当前位置:网站首页>Overlayfs source code parsing
Overlayfs source code parsing
2022-07-23 14:05:00 【LYSnowy】
overlayfs Source code parsing
mount mount
Register the file system
OverlayFS In the kernel, it exists in the form of kernel modules , The corresponding initialization function and cleanup function are as follows :
module_init(ovl_init);
module_exit(ovl_exit);
static int __init ovl_init(void)
{
return register_filesystem(&ovl_fs_type);
}
It involves register_filesystem function , The purpose of this function is to check linux Whether the file system with the same name already exists in the kernel , If it exists, return the file system structure , Otherwise, this file system (overlayfs) Insert into the linked list of the file system .
int register_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs)
{
int res = 0;
struct file_system_type ** p;
BUG_ON(strchr(fs->name, '.'));
if (fs->next)// Description has been in the file system type linked list
return -EBUSY;
write_lock(&file_systems_lock);
// Find out whether there is a file system with the same name in the linked list
p = find_filesystem(fs->name, strlen(fs->name));
if (*p)
res = -EBUSY;
else
*p = fs;// If it does not exist, insert the file system into the corresponding linked list
write_unlock(&file_systems_lock);
return res;
}
The whole linked list is shown in the figure below 
Through the analysis of the process, we can know that this part is no different from other file systems . After successfully registering a file system, you need to mount the file , That is, you can access the correct files through the directory .
Mount file system
The mount command is as follows :
sudo mount -t overlay overlay -o lowerdir=lower,upperdir=upper,workdir=work merged
This command may appear special device overlay does not exist. This mistake , This high probability is because your path is written incorrectly , Although I don't know why the path is wrong, it is such an error message , But after testing, it is really a path problem .
The mount command is called ovl_mount function ( It should be that the system call finally calls a fs Of mount function , This function is written to fs Structure of the mount Function )
static struct file_system_type ovl_fs_type = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "overlay",
.mount = ovl_mount,// Mount function
.kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
};
static struct dentry *ovl_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, const char *dev_name, void *raw_data)
{
return mount_nodev(fs_type, flags, raw_data, ovl_fill_super);
}
struct dentry *mount_nodev(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags, void *data, int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int))
{
int error;
// Get superblock
struct super_block *s = sget(fs_type, NULL, set_anon_super, flags, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(s))
return ERR_CAST(s);
// Fill superblock
error = fill_super(s, data, flags & SB_SILENT ? 1 : 0);
if (error) {
deactivate_locked_super(s);
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
s->s_flags |= SB_ACTIVE;
// Return to the root directory of the mounted file system ,s_root Itself is dentry, This is just to add a reference count
return dget(s->s_root);
}
You can see mount Function called directly mount_nodev function , The main function of this function is to fill super fast super block, Search first fs_supers Field refers to the linked list of mounted file system instances composed of super blocks , If you find a superblock associated with a block device , Then return its address , Otherwise, allocate and initialize a new superblock , And insert into OverlayFS The linked list of mounted file system instances and the linked list of global mounted file system instances .
