当前位置:网站首页>Page replacement of virtual memory paging mechanism
Page replacement of virtual memory paging mechanism
2022-06-24 21:12:00 【The smell of tobacco】
Preface
Previously, I briefly introduced how virtual memory and physical memory are mapped : Address mapping of virtual memory paging mechanism , But address mapping alone is not enough , In the address mapping, it is said that there will be missing pages , At this point, the operating system is required to load the missing pages into memory . however , What if the memory is full ? After all, virtual memory is usually larger than physical memory , It is impossible to load all the contents of virtual memory into physical memory .
When you need to load the contents of virtual memory , It is found that there is no free space in the physical memory . What about swelling ? Eliminate an old page , You can make room to load new pages . Since elimination is involved , So which page to eliminate is a problem . This article briefly introduces several page replacement algorithms , Or the algorithm of page elimination .
Page replacement algorithm
What kind of page replacement algorithm is good ? In short , Is to reduce the number of page breaks as much as possible . When a page break occurs , Is to lose some performance .
Optimal page replacement
If there is 4 Pages have been loaded , Now choose one of them to be eliminated , Which one to choose ? To minimize the number of interrupts , Then the pages that will be used immediately cannot be eliminated , So calculate it , The last page in the access sequence should be eliminated . for instance :

Why fill the memory first , Instead of loading it when you need it ? Personally think that , It has the following benefits
- According to the principle of sequential execution , Consecutive pages are likely to be used soon . Therefore, the number of missing pages in the future can be reduced
- Even if the loaded page doesn't use , Page breaks are eliminated without performance loss .
- When the program starts , Although it can not occupy all the physical memory , But some of the starting memory will still be allocated . Memory is empty , It is better to load the program first
Because of the limitations of the example , The example is only used as an understanding of the replacement rule , There is no need to compare the advantages and disadvantages of each algorithm
