当前位置:网站首页>Metadata of database
Metadata of database
2022-06-27 10:29:00 【Everything will always return to plain】
Catalog
1.2 The role of database metadata
2.2 Obtain comprehensive information of the database
2.4 Get all the table information in a database
2.5 Get the field properties in the specified database table
3.1 Get precompiled SQL The number of placeholder parameters in the statement
1、 Metadata in the database
1.1 What is database metadata
Metadata (MetaData), It refers to the data that defines the data structure .
For example, the header of this table ( Name )

Of course, there are database names and table names .

In addition to these, there are user names 、 Version name and from SQL Most of the strings in the result of the statement are metadata .
1.2 The role of database metadata
What is the role of metadata in the database ?
There are two main aspects :
- Application design , For example, code generator , It requires database metadata .
- If you know database metadata , You can have a deeper understanding of some frameworks of the database , for example jpa,Mybatis.
1.3 How to get metadata
We are JAVA Operation database , does JDBC, Whether it's MySQL still Oracle Or other databases , Basically through JDBC To deal with the database .
Use JDBC There are three main interfaces to handle databases , namely Connection,PreparedStatement and ResultSet These three interfaces .
For these three interfaces , You can also get different types of metadata .
Interface | explain |
Connection | Get database metadata (DatabaseMetaData) |
PreparedStatement | Get the parameter metadata we get by sending the request (ParameterMetaData) |
ResultSet | Get result set metadata (ResultSetMetaData) |
The following will introduce the three types of metadata objects respectively and use MYSQL Database for case description .
2、 Database metadata
Database metadata (DatabaseMetaData): By Connection Object passing getMetaData Method , It mainly encapsulates some overall comprehensive information about the database itself , For example, the name of the database , Version number of the database , Database URL, Whether transactions are supported .
Here are some about DatabaseMetaData The common method of :
Method | explain |
getDatabaseProductName | Get the name of the database |
getDatabaseProductName | Get the version number of the database |
getUserName | Get the user name of the database |
getURL | Get the database connection URL |
getDriverName | Get the driver name of the database |
driverVersion | Get the driver version number of the database |
isReadOnly | Check whether the database only allows read operations |
supportsTransactions | Check whether the database supports transactions |
2.1 Constructing environment
I just picked up one that I used to do Demo Of project (SpringBoot project ) To write .
Introduced mySql rely on .
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>Since it is SpringBoot project , That is, of course, direct use yml file Configure the database connection .
server:
port: 80
spring:
application:
name: mp
datasource: # Configure data source information
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis_plus?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 1234
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver2.2 Obtain comprehensive information of the database
@SpringBootTest
class MetadataTest {
// data source
@Resource
DataSource dataSourcee;
@Test
void Test01() {
try {
// Get database metadata
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = dataSourcee.getConnection().getMetaData();
// Get database product name
String productName = dbMetaData.getDatabaseProductName();
System.out.println(" Database product name :" + productName);
// Get the database version number
String productVersion = dbMetaData.getDatabaseProductVersion();
System.out.println(" Database version number :"+productVersion);
// Get the database user name
String userName = dbMetaData.getUserName();
System.out.println(" Database user name :"+userName);
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
} Here are three , It's all the same anyway , The rest of us try it by ourselves .
effect :

