当前位置:网站首页>Analysis and application of ThreadLocal source code
Analysis and application of ThreadLocal source code
2022-06-23 22:32:00 【Star sink】
One 、 brief introduction (What)
ThreadLocal, That is, thread variables , Its purpose is to solve the problem of multi-threaded concurrent access , Provides a thread local variable , Let the thread accessing a variable have its own thread local variable value , In this way, there is no contention in the access of threads to variables , And there's no need to synchronize . And locking shared variables , This makes it different for threads to access shared variables serially ,ThreadLocal It is equivalent to letting each thread have its own copy of variables , Trade space for time .
Each thread has one ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap object ( Properties, :threadLocals). stay ThreadLocalMap in ,Entry<key, value=""> Node key by :ThreadLocal t = new ThreadLocal(),value by : The stored variable value of the thread . among ,ThreadLocalMap Of Entry Node key Point to ThreadLocal Is a weak reference , Virtual machines can be garbage collected as soon as they are discovered .
Threadlocal The root cause that can solve the problem of multi-threaded concurrent access is :threadlocal yes Thread Local variables of , Other threads cannot access , Therefore, data isolation in multithreading concurrency can be realized .
Pay attention to distinguish between thredLocals、ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap In the source code ,threadLocals yes Thread Properties of ,threadLocals The corresponding data type is ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap in key The type of ThreadLocal
To make a long story short ,ThreadLocal Is the thread Thread Middle attribute threadLocals The manager of . That is to say, we are interested in ThreadLocal Of get、set、remove All the operation results are for the current thread Thread Example of threadLocals save 、 take 、 Delete operation .
Note the four reference relationships : Strong citation : finger new Out object , Generally, the objects that are not specifically stated are strong references . This kind of object only exists in GCroots It's recycled when it's not found . Soft citation (SoftReference Subclasses of ):GC In case of insufficient memory, only the referenced objects will be recycled . Weak reference (WeakReference Subclasses of ):GC Only this reference object is recycled ( No matter if there is not enough memory ). Virtual reference (PhantomReference Subclass ): No special function , Like a tracer , Cooperate with reference queue to record when the object is recycled .( In fact, all four kinds of references can be used with reference queues , Just pass in the reference queue that needs to be associated in the constructor , In the object call finalize Method will be written to the queue )
Two 、 principle (Why)
1. ThreadLocal Class structure
stay Thread Class , There are two properties :threadLocals、inheritableThreadLocals
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; /* * InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is * maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
and , By looking for Thread Attributes of a class , Find out Thread No member variable provided threadLocals Settings and access methods of , Then the instance pairs of each thread threadLocals How to operate the parameter ?
Then you need to ThreadLocal 了 ,ThreadLocal Provides access to threads Thread Middle attribute threadLocals Of get、set、remove operation .
Make an analogy :
Thread: The product manager ;threadLocals: Ordinary programmers ;ThreadLocal: technology leader
The product manager (Thread) You can't directly influence ordinary programmers (threadLocals) Development task of , Only through technology leader(ThreadLocal) To give programmers (threadLocals) Assigned tasks .
2. ThreadLocal The internal properties of
// Get the next one ThreadLocal Hash magic number of instance
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
// As an atomic counter used by multiple threads at the same time ,AtomicInteger Class provides methods to add and subtract atomically
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();
// Hash magic number ( Growth ), It's also signed 32 Take the positive value of the golden section of the bitwise integer value
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
// Generate next hash magic number
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}Here's a little bit of attention ,threadLocalHashCode It's a final Properties of , And the atomic counter variable nextHashCode And generate the next hash magic number nextHashCode() It's static variables and static methods , Static variables are initialized only once .
Every new one ThreadLocal example , Its internal threadLocalHashCode Will increase 0x61c88647. for instance :
//t1 Medium threadLocalHashCode Variable is 0x61c88647 ThreadLocal t1 = new ThreadLocal(); //t2 Medium threadLocalHashCode Variable is 0x61c88647 + 0x61c88647 ThreadLocal t2 = new ThreadLocal(); //t3 Medium threadLocalHashCode Variable is 0x61c88647 + 0x61c88647 + 0x61c88647 ThreadLocal t3 = new ThreadLocal();
The inductive formula is :
hashCode(i) = (i-1)*HASH_INCREMENT + HASH_INCREMENT (i>0), That is, add one element each time (threadLocal) Into the Entry[], Self increasing 0x61c88647
be address(i)= hashCode & (length-1), namely i The storage location of the location element
threadLocalHashCode It's the following ThreadLocalMap The core variable of the hash algorithm used in the structure , For each ThreadLocal example , its threadLocalHashCode Is the only one. .
threadLocalHashCode The golden section number is used to realize the perfect hash of elements .
