当前位置:网站首页>Model loading of assimp Library under QT
Model loading of assimp Library under QT
2022-07-23 20:09:00 【Elsa's fan brother】
Assimp Library overview
A very popular model import library is Assimp, It is Open Asset Import Library( Open asset import library ) Abbreviation .Assimp Can import many different model file formats ( And can also export part of the format ), It will load all the model data into Assimp In the general data structure of . When Assimp After loading the model , We can start from Assimp Extract all the data we need from the data structure . because Assimp The data structure remains unchanged , No matter what kind of file format you import , It can abstract us from these different file formats , Access the data we need in the same way .
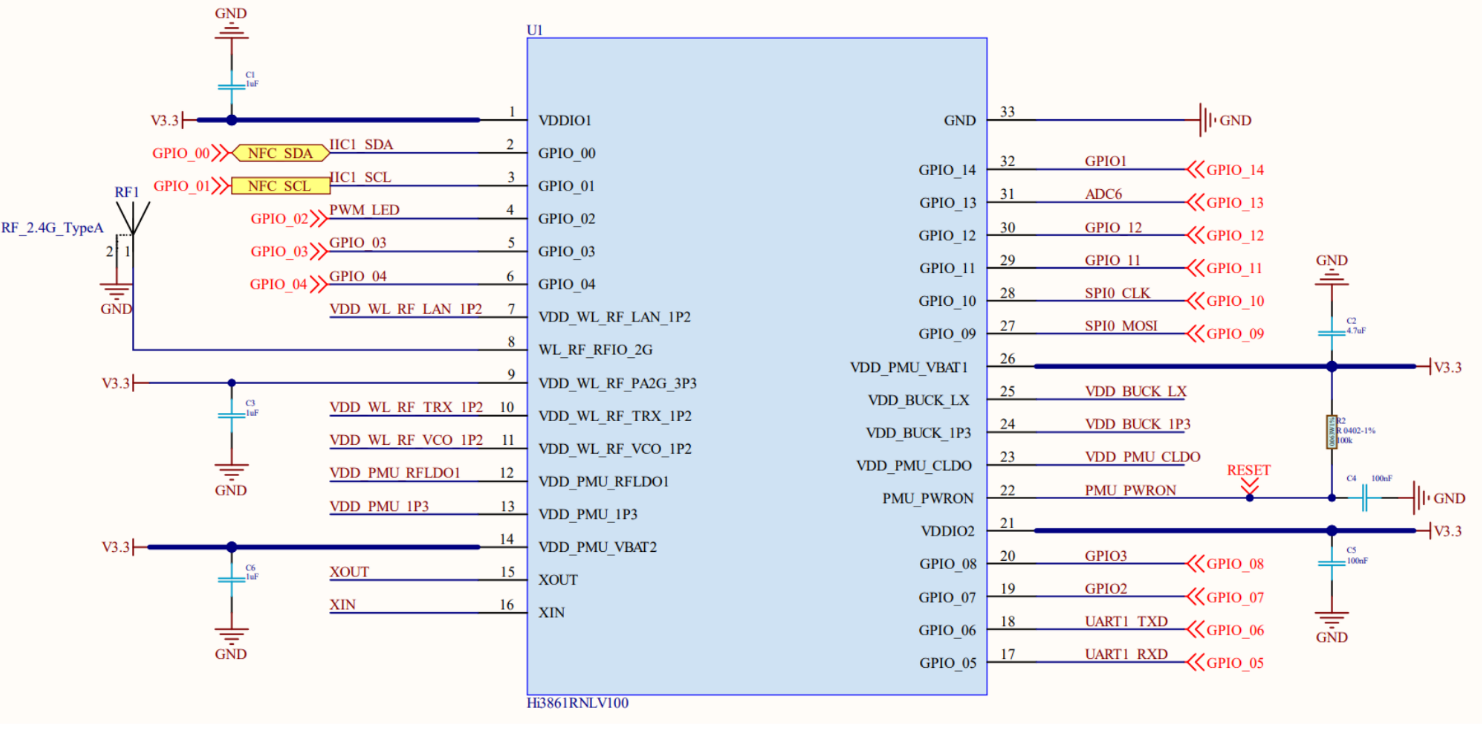
When using Assimp When importing a model , It usually loads the entire model into a scene (Scene) object , It will contain the imported model / All data in the scene .Assimp The scene is loaded as a series of nodes (Node), Each node contains an index of the data stored in the scene object , Each node can have any number of child nodes .Assimp data-structured ( simplify ) Model as follows :
List of articles
Load model
void Model::loadModel(const QString& path)
{
Assimp::Importer importer;
const aiScene *scene=importer.ReadFile(path.toLatin1(),
aiProcess_Triangulate |
aiProcess_GenSmoothNormals |
aiProcess_FlipUVs |
aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace);
if(!scene || scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE || !scene->mRootNode)
{
qDebug() << "ERROR::ASSIMP:: " << importer.GetErrorString() << endl;
return;
}
int index=path.lastIndexOf('/');
rootPath=path.left(index);
processNode(scene->mRootNode,scene);
processMaterials(scene);
}
class Assimp::Importer
CPP-API:Importer Class forms a to Open Asset Import Library Functional c++ Interface .
