当前位置:网站首页>BGP summary of hcip operation
BGP summary of hcip operation
2022-06-23 05:13:00 【Empty and white】
List of articles
- The first day content
- One 、BGP: Border gateway routing protocol
- Two 、BGP characteristic :
- 3、 ... and 、BGP Data packets
- Four 、BGP Working process of
- 5、 ... and 、 Noun
- 6、 ... and 、BGP Routing black hole problem
- 7、 ... and 、BGP The anti ring mechanism of – Horizontal segmentation
- 8、 ... and 、BGP Basic configuration
- Nine 、 Announce routing
- The next day's content
- The content of the third day
The first day content
One 、BGP: Border gateway routing protocol
Classless path vector EGP agreement ; Work in AS Between ;
AS— Autonomous systems standard AS Number 16 Bit binary 0-65535
Expand AS Number 32 Bit binary
Path vector ( One AS For a jump )— Distance vector ( One router is one hop )
https://www.cidr-report.org
BGP The protocol itself does not generate routing , Instead, it forwards the routing entries generated from other protocols in the local routing table ;
AS There are a lot of BGP Neighborhood , And BGP The protocol does not calculate the best path ; So in BGP In the protocol, the administrator needs to carry out policies to interfere with routing ;
IGP Agreement pursuit :1、 acyclic ( Lu Jia Xuan ) 2、 Fast convergence 3、 Less occupied resources
EGP The pursuit of agreement 1: Controllable ( Administrators can facilitate policy interference and routing )
2、 reliability (BGP Protocol devices need to interact with a large number of routing entries , However, periodic update cannot be selected to occupy link resources , Therefore, only trigger updates can be performed ; And BGP In order to save cost in the agreement working environment , There must be indirect connections, and it is necessary to establish neighbor relations — Unicast neighbors )— be based on TCP Work - Three handshakes, four disconnects 4 A reliable transmission mechanism – TCP Can only work based on unicast
unicast — need IP Can be up to — rely on IGP BGP Carried on IGP above
3、AS-BY-AS With a AS For a jump ;
Two 、BGP characteristic :
1) Classless path vector ----- Upgraded version of distance vector —AS–BY–AS
2) Use unicast updates to send all information ; be based on TCP 179 Port operation
3) Incremental updating – Trigger only aperiodic
4) Have rich attributes to replace IGP Route selection based on measurement ---- Multiple parameter control protocol
5) You can implement a strong strategy for traffic in and out – Controllability
6) The default is not used for load balancing ----- Only one optimal path is generated through various routing rules
7)BGP Support authentication and aggregation ( Summary )
3、 ... and 、BGP Data packets
be based on TCP Of 179 Port operation ; so BGP All data packets in the protocol need to be in tcp After the session is established , be based on TCP To ensure the transmission and reliability ;
First, through TCP Three handshakes to find a neighbor ;
Open Only responsible for the establishment of neighborhood relations , Normal receiving and sending can be done once ; carry route-id;
Keeplive Keep alive cycle 1min Query whether the neighbor relationship exists ; Actually keep alive TCP conversation ;hold time Default 3min
Update Carry routing entries Target network number + Various attributes
Notification Send and receive error data ;
Four 、BGP Working process of
1、 When the configuration is complete , Unicast between neighbors TCP Three handshakes , Target port 179, establish TCP Conversation ; After that all BGP Protocol packets are transmitted based on the session ;
After the session is established , Normal sending and receiving between neighbors once open Message establishment BGP The neighborhood of , Generate neighbor table ;
BGP Agreed open The message will carry the local RID— Generation method and OSPF Agreement ; Only local and all local neighbors need to be unique ;
After the neighbor relationship is established , The default for each 1min, Use keeplive Keep the neighborhood alive periodically ( Life cycle TCP conversation )
2、 After the neighbor relationship is established , The administrator can select the route entries obtained from any source in the local route table , towards BGP Declare in the agreement ; Use updata Packets are shared among neighbors ; Then generate BGP surface ;— Load all routing entries sent and received locally ;