3. ThreadLocal Class structure in
stay ThreadLocal Class , It mainly includes initialValue() Initialization method and getMap()、set()、get()、remove()4 There are three core operating methods .
(1)initialValue(): Initialization method
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}This method will be used for the first time by the thread get() Method is called when accessing a variable . But if the thread has previously called this set(T) Method , Will not be called for this thread initialValue() Method .
This implementation only returns null; If the programmer wants the thread local variable to have division null The initial value beyond , Must be right ThreadLocal Subclass , And override this method . Usually , Anonymous inner classes will be used .
(2)getMap(Thread t): obtain ThreadLocalMap example
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}adopt getMap() You can get each child thread Thread Held ThreadLocalMap example , Therefore, there is no concurrent competition .
(3)get(): Get stored local variables
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked"): Involving generic transformations , This note is used to suppress compiler warnings generated due to unchecked type conversions .
Returns the value in the current thread copy of this thread local variable . If the variable has no value for the current thread , First initialize it to call the initialValue() The value returned by the .
(4)set(T value): Set local variables
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}Sets the current thread copy of this thread local variable to the specified value . Most subclasses will not need to override this method , Rely solely on this initialValue() Method to set the value of thread local variables .
(5)remove(): Delete local variables
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}Delete the current thread value of this thread local variable .
From these methods we can see ,set、get、remove The operation objects of are ThreadLocalMap, among ,key= Current thread ,value= Current thread local variable cache value .
3、 ... and 、ThreadLocal Inner class :ThreadLcoalMap
ThreadLocalMap The essence is a HashMap, Used to store thread local values .ThreadLocalMap Class is package private , Allow in Thread Class to declare fields .
ThreadLocalMap Of entry Weak references are used , be conducive to GC Recycling . Key value Key by ThreadLocal The instance itself , Here we use infinite generic wildcards .
Why use Weak reference Well ?
Because when the thread execution ends , We hope to recycle the resources generated in this part , Including so it is used Weak reference , adopt GC To recycle resources .
Be careful , When entry.get() == null when , It means that the key, So you can delete this... From the table entry.
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}1. ThreadLocalMap Member variables
// Initial initialization capacity ,2^4=16
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
// Size as needed ,table.length Must always be 2 The power of
private Entry[] table;
// initialization table The size is 0
private int size = 0;
// threshold , Reach the threshold to expand
private int threshold; // Default to 0
// Set the threshold , threshold = Capacity * Loading factor ( The loading factor is 2/3, The size of the optimal load factor under statistics )
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
// adopt i Calculate next index position ,(i+1)mod len
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
// adopt i Calculate the previous index position ,(i-1)mod len
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}2. ThreadLocalMap Internal methods
(1) Construction method
Initialize a (firstKey, firstValue) New mapping of . ThreadLocalMaps It's inert , Only when there is at least one mapping that can be put in can it really be created .
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// Calculate the mapping location ,threadLocalHashCode Do bit operation with capacity
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}Construct a containing all inheritable from a given parent mapping ThreadLocals New mapping of . This method consists only of createInheritedMap call .
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();
if (key != null) {
Object value = key.childValue(e.value);
Entry c = new Entry(key, value);
int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
while (table[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
table[h] = c;
size++;
}
}
}
}(2)getEntry()
To obtain and key Corresponding Entry. This method itself only deals with direct hash, That is, directly hit the existing key The situation of ; If you don't hit, Will pass getEntryAfterMiss() Method to find the
This is designed to maximize the performance of direct hits , Part of the reason is that it makes the method easy to inline .