Create an object of this class , And call ReadFile() To import files . If the import is successful , Function returns a pointer to the imported data . Data preserves the properties of the object , For read-only access . The imported data will match Importer Objects are destroyed together . If the import fails ,ReadFile() Return to one nullptr The pointer . under these circumstances , You can call GetErrorString() To retrieve human readable error descriptions . You can use a single Importer Instance called more than once ReadFile(). actually , structure Importer Objects involve considerable allocation , It may take some time , So it's best to reuse them as often as possible .
If you need Importer Do custom file processing to access files , Realization IOSystem and IOStream, And in the call ReadFile() Previous call SetIOHandler() To provide a custom IOSystem Examples of implementation . If customization is not specified IO The handler , Then use the standard c++ IO Default handler for logic .
Be careful :
One Importer Instances are not thread safe . If you use multiple threads to load , Each thread should maintain its own Importer example .
ReadFile
const aiScene *ReadFile(const char *pFile, unsigned int pFlags)
Read the given file , If it succeeds, the file content is returned .
If the call succeeds , The contents of the file will point to a aiScene The pointer of the object returns . The returned data is read-only , The importer object retains ownership of the data , And the data will be destroyed at the time of destruction . If the import fails , return nullptr. You can call GetErrorString() To retrieve human readable error descriptions . The previous scenario will be deleted in this call .
return:
Pointer to imported data , If the import fails nullptr. The pointer to the scene still belongs to Importer example . Use GetOrphanedScene() To get its ownership .
Note:
Assimp It can automatically determine the file format of the file .
Parameters:pFile: Path and file name of the file to be imported .pFlags: Optional post-processing steps after successful import . Provide aiPostProcessSteps Bitwise combination of signs . If you want to check the imported scene first to adjust your post-processing settings , Consider using ApplyPostProcessing().
ApplyPostProcessing
constaiScene *ApplyPostProcessing(unsigned int pFlags)
Apply post-processing to an imported scene .
This is strictly equivalent to calling ReadFile(). however , You can use this separate function to check the imported scene , To fine tune your post-processing settings .
pFlags
pFlags Optional post-processing steps to be performed after successful import , It's some post-processing (Post-processing) The option to , Can be found in Official website Find specific information .
for example :
- aiProcess_Triangulate, We tell Assimp, If the model is not ( All ) It's made up of triangles , It needs to transform all the primitive shapes of the model into triangles .
- aiProcess_FlipUVs Will be flipped during processing y Texture coordinates of the axis
- aiProcess_GenNormals: If the model does not contain a normal vector , Create normals for each vertex .
- aiProcess_SplitLargeMeshes: Divide the larger mesh into smaller sub meshes , If your rendering has a maximum number of vertices , Only smaller meshes can be rendered , Then it will be very useful .
- aiProcess_OptimizeMeshes: Contrary to the previous option , It will splice several small grids into a large grid , Reduce drawing calls for optimization .
Process the imported model

void Model::processNode(aiNode *node,const aiScene *scene)
{
for(unsigned int i=0;i<node->mNumMeshes;i++)
{
aiMesh* mesh=scene->mMeshes[node->mMeshes[i]];
matrialMeshesMap[mesh->mMaterialIndex].push_back(meshes.size());
meshes.push_back(processMesh(mesh));
}
for(unsigned int i=0;i<node->mNumChildren;i++)
{
processNode(node->mChildren[i],scene);
}
}
aiScene

main parameter
unsigned int aiScene:: mFlags
AI_SCENE_FLAGS_XXX Any combination of signs .