The optimal path is loaded into the routing table by default ( The optimal - Just based on BGP Routing rules for , Not necessarily the best path ;BGP Load balancing is not supported by default )
3、 Convergence complete , only keeplive Keep the cycle alive ;
4、 If an error message appears , Neighbors will use Notification Message error reporting operation
5、 Structural mutation
1) newly added — Local use updata Inform all local neighbors , Provided that the route is not included by the issued aggregate route
2) To break off — Local use updata Inform all local neighbors , Provided that the route is not included by the issued aggregate route
Only all detailed routes contained in the aggregation entry are invalidated locally , Just tell neighbors to delete aggregation entries
3) Unable to communicate — hold time by 3min, continuity 3 I haven't received a neighbor's keeplive; Break the neighborhood 、TCP conversation , Delete all routes learned from the neighbor ;
5、 ... and 、 Noun
neighbor — Direct connection because BGP There is a demand for non direct neighbors in the protocol , so BGP Neighbors are called adjacency ;
EBGP Neighborhood ---- external BGP Neighborhood , The two adjacent equipment are in different positions AS in
IBGP Neighborhood ---- Inside BGP Neighborhood , The two adjacent devices are in the same AS in
6、 ... and 、BGP Routing black hole problem
The routing entry of non direct link neighbor building to the control level can be passed , Recursively calculate the route ;
The actual data level traffic is not running after BGP The router of the protocol cannot pass , In the end, there is no return
1、 Physics 、 Logical topology connection – Physical link direct connection 、 perhaps vpn
2、 Neighbors are connected – All devices in the network are running BGP
3、BGP Republish to IGP(LAB)
4、MPLS Multiprotocol label switching — The recommendation
7、 ... and 、BGP The anti ring mechanism of – Horizontal segmentation
1、EBGP Horizontal segmentation — solve EBGP The loop ;
Rely on BGP A property in the routing entry to prevent ring ;AS-PASH Path properties ;
BGP The protocol is in the process of transmitting routing entries , Will record all the AS The number of ;
EBGP Horizontal segmentation — In the received route entry , If there is a local AS No. will reject the entry into ;
2、IBGP Horizontal segmentation — solve IBGP The loop consists of a mechanism in
From a local IBGP Route entries learned from neighbors , Do not pass to other local IBGP neighbor ;
AS-BY-AS In a AS During the transfer of internal items , No properties will be modified by default ;
because BGP You can establish a neighbor relationship indirectly , So in a AS Inside , You can run with multiple computers BGP Protocol router establishment BGP Neighborhood , To stabilize the network ; So in a AS Internal operation BGP Agreed devices , Normal all exist EBGP neighbor ( Are connected to other devices at the same time AS)
stay IBGP Under the limitation of horizontal segmentation , Although avoid IBGP Loop generation of , But it also makes AS Internal in order to be able to pass routing entries , Must be established between two IBGP Neighborhood , Neighborhoods are rising exponentially , Huge amount of configuration ;
In the later stage, we can rely on the mechanism of breaking the horizontal segmentation to solve — The federal 、 Routing reflectors
8、 ... and 、BGP Basic configuration
【1】 establish BGP Neighborhood
[r1]bgp 1 When starting, you need to define AS Number , There is no concept of multiple processes ; A device can only work in one AS Work in China
[r1-bgp]router-id 1.1.1.1 // Recommended configuration RID;RID The generation rules of are the same as OSPF;
1、 Single chain EBGP Neighborhood
[r1-bgp]peer 12.1.1.2 as-number 2
Peer interface ip Address Where the opposite end is located AS Number
2、 establish IBGP Neighborhood ;– Due to a AS Most of the internal topology redundancy is rich , If you use a physical interface as a source 、 Objective IP Address establishment BGP neighbor , Will waste redundant resources ; It is recommended to use the loopback interface as the source / Objective ip Address ;
Stable / And multiple link resources can be used at the same time
Bear in mind : When using loopback address as source 、 Objective ip Address time ; And a loopback to define the target as the opposite end , You also need to change the source of this end to loopback , Otherwise, the local physical exit will be automatically used as the source ;