Parameters :key – Thread local object
return : And key The associated entry, without , Then for null
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
// Calculate index location
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
// find , Go straight back to
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
// Can't find , Based on linear detection , from i The position starts to traverse backwards
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}(3)getEntryAfterMiss()
When in its direct hash Cannot find... In slot key Search used when Entry Methods
Parameters :key – Thread local object
i – key Of hashcode Table index of
e – table[i] Medium entry
return : And key The associated entry, without , Then for null
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// Traverse backward
while (e != null) {
// Get the entry Of key
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// find , return
if (k == key)
return e;
// The entry Upper key by null, Trigger a continuous segment cleanup
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
// Not for null, It's not equal , Calculate next index , Then make a judgment
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}(4)set(ThreadLocal key, Object value)
Save variables to ThreadLocalMap in .
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// Backup ,backup
Entry[] tab = table;
// obtain table The length of
int len = tab.length;
// Get corresponding ThreadLocal stay table The subscript in
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
/**
* Loop through from this subscript
* 1、 In case of the same key, Then directly replace value
* 2、 If it's time to key Has been recycled out of effect , Replace the invalid key
*/
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// In case of the same key, Then directly replace value
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
// If k by null, Replace the currently invalid k Where Entry node
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
// Find an empty place , establish Entry Object and insert
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
// table Internal elements size Self increasing
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}(5)remove(ThreadLocal key)
rivate void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
// Set the reference to null, convenient GC
e.clear();
// A continuous section cleaning shall be carried out from this position
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}(6)replaceStableEntry(ThreadLocal key, Object value, int staleSlo)
Failures encountered during the operation will be set entry Replace with specified key Of entry. stay value The value passed in the parameter is stored in entry in , Regardless of designation key Of entry Does it already exist .
This method clears the inclusion invalidation entry Of the two null slot All failures in entry
Parameters :key,value
staleSlot – Search for key The first failure encountered in entry The index of
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value, int staleSlot) {
// Backup
Entry[] tab = table;
// obtain table The length of
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
// Record currently retired node subscripts
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
// from staleSlot Subscript starts scanning forward , Find and record the top position value by null The subscript
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
// from staleSlot Subscript start scanning backward , Find and record the last position value by null The subscript
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
// obtain Entry Node corresponding ThreadLocal object
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// If with the new key Corresponding , Direct assignment value, And exchange directly i And staleSlot Value on
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e;
// Re record the invalid node subscript
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
/**
* Calling cleanSomeSlots Before heuristic cleanup
* Will call first expungeStaleEntry Methods from slotToExpunge To table The subscript is null A continuous section of
* The return value is table[] by null The subscript
* then , From this subscript to len Between Do a heuristic cleanup
* In the end, the method inside actually calls expungeStaleEntry
* It can be seen that expungeStaleEntry The method is ThreadLocal Core cleanup function
*/
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
/**
* If the current subscript is invalid , And during the backward scanning process, no invalid Entry node
* be slotToExpunge Assign to current position
*/
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
}
// If not in table Find the right one key, Directly in the current position new One Entry
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
/**
* Above for During the cycle detection
* If you find any invalid Entry node , be slotToExpunge It's going to be reassigned
* It will trigger continuous segment cleanup and heuristic cleanup
*/
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}(7)expungeStableEntry(int staleSlot)
For threads , Segregated The local variable , And it USES the Weak reference , Are likely to GC It was recycled .
- If there are many Entry The node has been recycled , But in table There are still positions in the array , If we don't clean up at this time, we will waste resources
- While cleaning the nodes , Can be followed by non empty Entry The node recalculates the subscript for emission , In this way get We can quickly locate resources , Speed up efficiency .
Parameters :staleSlot – The index of a slot with a null key is known
return :staleSlot Index of the next empty slot after ( All in staleSlot And this slot will be checked for removal ).
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
// Backup
Entry[] tab = table;
// To obtain the length of the
int len = tab.length;
// Will specify the location of value And array subscript location setting null
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
// table Size -1
size--;
Entry e;
int i;
// Traverse all subsequent nodes of the specified node , To be recycled ThreadLocal Nodes are deleted in sequence
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// If it's time to ThreadLocal The node is null, Will value And array subscript location setting null, convenient GC, And put size-1
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
// Not for null, Recalculate the subscript position of the node
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
// If the new subscript position is not the current position
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// From again i Start to find the next one for null The coordinates of the
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}(8)cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n)
Heuristically clean up the recycled Entry,i Corresponding Entry Right or wrong is invalid , It's possible that the failure was recovered , It could be null
There are two places to call this method
1、set Method , Judging whether it is necessary to resize Before , Will clean up and rehash Again
2、 When replacing a failed node , There will also be a clean up
Parameters :
i – Known not to hold invalid entry The location of , Scan from i After the elements
n – Scan control : scanning log2(n) Location , Until we find the invalid entry
return : If any lapses have been deleted entry, Then for true.