2.3 Get the database list
@SpringBootTest
class MetadataTest {
// data source
@Resource
DataSource dataSourcee;
@Test
void Test01() {
try {
// Get database metadata
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = dataSourcee.getConnection().getMetaData();
// Get the database list
ResultSet rs = dbMetaData.getCatalogs();
// Traverse to get all database tables
while (rs.next()) {
// Print database name
System.out.println(" Table name :"+rs.getString(1));
}
// Release resources
rs.close();
dataSourcee.getConnection().close();
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.4 Get all the table information in a database
@Test
void Test01() {
try {
// Get database metadata
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = dataSourcee.getConnection().getMetaData();
// Get the specified table information in the specified database
ResultSet tablers = dbMetaData.getTables(null, null, "t_user", new String[]{"TABLE"});
// assemble table
while (tablers.next()) {
// Database 1 || TABLE_CAT
System.out.println(" Database :" + tablers.getString("TABLE_CAT"));
// Table mode 2 || TABLE_SCHEM
System.out.println(" Table mode :" + tablers.getString("TABLE_SCHEM"));
// Table name 3 || TABLE_NAME
System.out.println(" Table name :" + tablers.getString("TABLE_NAME"));
// Database table type 4 || TABLE_TYPE
System.out.println(" type :" + tablers.getString("TABLE_TYPE"));
// Database table remarks 5 || REMARKS
System.out.println(" remarks :" + tablers.getString("REMARKS"));
}
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}The method of obtaining table data getTables Medium 4 The parameters are :
Parameters | explain |
catalog | Database name ,null All databases |
schemaPattern | Schema name , stay mysql There is no special significance in , So fill it directly null . |
tableNamePattern | Table name ,null Is all the tables |
types[] | type : TABLE: surface VIEW: View |
Let's see the implementation effect :
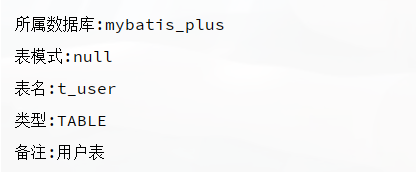
2.5 Get the field properties in the specified database table
@Test
void Test01() {
try {
// Get database metadata
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = dataSourcee.getConnection().getMetaData();
// Get the field information in the specified database table
ResultSet columns = dbMetaData.getColumns("mybatis_plus", null, "t_user", null);
// assemble table
while (columns.next()) {
// Database 1 || TABLE_CAT
System.out.println(" Database :" + columns.getString("TABLE_CAT"));
// Table mode 2 || TABLE_SCHEM
System.out.println(" Table mode :" + columns.getString("TABLE_SCHEM"));
// Table name 3 || TABLE_NAME
System.out.println(" Table name :" + columns.getString("TABLE_NAME"));
// Name 4 || COLUMN_NAME
System.out.println(" Name :" + columns.getString("COLUMN_NAME"));
// Database table type 5 || DATA_TYPE
System.out.println(" type :" + columns.getString("DATA_TYPE"));
// Database table remarks 12 || REMARKS
System.out.println(" remarks :" + columns.getString("REMARKS"));
}
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}This has not changed much , Just another way getColumns
The same parameter is that the last one becomes Name ,null It means finding all the columns .
3、 Parameter metadata
Parameter metadata (ParameterMetaData): By PreparedStatement Object passing getParameterMetaData Method , Mainly aimed at PreparedStatement Object and its precompiled SQL Command statements provide some information ,ParameterMetaData The number of placeholder parameters that can be provided , Gets the placeholder for the specified location SQL Type, etc. .
3.1 Get precompiled SQL The number of placeholder parameters in the statement
@Test
void Test01() {
try {
String sql = "select * from t_user where uid = ?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = dataSourcee.getConnection().prepareStatement(sql);
// obtain ParameterMetaData object
ParameterMetaData paramMetaData = pstmt.getParameterMetaData();
pstmt.setString(1, "1");
// Get the number of parameters
int paramCount = paramMetaData.getParameterCount();
System.out.println(paramCount);
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}Of course, there are many other ways . This pair just learned JDBC Students who connect to the database should be familiar with , Anyway, I almost forgot .
4、 ResultSet Metadata
ResultSet Metadata (ResultSetMetaData): By ResultSet Object passing getMetaData Method , Mainly for the data Library executed SQL The result set object obtained by the script command ResultSet Some of the information provided in , For example, the number of columns in the result set 、 Specify the name of the column 、 Specifies the name of the column SQL Type, etc. , It can be said that this is a very important object for the framework .
Common methods are :
Method | explain |
getColumnCount | Get the number of column items in the result set |
getColumnType | Gets the SQL The type corresponds to Java in Types Class field |
getColumnTypeName | Gets the SQL type |
getClassName | Get the specified column SQL The type corresponds to Java The type of ( Package name plus class name ) |
@Test
void Test01() {
try {
String sql = "select * from t_user where uid = ?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = dataSourcee.getConnection().prepareStatement(sql);
// obtain ParameterMetaData object
ParameterMetaData paramMetaData = pstmt.getParameterMetaData();
pstmt.setString(1, "1");
// perform sql sentence
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
// obtain ResultSetMetaData object
ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
// Get the number of query fields
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
// Get column name
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
// obtain java type
String columnClassName = metaData.getColumnClassName(i);
// obtain sql type
String columnTypeName = metaData.getColumnTypeName(i);
System.out.println(" Column name "+columnName);
System.out.println("java type "+columnClassName);
System.out.println("sql type "+columnTypeName);
}
System.out.println(columnCount);
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
边栏推荐
- 学习笔记之——数据集的生成
- LVI Sam summary
- User authentication technology
- Reorganize common shell scripts for operation and maintenance frontline work
- 迪米特法则
- Brother sucks 590000 fans with his unique "quantum speed reading" skill: look at the street view for 0.1 seconds, and "snap" can be accurately found on the world map
- 手机影像内卷几时休?
- Ubuntu手动安装MySQL
- JS file upload and download
- Error im002 when Oracle connects to MySQL
猜你喜欢
Design and Simulation of direct torque control system for induction motor (motion control matlab/simulink)

Your brain is learning automatically when you sleep! Here comes the first human experimental evidence: accelerate playback 1-4 times, and the effect of deep sleep stage is the best

红包雨: Redis 和 Lua 的奇妙邂逅

When does the mobile phone video roll off?

lvi-sam 总结

详细记录YOLACT实例分割ncnn实现
测试同学怎么参与codereview

浅析基于边缘计算的移动AR实现(中)
在外企远程办公是什么体验? | 社区征文

Feedforward feedback control system design (process control course design matlab/simulink)
随机推荐
Exception in Chinese character fuzzy query of MySQL database
Stop using system Currenttimemillis() takes too long to count. It's too low. Stopwatch is easy to use!
[learn FPGA programming from scratch -47]: Vision - current situation and development trend of the third generation semiconductor technology
产品力对标海豹/Model 3,长安深蓝SL03预售17.98万起
【TcaplusDB知识库】Tmonitor单机安装指引介绍(一)
JS all network request modes
Future & CompletionService
In the three-tier architecture, at which layer is the database design implemented, not at the data storage layer?
Mail system (based on SMTP protocol and POP3 protocol -c language implementation)
片刻喘息,美国电子烟巨头禁令推迟,可暂时继续在美销售产品
嵌入式软件架构设计-模块化
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb tmonitor module architecture introduction
Technology is as important as business. It is wrong to favor either side
迪米特法则
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB Tmonitor模块架构介绍
torchvision. models._ utils. Intermediatelayergetter tutorial
细说物体检测中的Anchors
前馈-反馈控制系统设计(过程控制课程设计matlab/simulink)
. Net
Win10快捷键整理