[r2-bgp]peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
3、 Multilink EBGP Neighborhood
Loopback is recommended as the source 、 Target interface
1)IP Accessibility issues — Generally use static
[r4]ip route-static 5.5.5.0 24 45.1.1.2
[r4]ip route-static 5.5.5.0 24 54.1.1.2
2) establish EBGP Neighborhood
[r4]bgp 2
[r4-bgp]peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 3
[r4-bgp]peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
3)TTL problem , Default IBGP Packets between neighbors TTL The value is 255,EBGP Between neighbors TTL The value is 1;
So if you use ring back to build EBGP Neighborhood ,TTL Not enough ; so , Must be modified
[r4-bgp]peer 5.5.5.5 ebgp-max-hop 2
After the configuration of both ends is completed , Between neighbors first TCP Three handshakes of , establish TCP Conversation ;
[r1]display tcp status
When TCP After the session is established , Send and receive between neighbors once open package ( carry RID), establish BGP The neighborhood of ; Generate neighbor table :
BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1
Local AS number : 1
Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1
Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv
12.1.1.2 4 2 5 6 0 00:03:22 Established 0
The number at the end of the table 0, Represents the number of routing entries learned from the neighbor ;
Nine 、 Announce routing
BGP The route declared by the protocol is the route information generated by any source in the local route table ;
At the announcement , The routing information in the local routing table can be selected one by one :
[r1]bgp 1
[r1-bgp]network 1.1.1.0 24
Bear in mind : At the announcement , The declared network number must be exactly the same as the record in the local routing table ;
When the configuration is declared complete , Locally generated BGP surface ;- Load and receive all locally BGP route
Total Number of Routes: 1
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 i
state Target network number attribute
. * You can use
. > good
Use i Identify the entry through local IBGP Neighbors learn
Only when an entry is available and excellent can it be transmitted to other local neighbors ; Can be loaded into the local routing table ;
Excellent conditions for entry :
1、 Synchronization problem — The current device synchronization rule is off by default , This problem doesn't need attention at present
Synchronization problem — Local must first notify IGP Learn the route , Through BGP Study
2、 Next hop unreachable problem — because AS-BY-AS The rules Make the next hop address in a AS Internal transfer , No modification by default ; Therefore, through local IBGP Routes learned by neighbors , Most of the next jump is not reachable
[r2]bgp 2
[r2-bgp]peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local
//R2 Route to 3.3.3.3 when , Change the next hop address to R2;
The next day's content
One 、BGP The announcement problem :
If through BGP The routing entry delivered by the protocol is consistent with the entry target learned locally through other protocols , Will appear :
1、 This route acts as a link to other BGP The underlying route when neighbors establish neighbor relationship , So this one BGP Routing will not be optimal , Cannot pass or add table
2、 This route is not used to establish other routes BGP The routing of neighbors , No tables will be added locally , But it can convey , It belongs to excellent routing ;
example :R2 And R3 It's running OSPF, after R2 Learned R3 Of 32 Bit loopback host routing ;
Again R2 And R3 establish BGP The neighborhood of ; after R3 stay BGP The agreement declares 32 Bit loopback route , Then the entry arrives at R2 after , Will not be excellent ; --BGP Neighbor building routing and BGP The delivery routes of are the same ;
but R2 And R3 When building neighborhoods ,ospf take R3 Loop back to 32 Bit transfer , but BGP Use 24 Bit to pass the loopback route , So is equal to the BGP Build a neighborhood as 32 position ,bgp Pass it on to 24 position , Not the same route , Can be excellent , It can deliver , You can also add a watch ;
notes : The above problems will occur in Huawei equipment , but cisco Zhongruo bgp The delivery route has passed other routes in the local route table IGP Have , Will be marked as r-RIB Do not load — No tables are added locally , But it can convey ;
stay BGP When declared in the agreement , Is to declare any route in the local route table , Don't pay attention to how these items are generated ;
