当前位置:网站首页>2020:VL-BERT: Pre-training of generic visual-linguistic representation
2020:VL-BERT: Pre-training of generic visual-linguistic representation
2022-06-23 04:56:00 【weixin_ forty-two million six hundred and fifty-three thousand 】
Abstract
We introduce a A new general representation of pre trainable visual language tasks --- Vision - Language BERT(VL-BERT).VL-BERT use Transformer Model as the backbone , Take visual and linguistic features as input . Each input element is either a word in the input sentence , Or a region of interest in the input image . It is designed to fit most of the visual - Downstream tasks of language . In order to make better use of the common representation , We are On a large scale Conceptual Captions Pre training on data sets and text only corpora . Extensive experiments show that , Pre training can better align the vision - Language clues , Conducive to downstream tasks .
One 、 Introduce
Vision before - The language task is to be used for image recognition and NLP The pre - trained basic networks of are combined in a task - specific manner , The model of a specific task is directly used for the fine-tuning of a specific target task , There is no general vision - Language pre training . When data for the target task is scarce , Task specific models are likely to have been fitted . Besides , Due to the model design of specific tasks , It's hard to benefit from pre training , The pre training task may be very different from the target . Study vision - The characteristic design and pre training of language task are lack of common ground .
stay VQA in , We seek to derive universal representations that can effectively aggregate and align visual and linguistic information . We developed VL-BERT, One used for vision - A general, trainable representation of language tasks , Pictured 1. The backbone is transformer modular , Visual and linguistic embedded features as input . Each element is either a word in the input sentence , Or input a region of interest in the image (RoI), And certain elements , To disambiguate different input formats . Each element can be based on its content 、 Location 、 Compatibility defined on categories, etc , Adaptively aggregate information from all other elements . A word / One RoI The content features of are domain specific ( The character of the word is Word Piece The embedded 、RoIs yes Faster R-CNN features ), By stacking multiple layers of multimode Transformer Attention module , The exported representation With rich vision - The ability to aggregate and align language cues , And the branches of specific tasks can be added to the above for specific visual - Language task .
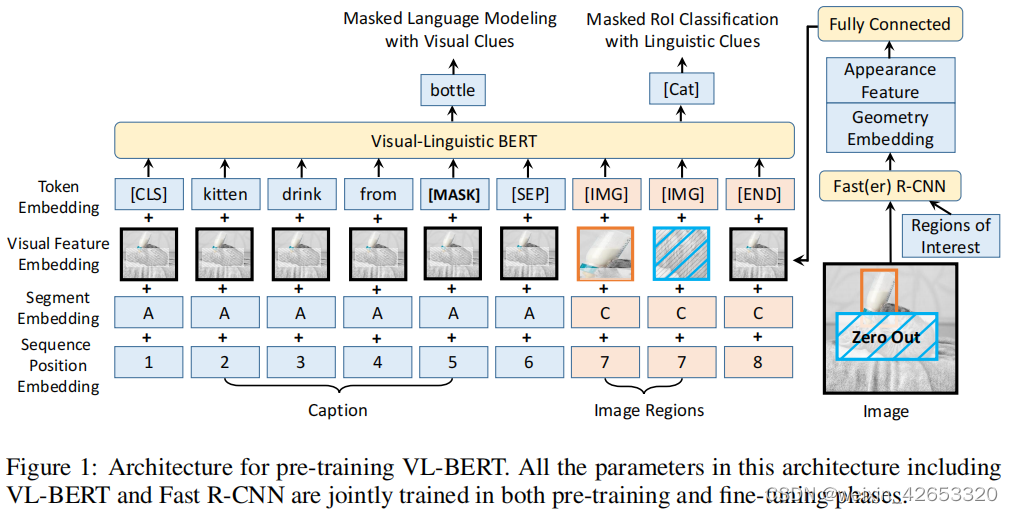
To make better use of common representations , We are Big vision - Language corpora and plain text data sets Yes VL-BERT pretraining . Vision - The pre training loss of language corpus is through Predict random masked words or RoIs And the . This pre training enhances VL-BERT In gathering and aligning vision - The ability to use verbal cues . The loss of pure text corpus is BERT Medium standard MLM Loss , It improves the generalization of long and complex sentences .
Comprehensive experimental evidence shows that , The proposed VL-BERT It has achieved the most advanced performance in various downstream visual language tasks .
Two 、 Related work
Pre training of computer vision Recent studies have shown that , Train from scratch on large-scale target data sets CNN, And ImageNet The effect of pre training is quite . They also noticed , Pre training on appropriate large-scale data sets is very important to improve the performance of target tasks with scarce data .
NLP Pre training A large number of methods based on Transformer Methods , Such as GPT、BERT、GPT-2、XLNet、XLM and RoBERTa. among ,BERT Probably the most popular one , Because of its simplicity and superior performance .
Vision - Pre training of language tasks Before , Design models for specific tasks , among , From existing computer vision and NLP The features derived from the model are combined in a specific way , Only task specific dataset training . stay ViLBERT and LXMERT in , Two single-mode networks are used to input sentences and images respectively , Then there is a cross modal Transformer Combine information from two sources . Cross modal Transformer Your attention patterns are limited , This can improve performance .ViLBERT The author claims that , This two stream design is superior to the single stream unified model . At the suggestion of VL-BERT in , It is based on transformer Unified architecture , There are no restrictions on attention patterns . Visual and linguistic content is fed into VLBERT, In which they interact early and freely . We found that , such VL-BERT The unified model is superior to the two flow designs .
VisualBERT、B2T2 and Unicoder-VL It is also a unified single stream architecture , surface 5 It shows the difference between these models . The simultaneous emergence of these studies shows that , For vision - It is important for language tasks to obtain a general, pre trainable representation .

