当前位置:网站首页>Process and planned task management
Process and planned task management
2022-07-24 06:24:00 【Aka · Brooklyn Fairy】
Catalog
One , The relationship between program and process
2, The difference between process and multithreading
1, View process static information :ps
4, View process dynamic information :top
1, Process dynamic information
2, Process information area noun explanation
5, View process information :pgrep
6, View the process tree :pstree
Four , Planning task management
2, Periodic task setup :crontab
One , The relationship between program and process
Program
- Save on hard disk , Executable code and data in media such as optical disc
- Code stored statically in a file
process
- stay CPU And the program code running in memory
- Dynamically executed code
- Father child process
- Each program can create one or more processes
1, Thread state
1, newly build (NEW): A new thread object is created
2, Can run (RUNNABLE); After the thread object is created , Other threads ( such as main Threads ) Called the object's start( Method ). Threads in this state can only run in the thread pool , Waiting to be selected by thread scheduling , obtain cpu Right to use
3, function (RUNNING); Operational state (runnable) The thread of the cpu Time slice (timeslice) Execute program code .
4, Blocking (BLOCKED): Blocking state means that the thread has given up for some reason cpu Right to use , It also gives way cpu timelise Go to run (running) state . There are three types of congestion :
( One ) Waiting for a jam : The running thread executes o.wait Method ,JVM Will put the changed thread into the waiting queue .
( Two ) Synchronous blocking : Running 1 The thread is getting the synchronization lock time of the object , If the synchronization lock is occupied by other threads , be JVM Will put the changed thread into the lock pool .
( 3、 ... and ) Insufficient system resources ) function (running) Thread execution of Thread.sleep (longms)ms) or t. join() Method , Or send out I/o When asked ,JVM It puts the thread in a blocking state . When sleep() Status timeout 、join() Wait for the thread to terminate or timeout 、 perhaps I/o When it's done , The thread goes back to runnable (runnable) state .
5, Death (DEAD) Threads run()、main() Method execution ends , Or quit because of an exception run() Method , The thread ends its life cycle . Dead threads cannot be reborn
2, The difference between process and multithreading
Process is the basic unit of operating system resource allocation , Thread is the basic unit of task investigation and execution . Processes without threads can be treated as single threads , If there are multiple threads in a process , The execution process is not a line , It is accomplished by multiple lines , Threads are part of the process , So threads are also called lightweight processes or lightweight processes
Two , Check the process
1, View process static information :ps
Method 1 :ps aux

| a | Display all processes on the terminal , Include other users' processes |
| u | Represents the user who lists the processes |
| x | Display the process of all terminals |

Explanation of terms
| USER | Users of the process |
| PID | Process ID |
| %CPU | Process occupied cpu percentage |
| %MEM | Percentage of memory used |
| VSZ | The amount of virtual memory used by the process |
| RSS | The amount of physical memory consumed by the process |
| TTY | The terminal name of the startup process , Processes that are not started from the terminal are displayed as |
STAT | D: Non interruptible sleep state ;R: Running state ;S: In a dormant state , Can be awakened ;T: Stop state , It could be a pause in the background or the process is tracking Debug status ;Z: Zombie process , The process has been aborted , But some programs are still in memory |
| START | The time the process was triggered to start |
| TIME | The process actually uses CPU Running time |
| COMMAND | The start command of the process |
2, ps -elf

Explanation of terms
| F | The system token that the kernel assigns to a process |
| S | State of process |
| UID | The user who started these processes |
| PID | Process of process ID |
| PPID | The process number of the parent process ( If the process is started by another process ) |
| C | In the life cycle of a process CPU utilization |
| PRI | Priority of the process ( The higher the number, the lower the priority ) |
| NI | Humility value is used to participate in determining priority |
| ADDR | The memory address of the process /td> |
| SZ | If the process is swapped out , The approximate size of the swap space required |
| WCHAN | If the process is sleeping , The system function name in sleep is displayed |
| STIME | System time when the process started |
| TTY | The terminal device when the process starts |
| TIME | The cumulative amount required to run the process CPU Time |
| CMD | The start command of the process |
3、 ... and , Zombie process
A process is over , But if the parent process of the process has ended , Then the process will not become a zombie process , Because every process ends 1 When , The system will scan the current system running 1 So the process , See if that process is a child process that just ended , If so , Just from init To take over it , Become its parent process , After the subprocess exits init It will recycle the relevant resources it occupies .
But when the child process ends before the parent process , The parent process does not recycle the child process , Release the resources occupied by the subprocess , At this point, the subprocess will become a zombie process .
4, View process dynamic information :top

