当前位置:网站首页>Common sort -- merge sort (recursive and non recursive) + count sort
Common sort -- merge sort (recursive and non recursive) + count sort
2022-07-23 12:38:00 【Diving boy requests to fight】
List of articles
4 Merge sort
The basic idea :
Merge sort (MERGE-SORT) It is an effective sorting algorithm based on merge operation , The algorithm is Divide and conquer (Divide andConquer) A very typical application . Merges ordered subsequences , You get a perfectly ordered sequence ; So let's make each subsequence in order , Then make the subsequence segments in order . If two ordered tables are merged into one ordered table , It's called a two-way merge . The core steps of merging and sorting :( In fact, it is a post order sort , First decompose to an order and then merge )
4.1 Recursive form
The difficulty lies in merging : A simple example : It is the combination of two arrays into an ordered array. The method is similar
Method : It's two arrays, one by one, than the size , Take the small one down ( We need an extra array - It's called tmp To achieve ), There is tmp The array taken from the array moves back to the next number , Then we can ensure that at least one array is taken , We take down the rest in turn , Finally, put tmp Assign to the original array .
(begin1: and begin2: Is the beginning of two arrays . )
This piece is realized in this way :
int begin1 = left, begin2 = mid + 1;
int end1 = mid, end2 = right;
int i = begin1; //begin1 Is not necessarily 0
while (begin1<=end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begin1] <= a[begin2])
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
// Three possibilities .1. The left half is finished , The right half is not finished .2. The right half is finished , The left half is not finished .
//3. It's all over . We don't really care , Who's left .
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin2++];
}
memcpy(a + begin, tmp + begin, (end - begin + 1) * sizeof(int));
}
Be careful : Last tmp Need to release .
Code block :
void _mergeSort(int* a, int begin, int end, int* tmp)
{
assert(a);
if (begin >= end)
return;
int left = begin;
int right = end;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;//(right+left)/2
_mergeSort(a, left, mid, tmp);
_mergeSort(a, mid + 1, right, tmp);
int begin1 = left, begin2 = mid + 1;
int end1 = mid, end2 = right;
int i = begin1; //begin1 Is not necessarily 0
while (begin1<=end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begin1] <= a[begin2])
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
// Three possibilities .1. The left half is finished , The right half is not finished .2. The right half is finished , The left half is not finished .
//3. It's all over . We don't really care , Who's left .
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin2++];
}
memcpy(a + begin, tmp + begin, (end - begin + 1) * sizeof(int));
}
void MergeSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int* tmp = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("calloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
_mergeSort(a, 0, n - 1, tmp);
free(tmp);
}
4.2 Non recursive form
To put it bluntly, let's start with the merging step , Let's rub a recursive formation .
Non recursive sorting is the opposite of recursive sorting , An element and adjacent elements form an ordered array , And then form an ordered array with the adjacent array , Until the whole array is in order .
Want to have mid The pointer passes in , Because when there is less than a set of data , Recalculate mid There will be problems with the division, which needs to be specified mid The location of
The diagram is helpful to understand :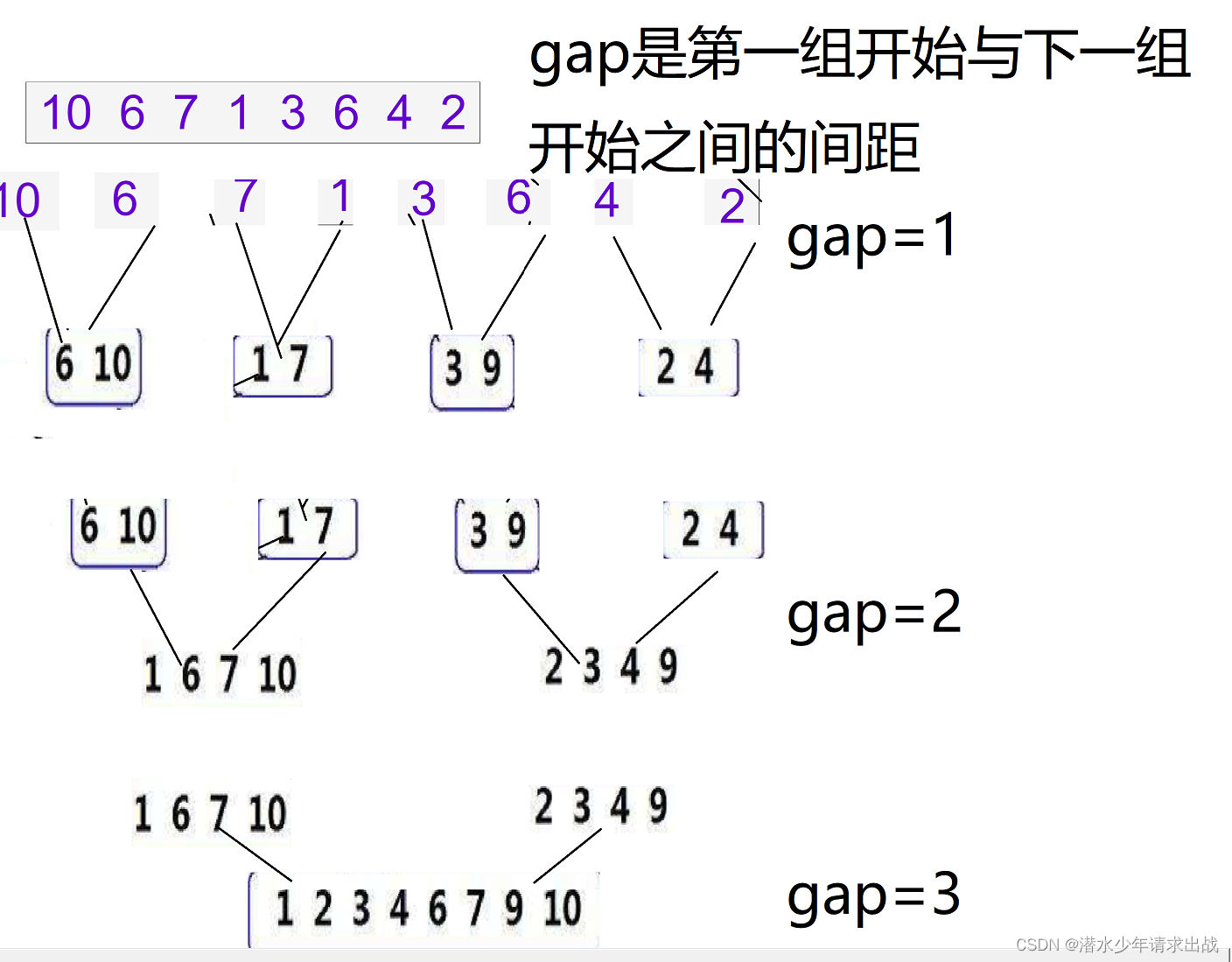
This is the step , This is not simple Let's look at the following code first
void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int* tmp = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("calloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
int gap = 1;
while (gap < n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap)
{
int begin1 = i, begin2 = i + gap;
int end1 = i + gap - 1, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
int j = begin1;
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begin1] <= a[begin2])
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
// Three possibilities .1. The left half is finished , The right half is not finished .2. The right half is finished , The left half is not finished .
//3. It's all over . We don't really care , Who's left .
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
memcpy(a, tmp, n * sizeof(int));
gap *= 2;
}
free(tmp);
}
Any problems? ?
First look at a picture of each group begin and end Scope map of :
We clearly found , It's out of bounds .
int begin1 = i, begin2 = i + gap;
int end1 = i + gap - 1, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
We can know begin1 Will not cross the border , Everything else is possible . At this time, we need to trim the edges .( Be careful not to change all those that cross the border into n-1, This may lead us to end up from tmp Data will be lost after copying back )
operation : We can make its range invalid or have only one value
// Trimming
if (end1 >= n)
{
end2 = end1 = n - 1;
begin2 = n;
}
else if (begin2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
begin2 = n;
}
else if (end2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
}
To sum up, we can get
Code block :
void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int* tmp = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("calloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
int gap = 1;
while (gap < n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap)
{
int begin1 = i, begin2 = i + gap;
int end1 = i + gap - 1, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
// Trimming
if (end1 >= n)
{
end2 = end1 = n - 1;
begin2 = n;
}
else if (begin2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
begin2 = n;
}
else if (end2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
}
int j = begin1;
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begin1] <= a[begin2])
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
// Three possibilities .1. The left half is finished , The right half is not finished .2. The right half is finished , The left half is not finished .
//3. It's all over . We don't really care , Who's left .
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
memcpy(a, tmp, n * sizeof(int));
gap *= 2;
}
free(tmp);
}
5 Count sorting
With the help of some properties of hash bucket , It's nothing .
This is applicable to repeated integer parts in a small range . We need an array to complete –tmp.
( The simple understanding is that we treat the value of each number as a subscript , Let's make this number appear several times in tmp The number stored in the array subscript is . Negative numbers are not suitable )
Ideas : actually , We can save the smallest integer to the first . How to do it ? Yes, we can subtract the minimum value from each number – This not only ensures that negative numbers can be saved, but also eliminates space waste . Finally, we can take it out in turn
void CountSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int min = a[0], max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
if (min > a[i])
min = a[i];
if (max < a[i])
max = a[i];
}
int range = max - min + 1;
int* tmp = (int*)calloc(range, sizeof(int));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("calloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
tmp[a[i] - min]++;
}
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < range; ++j)
{
while (tmp[j]--)
{
a[i++] = j + min;
}
}
free(tmp);
}
6 summary
Run a screenshot :
Complexity and stability analysis of sorting algorithm :