VL-BERT There are three significant differences from other synchronous work :(1) We found that in all other simultaneous work (ViLBERT and LXMERT) Used in The sentence - Image relationship prediction for pre training vision - Language doesn't help , therefore , Such tasks have not been incorporated into VL-BERT in .(2) We're seeing - Language and plain text datasets VL-BERT pretraining , We found that This joint pre training improves the generalization effect of long sentences and complex sentences .(3) Improved adjustment of visual representation . stay VL-BERT in , Used to export visual features Faster R-CNN Of Parameters are also updated . To avoid the mask of language clues RoI Visual cue leakage in classification pre training task , In addition to the characteristic map generated by the convolution layer , also Mask the input raw pixels .
3、 ... and 、VL-BERT
3.1 review BERT Model
BERT In pre training , Introduce mask language modeling (MLM) And the next sentence prediction pre training task .
3.2 Model structure
Pictured 1, It modifies the original BERT Model , Adapt visual content by adding new elements , A new visual feature is embedded into the input feature . And BERT similar , The backbone is multi-layer and bidirectional Transformer Encoder , Dependency modeling can be done between all input elements .VL-BERT The input of is the region of interest in the image (RoIs) And input the subwords of the sentence ,RoI It can be a bounding box generated by an object detector , It can also be a bounding box annotated in some tasks .
It is worth noting that , Different vision - The input format of language task is different , But because of Transformer The disorderly representation of attention ( For example, the position of a word in a sentence is only encoded by position embedding , Instead of entering the order in the sentence ), As long as the input elements and embedded features are properly designed , You can export a generic representation . There are three types of input elements involved , That's vision 、 Language and special elements , Used to disambiguate different input formats . The input sequence is always represented by a special classification element ([CLS]) Start , Then there are language elements , Then there are visual elements , Finally, a special closing element ([END]) end . Between different sentences in language elements , And a special separation element is inserted between the language element and the visual element ([SEP]). For each input element , Its embedding feature is the sum of four embedding types , That is, mark embedding 、 Visual feature embedding 、 Segmentation embedding and sequence position embedding . among , Visual feature embedding is a newly introduced method to capture visual cues , The other three embeddings follow the original BERT Design of the thesis .
The mark is embedded according to BERT, Language words are embedded as WordPiece The embedded , Assign a special tag to each special element . For visual elements , Assign a special... To each element [IMG] Mark .
Visual feature embedding Firstly, we describe visual appearance features and visual geometry embedding respectively , Then how to combine them to form visual feature embedding . Visual elements correspond to a RoI, adopt Faster R-CNN Extract visual appearance features , Each before the eigenvector RoI The output layer of is embedded as a visual feature . For non visual elements , The corresponding visual appearance feature is the feature extracted from the whole input image , By covering the entire input image RoI On the application Faster R-CNN.
Visual geometry embedding is designed to inform VL-BERT The geometric position of each input element in the image . Visual feature embedding is attached to each input element , This is the output of a full connection layer with the input of visual appearance features and the connection embedded in visual geometry .
Split embed Three types of segmentation , To separate input elements from different sources ,A and B The words from the first and second input sentences, respectively ,C Represents... From the input image RoI.
Sequence position embedding A learnable sequence position embedding is added to each input element , Indicates its order in the sequence , Such as BERT. The sequence position embedding in visual elements is the same .
3.3 Preliminary training VL-BERT
We are in two visions - Pre training on language and plain text datasets VL-BERT, Use Conceptual Captions Data set as visual language corpus , To avoid in this short 、 Over fitting in simple text scenes , We also perform pre training on a plain text corpus with long and complex sentences , utilize BooksCorpus And the English Wikipedia dataset .
Mask language modeling with visual cues This task not only models the dependencies between sentences and words , It also aligns visual and linguistic content . During pre training , stay Softmax Driven by cross entropy loss , Input the final output features corresponding to the masked words into the classifier of the whole vocabulary .
Mask with language clues RoI classification
3.4 fine-tuning VL-BERT
We just need to ask VL-BERT Provide input and output in appropriate format , And fine tune all network parameters end-to-end .
Four 、 experiment
4.2.2 Visual Q & A


