当前位置:网站首页>Iterators and generators
Iterators and generators
2022-07-24 06:33:00 【Laughter addiction】
Iterators and generators
One 、python The derived type
1. List derivation
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
b = [x**2 for x in a if x%2 == 1]
print(b)
result :
[1, 9, 25, 49]
practice :
1.1 Use list derivation , Output 200 The inner square is the number of integers
# Method 1 :
result = [i*i for i in range(15) if i*i<200]
print(result)
# Method 2 :
import math
tmp = [i for i in range(200) if math.sqrt(i).is_integer()]
#tmp = [i for i in range(200) if math.sqrt(i)%1==0]
print(tmp)
1.2 Number in the list , Take two decimal places
tmp = [2.45345,4.3454325,9,82.234324,9.841234]
num = [round(i,2) for i in tmp ]
# num = ['%.2f'%i for i in tmp ]
print(num)
2. Nested derivation
# Count the names that contain e More than twice ,
# Method 1 : Conventional methods
result = []
names = [['Tom', 'Billy', 'Jefferson', 'Andrew', 'Wesley', 'Steven', 'Joe'],
['Alice', 'Jill', 'Ana', 'Wendy', 'Jennifer', 'Sherry', 'Eva', 'Elven']]
for i in names:
for j in i:
if j.lower().count("e")>=2:
result.append(j)
print(result)
# Method 2 : Nested derivation implementation
names = [['Tom', 'Billy', 'Jefferson', 'Andrew', 'Wesley', 'Steven', 'Joe'],['Alice', 'Jill', 'Ana', 'Wendy', 'Jennifer', 'Sherry', 'Eva', 'Elven']]
print([name for lst in names for name in lst if name.lower().count('e')>=2])
3. Dictionary derivation
d1 = {
"a":1,"b":2,}
d2 = {
v:k for k,v in d1.items()}
print(d2)
result :
{
1: 'a', 2: 'b'}
practice
3.1 Count the number of occurrences of each character in the string
# Method 1 :
str1 = "fasfasgwreasdg3tagjdhg"
print({
x:str1.count(x) for x in str1 })
# Method 2 :
tmp = {
}
for i in str1:
tmp[i] = tmp.get( i, 0) +1
4. Set derivation
Consistent with the list derivation , It's just used here {}, Bring your own weight removal function
lst = [-1,1,2,1]
s1 = {
i*i for i in lst}
print(s1)
result :
{
1, 4}
5. Deductive comprehensive exercise

answer
1、q1 = ['a','ab','abc','abcd','abcde']
print([x.upper() for x in q1 if len(x)>=3])
2、print([(x,y) for x in range(6) for y in range(6) if x%2==0 and y%2!=0])
3、dict1 = {
'a': 10, 'b': 34}
print({
x:y for y,x in dict1.items()})
4、q4 = {
'B':3,'a':1,'b':6,'c':3,'A':4}
print({
x.lower():q4.get(x.lower(),0)+q4.get(x.upper(),0) for x,y in q4.items() })
python Iteratable objects and iterators
1. Iteratable object :
Realized __iter__ Method , And the method returns the object of an iterator
lst = ["x","y",1,2,3]
print(dir(lst))
from collections.abc import Iterable
print(isinstance(lst,Iterable))
print(isinstance(lst,list))
print(isinstance(lst,str))
2. Iteratable objects currently in contact – Container type
str、list、tuple、dict、set, Open file files、range wait
3. iterator , Realized __iter__() and __next__() Methods are called iterators
__iter__ Method returns itself
__next__ Method keeps returning the next value
The iterator must be an iteratable object
str1 = "abc"
result = str1.__iter__()
print(result)
print(dir(result))
print(result.__next__())
print(result.__next__())
print(result.__next__())
range_iter = iter(range(10))
from collections.abc import Iterable,Iterator
print(isinstance(range_iter,Iterable))
print(isinstance(range_iter,Iterator))
4.for Grammatical sugar
for Call the of the iteratable object first __iter__ Method , Returns an iterator , Then call... On the iterator __next__ Method , Constantly return the next value , Until the last one to quit ,
There are no more elements in the container , Throw out StopIteration,for The loop exits when it encounters an exception
5. Lazy loading
Lazy evaluation , Generate when necessary
The function of iterator : It will not consume a lot of memory at one time , Load one by one
lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] # Generate all at once , Save in memory
#range(1,9)
for i in range(1,9):
print(i)
6. Generate infinite sequence
from itertools import count
counter = count(start=10)
print(counter,type(counter))
print(next(counter))
print(next(counter))
print(next(counter))
result :
count(10) <class 'itertools.count'>
10
11
12
7. Generate infinite sequences from finite sequences

8. Implement an iterator
class NumIter():
def __init__(self):
self.num = 0
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
self.num +=1
return self.num
n1 = NumIter()
print(dir(n1))
for i in n1:
if i ==10:
break
print(i)
9. Write iterators to implement range
class MyRange():
def __init__(self, num):
self.num = num
self.i = 0
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.i < self.num:
flag = self.i
self.i += 1
return flag
else:
raise StopIteration
ran = MyRange(10)
for i in ran:
print(i)
10、 Write iterators to realize fiboracci sequence
class Fib():
def __init__(self, num):
#num Indicates before calculation n term To judge the conditions of iteration
self.num = num
#i Used to record the location of access
self.i = 0
self.num1 = 0
self.num2 = 1
def __iter__(self):
# Iteratible objects need to provide __iter__ An iterator , stay python in , iterator Itself is an iteratable object , Return to yourself
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.i < self.num:
self.num1,self.num2 = self.num2,self.num1+self.num2