1, Process dynamic information
first line : Task queue information
| 19:29:21 | system time |
| up 10:20 | The system has been running for a long time |
| 1 user | Number of currently logged in users |
| load average:0.03,0.02,0.05 | System load , That is, the number of tasks processed by the system per unit time , The last three values are 1 minute ,5 minute ,15 The average from minutes ago to now |
The second line : Process information
| tasks | The total number of processes |
| running | Number of running processes |
| sleeping | Number of dormant processes |
| stopped | Number of processes terminated |
| zombie | The number of dead processes |
The third line :CPU Information
| us | User occupied |
| sy | Kernel occupancy |
| ni | Priority scheduling occupies |
| id | Free CPU( To understand leisure CPU percentage . It mainly depends on %id part ) |
| wa | l/o Waiting for occupation |
| hi | Hardware interrupt occupation |
| si | Software interrupt occupancy |
| st | Virtualization takes up |
In the fourth row : Memory information
| total | Total memory space |
| free | Free memory |
| used | Used memory |
| buff/cache | The total buffer of physical memory and interactive memory |
The fifth row : Exchange space information
| total | Total swap space |
| free | Free swap space |
| used | Used swap space |
| avail Mem | Available physical space |
2, Process information area noun explanation
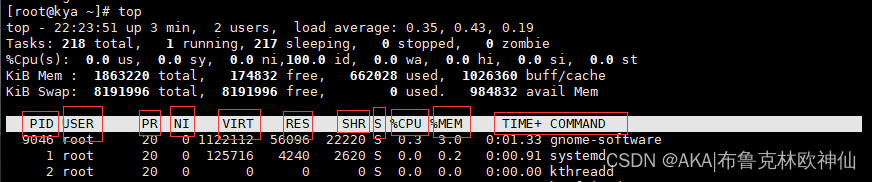
| PID | process ID |
| USER | Process users |
| PR | priority |
| NI | Humility value , Negative value indicates high priority , A positive value indicates a low priority |
| VIRT | The size of virtual memory used by the process , Company kb |
| RES | The amount of physical memory used by the process , Company kb |
| SHR | Shared memory size , Company kb |
| S | Process status |
| %CPU | Last updated to now CPU Percentage occupied |
| %MEM | Percentage of physical memory used by the process |
| TIME | Used by process CPU Total time , Company 1/100 second |
| COMMAND | Command name / Command line |
4,top Common commands
| P | according to CPU Sort by percentage size |
| M | Sort by resident memory size |
| N | Sort by start time |
| c | Toggle display command name and full command line |
| h | You can get top Online help information for the program |
| k | Enter... Of the specified process according to the prompt PID Sign and press Enter Key to terminate the corresponding process |
| q | sign out top Program |
| Numbers 1 | Show CPU Number and state |
5, View process information :pgrep

6, View the process tree :pstree

7,& and job
&: Indicates that the current process is suspended without output

jobs -l : View tasks in the background

bc command : You can resume the specified tasks suspended in the background
fg command : You can put the background tasks on the front desk

kill command

Four , Planning task management
1, Plan tasks at once :at


2, Periodic task setup :crontab
Edit scheduled task
crontab -e [-u user name ]
View scheduled tasks
crontab -l [-u user name ]
Delete task plan
crontab -r [-u user name ]

Every three minutes , Automatically view the time and mount the disk partition table , And output the result to /opt/kk.txt

