当前位置:网站首页>Mongodb aggregate query implements multi table associated query, type conversion, and returns specified parameters.
Mongodb aggregate query implements multi table associated query, type conversion, and returns specified parameters.
2022-06-23 02:05:00 【answer】
Query scenario
mongodb The parameter types of the fields are inconsistent and cannot be associated queried , such as ,id The default is ObjectId, Another table id by String type , You cannot perform an associated query at this time ; For example, the stored data is BigDecimal type , that java Aggregate query in sum It can't be . So if between the tables , Or the field constructed by the constructor is inconsistent with the field type of the database , So the data can not be found .
data structure
From the table 1( License plate table )
@Data
public class Truck{
@Id
protected String id;
/**
* Transportation company ID( Main table id)
*
* @notExist
*/
private String transportId;
/**
* license plate number
*
* @condition
* @notExist
*/
private String truckNo;
/**
* Creation time
*
* @notView
*/
private String createTime;
/**
* Transportation unit ( Fields of the associated table )
*/
private String unitName;
/**
* Invitation code ( Fields of the associated table )
*/
private String inviteCode;
}I only show the key fields , Redundant fields are not displayed , This time, three table associated query is processed . The watch above is from 1 surface , It's not the main table , Put it first because the table is used as a return .
From the table 2( Invitation code table )
notes : Invite people to enter the transportation unit's form , No need to focus on my actual business .
/**
* Invitation code management
* @access=inviteCode
* @parent=appcommon
* @parentName= Daily business management
*/
@Data
public class InviteCode{
@Id
protected String id;
/**
* Invitation code
* @condition
* @notExist
*/
private String code;
/**
* Transportation unit id
*/
private String belongTransportId;
}Main table ( Transportation unit table )
/**
* Transportation unit
*/
@Data
public class TransportUnit{
@Id
protected String id;
/**
* Name of the company
*
* @condition
* @notExist
*/
private String unitName;
/**
* founder ( The invitee )
*
* @notView
*/
private String creator;
}
Three tables I went to some useless content , The key fields of three table associated query are reserved .
mongoDB sql Statements for
As you can see from the table structure , As the primary table, the transportation company table needs to be associated with two other tables . From the return table, we can see what we want to return .
One thing to note is that , Why is the transportation unit used as the main table , Not just because of the Lord id In this table , and ObjectId turn String Good conversion , On the contrary, it is troublesome to handle .
db.transportUnit.aggregate([
{
$project: {
id: {
$toString: "$_id"
},
unitName: 1,
}
},
{
$lookup:
{
from: "truck",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "transportId",
as: "truck"
}
},
{
$unwind: "$truck"
},
{
$lookup:
{
from: "inviteCode",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "belongTransportId",
as: "inviteCode"
}
},
{
$unwind: "$inviteCode"
},
{
$project:{
title:1,
truck:{
unitName:"$unitName",
truckNo:1,
code: '$inviteCode.code',
transportId:1,
creator: 1,
createTime: 1,
}
}
},
]);
Explain it. sql,
- first lookup After using unwind Will single Bson Split into Bson Array , This is indispensable , Or the second floor lookup Will not be related to .
- It's used here project to ObjectId To String, Of course, this is also used to return the specified field .
- Because I used unwind, Finally used group Another compression polymerization .
Query results :