By default , The value is 0, There is no sign . Most applications want to reject all settings AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE Bit scene .
if(...||scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE||...){
...
}
Said when scene->mFlags When this item is included .
struct aiNode
mRootNode,aiNode->mChildren[i] All are aiNode type
There are members
C_STRUCT aiNode ** mChildren
Children of this node . If mNumChildren by 0 Then for nullptr.unsigned int * mMeshes
The mesh of this node .aiString mName
The name of the node .unsigned int mNumChildren
The number of child nodes of this node .unsigned int mNumMeshes
Number of meshes for this node .aiNode * mParent
Parent node .aiMatrix4x4 mTransformation
Transformation relative to the parent node of the node .
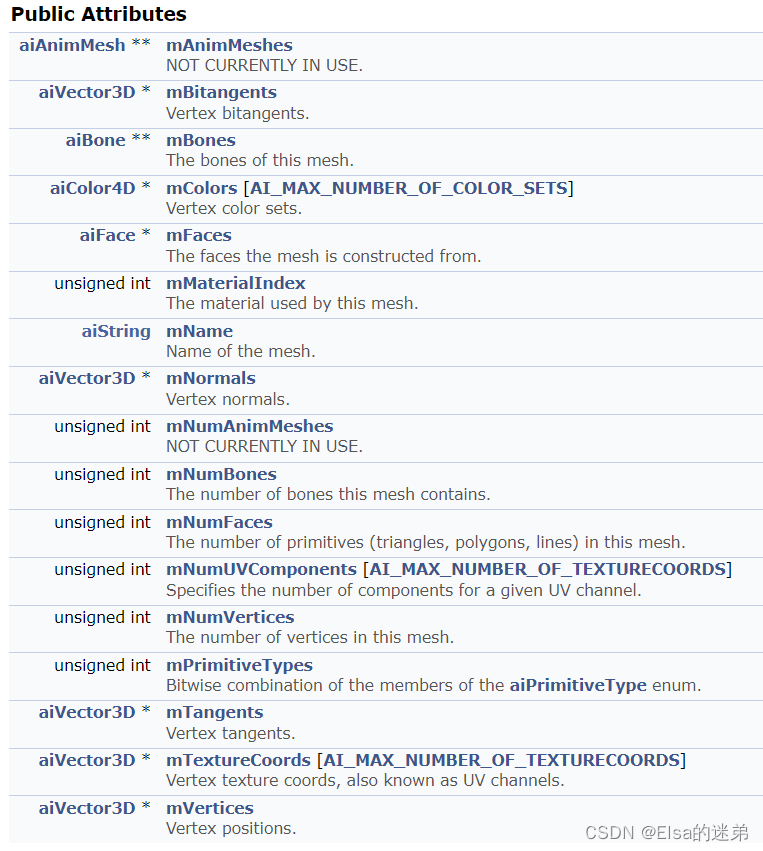
aiMesh** mMeshes
A mesh represents a geometry or model and a material .
Grid contains :
- name (
aiString mName) - The vertices (
aiVector3D * mVertices) Number of vertices (unsigned int mNumVertices) - normal (
aiVector3D * mNormals) - Tangent line , Double tangent (
aiVector3D * mTangents,aiVector3D * mBitangents) - Noodles (
aiFace * mFaces) Number of faces (unsigned int mNumFaces)【 Faces form a network 】 - Material subscript (
unsigned int mMaterialIndex)【 One mesh There is only one material 】 - bones (
aiBone ** mBones) Number of bones (unsigned int mNumBones) - Vertex color set (
aiColor4D * mColors [AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_COLOR_SETS]) - Vertex texture coordinates , Also known as UV passageway .(
aiVector3D * mTextureCoords [AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS]) - UV Number of channel components (
unsigned int mNumUVComponents [AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS])

aiMaterial** mMaterials
Data structure of materials .
Material data is stored in key value structure . A single key value pair is called “ Material properties ”.c++ Users should use aiMaterial Provide member functions to handle material properties ,C Users must insist on using aiMaterialGetXXX Unbound functions of the family . The standard library defines a set of standard keys (AI_MATKEY_XXX).