These routes will be carried by default cost It's worth it BGP In the routing entry of ; If the local will be declared locally BGP Route to local EBGP neighbor , Will carry these cost, Convenient for local EBGP The neighborhood AS Internal equipment routing , Of course, this route is entering other AS The measurement will not be modified ;
If it passes locally IBGP The neighbors learned BGP route , Superior and existing cost value , These routes are passed locally to the local EBGP Neighbor time , take cost Value return 0, Because these metrics are not locally generated ;
example :R2 And R1 by EBGP neighbor , that R2 Declare local passage OSPF Routing learned by the protocol 4.4.4.4/32 The measure is 2, Then this route is entering BGP The table carries the measure 2, Pass to R1,R1 Show this metric in the routing table , At the same time R1 Inside AS The time measurement does not change ;
In this topology R2 And R4 by IBGP neighbor , This article BGP Routing will also be R2 Pass to R4, but R4 Then pass the route to R4 Of EBGP Neighborhood R5 when , Reduce the measurement to 0; if R4 Also declare 4.4.4.4/32 This route , So pass it on to R5 Will carry R4 To the network segment cost value , Because only the local optimal route can be passed , Local claims are superior to those passed on by other neighbors BGP route ;
summary : There is EBGP Neighborhood ( Connect other AS) All of the BGP It is recommended that the equipment be declared internal AS The routing ;
Two 、 Reissue
BGP Protocol declared route , It is basically local IGP What we have learned as route ; A large number , If it is announced one by one , There is a large amount of configuration , But it is controllable ; You can also run at the same time BGP and igp The equipment , take IGP Agreement republished to BGP Agreement , To achieve batch route announcement effect ;
An announcement is equivalent to an article by article reissue , Republishing is equivalent to a batch of announcements ; Routing entries generated by both , Different origin properties , Other attributes are exactly the same by default ;
summary : There is EBGP Neighborhood ( Connect other AS) All of the BGP The equipment is recommended to be reissued IGP To BGP;
3、 ... and 、 Automatic summarization
Default cisco And Huawei devices have turned off automatic summarization
Auto summary for BGP Pass normally network The route generated by the declaration has no effect ;
Only for from IGP Republish to BGP The routing entry of the has an impact ;— Route entries are sent in main class length , Do not carry cost value ;
[r1]bgp 1
[r1-bgp]summary automatic // Turn on automatic summary , It is recommended to maintain the default off state
Four 、 Manual summary — polymerization
1) Take advantage of BGP The characteristics of the announcement , Any route in the local routing table , Can be declared without paying attention to the source BGP in ;
There is no need to declare detailed routes one by one , First, manually static an empty interface anti ring route pointing to the summary network segment , Then announce it to BGP In the agreement ; from IGP The table declares that BGP Items in the agreement , Carry only the target network number and measurement value ;
The disadvantage of aggregation is to combine multiple network numbers into one , This results in accessing the entire aggregation network segment , Only unique paths exist ;
If under the premise of multi-path neighbor building , Will not be able to accurately choose the way ; Therefore, in large multi link networks, in order to better control routing , Must pass the aggregation entry at the same time , Then pass part of the detailed route at the best path ;
If you need to pass the aggregation entry at the same time , Pass part of the detailed route , Only after the declared empty interface route , Declare the required detailed routes one by one ;
The disadvantage of the above method is that the original detailed route cannot be carried cost value , Because it is declared that the static empty interface route is artificially added in the local route table ;
2) The standard BGP Route aggregation — First, manually announce the details one by one , Or republish routes in batches ;
Then perform aggregation configuration ; By default, an empty interface anti ring route is generated locally ;
[r2-bgp]aggregate 3.3.0.0 21 // Aggregation and all detailed routes are sent