The specific data structure relationship is shown in the figure below :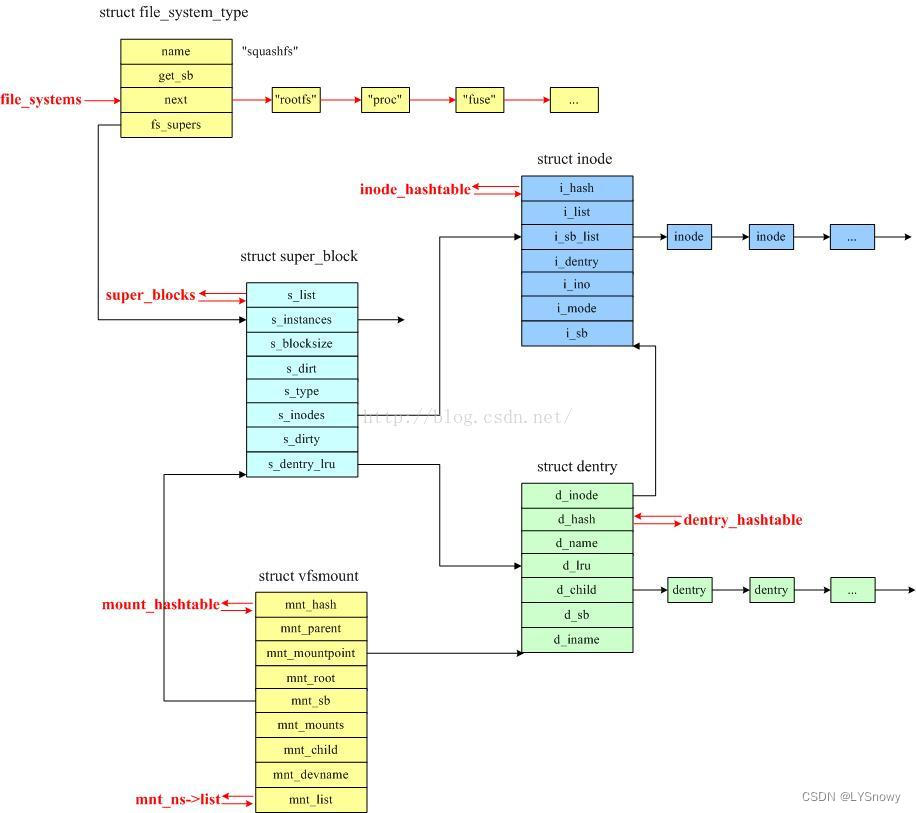
Call function fill_super() Fill in this super_block, To include OverlayFS Specific information about , It is also the main part of the mount function , After filling, return dentry The information is successfully mounted . So it mainly introduces fill_super function .
First of all, you can know through the above function fill_super It's actually a function pointer passed from a function parameter , Finally, it shows that the function body is at the top ovl_mount in , Indicates that the function called is ovl_fill_super This function , That is, the function specified in the structure .
fill_super This function mainly deals with some upper、lower these overlayfs Special part .
fille_super It is mainly filled with the following two structures .

Read write directory
Directory search is mainly for ls merged Similar commands are parsed .
ls This command will call two system calls , among openat() Open Directory merged, Return the corresponding descriptor .getdents() according to openat() The returned descriptor searches the directory . therefore ,overlayfs Directory search in mainly accomplishes two things : Open Directory 、 search for directory
openat The system call opens the directory
openat The system call will eventually call the following code :
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(openat, int, dfd, const char __user *, filename, int, flags,umode_t, mode)
{
if (force_o_largefile())
flags |= O_LARGEFILE;
return do_sys_open(dfd, filename, flags, mode);
}
In the end, I call do_sys_open function . The specific meaning of this function parameter is as follows :
- Parameters filename : It's the file path , Can be a relative path ( That is not to say “/” start ), It could be an absolute path ( That is to “/” start ).
- Parameters dirfd: Is the file descriptor obtained after opening a directory , As a base directory for relative paths . If the file path is relative , So in function openat Relative file descriptors dirfd List of references ,open Function is interpreted as relative to the current working directory of the calling process . If the file path is absolute , openat Ignore parameters dirfd.
- Parameters flags: Contains multiple file creation flags and file status flags .
The difference between the two groups of signs is : The file creation flag only affects the open operation , The file status flag affects subsequent read and write operations . - Parameters mode: Specifies the file mode when creating a new file . When parameters flags Specify flag bits O_CREAT or O_TMPFILE When , Parameter... Must be specified mode, In other cases, parameters are ignored mode.
such as flags by CREATE, Indicates that you want to create a file ,mode by 0744, Indicates the user rights of the file .
