The department product line itself does DEVOPS platform , Recently, the deployment architecture is also moving forward K8S It's up against , I have to learn K8S. I built it myself K8S Cluster and harbor Warehouse to learn .
1、kubernetes Common core resource objects
1.1、K8s Service deployment
Kubernetes: Used to arrange ( management ) Container of , however kubernetes Do not deploy containers directly , But by deploying a pod Services to indirectly manage containers ,pod What is encapsulated inside is a container .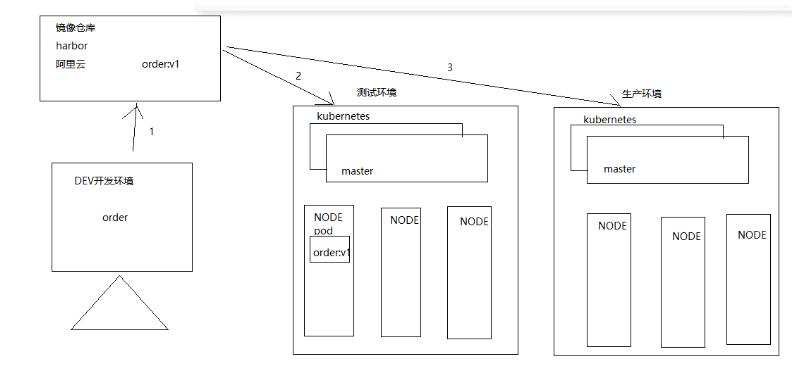
1.2、POD
POD yes kubernetes The smallest task scheduling unit of the cluster .
Kubernetes All resource objects in can use YAML perhaps JSON Format file to define the description . Like the following POD Definition :
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mytomcat
labels:
name: mytomcat
spec:
containers:
- name: mytomcat
image: harbor.hyz.com/library/mytomcat:v1
prots:
- containerPort: 8080
1.3、 label label
Tag definition : Tags are used to distinguish objects ( such as Pod、Service), key / Value to exist ; Each resource object can have multiple tags , Associating objects by tags .
Kubernetes In any API Objects are passed Label Are identified ,Label The essence is a series of Key/Value Key value pair , among key On value Specified by the user .
Label Can be attached to a variety of resource objects , Such as Node、Pod、Service、RC etc. , A resource object can be defined in any number of Label, The same Label It can also be added to any number of resource objects .
Label yes Replication Controller and Service Foundation of operation , Both by Label To correlate Node Running on Pod.
We can bind one or more different resources to the specified resource object Label To achieve multi-dimensional resource grouping management function , For flexibility 、 Convenient resource allocation 、 Dispatch 、 Configuration and other management work .
Some commonly used Label as follows :
Version label :"release":"stable","release":"canary"......
Environment label :"environment":"dev","environment":"qa","environment":"production"
Architecture Tags :"tier":"frontend","tier":"backend","tier":"middleware"
Partition label :"partition":"customerA","partition":"customerB"
Quality control label :"track":"daily","track":"weekly"
problem : In the container cloud environment of server deployment , There are thousands of POD service , So how does the replica controller know what pod The service is controlled by the current replica controller ?
answer : Use tags to determine which services belong to who controls ;
1.4、volume
Volume yes kubernetes Abstract data storage resource object ; and docker Of volume It doesn't matter. ,volume The data volume will put the storage medium ( disk , Network file system ) The data in is attached to pod In the container of service content ,volume yes k8s Managed data volumes ;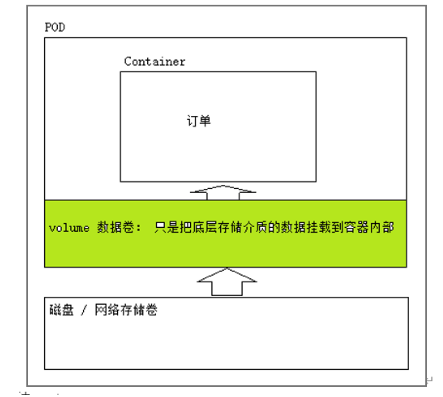
Summary :
1、volume The data volume itself does not store data , Just mount the data to pod In the container inside the service ,volume just k8s Managed resource objects
2、pod Internal service container down ,volume Data volumes are not lost .