[r2-bgp]aggregate 3.3.0.0 21 detail-suppressed
// Suppress all detailed routes , Send only aggregate entries ;
The above operation method : If it is necessary to carry part of the detailed route while sending the aggregated items , Need to use policy
1、 Suppress list
[r2]ip ip-prefix ss permit 3.3.4.1 32
[r2]route-policy ss permit node 10
[r2-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix ss
[r2]bgp 2
[r2-bgp]aggregate 3.3.0.0 21 suppress-policy ss
// While passing aggregation entries , In inhibition 3.3.4.1/32 This is a detail , Other details are forwarded normally ;
2、 Use the routing strategy to directly manage the sending and receiving routes between neighbors
[r2]ip ip-prefix qq permit 3.3.3.3 32
[r2]route-policy qq deny node 10
[r2-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix qq
[r2-route-policy]q
[r2]route-policy qq permit node 20
[r2]bgp 2
[r2-bgp]aggregate 3.3.0.0 21
[r2-bgp]peer 12.1.1.1 route-policy qq export
3、 Directly use the prefix list to realize the function of the method
[r2]ip ip-prefix ww deny 3.3.3.3 32
[r2]ip ip-prefix ww permit 0.0.0.0 0 le 32
[r2]bgp 2
[r2-bgp]pe 12.1.1.1 ip-prefix ww export
5、 ... and 、 Conditional break IBGP Horizontal segmentation ;
IBGP Horizontal segmentation , Used to avoid being in a AS Internal by IBGP Loops between neighbors ;
The rules : From a iBGP Learned from neighbors BGP The route cannot be passed to the next IBGP neighbor ; because BGP Non direct link neighbor building capability , So you can AS Establish multiple neighbors internally to realize the role of connection relationship backup ; Therefore, a normal equipment only needs to operate bgp, Then it should be in AS The boundary of the , There is ebgp neighbor ;
All runs bgp The devices of the protocol will normally be transferred from other devices AS Learn the routing entry , Then share to the local AS, because IBGP Horizontal segmentation , Lead to local needs and all this AS Inside BGP Equipment setup IBGP Neighborhood ;
IBGP The number of neighborhoods has increased exponentially ;
The so-called conditional breaking means breaking IBGP When dividing horizontally , No loop can be generated ;–AS-BY-AS
1、 Routing reflectors – RR( Reflector )、 client 、 Non client ;
client 、 Non clients must be RR Of IBGP Neighborhood ; The three roles are built into a cluster ( Group );
There can be multiple devices in a cluster , But at least one cluster has one RR And a client ;
The rules :
1)RR From one EBGP Routes learned from neighbors can be shared with other local clients 、 Non client 、EBGP neighbor ;
2)RR Routes learned from a client's neighbor can be shared with other clients locally 、 Non client 、EBGP neighbor ;
3)RR Routes learned from a non client neighbor can be shared with other local clients 、EBGP; Cannot be shared with other non clients ;
notes : Reflected route , During reflection , Its properties do not change ; if RR The received entry is not good , It's not transitive , Will not be reflected ;
[r3-bgp]peer 2.2.2.2 reflect-client //ibgp neighbor 2.2.2.2 Become a local client , At the same time, local become RR;
2、 The federal
Will be a big as Logic is multiple small as; Small AS Use private AS Number , Small AS Inter federal bepg Neighborhood , Can be like EBGP Same delivery route , But you can't modify the properties ; For non federal AS, Only big AS Number ;
1) All starts , Jianlin 、 Management is based on small AS No
2) All devices in the Federation need to declare their location AS Number
3) Small AS Between the ebgp Neighbors need to point to each other as Number
[r3]bgp 64512
[r3-bgp]router-id 3.3.3.3
[r3-bgp]confederation id 2 // Declare local big AS Number
[r3-bgp]confederation peer-as 64513 // The opposite end is small AS Number
[r3-bgp]pe 2.2.2.2 as-number 64512
[r3-bgp]pe 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[r3-bgp]pe 4.4.4.4 as-number 64513
[r3-bgp]pe 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[r3-bgp]pe 4.4.4.4 ebgp-max-hop 2
notes : In practical engineering , Router reflectors are combined with federated technology , Used together in a topology ;
The content of the third day
One 、BGP The right way :
Compare the premises , multiple BGP The routing target is the same , And both are excellent ( The next jump can reach 、 Sync off ), With the same priority ( Manage distance )
optimization Preference_Value The route with the highest value ( Private property , Only valid locally ).
