当前位置:网站首页>Bug STL string
Bug STL string
2022-06-26 13:49:00 【Hua Weiyun】
STL
What is? STL
STL(standard template libaray- Standard template library ):== yes C++ An important part of the standard library ==, Not just a reusable component library , and == It is a software framework including data structure and algorithm ==
STL edition
The original version
Alexander Stepanov、Meng Lee The original version completed in HP Labs , In the spirit of open source , They declared that anyone was allowed to use 、 Copy 、 modify 、 spread 、 Business uses these codes , There is no need to pay . The only condition is that it needs to be used as open source as the original version . HP edition – all STL The ancestor of the implementation version
P. J. edition
from P. J. Plauger Development , Inherited from HP edition , By Windows Visual C++ use , Cannot disclose or modify , defects : Low readability , The symbol naming is weird
RW edition
from Rouge Wage Companies to develop , Inherited from HP edition , By C+ + Builder use , Cannot disclose or modify , The readability is average .
SGI edition
from Silicon Graphics Computer Systems,Inc Companies to develop , Inherited from HP edition Ben . By GCC(Linux) use , Good portability , It can be made public 、 Modify or even sell , From naming style and programming In style , Reading is very high .== We learn from the back STL To read part of the source code , The main reference is this version .==
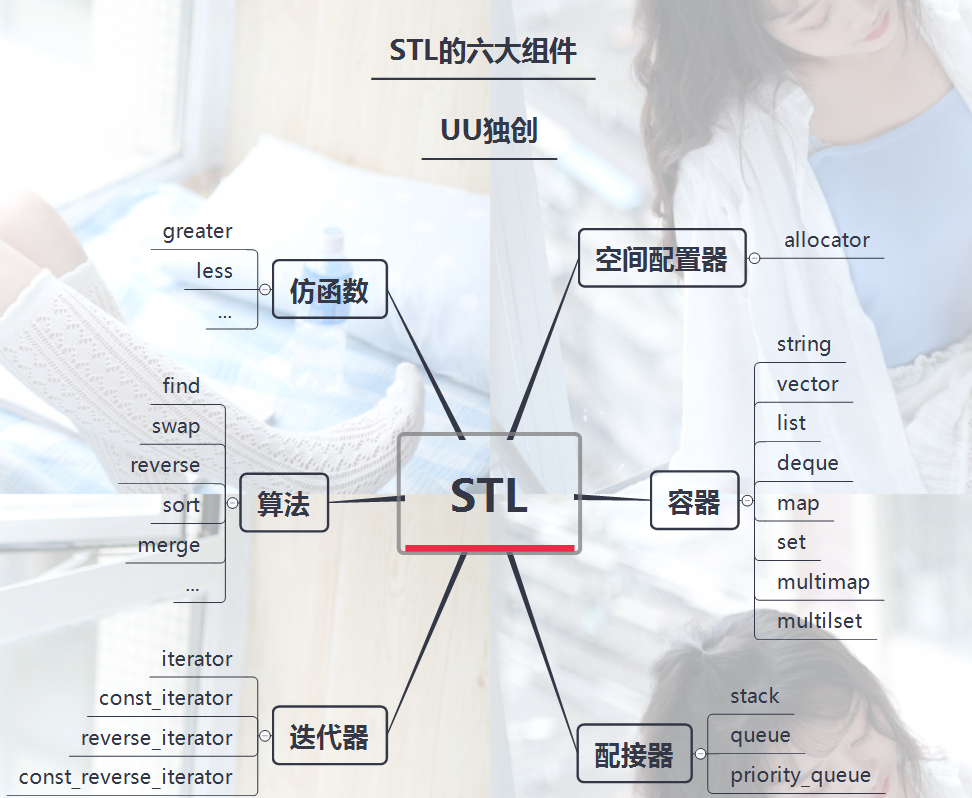
STL Six components of
How to learn STL
Just to summarize :
== Study STL The three realms of :==
- It works ,
- sensible ,
- Can expand .
== Before you enter the company, you should be familiar with the first two levels of cultivation , The third layer is cultivated in the company ==
STL The defects of
- STL The update of the library is too slow . Make complaints about this. , The last edition was reliable C++98, In the middle of the C++03 Some basic revisions .C++11 Out
It's been a long time 13 year ,STL To further update .- STL Thread safety is not supported now . In the concurrent environment, we need to lock ourselves . And the granularity of the lock is relatively large .
- STL Extreme pursuit of efficiency , It leads to internal complexity . Such as type extraction , Iterator extraction .
- STL The use of will have the problem of code inflation , For example, use vector/vector/vector This will generate multiple copies of code , Of course, this is the template language
Law itself .
The first container we will learn next is string
Why study string class ?