however , Don't be happy too early , This situation is too idealistic , The operating system cannot predict the future , Therefore, this algorithm can not be applied in practice . He spoke , Why can't you mention him , Although it can not be actually realized , But it can be used as a standard to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of other algorithms , The closer to the optimal page replacement, the better .
Next , Several practical permutation algorithms will appear one after another ( Because you can't predict the future , They are all based on historical interviews ):
fifo
Both FIFO, You can tell by name , That page comes in first , Which page will be eliminated first . The same sequence is also used for example :
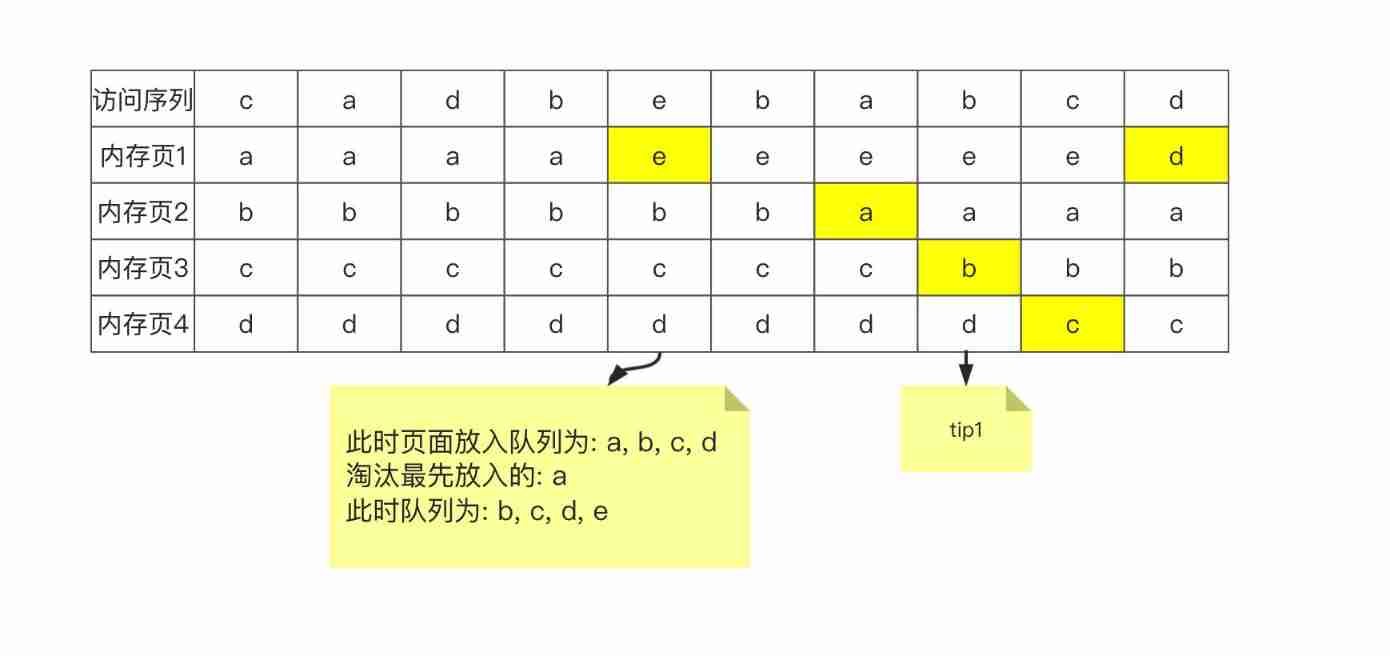
however , Pay attention to my marks tip1 The place of , page b It was just eliminated during the last visit , It will be used again soon , This is this. …
Realization
First in, first out , It's easy to implement , You only need to maintain a queue for page swapping in . Take out from the head of the team to eliminate , Add "yes" to the end of the team .
Belady The phenomenon
Referred to the fifo , So let's talk about the anti attempt of this algorithm Belady The phenomenon . Don't have to go to belady The meaning of this word , It was the first time that he found such a distinguished name .
In common sense , As the physical page capacity increases , Then the frequency of page break will also decrease , Because you can put more pages into memory . however , FIFO There may be such a situation : As the physical page capacity increases , The frequency of page break also increases .
for instance : There is such an access sequence : [a, b, c, d, a, b, e, a, b, c, d, e]. At this time, the physical data is also empty , Read pages into memory in turn . I won't talk about the process , Say the result directly :
- When the number of physical pages is 3 when , produce 9 Page missing interrupt
- When the number of physical pages is 4 when , produce 10 Page missing interrupt
And this kind of Belady The phenomenon , Only FIFO Yes , None of the other algorithms , I specially created a write access sequence , Want to find other algorithms that also have this phenomenon , It is a pity that , Can't find . However, a paper has been written on this phenomenon , Have time to try this .
Most recently unused (LRU)
This is the famous LRU 了 . When it needs to be eliminated , Pages that have just been visited cannot be eliminated , Then eliminate the page that has not been visited for a long time . Another example :