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
// Entry The object is not empty , however ThreadLocal This key Have been to null
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
/**
* Call this method to recycle
* It's not just recycling i This is just a node
* It's right i Start to table The subscript is null Within the scope of , Clean up those nodes and rehash
*/
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}(9)rehash()
Repack / To readjust table Size . First scan the entire table , Delete invalid Entry. If this doesn't shrink enough table Size , You need to table super-popular .
private void rehash() {
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use threshold 3/4 For boundaries , When the cleaning is finished table after , If the remaining capacity is still less than the limit, the capacity shall be expanded
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}(10)resize()
Yes table super-popular , Capacity expansion 1 times , It's twice the capacity , Because to guarantee table Is the length of the 2 Of
private void resize() {
// Get old table The length of , And create a length of the old length 2 Times Entry Array
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
// Record the validity of insertion Entry Number of nodes
int count = 0;
/**
* From the subscript 0 Start , Iterate backward one by one to insert the new table among
* 1、 If encountered key Have been to null, be value Set up null, convenient GC Recycling
* 2、 adopt hashcode & len - 1 Calculate subscript , If there is already Entry Array , Then the insertion is detected backward by linear detection
*/
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
// Reset the threshold for expansion
setThreshold(newLen);
// to update size
size = count;
// Point to the new Entry Array
table = newTab;
}(11)expungeStableEntries()
Clear all invalid in the table Entry( A reference object that has been cleared by a program or garbage collector Entry)
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
// e.get() Returns the reference object of this reference object . If this reference object has been cleared by a program or garbage collector , This method returns null .
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}Four 、 Use standard (How)
1. Step on the pit
(1) Step on the pit : Cause memory leaks
Pay attention to distinguish between memory overflow and memory leak :
(1) out of memory :Memory overflow, There is not enough memory for the applicant .
(2) Memory leak :Memory leak, After the program applies for memory , Unable to free requested memory space , The accumulation of memory leaks will eventually lead to memory overflow .
As the picture at the beginning shows , As a key Of ThreadLocal Object has no external strong reference , The next time GC Will produce key The value is null The data of , If the thread does not end in time , A strong reference chain will appear :Thread Ref–>Thread–>ThreadLocalMap–>Entry, This will lead to memory leaks
Use ThreadLocal Preconditions for memory leakage :
- ThreadLocal The reference is set to null, And there is no set,get,remove operation .
- The thread is running all the time , Don't stop .( Thread pool )
- Garbage collection triggered .(Minor GC or Full GC)
We see ThreadLocal Memory leakage conditions are still very harsh , So we can avoid memory leakage by breaking one of the conditions , But in order to better avoid this situation, we use ThreadLocal Follow the following two small principles when :
① ThreadLocal Stated as private static final.
- Private And final Try not to let others modify or change references ,
- Static Represented as a class attribute , Only at the end of the program will it be recycled .
② ThreadLocal Be sure to call... After use remove Method .
- The simplest and most effective way is to remove it after use .
(2) Step on the pit : Thread reuse leads to information confusion
ThreadLocal Thread exclusive mode solves thread safety ThreadLocal It is suitable for isolating variables between programs , And shared scenarios between methods or classes .
The program runs in Tomcat in , The thread that executes the program is Tomcat Worker thread , and Tomcat The worker thread of is based on the thread pool . in other words , The thread pool reuses a fixed number of threads , Once threads are reused , Well, it's likely that for the first time from ThreadLocal The value obtained is the value left over by previous requests from other users . At this time ,ThreadLocal The user information in is the information of other users .
In the code of finally Block of code , Clear... Explicitly ThreadLocal Data in . thus , The new request will not get the wrong user information even if the previous thread is used .
therefore , Similar in use ThreadLocal Tools to store some data , Special attention needs to be paid to after the code runs , Explicitly clear the set data .
