need one ActionListener, So construct a
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
button.addActionListener(myActionListener);
frame.add(button, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.pack();
windowClose(frame);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
// Event that closes the window
private static void windowClose(Frame frame) {
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("lalalala");
}
}
Multiple buttons , Share an event
package com.song.lesson02;
import org.omg.PortableInterceptor.ACTIVE;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class TestActionTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Two buttons Implement the same monitor
// Start stop it
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button1 = new Button("start");
Button button2 = new Button("stop");
button1.setActionCommand("button1-start");
//button2.setActionCommand("button2-stop");// Show default values when definitions are not displayed stop
MyAction myAction = new MyAction();
button1.addActionListener(myAction);
button2.addActionListener(myAction);
frame.add(button1, BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(button2, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.setSize(400, 400);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
class MyAction implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//getActionCommand() Get information about the button
System.out.println(" The button is clicked :msg " + e.getActionCommand());
}
}
2.5 Input box
package com.song.lesson02;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class TestText01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// normal main There is only one startup in the method
MyFrame myFrame = new MyFrame();
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame {
public MyFrame() {
TextField textField = new TextField();
add(textField);
// Listen to the text input in this text box
MyActionListener2 myActionListener2 = new MyActionListener2();
// Press down Enter, Will trigger an event in the input box
textField.addActionListener(myActionListener2);
// Set the code to replace the display
textField.setEchoChar('*');
setVisible(true);
setSize(400, 400);
pack();
}
}
class MyActionListener2 implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
TextField field = (TextField) e.getSource();// Get some resources , Return to an object
System.out.println(field.getText());
;// Get the text in the input box
field.setText("");// Press enter to clear
}
}
2.6 Clean Calculator Beta , Combine + Inner class
oop principle : Combine , Greater than inheritance ( Give priority to combinations )
Inherit :
class A extends B{
}
Combine :
class A{
public B b;}

Implementation method :( Process oriented )
package com.song.lesson02;import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;// Clean Calculator Beta public class TestCalculator { public static void main(String[] args) { Calculator myFrame2 = new Calculator(); }}// Calculator class class Calculator extends Frame { public Calculator() { //3 Textboxes 、1 Button 、1 A label TextField textField1 = new TextField(10);// Number of characters , That is, the size of the box TextField textField2 = new TextField(10); TextField textField3 = new TextField(20); Label label = new Label("+"); Button btn = new Button("="); btn.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener(textField1, textField2, textField3)); // Layout setLayout(new FlowLayout()); add(textField1); add(label); add(textField2); add(btn); add(textField3); setVisible(true); pack(); }}// Monitor class class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener { // Get three variables private TextField num1, num2, num3; public MyCalculatorListener(TextField num1, TextField num2, TextField num3) { this.num1 = num1; this.num2 = num2; this.num3 = num3; } @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { //1. Get the addend and the addend int n1 = Integer.parseInt(num1.getText()); int n2 = Integer.parseInt(num2.getText()); //2. Addition operation 、 Put it in the third box num3.setText("" + (n1 + n2)); // Clear the first two boxes num1.setText(""); num2.setText(""); }}