Get the number of textures for a specific texture type .
unsigned int GetTextureCount (aiTextureType type) const
enum aiTextureType
aiTextureType_NONE,aiTextureType_DIFFUSE,aiTextureType_SPECULAR,aiTextureType_AMBIENT,aiTextureType_EMISSIVE( Self illumination texture ),aiTextureType_HEIGHT( Bump map ),aiTextureType_NORMALS( Normal map ),aiTextureType_SHININESS ( The glossiness of the material ),aiTextureType_OPACITY ( Pixel opacity ),aiTextureType_DISPLACEMENT ( Displacement mapping ),aiTextureType_LIGHTMAP ( Light map texture , Also known as ambient occlusion ),aiTextureType_REFLECTION Reflective structure .
Contains the perfect mirror reflection color . Rarely used , Almost never used in real-time applications .aiTextureType_UNKNOWN Unknown texture .
A texture reference that does not meet any of the above definitions is considered “ Unknown ”. It is still imported , But it is excluded from any further post-processing .
Get all parameters related to a specific texture groove from the material .
aiReturn GetTexture ( aiTextureType type,
unsigned int index,
aiString *path,
aiTextureMapping *mapping=NULL,
unsigned int *uvindex=NULL,
float *blend=NULL,
aiTextureOp *op=NULL,
aiTextureMapMode *mapmode=NULL
) const
adopt type and index You can get specific textures , The return value is path route ,
Parameters :
- mapping Texture mapping . allow NULL As value .
- uvindex Receive texture UV Indexes .NULL Is a valid value .
- blend Receive the blending factor of the texture ,NULL Is a valid value .
- op Receive the texture operation to be performed between the current texture and the previous texture . allow NULL As value .
- mapmode Receive the mapping mode for texture . Parameters can be NULL,
But if it is a valid pointer , It must point to an array 3 individual aiTextureMapMode
( One for each axis :UVW The order (=XYZ)).
Example :
texCount=scene->mMaterials[i]->GetTextureCount(aiTextureType_DIFFUSE);
if(texCount>0)
{
scene->mMaterials[i]->GetTexture(aiTextureType_DIFFUSE,0,&texturePath);
textureId=findTextureIndex(&texturePath);//findTextureIndex For custom functions
mat.diffuseTexture=textureId;
}
Back to texturePath Is the file name , So in use QImage image=QImage(path).mirrored(false,false); when path To add the root directory and the file name .
Be similar to
QString texPath=QString("%1/%2").arg(rootPath).arg(texturePath->C_Str());
or
QImage data(directory.filePath(str.C_Str()));
Get color information
aiColor3D color;
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_AMBIENT,color);
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_DIFFUSE,color);
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_SPECULAR,color);
Get gloss information
scene->mMaterials[i]->Get(AI_MATKEY_SHININESS,mat.shininess);

边栏推荐
- Powercli moves virtual machines from host01 host to host02 host
- Redis坏了怎么办?
- Decryption: PTP clock synchronization in intelligent substation (Beidou clock server)
- Viewing the "Empathy" energy of iqoo 10 pro from 200W super flash charging
- 梅科爾工作室-小熊派開發筆記2
- 安装Win11找不到固态硬盘如何解决?
- 3D point cloud course (VII) -- feature point description
- C language leak detection and filling (1)
- 2022 Shandong old age Expo, Shandong elderly care exhibition, China International elderly care service industry exhibition was held in September
- 2022DASCTF MAY
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
21. Mix in details
Energy principle and variational method note 14: summary + problem solving
Leetcode 151. invert words in strings
Training log on July 22, 2022
MySQL data recovery - using the data directory
TASK03|回归
新品上市|A股场内衍生品大盘点
干货!神经网络中的隐性稀疏正则效应
梅科尔工作室-华为14天鸿蒙设备开发实战笔记四
Viewing the "Empathy" energy of iqoo 10 pro from 200W super flash charging
20.ref与props
BM14 链表的奇偶重排
Leetcode - the nearest sum of three numbers
Non local mean filtering / attention mechanism
R language ggplot2 visualization: use ggplot2 to visualize the scatter diagram, and use the theme of ggpubr package_ The classic2 function sets the visual image to classic theme with axis lines
Energy principle and variational method note 18: virtual force principle
Powercli management VMware vCenter batch deployment export import
能量原理与变分法笔记16:虚位移原理的求解
[unity project practice] level unlocking
Huawei cloud stack [interview]



![[激光器原理与应用-8]: 激光器电路的电磁兼容性EMC设计](/img/98/8b7a4fc3f9ef9b7e16c63a8c225b02.png)