Don't deliver The highest attribute of authority Can interfere with EBGP/IBGP Route selection
Preferred local priority (Local_Preference) The highest route .
IBGP Pass between neighbors Can only , Most often interfere with IBGP The choice of relationship
Preferred manual aggregation > Automatic aggregation >network>import> What we learned from the equivalent .
optimization AS_Path Short routes .
EBGP/IBGP Relationships can be interfered with , But only in EBGP Change between neighbors ;
Origin type IGP>EGP>Incomplete.
Origin attribute i be better than e be better than ?; It can be modified at any interface at the control level ;
For from the same AS The routing , optimization MED Low value .
The default is 0, Announce or reissue ( Turn off auto rollup ) When routing, it carries the local to the destination cost
Most commonly used for interference EBGP The properties of route selection
Preferably from EBGP Routes learned (EBGP>IBGP).
optimization AS Inside IGP Of Metric Measure (cost) The smallest route . Local to BGP Next hop address IGP Of cost Minimum value ;
optimization Cluster_List The shortest route .
optimization Orginator_ID The smallest route .
optimization Router_ID The smallest router publishes routes .
It is preferred to have smaller IP The neighbor of the address learned the routing .
Two 、 attribute : Huawei and cisco All exist 6 Two basic properties The first is a private property
1、 The private property of Huawei equipment Preference_Value
The scope of communication The default value is Big or small
No transmission 0 Big
Global operation :
[r3-bgp]pe 2.2.2.2 preferred-value 1 Local from neighbor 2.2.2.2 All route priority values learned at are modified to 1;
Load sharing : When accessing different target segments , Let traffic flow into different links to communicate ; Take advantage of all the links , Instead of just communicating on a single link ;
Use the prefix to grab the network segment that needs to be modified
[r3]ip ip-prefix w permit 1.1.1.0 24 // Customize the strategy to modify , Pay attention to whether an empty table is needed to allow other routes to pass through
[r3]route-policy w permit node 10
[r3-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix w
[r3-route-policy]apply preferred-value 1
[r3-route-policy]q
[r3]route-policy w permit node 20
[r3-route-policy]q // In the protocol, it is called for a neighbor
[r3]bgp 2
[r3-bgp]peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy w import
// Because the property is private, it is not passed , So when calling , Can only be called in the control level , To influence the local BGP Generate ;
2、 Local priority
The scope of communication The default value is Big or small good
IBGP Between neighbors 100 Big
The first public property
It is also most commonly used for interference IBGP Route selection ,
The most commonly used attribute
Global modification ;
[r4-bgp]default local-preference 101
All local transmissions to IBGP The routing entry for , The local priority is changed to 101;