Task configuration format

| Field | explain |
| minute | The value is 0~59 Any integer between |
| Hours | The value is 0~23 Any integer between |
| date | The value is 1~31 Any integer between |
| month | The value is 1~12 Any integer between |
| week | The value is 0~7 Any integer between ,0 or 7 On behalf of Sunday |
| command | Command or program script to execute |
| Special representation of time value | |
|---|---|
| * | This is an arbitrary range of time |
| , | Represents multiple discontinuous time points of an interval |
| - | Represents a continuous time range |
| / | Specify the time and frequency of the interval |
边栏推荐
- How to build a website full of ritual sense and publish it on the public website 1-2
- NTP error: no server suitable for synchronization found
- 如何建立一个仪式感点满的网站,并发布到公网 1-2
- 【测试工具】
- Simple three-step fast intranet penetration
- Top 10 vulnerability assessment and penetration testing tools
- ue4换装系统 1.换装系统的基本原理
- UE4 replacement system 3. Final results
- IP笔记(6)
- Quickly and simply set up FTP server, and achieve public network access through intranet [no need for public IP]
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Do not rent servers, build your own personal business website (1)
Batch operation of generating MySQL statements from Excel
Use intranet penetration to realize public network access to the Intranet
Summary of ten common vulnerabilities (principle, harm, defense)
Sorting of common AR and MR head mounted display devices
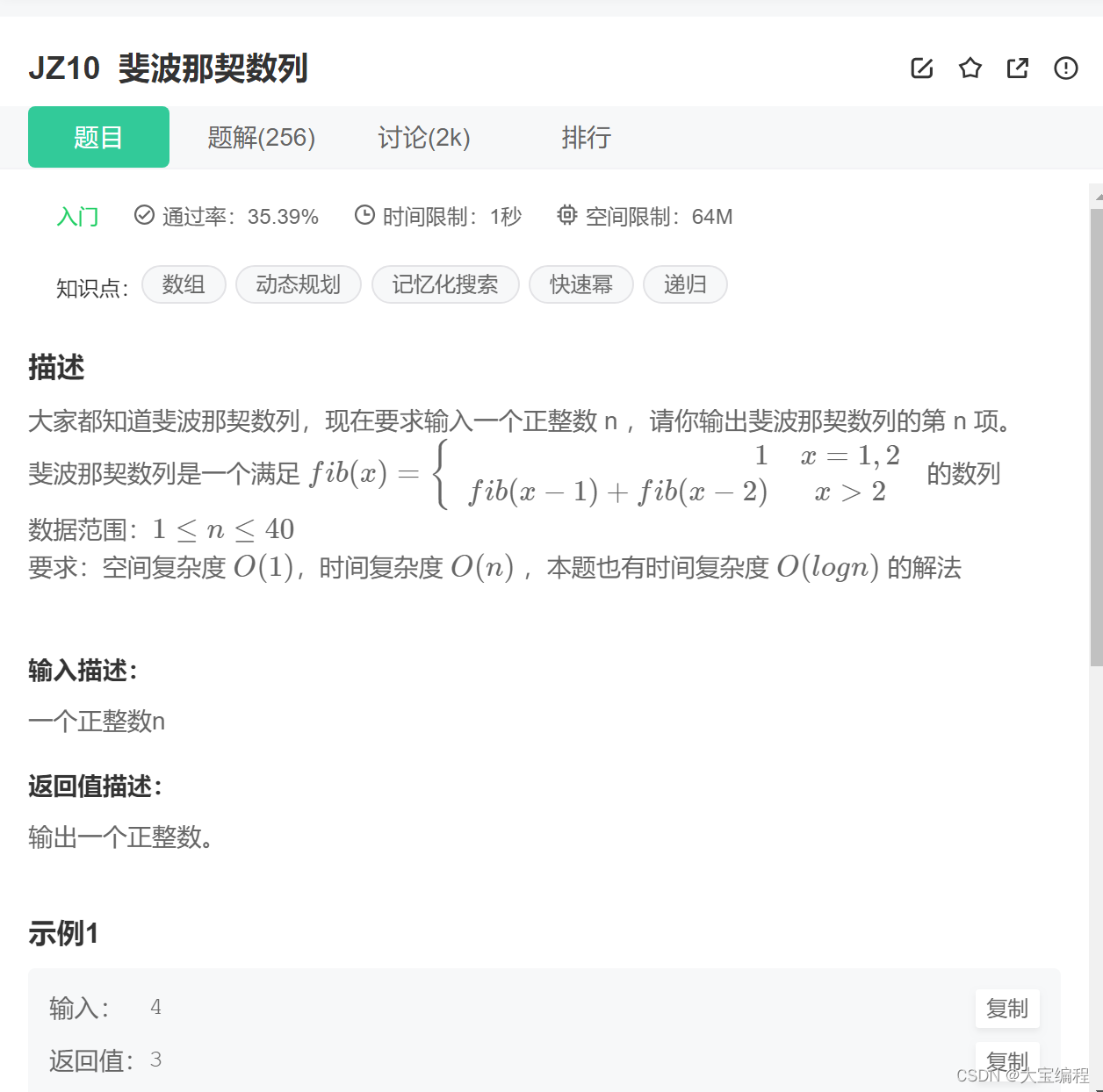
剑指offer JZ10斐波那契数列
Hololens2 development: use MRTK and simulate eye tracking
Unity2d horizontal game jump real-time response
【214】什么是自动化框架
【无需公网IP】为远程桌面树莓派配置固定的公网TCP端口地址
IP notes (11)
Dameng database_ Common user management commands
IP class notes (4)
[222] memory overflow and location
Metersphere one stop open source continuous testing platform
jz47 礼物的最大价值(动态规划思路)
Hololens 2 development: development environment deployment
UE4: what is the gameplay framework
进程和计划任务管理
【218】CS架构和BS架构以及数据放在服务端和客户端的利与弊?