Method improvement 1:( Combine )
package com.song.lesson02;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
// Clean Calculator Beta
public class TestCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Calculator().loadFrame();
}
}
// Calculator class
class Calculator extends Frame {
// attribute
TextField num1, num2, num3;
// Method
public void loadFrame() {
//3 Textboxes 、1 Button 、1 A label
num1 = new TextField(10);// Number of characters , That is, the size of the box
num2 = new TextField(10);
num3 = new TextField(20);
Label label = new Label("+");
Button btn = new Button("=");
btn.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener(this));//this Is refers to Calculator own
// Layout
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(num1);
add(label);
add(num2);
add(btn);
add(num3);
setVisible(true);
pack();
}
}
// Monitor class
class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener {
// Get calculator object , Combine one class with another
Calculator cal = null;
public MyCalculatorListener(Calculator calculator) {
this.cal = calculator;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//1. Get the addend and the addend
//2. Addition operation 、 Put it in the third box
// Clear the first two boxes
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(cal.num1.getText());
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(cal.num2.getText());
cal.num3.setText("" + (n1 + n2));
cal.num1.setText("");
cal.num2.setText("");
}
}
Method improvement 2:( Completely object-oriented —— Inner class )
package com.song.lesson02;import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;// Clean Calculator Beta public class TestCalculator { public static void main(String[] args) { new Calculator().loadFrame(); }}// Calculator class class Calculator extends Frame { // attribute TextField num1, num2, num3; // Method public void loadFrame() { //3 Textboxes 、1 Button 、1 A label num1 = new TextField(10);// Number of characters , That is, the size of the box num2 = new TextField(10); num3 = new TextField(20); Label label = new Label("+"); Button btn = new Button("="); btn.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener());//this Is refers to Calculator own // Layout setLayout(new FlowLayout()); add(num1); add(label); add(num2); add(btn); add(num3); setVisible(true); pack(); } // Monitor class , Set to inner class // The biggest benefit of inner classes , You can have unimpeded access to methods of external classes private class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { //1. Get the addend and the addend //2. Addition operation 、 Put it in the third box // Clear the first two boxes int n1 = Integer.parseInt(num1.getText()); int n2 = Integer.parseInt(num2.getText()); num3.setText("" + (n1 + n2)); num1.setText(""); num2.setText(""); } }}
2.7 paint brush
package com.song.lesson03;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestPaint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyPaint().loadFrame();
}
}
class MyPaint extends Frame {
public void loadFrame() {
setBounds(200, 200, 800, 500);
setVisible(true);
}
// paint brush
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
//super.paint(g);
// The brush needs color
g.setColor(Color.pink);
// The brush needs to be able to draw
g.fillOval(100, 100, 100, 100);// Solid circle
g.setColor(Color.green);
g.fillRect(150, 200, 200, 200);
// When the brush is used up, you need to restore it to its original color
g.setColor(Color.black);
}
}

2.8 Mouse monitor
Purpose : Realize the mouse drawing ( Click on )
Ideas :

package com.song.lesson03;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TestMouseListener {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame(" drawing ");
}
}
// My own class
class MyFrame extends Frame {
// Painting needs a brush , Need to monitor the current mouse position , You need a collection to store this
//ArrayList Class is an array that can be dynamically modified , The difference from ordinary arrays is that there is no fixed size limit , We can add or remove elements .
ArrayList points;
public MyFrame(String title) {
super(title);
setBounds(200, 200, 400, 300);
// Store mouse clicks
points = new ArrayList<>();
setVisible(true);
// Mouse monitor , Facing this window
this.addMouseListener(new MyMouseListener());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
// Drawing a picture , Monitor mouse events
// Using Iterators , Draw all the dots in the set
Iterator iterator = points.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Point point = (Point) iterator.next();
g.setColor(Color.blue);
g.fillOval(point.x, point.y, 10, 10);
}
}
// Add a point to the interface , Draw up
public void addPaint(Point point) {
// Add points to the set of storage points
points.add(point);
}
// Monitor class
// Adapter pattern
private class MyMouseListener extends MouseAdapter {
// mouse : Press down 、 Spring up 、 Release
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
MyFrame frame = (MyFrame) e.getSource();
// When we click on this , It creates a point in the interface
// This point is the point of the mouse , Add to collection
frame.addPaint(new Point(e.getX(), e.getY()));
// Every time you click the mouse, you have to redraw the window , Otherwise, the canvas will not display
frame.repaint();// Refresh
}
}
}