2. ThreadLocal Application scenarios of
(1) The transaction operations
In transaction management , stay service Class that involves transactions , The context of each transaction should be independently owned by the database connection Connected , Otherwise, conflicts will occur during data submission and rollback ( To ensure that each time you get the connection, you get the same of the current thread connection).
Spring Use in ThreadLocal To design TransactionSynchronizationManager class , The decoupling of transaction management and data access service is realized , At the same time, it also ensures that connection Thread safety of .
(2)pipeline operation
Use Threadlocal It can be guaranteed in pipeline In operation , Use the same connection to transfer data in batches , Then wait for the return result from the server
(3) Multiple data source switching
- Multiple data source switching , First, you need to instantiate multiple data sources DataSource
- The processing unit of a program is a thread , So with ThreadLocal Dynamically set the data source instance of the current thread
- Last , Need to write a AOP, Intercept methods that require switching data sources , Implement data source modification in the interceptor
(4) Storage Redis Configuration information
redis Although it is a single thread , But if the business is multithreaded redis Words , It may cause thread insecurity .
Use to ThreadLocal It can be used for jedis The storage , So as to realize single thread operation redis, Used for data isolation between threads .
// ThreadLocal Storage redis Client object
private static ThreadLocal<Jedis> LOCAL_JEDIS = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static redis.clients.jedis.Jedis getJedisClient() {
Jedis jedis = LOCAL_JEDIS.get();
if (Objects.isNull(jedis)) {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
LOCAL_JEDIS.set(jedis);
}
return jedis;
}
public static void releaseJedisClient() {
// get obtain redis client
Jedis jedis = LOCAL_JEDIS.get();
if (Objects.nonNull(jedis)) {
jedis.close();
}
LOCAL_JEDIS.remove();
}(5) establish SimpleDataFormat object
calender yes SimpleDateFormat Member variables of ,SimpleDataFormat stay format() Method to store the date in the calendar in , But then call subFormat() Member variables will be used again calendar. therefore , In multithreaded environment , If both threads use the same SimpleDateFormat example , Then it is possible that one of the threads has been modified calendar after , Another thread has also modified calendar, This makes threads unsafe . stay parse() There will also be corresponding problems in the method .
Use ThreadLocal You can make sure that each thread gets a separate SimpleDateFormat The object of , Then naturally there is no competition .
public class DateUtil {
private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> local = new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>();
private static SimpleDateFormat getDateFormat() {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = local.get();
// Create... By lazy loading SimpleDateFormat object
if (dateFormat == null) {
dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
local.set(dateFormat);
}
return dateFormat;
}
public static String format(Date date) {
return getDateFormat().format(date);
}
public static Date parse(String dateStr) throws ParseException {
return getDateFormat().parse(dateStr);
}
}边栏推荐
- Detailed explanation of GC principle
- How to select Poe, poe+, and poe++ switches? One article will show you!
- How to set secondary title in website construction what is the function of secondary title
- Interviewer: the difference between uselayouteffect and useeffect
- Some opinions on microservices
- Targeted, real-time audio and video optimization in remote control
- In the eyes of the universe, how to correctly care about counting East and West?
- How to deploy the deep learning model to the actual project? (classification + detection + segmentation)
- Redis source code analysis -- QuickList of redis list implementation principle
- 应用实践 | Apache Doris 整合 Iceberg + Flink CDC 构建实时湖仓一体的联邦查询分析架构
猜你喜欢

Slsa: accelerator for successful SBOM

openGauss Developer Day 2022正式开启,与开发者共建开源数据库根社区

为什么你的数据图谱分析图上只显示一个值?

為什麼你的數據圖譜分析圖上只顯示一個值?

Opengauss Developer Day 2022 was officially launched to build an open source database root community with developers

游戏安全丨喊话CALL分析-写代码

In the eyes of the universe, how to correctly care about counting East and West?

在宇宙的眼眸下,如何正确地关心东数西算?