Did you find , Actually LRU It is a quasi optimal algorithm , The idea is , Although I can't predict the future , But I used to know , According to the local principle of the program , If a page has just been visited , Then there is a high probability that he will visit again soon . Pages that have not been visited for a long time , May not visit in the future .
Although the past can not fully predict the future , But fortunately, the locality principle of the program saved us , It can be said to be an approximate solution of the optimal algorithm . But don't be happy too early , No matter how good the idea is, we must come up with a feasible plan .
Realization
To find out which page has not been visited for a long time , You can maintain a linked list of access sequences , The first is the page just visited , The tail is the page that has not been visited for a long time . In this way, when the pages are eliminated, the pages at the end are directly taken for elimination .
To maintain such a linked list , You need to access memory every time , Find this page from the linked list , Move it to the head
To maintain such a linked list , It adds an extra burden to every memory access , The longer the operating system takes up , The less time is left for the application to respond . It can be said that the gain is not worth the loss , It's too expensive .
therefore , although LRU It looks good , But there is no efficient algorithm to implement it
Clock page replacement ( Second chance )
When I introduced the address mapping of the page, I said , Each page in the page table has some flag bits , And one of the flag bits , Identifies whether the current page has been accessed , When a page is accessed , It will be the responsibility of the hardware to mark this as 1, Note that this is done by hardware , So the efficiency is very high .
Can we use this flag bit to realize page replacement ? Reference resources LRU Algorithm , Eliminate the page that has not been visited for a long time . if , First set all access locations to 0, Wait until the next time you need to eliminate a page , Finding an access bit is still 0 The page of , It means that this page has never been visited during this period
however , There are a few memories in reality G, If you change all the page identification bits every time , Efficiency is also very slow . In order to improve efficiency , This algorithm can be approximated again . Connect all the pages into one ring , Use a pointer to traverse the ring , Every time you need to eliminate a page , The pointer starts traversing , The first access bit found is 0 Your page is obsolete , While traversing , By the way, you can visit the page you have passed at 0. This will scan only part of the page at a time , Worst case scan all ( Will be preceded by 0, You'll get it after a scan 0), So the steps of this algorithm are as follows :
- If the page the pointer is currently pointing to , The access bit is 0, Go straight out and point to the next page . Otherwise, go to the next step
- If the current page access bit is 1, Change it to 0 And point to the next page , Go back to the previous step .
For visited pages , It will be eliminated during the second scan , It was given two chances .
We also use the sequence just now to give an example :

The clock algorithm can be said to be right LRU A realizable approximate solution of . It is said that in practical application , The efficiency is relatively close to LRU Of .
Enhanced clock algorithm
When selecting page elimination , If both pages are not accessed , Is there any difference between eliminating one and eliminating the other ? yes , we have , Don't forget , Page replacement , It's not just about switching in , And the operation of exchange , In other words, the data of obsolete pages will still be written back to disk , Of course, if the page has not been modified, there is no need to write back , The data are the same . How do I know if the page has been modified ? As it happens , There is also a tag bit that marks the page modification .
The clock algorithm just used the... In the flag bit Access to a , So how to Modify bit Also added to the criteria , Prioritize pages that have not been modified , It can improve the efficiency of page replacement . Two flags , There are four situations as follows , Discussion by situation :
( Access to a 1, Modify bit 0): Recently visited , Access location is 0( Access to a 1, Modify bit 1): Recently visited , Access location is 0( Access to a 0, Modify bit 0): Not accessed and not modified recently , It can be directly replaced( Access to a 0, Modify bit 1): Not visited recently but modified , Change the location to 0, Waiting for the next visit
however , however , Have you ever thought about it , If the change position in the flag bit is 0 了 , When the operating system performs page replacement , What is the basis for judging whether the current page needs to write back to the disk ? therefore , The modification bit cannot be moved . If you do not change the bit , How to realize it ? Then we need to add additional variables to record :
- On the first scan , Eliminate
( Access to a 0, Modify bit 0)The page of- At the same time, the access bit is changed to 0
- If the first lap is not found , Then the second round is eliminated
( Access to a 0, Modify bit 1)The page of
in other words , and Clock algorithm The data processing rules are the same , The only difference is that the current number of laps for adding additional temporary variable records , The first round is eliminated ( Access to a 0, Modify bit 0) The page of , The second lap will be eliminated ( Access to a 0, Modify bit 1) The page of . That is, the modified page will be reduced .( Of course , There can also be other implementations , But the general meaning remains the same ) Another example :

Do this , Make the modified page more difficult to change out , So as to improve the efficiency of page replacement . Realize and Clock algorithm be similar . yes Clock algorithm Enhanced Edition .
The least commonly used (LFU)
Both LFU, At the time of elimination , Eliminate the least used pages . It is also a way to predict the future based on the past , Used to use more pages , It is likely to be visited many times in the future . LRU The latitude of investigation is time , and LFU The latitude of investigation is the number of times . Again, the figure above :