Java Realization
public PageInfo<Truck> findAllByLike(Truck truck, int page, int size) throws GenericException {
String truckNo = truck.getTruckNo();
String transportName = truck.getTransportName();
Criteria criteria;
criteria = Criteria.where("id").not();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(truckNo)){
criteria.and("truckNo").regex(truckNo);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(transportName)){
criteria.and("unitName").regex(transportName);
}
Aggregation agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
project("id").andExpression("toString(_id)").as("id")
.and("unitName").as("unitName"),
lookup(Fields.field("truck"),Fields.field("id"),Fields.field("transportId"),Fields.field("truck")),
unwind("truck"),
lookup("inviteCode","id","belongTransportId","inviteCode"),
unwind("inviteCode"),
project("unitName")
.and("truck.transportId").as("transportId")
.and("inviteCode.code").as("inviteCode")
.and("truck.creator").as("creator")
.and("truck.createTime").as("createTime")
.and("truck.truckNo").as("truckNo"),
match(criteria),
skip((page)*size),
limit(size)
);
Aggregation agg1 = Aggregation.newAggregation(
project("id").andExpression("toString(_id)").as("id")
.and("unitName").as("unitName"),
lookup(Fields.field("truck"),Fields.field("id"),Fields.field("transportId"),Fields.field("truck")),
unwind("truck"),
lookup("inviteCode","id","belongTransportId","inviteCode"),
unwind("inviteCode"),
project("unitName")
.and("truck.transportId").as("transportId")
.and("inviteCode.code").as("inviteCode")
.and("truck.creator").as("creator")
.and("truck.createTime").as("createTime")
.and("truck.truckNo").as("truckNo"),
match(criteria)
);
AggregationResults<Truck> results = mongoTemplate.aggregate(agg,
"transportUnit", Truck.class);
AggregationResults<Truck> results1 = mongoTemplate.aggregate(agg1,
"transportUnit", Truck.class);
List<Truck> trucks = results.getMappedResults();
List<Truck> mappedResults = results1.getMappedResults();
System.err.println(results.getMappedResults().size());
PageInfo<Truck> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(trucks);
pageInfo.setTotal(mappedResults.size());
return pageInfo;
}Here's the problem , Aggregate query , The total number of entries cannot be returned in the case of paging , So we have to pass the same conditions , The total number of entries is also checked separately .
Be careful :match The query criteria must be placed after the associated query , like sql where Conditions are placed after the query results .
Another way to query
Don't use project It is more troublesome to query and perform type conversion , Use addFields It can also be realized .
sql:
db.transportUnit.aggregate([
{
$addFields: {
id: {
$toString: '$_id'
}
}
},
{
$lookup:
{
from: "truck",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "transportId",
as: "truck"
}
},
{
$unwind: "$truck"
},
{
$lookup:
{
from: "inviteCode",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "belongTransportId",
as: "inviteCode"
}
},
{
$unwind: "$inviteCode"
},
{
$project: {
title: 1,
truck: {
unitName: "$unitName",
truckNo: 1,
code: '$inviteCode.code',
transportId: 1,
creator: 1,
createTime: 1,
}
}
},
]);
The results are consistent , I'm not going to show it .
Maybe I'm right mongodb Not very familiar with , Although the other one has been found, it is a little troublesome to construct , I have only achieved a rough idea .
MongoCollection<Document> collection= mongoTemplate.getCollection("transportUnit");
List<Document> documentArrayList= new ArrayList<>();
collection.aggregate(
Arrays.asList(
// Aggregates.match(Filters.eq("_id", new ObjectId())),
Aggregates.addFields(new Field<>("id",new Document("$toString","$_id"))),
Aggregates.lookup("truck","id","transportId","truck"),
Aggregates.unwind("$truck"),
Aggregates.lookup("inviteCode","id","belongTransportId","inviteCode"))
).forEach((Block<? super Document>) documentArrayList::add);
if (documentArrayList.size()>0){
System.err.println(documentArrayList);
}
I owe this article to :https://blog.csdn.net/nyzzht123/article/details/109209847
边栏推荐
- Network module packaging
- MySQL -- how to access the database of a computer in the same LAN (prenatal education level teaching)
- There are animation characters interacting with each other when the mouse slides in the web page
- MySQL basic command statement
- C. Unstable String
- Bc110 tic tac toe chess
- For Xiaobai who just learned to crawl, you can understand it after reading it
- Array part
- Initial structure
- 5. explain function overloading
猜你喜欢

Detailed explanation of makefile usage

Cmake simple usage

II Data preprocessing

7.new, delete, OOP, this pointer

Performance testing -- Interpretation and practice of 16 enterprise level project framework

Arm assembly syntax
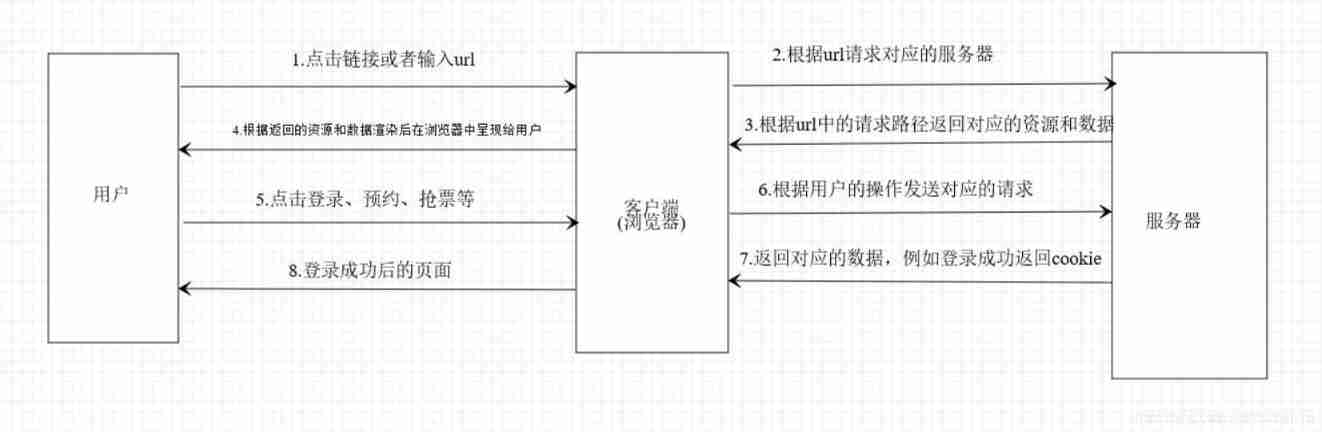
For Xiaobai who just learned to crawl, you can understand it after reading it

Analog Electronic Technology

Data analysis method - user group analysis

Interviewer: why does TCP shake hands three times and break up four times? Most people can't answer!
随机推荐
MySQL -- how to access the database of a computer in the same LAN (prenatal education level teaching)
Analysis of current mainstream video coding technology | community essay solicitation
Array part
//1.11 basic operators
Express framework installation and start service
6. const usage, combination of first and second level pointers
1. Mx6u bare metal program (2) - Lighting master (imitating 32 register version)
Garbled code of SecureCRT, double lines, double characters, unable to input (personal detection)
Common mistakes in C language (sizeof and strlen)
7.new, delete, OOP, this pointer
Vs Code inadvertently disable error waveform curve
Muduo simple usage
Stop automatically after MySQL starts (unable to start)
Performance test -- Jenkins environment construction for 15jmeter performance test
5g core network and core network evolution
278. digital combination
Information theory and coding
JS - single sign on
"Initial C language" (Part 2)
Digital circuit logic design