2.9 Window listening
// Inner class methods
package com.song.lesson03;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class TestWindow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new WindowFrame();
}
}
class WindowFrame extends Frame {
public WindowFrame() {
setVisible(true);
setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
setBackground(Color.pink);
addWindowListener(new MyWindowListener());
}
// Inner class , convenient
class MyWindowListener extends WindowAdapter {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
//setVisible(false);// Just hide , Not normally closed ; Through button , Hide the current window
System.exit(0);// The normal exit
}
}
}
// Anonymous inner class package com.song.lesson03;import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;public class TestWindow { public static void main(String[] args) { new WindowFrame(); }}class WindowFrame extends Frame { public WindowFrame() { setVisible(true); setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300); setBackground(Color.pink); // Anonymous inner class , More recommended this.addWindowListener( new WindowAdapter() { // close window @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.out.println("Window closing"); System.exit(0); } // Activate window @Override public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) { Frame frame = (Frame) e.getSource(); frame.setTitle(" Is activated "); System.out.println("Window activated"); } } ); }}
2.10 Keyboard monitor
package com.song.lesson03;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
public class TestKeyListener {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new KeyFrame();
}
}
class KeyFrame extends Frame{
KeyFrame(){
setBounds(100,100,400,400);
setVisible(true);
this.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
// Which key is pressed on the keyboard , The code of the current keyboard l
int keyCode=e.getKeyCode();// There is no need to record the value , Use static attributes directly VK_XXX
System.out.println(keyCode);
if(keyCode==KeyEvent.VK_UP){
System.out.println(" You press the up button ");
}
// According to the different operations pressed , Can produce different results
}
});
}
}
3.Swing
Use Swing To get a container Container, And put things on it ;AWT Unwanted , direct add
Container container=this.getContentPane();
Consider using constructors or initialization functions to define .
3.1 window JFrame
package com.song.lesson04;
import sun.java2d.loops.Blit;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JFrameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a window
new MyFrame().init();
}
}
class MyFrame extends JFrame{
//init(); initialization
public void init(){
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100,100,300,300);
//label It's actually on the container , Let the container initialize explicitly
// Get a container
Container container=this.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.blue);
// Set text
JLabel jLabel = new JLabel(" welcome !");
container.add(jLabel);
jLabel.setBackground(Color.PINK);
// Closing event
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
3.2 Popup JDialog
JDialog, There is a shutdown event by default , There is no need to write
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
// main window
public class DialogDemo extends JFrame {
DialogDemo() {
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 700, 500);
//this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);// Set default off
//JFrame Put things , Containers
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// Absolute layout
container.setLayout(null);
// Button
JButton jButton = new JButton(" Click to pop up a dialog box ");// establish
jButton.setBounds(30, 30, 200, 59);
// A pop-up window pops up when you click the button
jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// Popup
new MyDialog();
}
});
container.add(jButton);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DialogDemo();
}
}
// Pop up window
class MyDialog extends JDialog {
public MyDialog() {
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(300, 300, 500, 500);
Container container = new Container();
container.setLayout(null);
container.add(new JLabel(" learn Java"));
//this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
3.3 label JLable
new JLable(" label ");
1. Put an icon on the label (Icon Interface )
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class IconDemo extends JFrame implements Icon {
private int width;
private int height;
// No arguments structure
public IconDemo() {
}
// There are parametric structures
public IconDemo(int width, int height) {
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
public void init() {
IconDemo iconDemo = new IconDemo(15, 15);
// Icons can be placed on labels , It can also be placed on the button
JLabel label = new JLabel("icontest", iconDemo, SwingConstants.CENTER);
Container container = getContentPane();// Be careful !!
container.add(label);//lable To be added to the container
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 400, 400);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new IconDemo().init();
}
@Override
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
g.fillOval(x, y, width, height);
}
@Override
public int getIconWidth() {
return this.width;
}
@Override
public int getIconHeight() {
return this.height;
}
}
2. Put a picture on the label (ImageIcon class )
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.URL;
public class ImageIconDemo extends JFrame {
public ImageIconDemo() {
// Get image address
JLabel label = new JLabel("ImageIcon");
// Get current IamgeIconDemo Peer resources of this class , Return an address URL. Try not to write dead !!!
URL url = ImageIconDemo.class.getResource("test.jpg");
ImageIcon imageIcon = new ImageIcon(url);// Note that ImageIcon class , Do not name conflicts
label.setIcon(imageIcon);// Set picture labels
label.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);// picture centering
Container container = getContentPane();
container.add(label);
setVisible(true);
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 500);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ImageIconDemo();
}
}
3.4 panel JPanle
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JPanelDemo extends JFrame {
public JPanelDemo(){
Container container=getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1,10,10));// Later parameters 10 It's spacing m
JPanel panle=new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
panle.add(new Button("button 1"));
panle.add(new Button("button 2"));
panle.add(new Button("button 3"));