In the process of the training VL-BERT Improved 1.6% Performance of , This proves the importance of pre training .VL-BERT And BUTD Share the same input ( That's the problem 、 Images and roi)、 Output and experimental setup ,BUTD Is a popular model designed specifically for tasks , For all that ,VL-BERT The accuracy of is still higher than BUTD Of 5% above . except LXMERT Outside , our VL-BERT Better performance than other parallel work . This is because LXMERT A large number of visual question answering data are pre trained ( It aggregates almost all the data based on COCO And the visual genome VQA Data sets ). Although our model is pre trained only on subtitle and text only datasets , But this is related to VQA There are still gaps in the task .
5、 ... and 、 summary
In this paper we propose that VL-BERT, One used for vision - Trainable universal representation of language tasks .VL-BERT Do not use modules specific to specific tasks , Instead, a simple and powerful Transforemr Model as the backbone . It is pre trained on large-scale concept Title datasets and plain text corpora . Extensive empirical analysis shows that , The pre training program can better align the vision - Language clues , Thus, it is beneficial to downstream tasks . some time , We are looking for better pre training tasks , This may benefit more downstream tasks ( for example , Image title generation ).
边栏推荐
- What are the types of independent station chat robots? How to quickly create your own free chat robot? It only takes 3 seconds!
- ICer技能03Design Compile
- 积分商城的三种运营方向
- Magnetoresistive saturation
- altium designer 09丝印靠近焊盘显示绿色警告,如何阻止其报警?
- const理解之二
- 云函数实现模糊搜索功能
- Kail 渗透基本素养 基础命令
- Current relay hdl-a/1-110vdc-1
- Abnova ABCB10(人)重组蛋白说明书
猜你喜欢

ICer技能03Design Compile

ApiPost接口测试的用法之------Post

Openwrt directory structure

PCB -- bridge between theory and reality

Abnova acid phosphatase (wheat germ) instructions

Dpr-34v/v two position relay

Abnova actn4 purified rabbit polyclonal antibody instructions

Common concepts and terms in offline warehouse modeling

Abnova liquidcell negative enrichment cell separation and recovery system

VGG 中草药识别
随机推荐
Halcon knowledge: binocular_ Discrimination knowledge
智能语音时代到来,谁在定义新时代AI?
PTA: price of 7-65 beverage
Pta:7-60 pet growth
Using editor How to handle MD uploading pictures?
使用Live Chat促进业务销售的惊人技巧
1183. 电力
const理解之二
关于php里tcp通讯用swoole框架出现的小问题
AD9使用技巧拾遗
DPR-34V/V双位置继电器
Const understanding one
Current relay hdl-a/1-110vdc-1
Laravel 通过服务提供者来自定义分页样式
Magnetoresistive saturation
Notes on writing questions in C language -- free falling ball
Altium designer 09 screen printing displays a green warning near the pad. How to prevent it from alarming?
重装Cadence16.3,失败与成功
ICer技能01正则匹配
项目总结1(头文件,switch,&&,位变量)