C Strings in languages
C In language , String is based on ’\0’ A collection of characters at the end , For ease of operation ,C The standard library provides some str Series of library functions , But these library functions are separate from strings , Not quite in line with OOP Thought , And the underlying space needs to be managed by users , If you don't pay attention, you may cross the border to visit
In the standard library string class
string class ( understand )
- A string is a class that represents a sequence of characters
- The standard string class provides support for such objects , Its interface is similar to that of a standard character container , However, a design feature has been added specifically for manipulating single byte character strings .
- string Class is to use char( As its character type , Use its default char_traits And distributor type ( More information about templates , see also basic_string).
- string Class is basic_string An instance of the template class , It USES char To instantiate basic_string Template class , And use char_traits and allocator As basic_string Default parameters ( For more template information, please refer to basic_string).
- Be careful , This class handles bytes independently of the encoding used : If used to handle multi byte or variable length characters ( Such as UTF-8) Sequence , All members of this class ( Such as length or size ) And its iterators , Will still be in bytes ( Not actually encoded characters ) To operate .
== summary :==
- string Is a string class that represents a string
- The interface of this class is basically the same as that of a regular container , And added some special operations for string General operation of .
- string At the bottom, it's actually :basic_string Alias of template class ,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>string;
- Cannot manipulate sequences of multibyte or variable length characters .
In the use of string Class time , Must contain #include Header files and using namespace std;
string Class ( Note that I will only explain the most commonly used interfaces below )
1.string Common constructions of class objects
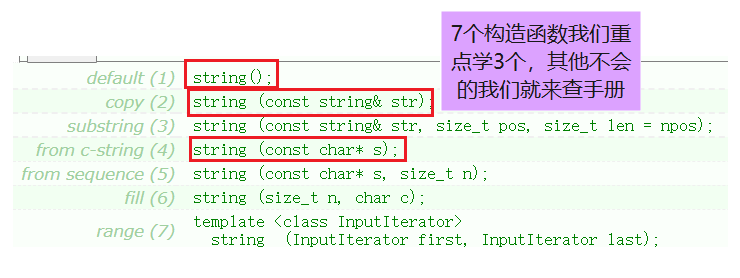
(constructor) The name of the function Functional specifications string() ( a key ) Construct empty string Class object , Empty string string(const char* s) ( a key ) use C-string To construct the string Class object string(size_t n, char c) string Class objects contain n Characters c string(const string&s) ( a key ) copy constructor
== learn STL, Focus on the most commonly used 30% Left and right interface functions , Others are rarely used , If one day we need to use , Just look at the documentation ==
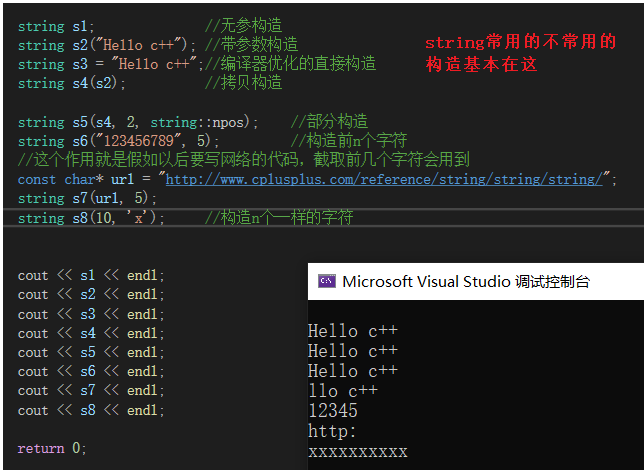