JPanel panle2=new JPanel(new GridLayout(2,2));
panle2.add(new Button("button 1"));
panle2.add(new Button("button 2"));
panle2.add(new Button("button 3"));
panle2.add(new Button("button 4"));
JPanel panle3=new JPanel(new GridLayout(2,1));
panle3.add(new Button("button 1"));
panle3.add(new Button("button 2"));
container.add(panle);
container.add(panle2);
container.add(panle3);
setVisible(true);
setSize(300,300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JPanelDemo();
}
}
Scroll bar
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JScollDemo extends JFrame {
// The scroll bar normally does not , Only when the size is exceeded
public JScollDemo() {
Container container = getContentPane();
// Text domain
JTextArea jTextArea = new JTextArea(20, 50);
jTextArea.setText("Welcome!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
//Scroll panel
JScrollPane jScrollPane = new JScrollPane(jTextArea);
container.add(jScrollPane);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 400, 400);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JScollDemo();
}
}
3.5 Button JButton
Picture button
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.URL;
public class JButtonDemo01 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo01() {
Container container = getContentPane();
// Turn a picture into an icon
URL resource = JButtonDemo01.class.getResource("test.jpg");
Icon icon = new ImageIcon(resource);// Turn the picture into an icon
// Put the icon on the button
JButton jButton = new JButton("button");
jButton.setIcon(icon);
jButton.setToolTipText(" Picture button ");
//add
container.add(jButton);
setVisible(true);
setBounds(100,100,300,300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo01();
}
}
- Radio buttons
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JButtonDemo02 extends JFrame{
public JButtonDemo02(){
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// Radio buttons
JRadioButton jRadioButton1 = new JRadioButton("button01");
JRadioButton jRadioButton2 = new JRadioButton("button02");
JRadioButton jRadioButton3 = new JRadioButton("button03");
// Because only one radio box can be selected , Generally, they are grouped , Only one member of a group can be selected
ButtonGroup group = new ButtonGroup();
group.add(jRadioButton1);
group.add(jRadioButton2);
group.add(jRadioButton3);
//add
container.add(jRadioButton1,BorderLayout.CENTER);
container.add(jRadioButton2,BorderLayout.NORTH);
container.add(jRadioButton3,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo02();
}
}
- Check box
package com.song.lesson04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JButtonDemo03 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo03() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// Checkbox
JCheckBox box01 = new JCheckBox("JCheckBox01");
JCheckBox box02 = new JCheckBox("JCheckBox02");
JCheckBox box03 = new JCheckBox("JCheckBox03");
//add
container.add(box01, BorderLayout.CENTER);
container.add(box02, BorderLayout.NORTH);
container.add(box03, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo03();
}
}
3.6 list
- A drop-down box
package com.song.lesson05;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ComboboxDemo01 extends JFrame {
public ComboboxDemo01() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
JComboBox status = new JComboBox();
status.addItem(null);
status.addItem(" Is hit ");
status.addItem(" It's off the shelf ");
status.addItem(" To be shown soon ");
//status.addActionListener(); Get the selected content
container.add(status);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ComboboxDemo01();
}
}
- List box
package com.song.lesson05;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
public class ComboboxDemo02 extends JFrame {
public ComboboxDemo02() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// Generate the contents of the list , You can use arrays , Static , Cannot add dynamically
String[] contents = {
"1", "2", "3"};
// What needs to be put in the list
JList jList = new JList(contents);
// Generate the contents of the list , You can use data structures , Dynamic addition
Vector contents2 = new Vector();
// What needs to be put in the list
JList jList2 = new JList(contents2);
contents2.add("1111");
contents2.add("222");
contents2.add("33");
contents2.add("4");
//container.add(jList);
container.add(jList2);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ComboboxDemo02();
}
}
Application scenarios :
- A drop-down box —— Select a region or some individual options
- List box —— Used to show some information , General dynamic expansion
3.7 The text box
- The text box
package com.song.lesson05;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Vector;
public class TestTextDemo01 extends JFrame {
public TestTextDemo01() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
JTextField jTextField = new JTextField("Hello");
JTextField jTextField2 = new JTextField("world", 20);
container.add(jTextField, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
container.add(jTextField2, BorderLayout.NORTH);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestTextDemo01();
}
}
- Password box
package com.song.lesson05;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Vector;
public class TestTextDemo02 extends JFrame {
public TestTextDemo02() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
// For the convenience of layout , Try to be in the panel
JPasswordField jPasswordField = new JPasswordField();//***
jPasswordField.setEchoChar('*');
container.add(jPasswordField);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 300);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestTextDemo02();
}
}
- Text domain
The biggest difference between a text field and a text box is that the text field allows users to enter multiple lines of text information .
The text field is mainly used with the panel , Refer to the scroll bar settings .
4. actual combat —— Greedy Snake games
- frame : If the time slice is small enough , It's animation. , One second 30 frame 60 frame , Together, it's animation ; When disassembled, it is a static picture
- Keyboard monitor
- Timer Timer
边栏推荐
- 关于支付接口回调地址参数字段是“notify_url”,签名过后的特殊字符url编码以后再解码后出现错误(¬ , ¢, ¤, £)
- 6.1 - 6.2 公钥密码学简介
- Mongodb image configuration method
- 程序人生
- [unity3d] collider assembly
- Beidou navigation technology and industrial application of "chasing dreams in space and feeling for Beidou"
- Collections and dictionaries
- 红队得分方法统计
- Install the tp6.0 framework under windows, picture and text. Thinkphp6.0 installation tutorial
- Practical cases | getting started and mastering tkinter+pyinstaller
猜你喜欢