self.i += 1
return self.num1
else:
raise StopIteration
fib = Fib(10)
for i in fib:
print(i)
3、 ... and 、 generator
1. generator : There is no need to implement it manually __iter__ and __next__ Method , It's a more elegant way to write iterators
2. There are only two ways to write a generator :
One is called generator expression , One is called generator function
3. Generator Expressions
Lazy evaluation , Similar to list derivation
result = (x for x in range(1,31) if x%3 ==0) #=====》 Lazy evaluation
print(result)
print(dir(result))
result :
<generator object <genexpr> at 0x000002B1F715AC80>
['__class__', '__del__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__name__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__next__', '__qualname__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'close', 'gi_code', 'gi_frame', 'gi_running', 'gi_yieldfrom', 'send', 'throw']
4. Generator function :
Contains yield Keyword functions are called generator functions
1、yield keyword
yield Keep the intermediate algorithm , Continue next time
When calling next when , encounter yield Stop running , And back to yield The value of the following expression
When called again yield when , It will continue to run from the place where it was suspended , Until we meet the next one yield Or the whole generator ends
def get_content():
x = 2
yield x
y = 3
yield y
z = 4
yield z
g = get_content()
print(g)
print(dir(g))
print(next(g)) # First execution next When , encounter yield Quit , And back to yield The parameters carried behind , It also records the current execution location
print(next(g)) # The second time it was executed , It will continue from the place where it was last executed
print(next(g))
result :
<generator object get_content at 0x000001D2D9C9AAC0>
['__class__', '__del__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__name__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__next__', '__qualname__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'close', 'gi_code', 'gi_frame', 'gi_running', 'gi_yieldfrom', 'send', 'throw']
2
3
4
# Generator implementation range Method
def Myrange(num):
i = 0
while i<num:
yield i
i +=1
for i in Myrange(10):
print(i)
5. Generator function , Implementation of the fibulacci sequence
def Fib(num):
i = 0
num1 = 0
num2 = 1
while i<num:
num1,num2 = num2,num1+num2
yield num1
i +=1
for i in Fib(10):
print(i)
6. The benefits of the generator :
You can use less code to achieve the effect of iterators
Save more memory than container type
7. Generator processing of large files , Can give consideration to both efficiency and memory burst processing
def read_file(path):
SIZE = 65535
with open(path,"rb") as f:
while True:
block = f.read(SIZE)
if block:
yield block
else:
return
7.1、 Huge file processing :
generator + Cutting multiple small files for parallel processing
7.2、 Transmission of large files
Cut small files + Hash validation
8.send Method
def counter():
count = 1
while 1:
val = yield count
print(f'val is {val}')
if val is not None:
print(f'val is {val}')
count = val
else:
count +=1
count = counter()
#count.send(10) # Modifying data , The generator must be activated first , You can call next Activate
print(next(count))
count.send(10) # Return a new value to yield count
print(next(count))
# Manually close the current generator , You cannot continue to generate values after closing
# count.close()
# print(next(count))
9.yield and yield from
def f1():
yield range(10)
def f2():
yield from range(10)
iter1 = f1()
iter2 = f2()
print(iter1)
print(iter2)
print(next(iter1))
#print(next(iter1)) # Will report a mistake , Because it has stopped
print(next(iter2))
print(next(iter2)) #yield from Then you need to pass in an iteratable object
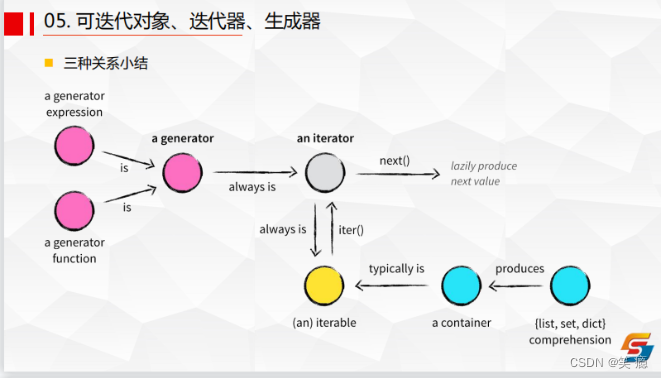
Four 、 generator 、 iterator 、 The relationship among the three iteratable objects
5、 ... and 、hash Algorithm
1、 Hash algorithm definition
The result is the concept of space for time
Put any length of input , It becomes a fixed-length output
2、 Common hash algorithms :
md5 sha1 sha2 sha256 sha512---》 One way encryption technology
3、 application :
Check the integrity of the file --》 File transfer ;
Password verification and password encryption
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
IP class notes (5)
PXE technology network installation
Function application of MySQL
Wasm vs EVM, Boca's choice predicts the future of the public chain
LVM and disk quota
Simple three-step fast intranet penetration
LVM与磁盘配额
Process and planned task management
[218] what are the advantages and disadvantages of CS architecture and BS architecture and data on the server and client?
LuckyFrameWeb测试平台(一款支持接口自动化、WEB UI自动化、APP自动化,并且支持分布式测试的全纬度免费开源测试平台)
rsync(一):基本命令和用法
[226] instructions for Wireshark parameters
Remember 20 classic interview questions of performance test in three minutes
UE4 reload system 1. basic principle of reload system
Remote connection to Qunhui NAS at home [no public IP, free intranet penetration]
Flink production environment configuration recommendations
history命令历史记录中加时间
Leetcode sword finger offer jz25 merges two sorted linked lists
【226】wireshark的参数使用说明
联合国农产品数据分析