int main(){ string s1; // No arguments structure string s2("Hello c++"); // Structure with parameters string s3 = "Hello c++";// Direct construction of compiler optimization string s4(s2); // Copy structure string s5(s4, 2, string::npos); // Part of the structure string s6("123456789", 5); // Pre tectonic n Characters // This function is if you want to write network code in the future , Intercepting the first few characters will use const char* url = "http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/"; string s7(url, 5); string s8(10, 'x'); // structure n The same characters cout << s1 << endl; cout << s2 << endl; cout << s3 << endl; cout << s4 << endl; cout << s5 << endl; cout << s6 << endl; cout << s7 << endl; cout << s8 << endl; return 0;}
2.string Class object capacity operation
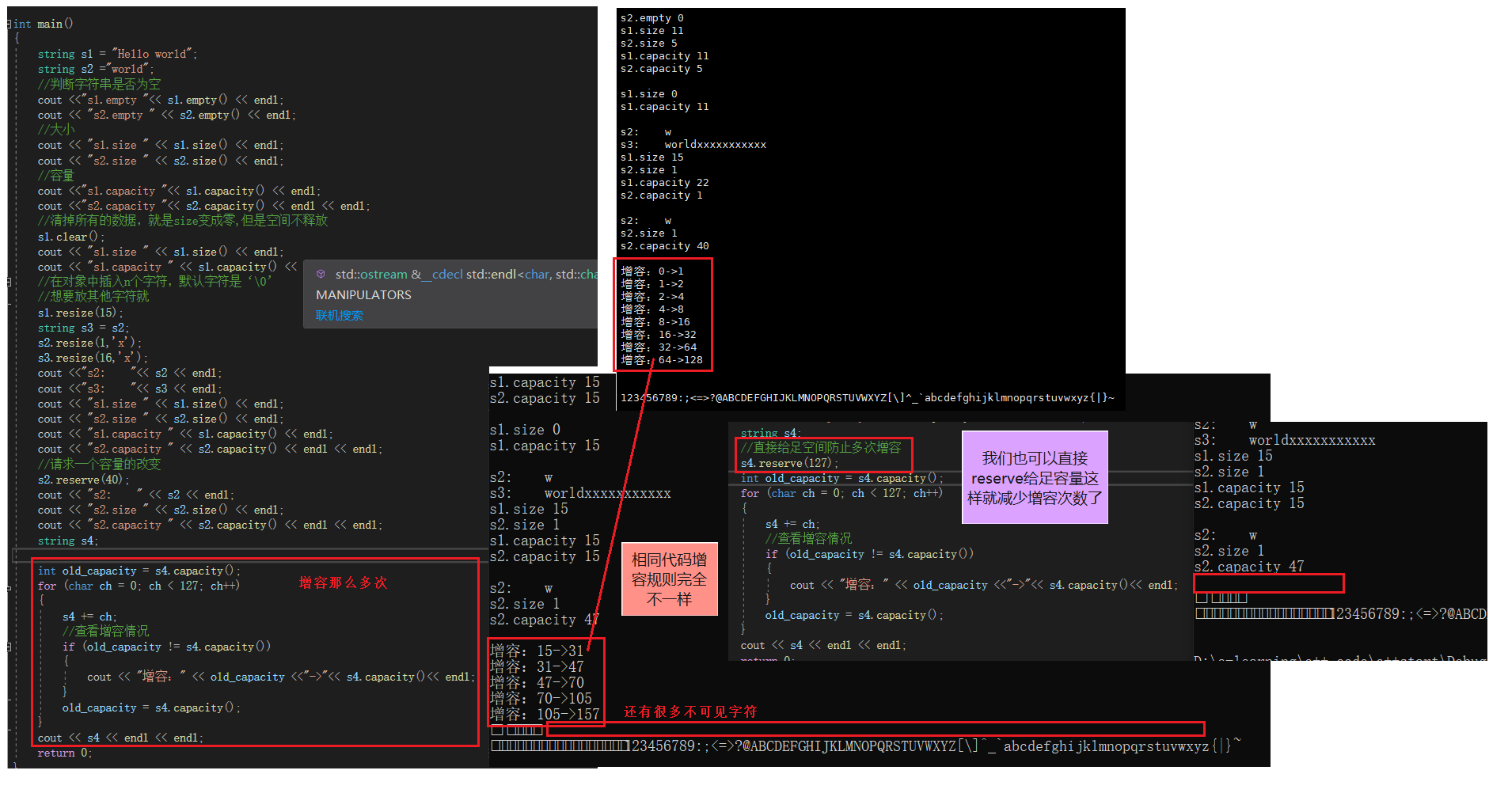
The name of the function Functional specifications size( a key ) Returns the valid character length of a string length Returns the valid character length of a string capacity Return the total size of the space empty ( a key ) Detection string released as empty string , Is to return true, Otherwise return to false clear ( a key ) Empty valid characters reserve ( a key ) Reserve space for Strings resize ( a key ) The number of valid characters should be n individual , Extra space with characters c fill == actually length stay string Is the array length , and size equally , Then why two of them are the same , Because in history string Come out more than stl Good morning! ,string Documents on the official website are not classified into containers ( But he is the container ), Instead, it is placed in the header file ,size It's common law ,length Is only used with string Of ==
Be careful :
- size() And length() The underlying implementation principle of the method is exactly the same , introduce size() The reason for this is to be consistent with the interfaces of other containers , In general, it's basically used size().
- clear() Just to string Empty the valid characters in the , Don't change the size of the underlying space .
- resize(size_t n) And resize(size_t n, char c) All are to change the number of valid characters in the string to n individual , The difference is that when the number of characters increases :resize(n) use 0 To fill in the extra element space ,resize(size_t n, char c) Use characters c To fill in the extra element space . Be careful :resize When you change the number of elements , If you increase the number of elements , It may change the size of the underlying capacity , If it is to reduce the number of elements , The total size of the underlying space remains unchanged .
- reserve(size_t res_arg=0): by string Reserve space , Do not change the number of effective elements , When reserve The parameter of is less than string The total size of the ground floor is ,reserver It doesn't change the size of the capacity .