long do_sys_open(int dfd, const char __user *filename, int flags, umode_t mode)
{
struct open_flags op;
int fd = build_open_flags(flags, mode, &op);
struct filename *tmp;
if (fd)
return fd;
//1. The pathname of user space is copied to kernel space
//1. according to filename Get a corresponding struct filename Variable
tmp = getname(filename);
if (IS_ERR(tmp))
return PTR_ERR(tmp);
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);//2. Get an unused file descriptor
if (fd >= 0) {
struct file *f = do_filp_open(dfd, tmp, &op);//3. Open file
if (IS_ERR(f)) {
put_unused_fd(fd);
fd = PTR_ERR(f);
} else {
fsnotify_open(f);
fd_install(fd, f);
}
}
putname(tmp);
return fd;
}
The main thing is to find an unused file descriptor fd, And then according to dfd That is, the file descriptor corresponding to the reference directory of the relative path opens the file , Yes op Perform assignment operation , And then fd and file Combine . The subject is this do_filp_open function .
struct file *do_filp_open(int dfd, struct filename *pathname,
const struct open_flags *op)
{
struct nameidata nd;//1. Initialize a nameidata Variable
int flags = op->lookup_flags;
struct file *filp;
set_nameidata(&nd, dfd, pathname);//2. Save the search information , to update current Corresponding fields
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_RCU);//3. Path finding , Open file
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)))
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags);
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)))
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_REVAL);
restore_nameidata();
return filp;
}
Mainly used path_openat function , If this function is called for the first time and it is found that another process is reading and writing the file, it will be called for the second time with a different flag To call , This can be applied to the situation of reading more and writing less , The first call is more efficient than the second call , If the file is found on the network, it will be called for the third time , use LOOPUP_REVAL The way .
nameidata It's the intermediate variable , It is used to store the parameters required by the function and the results . For example, it stores the currently traversed path inode etc. .
static struct file *path_openat(struct nameidata *nd, const struct open_flags *op, unsigned flags)
{
const char *s;
struct file *file;
int opened = 0;
int error;
file = get_empty_filp();
if (IS_ERR(file))
return file;
file->f_flags = op->open_flag;
if (unlikely(file->f_flags & __O_TMPFILE)) {
error = do_tmpfile(nd, flags, op, file, &opened);
goto out2;
}
//
s = path_init(nd, flags);
if (IS_ERR(s)) {
put_filp(file);
return ERR_CAST(s);
}
//
while (!(error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) &&
//
(error = do_last(nd, file, op, &opened)) > 0) {
nd->flags &= ~(LOOKUP_OPEN|LOOKUP_CREATE|LOOKUP_EXCL);
s = trailing_symlink(nd);
if (IS_ERR(s)) {
error = PTR_ERR(s);
break;
}
}
terminate_walk(nd);
out2:
...
return file;
}
path_openat Function mainly includes three main functions , Namely path_init、link_path_walk、do_last function ,
- path_init() initialization nd Path field in variable ( Set the search starting path ), Set according to the path inode Field : If you look up a string with ‘/’ start , Explanation is an absolute path , Therefore, according to current Process fs Field get root Path and set nd Medium root Fields and path Field . If not by ’/‘ start , Description is a relative path , According to current The process gets the current working path and sets nd Medium path Field . According to dentry obtain inode And set up nd Of inode Field
- link_path_walk() Perform path lookup , Find the directory where the last component is located , At this time, the last component has not been resolved : adopt nd Of inode Field to check whether the current directory has executable permissions ( Otherwise, we can't traverse ), If not, an error is returned . Skip the beginning of the path string ’/‘, Get find string next ’/‘ Before the string , That is, get the current search component string . Execute hash operation , Then deposit nd Medium last Field . With path Field dentry Is the parent directory item , according to last Field to find catalog items ( First, we will find the directory item cache , If not, it will pass real_lookup() call inode Of lookup Method to read the directory from the disk ), Get a directory entry corresponding to the component string . Update according to the directory entry and the mount point under the parent directory nd Of path Path and inode. Repeat the above steps , until nd Of last The information of the last component is saved in the field ( here , The last component has not been resolved )
- do_last() Complete the analysis of the final path component , The results will be saved in nd in , Fill the... With the parsing result 3 Step by step file In the field , Open file : according to nd Of path Field ( here , The path of the last component has been recorded ) Medium dentry Get the corresponding file inode, And then according to inode Set up file Field of , These include f_op Field , Get the file operation interface . call file->f_op->open() Open file , Pay attention to the filp That is, the return value is overlayfs Medium file structure , That is to say, it does not return overlayfs Of inode Corresponding file( These should not appear in ext4 It's really disk inode Of .
