当前位置:网站首页>Hcip--- BGP related configuration
Hcip--- BGP related configuration
2022-07-23 12:41:00 【Newcomer_ L】
BGP Detailed explanation of configuration problems
6,BGP Basic configuration
(1)BGP Basic configuration of neighbor building
1,EBGP Peer relationship direct connection and neighbor building
[r1]bgp 1
---- start-up BGP process
---- hinder 1 It's not a process number , Instead, configure the router AS Of AS Number [r1-bgp][r1-bgp]router-id 1.1.1.1
--- To configure RID
[r1-bgp]peer 12.0.0.2 as-number 2
--- Specify peer relationships manually
[r1]display bgp peer
--- see BGP Command of neighbor table
2,IBGP Loopback neighbor building between peer relationships
because IBGP Neighbors in the same AS in , In general , One AS in There are a large number of backup paths , If you use a physical interface to establish a neighbor relationship , These backup or load balancing resources will be wasted , Therefore, it is recommended to use Loop back to the interface IBGP Establishment of peer relationship .
[r2-bgp]peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 2
[r2-bgp]peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
--- Assigned to 3.3.3.3 Used in contracting Source IP The address is loopback interface 0 Of IP Address .
Be careful : When establishing peer relationships using loopback interfaces , Be sure to modify the sending interface .
- EBGP Indirect neighbor building between peer relationships
Be careful : stay EBGP Peer relationships , It's usually Do not have The routing basis of non direct connection and neighbor building , therefore , need Ensure that the address is reachable first Talent .
[r4-bgp]peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 3
[r4-bgp]peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[r4-bgp]peer 5.5.5.5 ebgp-max-hop 2
--- because EBGP Peers are usually directly connected to each other , therefore , In the packet TTL Value is set to 1, If you want to build a neighbor without direct connection , You need to increase this value .
[r5-bgp]peer 4.4.4.4 ebgp-max-hop
--- If it is not followed by parameters , Then it means that TTL Change the value to the maximum value 255
2, Publish route
1,network--- stay BGP Can only be used to publish routing entry information
Be careful : As long as it is Routing entry information in the routing table ,BGP Fine adopt Network To send .
[r1-bgp]network 1.1.1.0 24
--- The information and mask of the target network segment must be completely consistent with those in the routing table .
[r1-bgp]display bgp routing-table
--- see BGP surface
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 i
Network --- Target network segment information and mask information
NextHop---BGP A path attribute of ---- Who sent the routing information , The next jump is who , If you sent it yourself , Then the next jump is 0.0.0.0.
Status code
* --- representative You can use --- Every time the device receives a hop of routing information , Will check the accessibility of its next hop . That is, in the routing table according to the next hop recursive query , as long as Can be up to , Then change the routing information You can use .
> --- representative optimization --- When it arrives at the same network segment There are multiple routing information when ,BGP Will be in it According to the attribute, select one and load it into the routing table in . This preferred route will give this tag .
Be careful : Only one route entry is available and preferred , He can be added to the route
In the table , Can also be passed on to others BGP peers .
1.1.1.0/24 EBGP 255--- adopt EBGP What peers learn BGP Routing information , It is marked as EBGP, The default priority is 255.
- -- Status code I --- representative BGP Routing information is from oneself IBGP Learned from peers
i 1.1.1.0/24 12.0.0.1 --- Because in AS It's inside AS-BY-AS gauge be , therefore , Passed by default The attribute information is consistent Of , Because this next hop also belongs to one of the path attributes , By default, it will not pass , It may cause the routing availability verification to fail .
[r2-bgp]peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local
--- In giving 3.3.3.3 The transmission of routing information is to The next hop attribute is changed to local
1.1.1.0/24 IBGP 255 --- adopt IBGP What peers learn BGP Routing information , It is marked as IBGP, The default priority is 255.
In the routing table NextHop Direct use is BGP Property , Because availability verification has been carried out before , therefore , It can ensure that recursive search can find the next hop .
- Reissue
[r2-bgp]import-route ospf 1
--- take OSPF Import the routing information into BGP among .
OGN --- Origin code ---I,e,?--- Used to identify the origin of routing entries
I --- Represents that the routing information originates from IGP agreement ( Not limited to IGP agreement , Including static , Direct connection ), Represents that the route entry originated from AS Inside --- adopt network The origin code of the published routing information is I