Load sharing using local priority
[r2]ip ip-prefix p permit 1.1.1.0 24
[r2]route-policy p permit node 10
[r2-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix p
[r2-route-policy]apply local-preference 101
[r2-route-policy]q
[r2]route-policy p permit node 20
[r2-route-policy]q
[r2]bgp 2
[r2-bgp]pe 3.3.3.3 route-policy p export
// The out and in directions of the control level can be used when calling , But it has to be IBGP Neighborhood ;
3、as-path
· Optimization process AS Fewer paths ; The attribute is added automatically in the EBGP Between neighbors ;
[r4]ip ip-prefix as permit 1.1.1.0 24
[r4]route-policy as permit node 10
[r4-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix as
[r4-route-policy]apply as-path 3 4 5 additive
[r4-route-policy]q
[r4]route-policy as permit node 20
[r4-route-policy]q
[r4]bgp 2
[r4-bgp]pe 14.1.1.1 route-policy as import notes : It can be called in or out of the control level , But only in ebgp Operations between neighbors ; Can interfere with ebgp、ibgp Relationship choice ;
Out call x 3 4 5 x For the actual course of AS Number ; The front-end number is the latest AS Number ;
In call 3 4 5 x
Bear in mind :as-path Attributes are also used for EBGP The horizontal division of , If it's artificially added as Number , In the back end of the network , Will cause these routes to be unable to enter these AS; Solution : Add again and again what has passed AS Number ;
4、 Origin attribute
How items are generated
network Declare any route in the local routing table i
import Redistribute local routes learned through other protocols to BGP Agreement ?
egp In the early ebg Routing for protocol learning is redistributed to BGP Agreement e
This property can be modified at any interface of the whole control layer ;
[r4]ip ip-prefix o permit 1.1.1.0 24
[r4]route-policy o permit node 10
[r4-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix o
[r4-route-policy]apply origin egp 2 // Configured here AS For the opposite neighbor AS Number
[r4]route-policy o permit node 20
[r4-route-policy]q
[r4]bgp 2
[r4-bgp]pe 3.3.3.3 route-policy o export
5、MED Multi export authentication properties
BGP The agreement does not exist by default cost;MED It's the rule of using router to optimize the route — First, compare the management distance ( Huawei is the priority ), If you keep comparing metrics ( Huawei for cost)
BGP The protocol carries local to destination under certain conditions cost value ; Local announcement ( Reissue ) After routing in your own routing table , Pass it on to the local ebgp neighbor , Will carry cost value ; For others AS Learning from the same device as The route that comes in , optimization MED The smallest path ;
Administrators can deliver routing at the control level , To modify by hand MDE;
Most commonly used for interference ebgp Route selection ;
Often used in AS1 interference AS2 Yes AS1 The right way ;
[r1]ip ip-prefix med permit 1.1.1.0 24
[r1]route-policy med permit node 10
[r1-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix med
[r1-route-policy]apply cost 10