do_last Would call inode->f_open operation , That is to say inode Self defined open operation , And determine the return value according to the return value of this operation , Concrete open Function is ovl_dir_open.
static int ovl_dir_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct path realpath;
struct file *realfile;
struct ovl_dir_file *od;
enum ovl_path_type type;
od = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ovl_dir_file), GFP_KERNEL);//1. Allocate one ovl_dir_file Variable od
if (!od)
return -ENOMEM;
type = ovl_path_real(file->f_path.dentry, &realpath);//2. obtain file Path type and real path
realfile = ovl_path_open(&realpath, file->f_flags);//3. Open the real file according to the path type
if (IS_ERR(realfile)) {
kfree(od);
return PTR_ERR(realfile);
}
//4. Set a variable od Field of
od->realfile = realfile;
// Judge whether it exists at the same time upper and lower
od->is_real = !OVL_TYPE_MERGE(type);
// adopt upper_dentry Judge whether it is upper
od->is_upper = OVL_TYPE_UPPER(type);
file->private_data = od;
return 0;
}
First, through ovl_path_real Determine whether the function exists at the same time upper and lower Folder , If it exists at the same time, it proves that it is not real Of , Need merger , adopt dentry Medium ovl_entry Judge the data results
in other words , adopt upper and lower All of them ext4 file system , adopt merge That's what you're visiting overlay file system ,overlayfs All file systems are mounted and created dentry It's all stored ovl_entry, It's storing upper and lower Information about , This information comes from the path specified when mounting , Then all information under this path is complete , When creating a new file, the information will also be supplemented , That is to say, as long as the path is known , You can know everything
ovl_path_open Function open function , And then use it file This data structure returns the result . here file Has been identified and opened , That is to say, the directory file has been opened , Whether this directory is merged still real, All open merged Medium inode, because real Of inode stay merged There must be one of them , This ovl_inode Will record whether they are real , If it's not real , Will follow upper and lower Read in , Otherwise, only one is read .

Because here is_real yes false, meanwhile is_upper Is true , So the corresponding opening is open upper The file of , But because of is real The existence of , So at the end of the day lower Traversal read , If one exists at the same time lower and upper The catalog of , Indeed, it will merge in the folder and remove the duplicate of the same name
The above is the implementation logic , The specific code is as follows , That is to say getents system call
getdents system call , search for directory
getdents The system calls are as follows :
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(getdents, unsigned int, fd, struct linux_dirent __user *, dirent, unsigned int, count)
{
...
error = iterate_dir(f.file, &buf.ctx);//2. Directory search
...
return error;
}
struct fd {
struct file *file;
unsigned int flags;
};
The subject is iterate_dir function .
int iterate_dir(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);//file->f_inode, obtain file Corresponding inode Number
...
res = -ENOENT;
if (!IS_DEADDIR(inode)) {
ctx->pos = file->f_pos;// Update the context according to the file read / write location pos Field
res = file->f_op->iterate(file, ctx);// call f_op Medium iterate Interface
file->f_pos = ctx->pos;//iterate Will update ctx Of pos Field , Use it to update the read and write location of the file
fsnotify_access(file);
file_accessed(file);
}
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
out:
return res;
}
The end result is a call inode As indicated in iterate operation .