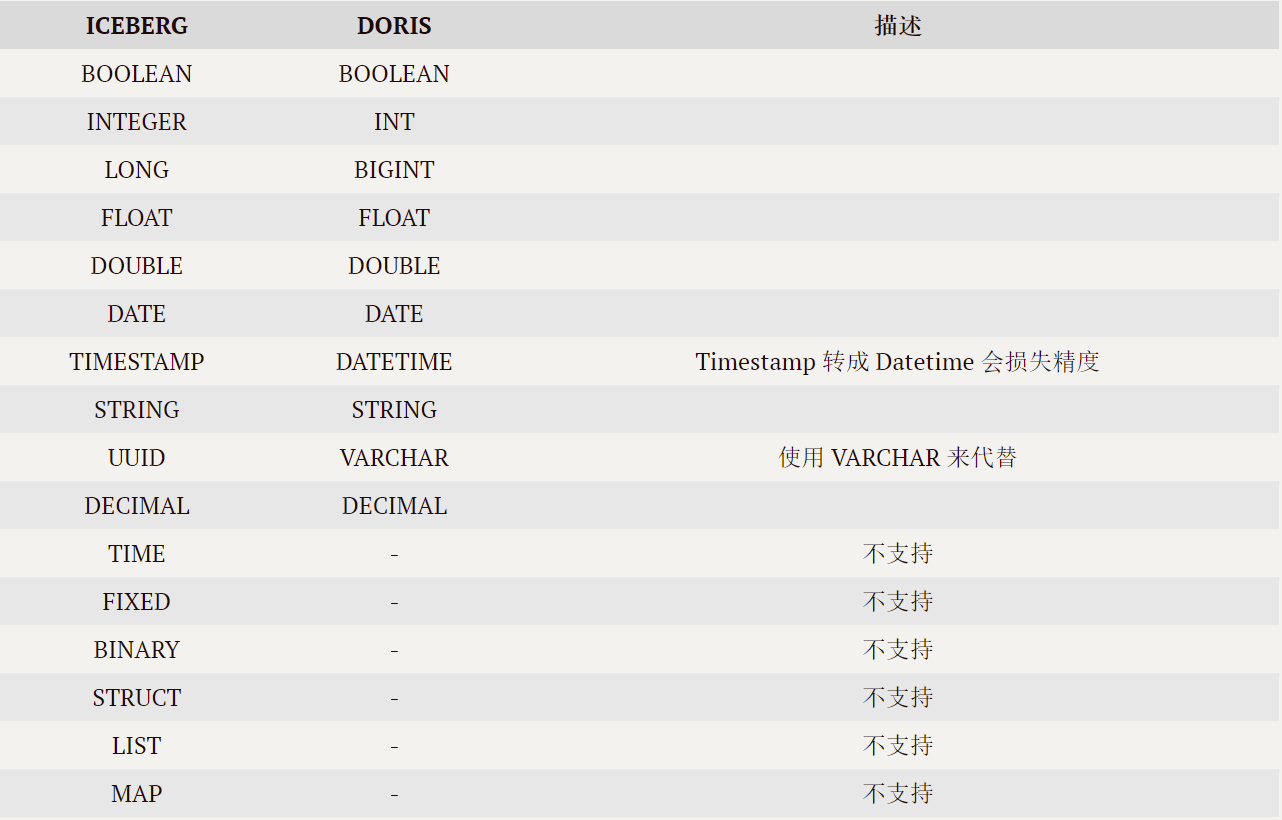
应用实践 | Apache Doris 整合 Iceberg + Flink CDC 构建实时湖仓一体的联邦查询分析架构

脚本之美│VBS 入门交互实战
随机推荐
Using nodejs and Tencent cloud API to identify invoices
What is stock online account opening? Is it safe to open a mobile account?
How to set secondary title in website construction what is the function of secondary title
Error message - Customizing incorrectly maintained – in transaction code ML81N
In depth understanding of Internet of things device access layer
WordPress preview email for wocomerce 1.6.8 cross site scripting
Valid read-only attribute
[tutorial] build a personal email system using Tencent lightweight cloud
How to shut down the server in the fortress machine? What other operations can the fortress machine perform?
Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection
Deep understanding of leakcanary
Ranking of high cost performance commercial endowment insurance products in 2022
Tencent cloud server ubuntu18 installs MySQL and logs in remotely
Some opinions on microservices
How to batch output EAN13 code to PDF
The time deviation is more than 15 hours (54000 seconds), and the time cannot be automatically calibrated
Pourquoi une seule valeur apparaît - elle sur votre carte de données?
Game security - call analysis - write code
Core features and technical implementation of FISCO bcos v3.0
VNC multi gear resolution adjustment, 2008R2 setting 1280 × 1024 resolution