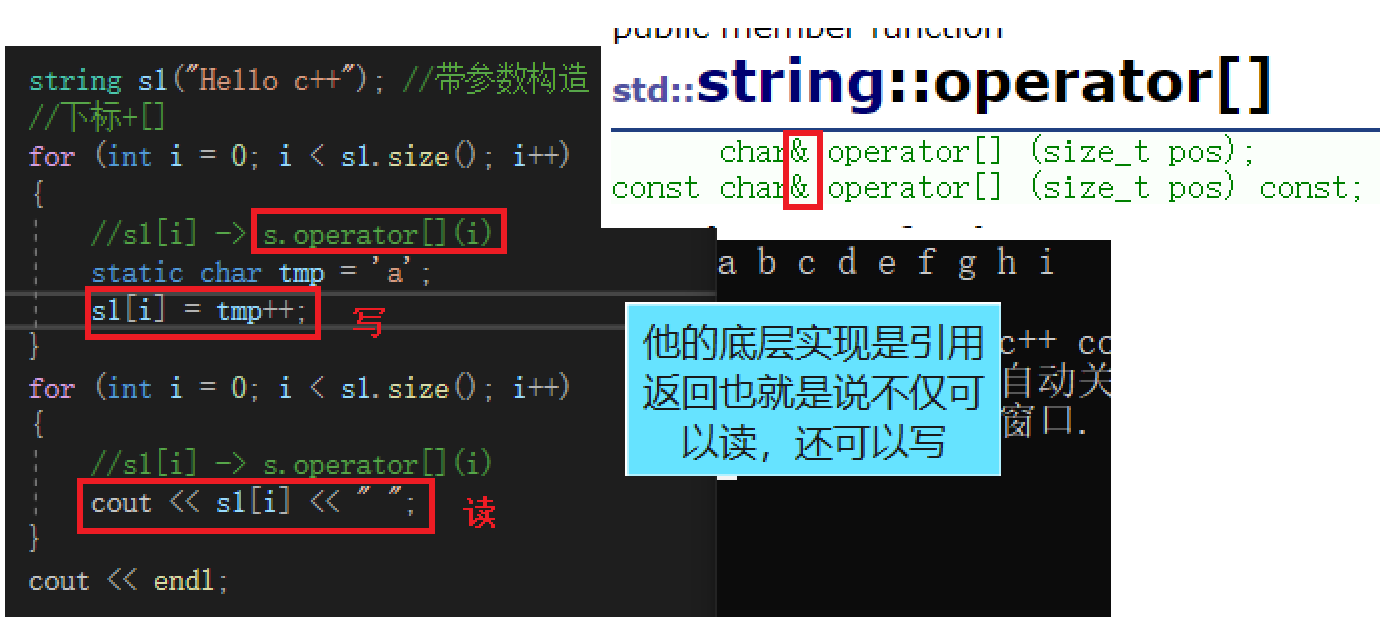
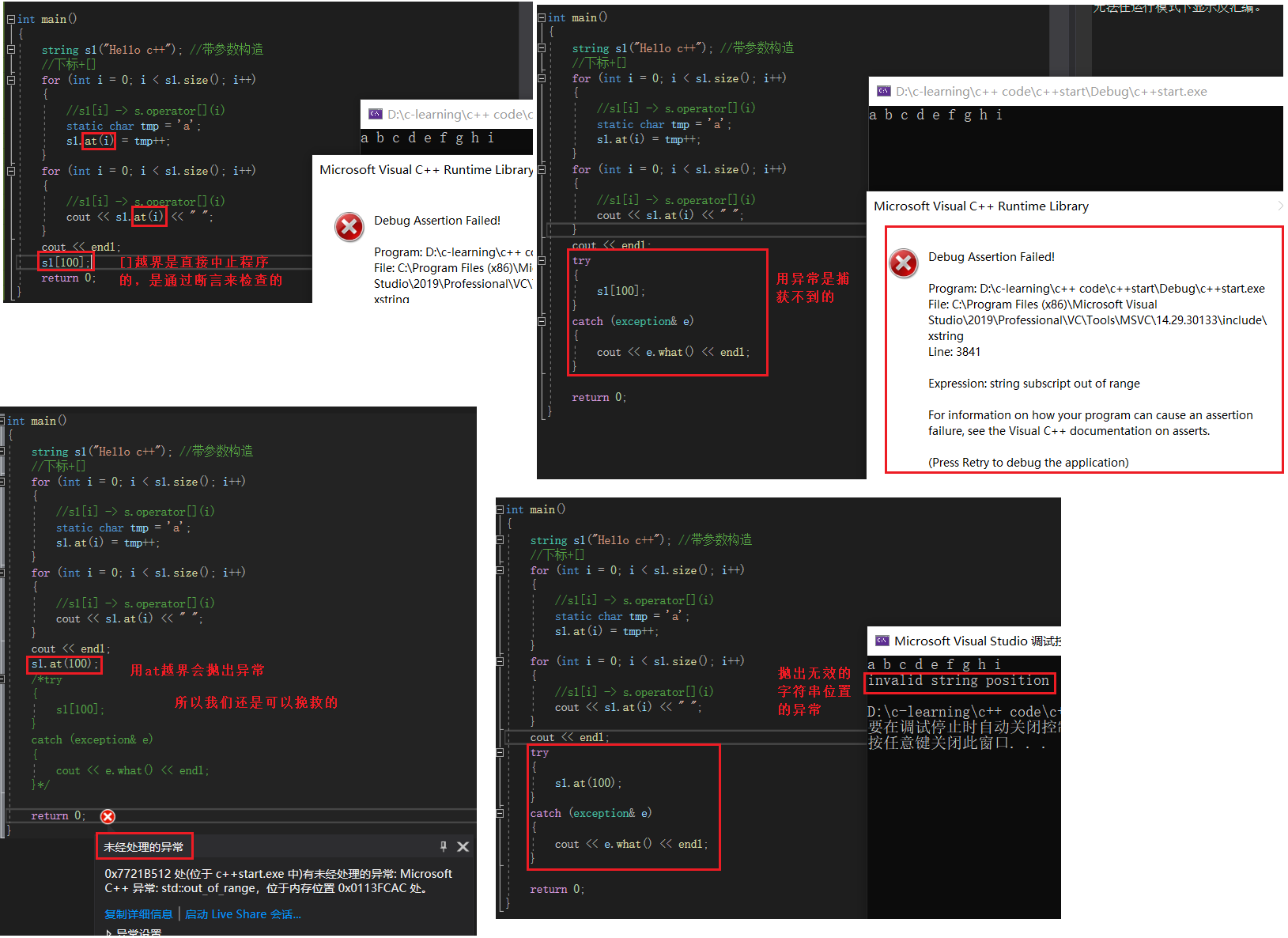
== Here's a word at Function and [] It's the same , It can be considered that the early grammar may not support [] That's why at This interface replaces , The following supports ,at It's basically unnecessary , They are not exactly the same , It's different when they cross the border ==
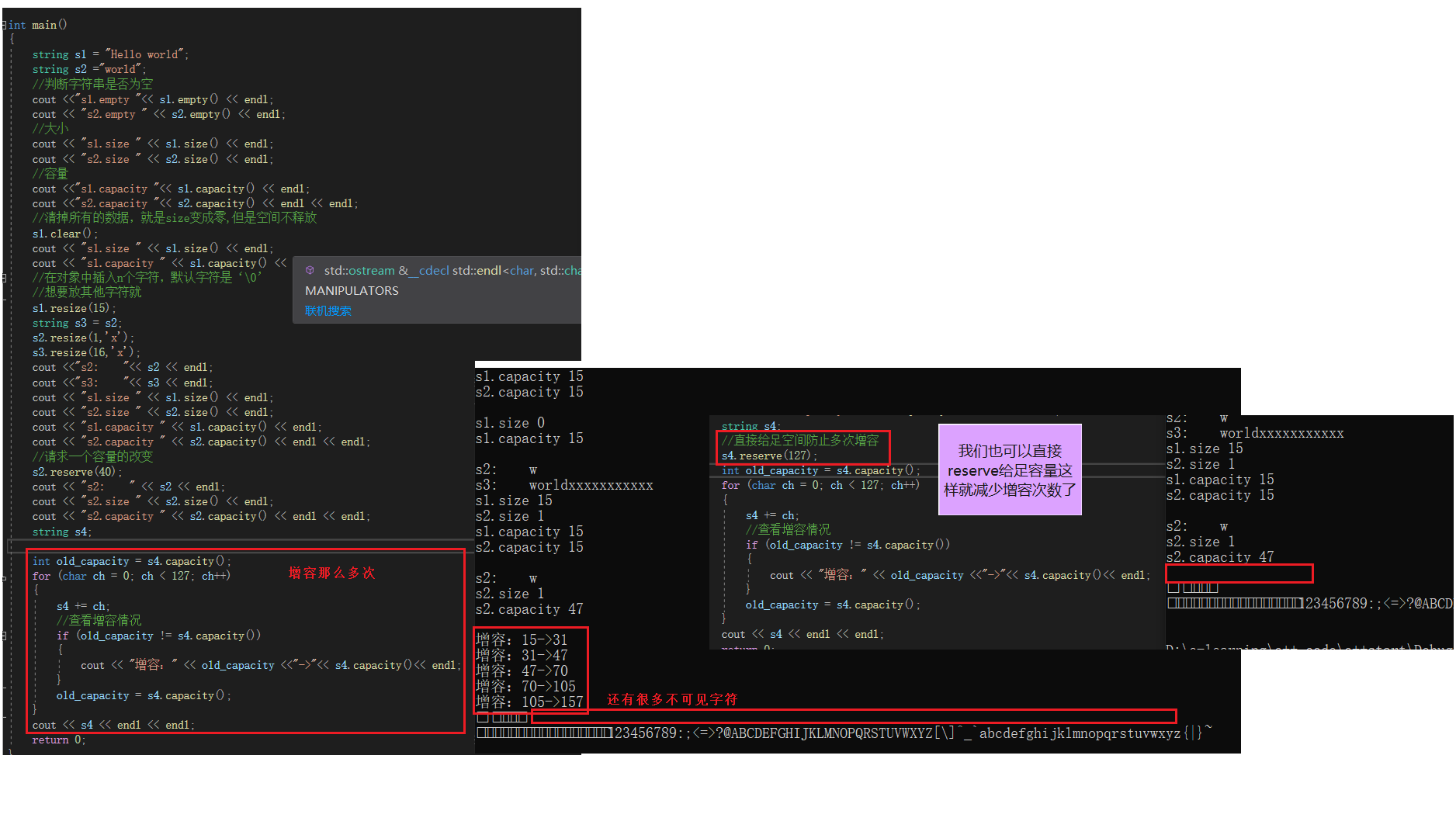
==reserve Enough space can prevent multiple capacity additions , that resize Is that OK ==
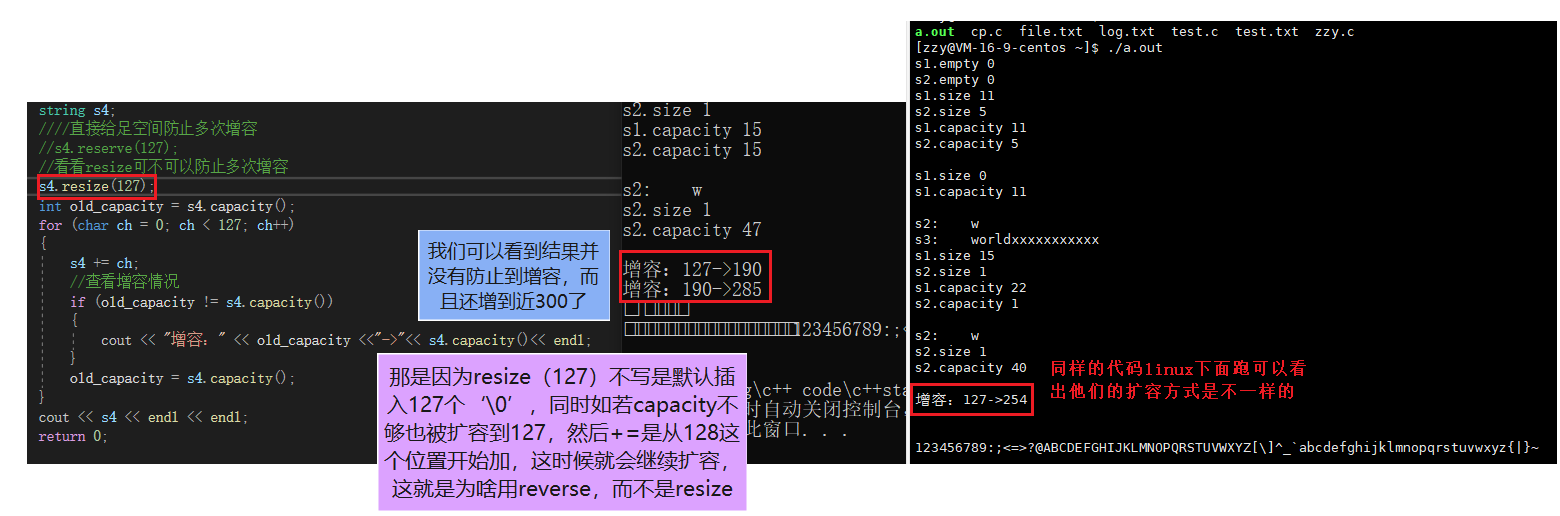
== We can also see the results of the same code running on different platforms ==
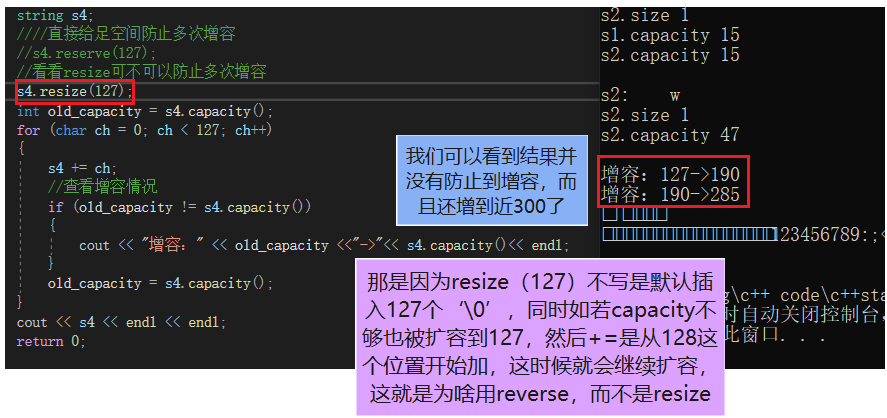
int main(){ string s1 = "Hello world"; string s2 ="world"; // Determines if the string is empty cout <<"s1.empty "<< s1.empty() << endl; cout << "s2.empty " << s2.empty() << endl; // size cout << "s1.size " << s1.size() << endl; cout << "s2.size " << s2.size() << endl; // Capacity cout <<"s1.capacity "<< s1.capacity() << endl; cout <<"s2.capacity "<< s2.capacity() << endl << endl; // Clear all the data , Namely size Become zero , But space doesn't release s1.clear(); cout << "s1.size " << s1.size() << endl; cout << "s1.capacity " << s1.capacity() << endl << endl; // Insert... Into the object n Characters , The default character is ‘\0’ // If you want to put other characters s1.resize(15); string s3 = s2; s2.resize(1,'x'); s3.resize(16,'x'); cout <<"s2: "<< s2 << endl; cout <<"s3: "<< s3 << endl; cout << "s1.size " << s1.size() << endl; cout << "s2.size " << s2.size() << endl; cout << "s1.capacity " << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << "s2.capacity " << s2.capacity() << endl << endl; // Request a change in capacity s2.reserve(40); cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; cout << "s2.size " << s2.size() << endl; cout << "s2.capacity " << s2.capacity() << endl << endl; string s4; //// Give enough space directly to prevent multiple capacity increases //s4.reserve(127); // have a look resize Can you prevent multiple capacity increases s4.resize(127); int old_capacity = s4.capacity(); for (char ch = 0; ch < 127; ch++) { s4 += ch; // Check the capacity increase if (old_capacity != s4.capacity()) { cout << " increase capacity :" << old_capacity <<"->"<< s4.capacity()<< endl; } old_capacity = s4.capacity(); } cout << s4 << endl << endl; return 0;}
3.string Class object access and traversal operation
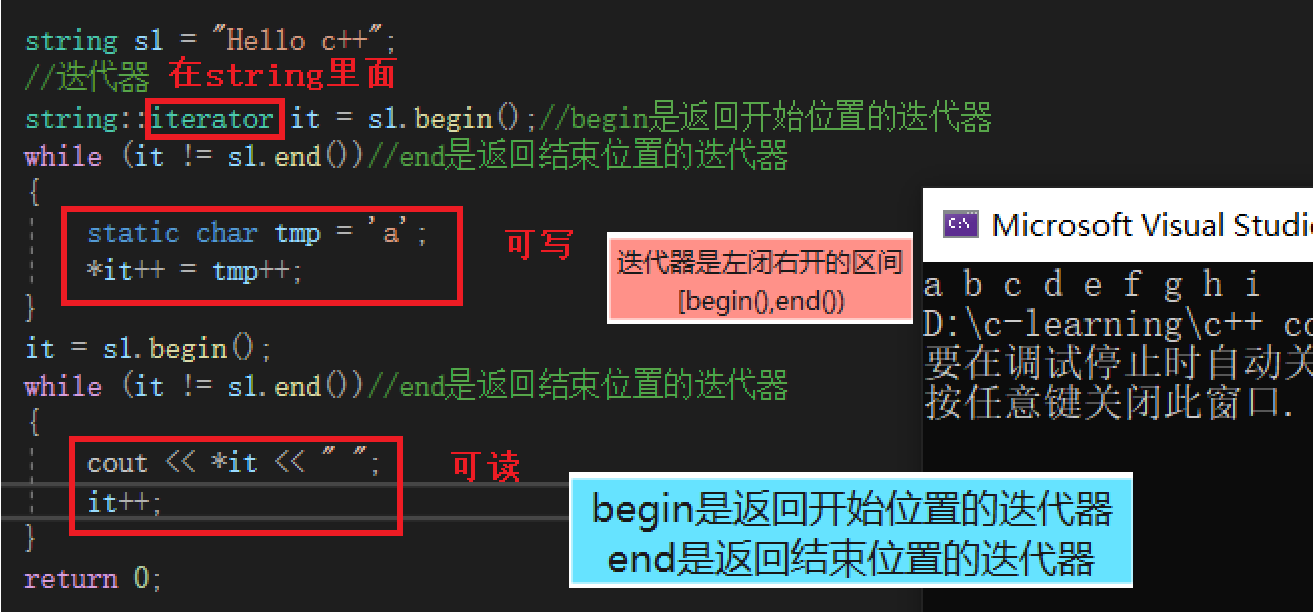
The name of the function Functional specifications operator[] ( a key ) return pos The character of position ,const string Class object call begin+ end begin Get an iterator of a character + end Gets the iterator at the next position of the last character rbegin + rend begin Get an iterator of a character + end Gets the iterator at the next position of the last character Range for C++11 Support more concise scope for New traversal method == iterator ==