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Interpretation of the paper: recognition of enhancer promoter interactions with neural networks based on pre trained DNA vectors and attention mechanisms
Blog Building III: comment system selection

5.4 Pyinstaller库安装与使用

Implementation of binary tree -c
高电压技术复习资料

快速排序的按区间的三个版本及优化--友友们不一定了解
博客搭建六:绑定自己域名的方法

主机字节序的判定

Interpretation of the paper: develop and verify the deep learning system to classify the etiology of macular hole and predict the anatomical results
C语言小项目——学生成绩管理系统
随机推荐
[AUTOSAR DEM iv.event memory]
(1)ASIO
Vs attribute configuration related knowledge
Prometheus
obs插件基础
嵌入式从入门到精通(入土)——超详细知识点分享3
Axure实现增删改查
Configure TX1 system + set to solid-state disk startup
Awk programming language
Redis——基础概念
常见排序--归并排序(递归和非递归)+计数排序
简单实现栈的功能
Dynamic programming - "coin exchange problem"
队列与堆的相互实现(纯c实现)
求矩阵的鞍点及其对应的下标。
【学习总结】
高电压技术试题及答案
AWK 程序设计语言
Anconda安装的pytorch依赖的cuda版本和系统cuda版本不一致问题
使用InfluxDB数据库的疑惑