E --- Represents that the routing information originates from EGP agreement ---EGP refer to BGP The external gateway protocol used before
?--- Routes learned through other than the above two methods --- Reissue The imported route origin codes are ?
- BGP Route aggregation for
Automatic aggregation
- This method can only be used for Reissue released Routing information takes effect .
2, The route of automatic aggregation can only follow Aggregate main classes , Will cause huge Routing black holes . therefore , Huawei equipment BGP The auto aggregation function of is turned off by default .
1, Grab traffic
[r1]ip ip-prefix aa permit 172.16.0.0 22 greater-equal 24 less-equal 24
2, Make routing strategy
[r1]route-policy aa permit node 10
Info: New Sequence of this List.
[r1-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix aa
[r1-route-policy]q
3, Call the routing policy during republishing
[r1-bgp]import-route direct route-policy aa
[r1-bgp]summary automatic
--- Turn on the method of automatic aggregation
Info: Automatic summarization is valid only for the routes imported through the
import-route command.
*> 172.16.0.0 127.0.0.1 --- A new summary route will be published through automatic aggregation , He is No subnet mask Of , Because it is summarized according to the main category , be The subnet mask takes the default value of the main class . And the next hop attribute of the route information published through aggregation is 127.0.0.1
Be careful : After automatic aggregation , The published summary routing information will generate an empty interface pointing to the summary in the local routing table , Automatic anti loop .
Status code ---S ---suppressed--- Inhibition --- Suppress the delivery of routing entries
Manual aggregation
--- Because automatic aggregation has two drawbacks , therefore , If the summary needs to be accurately controlled , Manual aggregation would be a better solution .
[r1-bgp]aggregate 172.16.0.0 22
--- Manual aggregation
*> 172.16.0.0/22 127.0.0.1 --- Published after manual aggregation The route entry will carry mask information , And the next jump also points to 127.0.0.1, Then it will also Automatically generate a route to the summary network segment and point to the empty interface for ring prevention .
The problem of manual aggregation :
1, In the case of publishing aggregate routes , Detailed routes will not be suppressed , As a result, the summary operation has not decreased Number of routing entries , Instead, increase 了 .
2, When summarizing , released Summary routes do not inherit the properties of detailed routes , In especial AS_PATH, Will Some attributes of the summary route are missing , even to the extent that There may be loops . In order to avoid the above two problems , We have to configure Increase the order To complete .
[r4-bgp]aggregate 172.16.0.0 22 detail-suppressed
--- Publishing summary route entries will suppress all detailed routes
however , because BGP Some particularity of the agreement , We tend to You cannot suppress all the detailed routes . Only can Suppress some routing information --- So we need to use suppressed -policy.
- Grab traffic , Use prefix list
[r4]ip ip-prefix aa permit 172.16.1.0 24
- Use routing policies to match traffic
[r4]route-policy aa permit node 10
Info: New Sequence of this List.
[r4-route-policy]if-match ip-prefix aa
[r4-route-policy]q
- Use the suppression policy to invoke the routing policy
[r4-bgp]aggregate 172.16.0.0 22 suppress-policy aa
For the second question , We specially designed a AS_SET keyword , If you are configuring commands , Activate this keyword , be BGP When summarizing routes , Will carry the detailed AS_PATH attribute , To protect the environment .
[r4-bgp]aggregate 172.16.0.0 22 suppress-policy aa as-set
*> 172.16.0.0/22 127.0.0.1 0 {1 4}?
--- If The detailed route carries AS_PATH Properties are different , It's in Activated AS_SET After attribute , Summary routing will route the details AS Numbers are carried and enclosed in braces , after , During Anti ring , Inside all AS No. will take effect , Can't send back . however , In the use of AS_PATH Attribute to select the path , As a AS To look at .
Because the aggregated routing information There is an attribute loss problem , therefore , Such aggregate routing requires special attention . So , We are BGP Two attributes are specifically introduced
--- ATOMIC_AGGREGATE,AGGREGATOR
ATOMIC_AGGREGATE --- Pure warning attribute --- Only when all detailed routes are suppressed
AGGREGATOR --- Will carry the summary of RID And where it is AS Number
Aggregator: AS 2, Aggregator ID 4.4.4.4, Atomic-aggregate
[r4]display bgp routing-table 172.16.0.0
--- Check the details of a route
- Routing reflectors
Router Reflector--- Routing reflectors ---RR ---- We can do it through configuration , Some devices are called route reflectors under certain conditions , after , The device will reflect what has been learned IBGP Routing information .