== Iterator meaning : image string,vector Support [] Traverse , however list,map Wait, the container does not support [], We're going to iterate through , So iterators are a uniform way to use them ==
int main(){ string s1 = "Hello c++"; // iterator string::iterator it = s1.begin();//begin Is an iterator that returns the start position while (it != s1.end())//end Is an iterator that returns the end position { static char tmp = 'a'; *it++ = tmp++; } it = s1.begin(); while (it != s1.end())//end Is an iterator that returns the end position { cout << *it << " "; it++; } return 0;}== reverse iterator ==
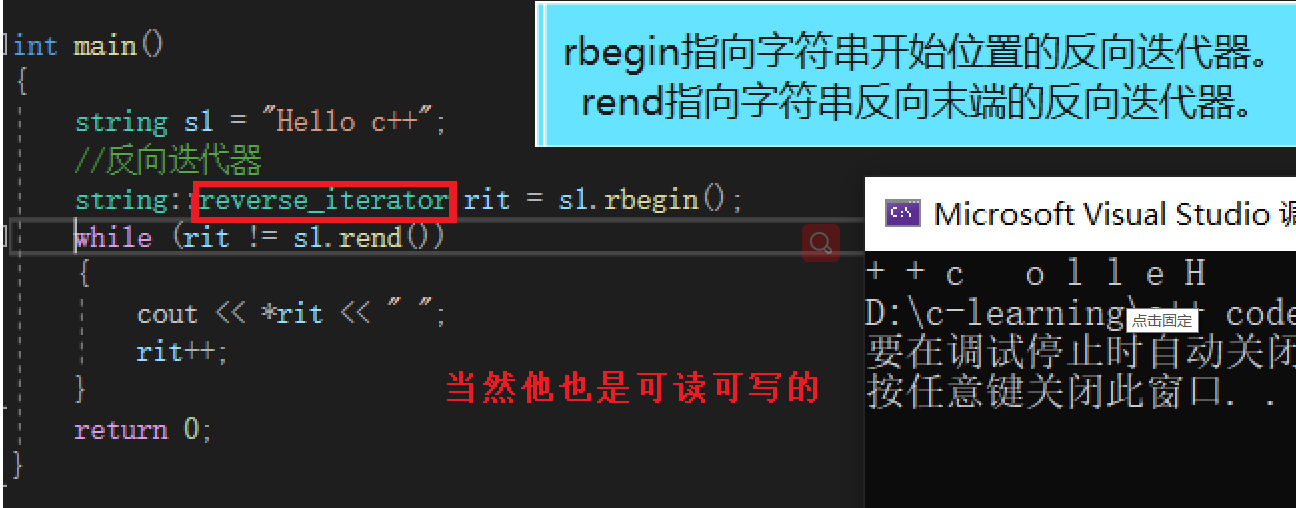
int main(){ string s1 = "Hello c++"; // reverse iterator string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); while (rit != s1.rend()) { cout << *rit << " "; rit++; } return 0;}
边栏推荐
- Mediapipe gestures (hands)
- 8.Ribbon负载均衡服务调用
- Range of types
- Thinking caused by the error < note: candidate expectations 1 argument, 0 provided >
- GO语言-管道channel
- Mongodb series window environment deployment configuration
- I have a good word to say, and I admire myself
- LeetCode_ Stack_ Medium_ 150. evaluation of inverse Polish expression
- ES基於Snapshot(快照)的數據備份和還原
- 防火墙介绍
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Es sauvegarde et restauration des données par instantané
33. Use rgbd camera for target detection and depth information output
嵌入式virlog代码运行流程
Thinking caused by the error < note: candidate expectations 1 argument, 0 provided >
Cloudcompare - Poisson reconstruction
网络远程访问的方式使用树莓派
免费的机器学习数据集网站(6300+数据集)
D中不用GC
Nlp-d60-nlp competition D29
es常用语法一
Logical operation
Traverse the specified directory to obtain the file name with the specified suffix (such as txt and INI) under the current directory
Wechat applet -picker component is repackaged and the disabled attribute is added -- above
LeetCode_ Stack_ Medium_ 150. evaluation of inverse Polish expression
Es common grammar I
d的is表达式
Detailed sorting of HW blue team traceability process
NVM installation tutorial
程序员必备,一款让你提高工作效率N倍的神器uTools
虫子 STL string上