There is such a situation , The program visits the page frequently at the beginning A, Wait until the program runs smoothly , No more visits to the page A 了 . however , Because the result of counting , page A Number of visits and high , As a result, it has not been eliminated , Long term resident in memory . How to avoid such a problem ? It's also very simple , The problem is that the time latitude is increased , You just need to shift the page count one bit to the left every time ( Divide 2), The number of visits to such pages will decrease over time .
Realization
Since the elimination is based on the number of page visits , So we need to know which page has been visited more often , Which page is visited less . The most intuitive way of thinking is , Record the number of visits to each page , Just find the one with the lowest value during elimination . however , There is one with LRU Same question , How do you implement this algorithm ? Perform the counter plus one operation every time you visit the page ? The price is too high .
Global page replacement
Several page replacement algorithms introduced earlier , It is assumed that the physical memory capacity is fixed and only one process is running in the operating system . But this is different from reality , There are many processes running in the operating system , Each process is allocated a different amount of physical memory . Or when a process starts running, it will switch access between multiple pages , The pages visited after running smoothly are concentrated in several of them .
What we're thinking about here is , How to determine the size of physical memory allocated to different processes so that the overall page failure rate is low . Even allocate different sizes of physical memory at different stages of the process .
There are many global page replacement algorithms , Here are a few , I will not start to say
Workset page replacement
A working set is a process that has recently t Pages visited at a time . The operation rules are as follows :
- When pages are obsolete , Limited elimination of those who no longer work intensively
- If you are all working in a concentrated way , It can be processed through the above page replacement
- If page is no longer in Workset , Will be released
- This is different from the previous algorithm , Even if there is no page break , The page will also be released
- Thus, free memory can be used by other processes
Page loss rate page replacement
be based on Workset page replacement Thought , Increase the working set size when the page loss rate becomes larger , So that more pages can be put into memory . Reduce the working set size when the page vacancy rate becomes small , To free the page , Improve overall memory utilization .
However, it is necessary to calculate the reason for the page vacancy rate , It will lead to an increase in additional expenses .
边栏推荐
- Nifi fast authentication configuration
- Open function
- Dijkstra seeking secondary short circuit (easy to understand)
- Leetcode(146)——LRU 缓存
- Postman assertion
- yeb_ Back first day
- Capture the whole process of accessing web pages through Wireshark
- Packaging_ Conversion between basic type and string type
- Limit summary (under update)
- Network flow 24 questions (round table questions)
猜你喜欢

Microsoft Certification (dynamic 365) test

Berkeley, MIT, Cambridge, deepmind and other industry leaders' online lectures: towards safe, reliable and controllable AI

How Fiddler works

Static routing job supplement

Common data model (updating)

Am, FM, PM modulation technology

(to be optimized and modified) vivado DDR4 SDRAM (MIG) (2.2) IP core learning record
![[普通物理] 光栅衍射](/img/f3/965ff7cd3bb76b4f71b69b9d12ece3.png)
[普通物理] 光栅衍射

Pytest testing framework

After idea installs these plug-ins, the code can be written to heaven. My little sister also has to arrange it
随机推荐
Procedural life: a few things you should know when entering the workplace
How to enhance influence
Go coding specification
After a few years in the testing industry, do you still know a little?
Haitai Advanced Technology | application of privacy computing technology in medical data protection
Background of master data construction
List set Introduction & common methods
Sequential stack traversal binary tree
IDEA Dashboard
Pytest test framework II
Appium introduction and environment installation
伯克利、MIT、劍橋、DeepMind等業內大佬線上講座:邁向安全可靠可控的AI
Vant component used in wechat applet
Create a multithreaded thread class
Berkeley, MIT, Cambridge, deepmind et d'autres grandes conférences en ligne: vers une IA sûre, fiable et contrôlable
Leetcode(455)——分发饼干
Golang daily question
A/B测试助力游戏业务增长
Adding subscribers to a list using mailchimp's API V3
Time standard and format