[r1-route-policy]q
r1]route-policy med permit node 20
[r1-route-policy]q
[r1]bgp 1
[r1-bgp]pe 14.1.1.2 route-policy med export
/* Because in the actual project , Administrators can only work in one AS Middle configuration , So it's impossible to check BGP Table to judge Disconnection results , You can extend ping To solve */
[r1]ping -r -a 1.1.1.1 3.3.3.3
3、 ... and 、BGP Community attributes of –BGP The extended properties of
By default, most manufacturers' products are in BGP Community property is not carried in the protocol
example : Community attributes that control the scope of communication
[r1]route-policy com permit node 10
[r1-route-policy]apply community no-advertise // Modify properties for all traffic
[r1]bgp 1
[r1-bgp]peer 12.1.1.2 route-policy com export
// By default, Huawei devices do not transfer community attributes , So when using the community attribute , Transitivity has to be defined
[r1-bgp]peer 12.1.1.2 advertise-community
// Hop by hop behavior , Every device needs to turn on transitivity
no-advertise If the community attribute exists in the received entry , The route will no longer be delivered
no-export If the received entry has the community attribute , Will not pass on to the next AS
no-export-subconfed If the received entry has the community attribute , Will not pass on to the next small AS
If the network is not small AS, There is only big AS when no-export and no-export-subconfed The effect is the same
边栏推荐
- 搭建一套 gocd 的环境
- How can functional testers spend one month to become advanced automation software test engineers
- Post processing of multisensor data fusion using Px4 ECL
- PHP move_uploaded_file上传移动图片失败
- HCIP第五次作业
- 入行软件测试5年,跳槽3次,我摸透了软件测试这一行
- Thesis reading_ Relation extraction_ CASREL
- 使用PX4的ECL进行多传感器数据融合的后处理
- mongodb分片原理
- LeetCode 797:所有可能的路径
猜你喜欢

LeetCode 797:所有可能的路径

微信小程序:星际旅行飞船乘坐票制作生成

【OFDM通信】基于matlab OFDM多用户资源分配仿真【含Matlab源码 1902期】

微信小程序:微信也可以发闪照了闪照制作生成微信小程序源码下载,自定义闪照时间
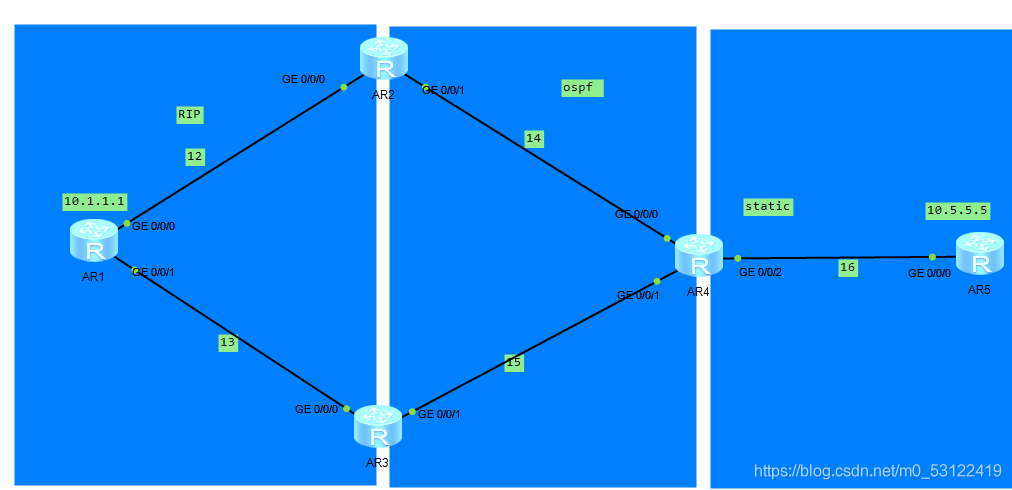
HCIP 重发布实验

Brief ideas and simple cases of JVM tuning - why do you need JVM tuning?

UI自动化定位利器-xpath实战

代码片段管理器SnippetsLab
vmware网络连接出错Unit network.service not found

Parameter passing of 18 generator function
随机推荐
【毕业季_进击的技术er】送别过去两年迷茫的自己。重整旗鼓,大三我来啦
Banner banner
How to use data to tell a wonderful story?
104. 简易聊天室7:使用 Socket 传递对象
How to better organize the minimum web api code structure
[MAC] there is no source option in security and privacy
Automatically add watermark to screenshot
insert into... where not exists插入避免重复的使用
百度飞桨“万有引力”2022首站落地苏州,全面启动中小企业赋能计划
Strong push, quick start to software testing
Getting started with the shutter AppBar
Wechat applet example development: run
传统意义上的互联网式的平台或将不复存在,一个融合的产业特质和互联网特质的全新产业
MVC三層架構
Implementation of the rotation chart
强推,软件测试快速入门,一看就会
Metadata management Apache Atlas Compilation (embedded) deployment and various error records encountered
dolphinscheduler 2.0.5 spark 任务测试总结(源码优化)
Arduino火焰传感器(含代码)
Introduction to s file generated by TEQC for GNSS data quality analysis