We are designating a router called Routing reflectors (RR) At the same time , Must be in his IBGP Select one or more devices in the peer relationship Called his Customer (client),RR And customers We call it Reflection cluster (Cluster). Each reflection cluster will Use RR Of RID As a cluster ID. rest Not called RR Customer's IBGP Peer relationship , We will call it Non customers .
Reflection rules of routing reflectors :
1, When a route reflector learns a route from its client , Then he will send this routing information Reflect to all customers and non customers
2, If the routing reflector learns one hop routing from its non clients , Then he will send this routing information Reflect to all your customers, but not to non customers .
“ Non non non transmission ”
3, When the router performs route reflection , He only uses the best BGP Route for reflection .
9, The federal
10,BGP The road selection principle
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Using one-way linked list to realize queue

unity3d:UGUI源码EventSystem输入系统常见问题
Enter the triangle side length and calculate the area

Questions and answers of basic principles of steel structure

Common sort -- merge sort (recursive and non recursive) + count sort

Analysis of 100 questions and answers in Higher Algebra

Prometheus Operator使用指南笔记

二叉树的实现-c

Review of basic principles of steel structure
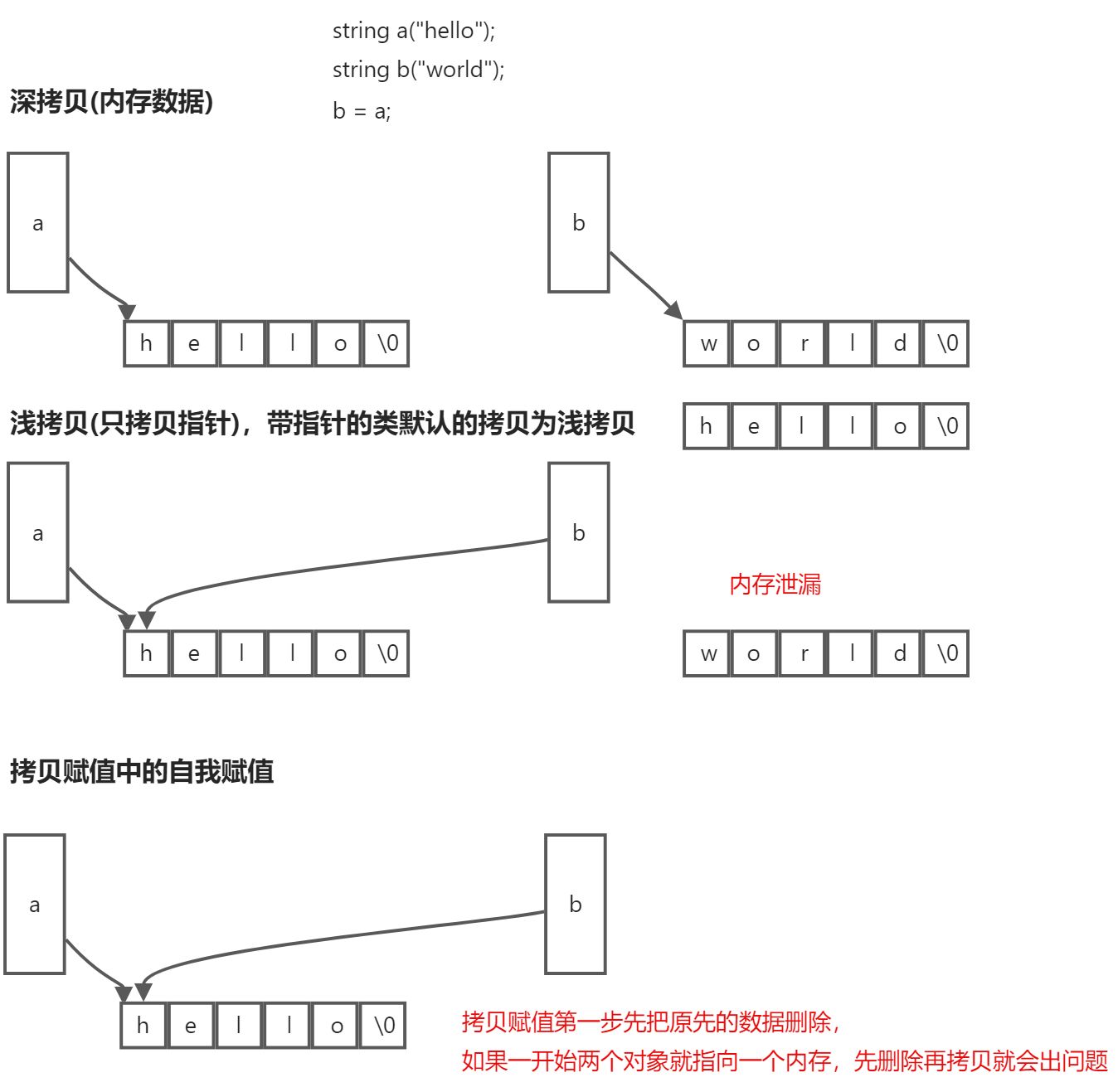
基于对象(Object Based)-两个经典类
随机推荐
常见排序--归并排序(递归和非递归)+计数排序
【无标题】
动态规划——“换硬币问题”
Common sort exchange sort
Implementation of heap and heap sorting
堆的实现与堆排序实现
unity3d:UGUI源码EventSystem输入系统常见问题
Unity在URP管线下使用TriLib插件加载模型材质不正确的问题
The CUDA version of pytorch installed by anconda is inconsistent with the CUDA version of the system
Prometheus
Desktop remote protocol - codec
Anonymous upper computer V7 waveform display
C语言基础练习题初学者可参考
C# 自定义集合
Blog building six: the method of binding your own domain name
vscode配置
刷题笔记:二叉树的中序遍历(三种解法-递归,迭代,Morris)
Unity3d+GameFramework:资源分析,资源依赖,循环依赖检测
0回溯/动态规划中等 LeetCode526. 优美的排列
[bootloader architecture and brushing process based on UDS service]