3、pod The service outage , Vanished .Volume Data volumes will also disappear , And all the data is lost .
1.5、 Copy controller
Replica controller resource object name : ReplicationController( Eliminate , Only a single label selector is supported ), ReplicaSet( Currently using this replica controller , Support compliance label selector )
effect : It is used to ensure that the number of service copies is consistent with the expected number , That is to say, the service always ensures that the service is in a highly available state .
scene : When the service is deployed online , A certain service after a period of time (POD) It's down. , The replica controller immediately reconstructs the service , Always ensure that the number of services is equal to the previously set number ( for example : Specify the number of services in the service cluster =3, Replica control will always ensure that the number of services is 3);
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: frontend
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
tier: frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: tomcat-demo
image: harbor.hyz.com/library/mytomcat:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: GET_HOST_FROM
value: dns
ports:
- containerPort: 80
problem 1: ReplicaSet The replica controller is simply controlling POD Copy number ( Just a replica controller ), Rolling updates are not supported , Capacity expansion, capacity reduction, etc ; So we have to introduce Deployment Resource objects , Realize service rolling update , Expansion shrinkage capacity .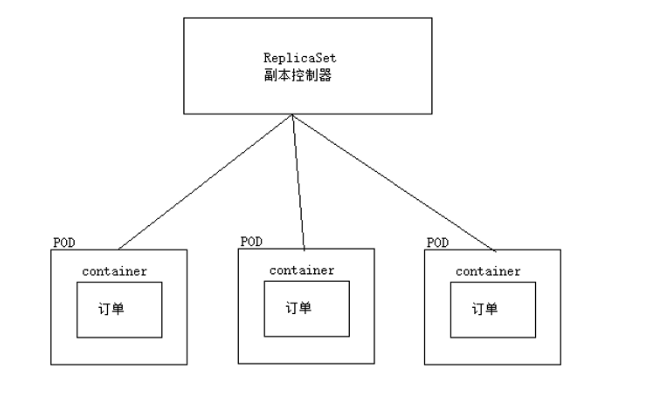
1.6、Deployment
Deployment by Pod and ReplicaSet Provides a Declarative definition method , amount to RC/RS Upgraded version . One of the biggest upgrade features is that we can always know the current pod“ Deploy ” Progress .
Typical application scenarios :
(1)、 Definition Deployment To create Pod and ReplicaSet
(2)、 Scroll upgrade and rollback applications
(3)、 Expansion and cable capacity
(4)、 Pause and resume Deployment
Deployment It's not just scrolling , And you can roll back , If found upgrading to V2 After version , Found service unavailable , You can roll back to V1 edition .
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80

1.7、DaemonSet
DaemonSet Make sure that all ( Or some [ node Smear it ( Think of it as a label ),pod If you don't define tolerance for this stain , that pod Will not be assigned to this by the scheduler node ])Node Run a Pod Copy of . When there is Node When joining a cluster , It will also add a new one for them Pod. When there is Node When removing from a cluster , these Pod It will also be recycled . Delete DaemonSet Will delete all the Pod, Use DaemonSet Some typical uses of :
(1) At every Node Run log collection on Daemon, for example :fluentd、logstash.
(2) At every Node On run monitoring Daemon, for example :Prometheus Node Exporter
Summary : DeamonSet controller , Let every one node Nodes deploy the same service ( copy ), therefore deamonSet It is usually used to deploy some public services .
These public services , Every node needs ;
for example :
demand : In the service cluster network , Collect the logs of each node ( Each node needs to deploy a log collector )
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: daemonset-logstash
namespace: default
labels:
k8s: logstash
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: daemonset-logstash
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: daemonset-logstash
spec:
tolerations:
# These tolerance settings are intended to allow daemons to run on the control plane nodes
# If you don't want to control the operation of plane nodes Pod, You can delete them
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: logstash
image: logstash
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
Reference resources :https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/daemonset/