瀚高数据库自定义操作符‘!~~‘

How to ensure the efficiency and real-time of pushing large-scale group messages in mobile IM?

递归遍历目录结构和树状展现

Classic theory: detailed explanation of three handshakes and four waves of TCP protocol

6.1 - 6.2 公鑰密碼學簡介

86. (cesium chapter) cesium overlay surface receiving shadow effect (gltf model)

Tp5.0框架 PDO连接mysql 报错:Too many connections 解决方法

5. < tag stack and general problems > supplement: lt.946 Verify the stack sequence (the same as the push in and pop-up sequence of offer 31. stack)

Learn from small samples and run to the sea of stars

【Unity3D】碰撞体组件Collider
随机推荐
Lstms in tensorflow_ Cell actual combat
Install the tp6.0 framework under windows, picture and text. Thinkphp6.0 installation tutorial
Replacing domestic image sources in openwrt for soft routing (take Alibaba cloud as an example)
apktool 工具使用文档
LeetCode 19. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list
cartographer_optimization_problem_2d
86. (cesium chapter) cesium overlay surface receiving shadow effect (gltf model)
cartographer_backend_constraint
ThreadPoolExecutor实现文件上传批量插入数据
C# 40. byte[]与16进制string互转
Tensorflow visualization tensorboard "no graph definition files were found." error
Computer Vision Tools Chain
Happy New Year!
Official image acceleration
Use to_ Numeric to numeric type
Codeforces Round #802 (Div. 2)(A-D)
cartographer_ pose_ graph_ 2d
PHP one sentence Trojan horse
Fedora alicloud source
app 应用安装到手机,不显示图标,引发的思考