static int ovl_iterate(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
struct ovl_dir_file *od = file->private_data;// obtain OverlayFS Unique information
struct dentry *dentry = file->f_path.dentry;// File corresponding dentry
struct ovl_cache_entry *p;
if (!ctx->pos)
ovl_dir_reset(file);
if (od->is_real)// Description is not a consolidated directory , When the directory only exists upper Layer or lower The layer time condition will hold
return iterate_dir(od->realfile, ctx);
//cache The value is the list of documents , So here is the list of files to get
if (!od->cache) {
// In the previous section, we know that this field is NULL, Conditions established
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
// Key functions , Get file list
cache = ovl_cache_get(dentry);// Get one ovl_dir_cache
if (IS_ERR(cache))
return PTR_ERR(cache);
od->cache = cache;// Set up od Of cache The field is the previous cache
ovl_seek_cursor(od, ctx->pos);// Set according to the position of the context od Of cursor Field , Point to the corresponding position of the linked list
}
// Traverse , Handle every item of the linked list
while (od->cursor != &od->cache->entries) {
p = list_entry(od->cursor, struct ovl_cache_entry, l_node);
if (!p->is_whiteout)
if (!dir_emit(ctx, p->name, p->len, p->ino, p->type))
break;
od->cursor = p->l_node.next;
ctx->pos++;
}
return 0;
}
static struct ovl_dir_cache *ovl_cache_get(struct dentry *dentry)
{
int res;
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
// obtain dentry Directory item specific information (dentry->d_fsdata, It points to a ovl_entry Variable of type ) Medium cache
cache = ovl_dir_cache(dentry);
if (cache && ovl_dentry_version_get(dentry) == cache->version) {
//cache Exist and work
// Existence and effectiveness may indicate that in the near future ls After that , So there is no need to traverse again
cache->refcount++;
return cache;
}
// It is set to null because it may have been traversed but failed , So it's simply empty
ovl_set_dir_cache(dentry, NULL);// Set up dentry In the information unique to the catalog item cache by NULL
cache = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ovl_dir_cache), GFP_KERNEL);// Allocate one cache
if (!cache)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
cache->refcount = 1;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cache->entries);// Initialize chain header
res = ovl_dir_read_merged(dentry, &cache->entries);
if (res) {
ovl_cache_free(&cache->entries);
kfree(cache);
return ERR_PTR(res);
}
cache->version = ovl_dentry_version_get(dentry);
ovl_set_dir_cache(dentry, cache);// Set up dentry In the information unique to the catalog item cache
return cache;
}
static int ovl_dir_read_merged(struct dentry *dentry, struct list_head *list)
{
int err;
struct path lowerpath;
struct path upperpath;
struct ovl_readdir_data rdd = {
.ctx.actor = ovl_fill_merge,
.list = list,
.root = RB_ROOT,
.is_merge = false,
};
ovl_path_lower(dentry, &lowerpath); // obtain lower Catalog
ovl_path_upper(dentry, &upperpath); // obtain upper Catalog
if (upperpath.dentry) {
// If upper Directory exists , Read upper List of files in the directory
err = ovl_dir_read(&upperpath, &rdd);
if (err)
goto out;
if (lowerpath.dentry) {
err = ovl_dir_mark_whiteouts(upperpath.dentry, &rdd);
if (err)
goto out;
}
}
if (lowerpath.dentry) {
// If lower Directory exists , Read lower List of files in the directory
list_add(&rdd.middle, rdd.list);
rdd.is_merge = true;
err = ovl_dir_read(&lowerpath, &rdd);
list_del(&rdd.middle);
}
This code has been modified in the latest kernel version , But the logic is the same , It's traversal upper and lower Of , Merge those with the same name , That is to ignore lower Of .
establish / Delete file
You can know that whether you create a file or delete a file, it is the same as reading and writing a file , There is no need to consider directly for lower and upper Folder operation , because inode Will be in ls Update when . Only for merged Special processing is required for the operation of files in , There are four situations , They exist alone in lower and upper And the situation that exists and does not exist at the same time .
It should be noted that , It is impossible to create a file with the same name , So the above four cases are for the location of the directory where the file is created .
create a file
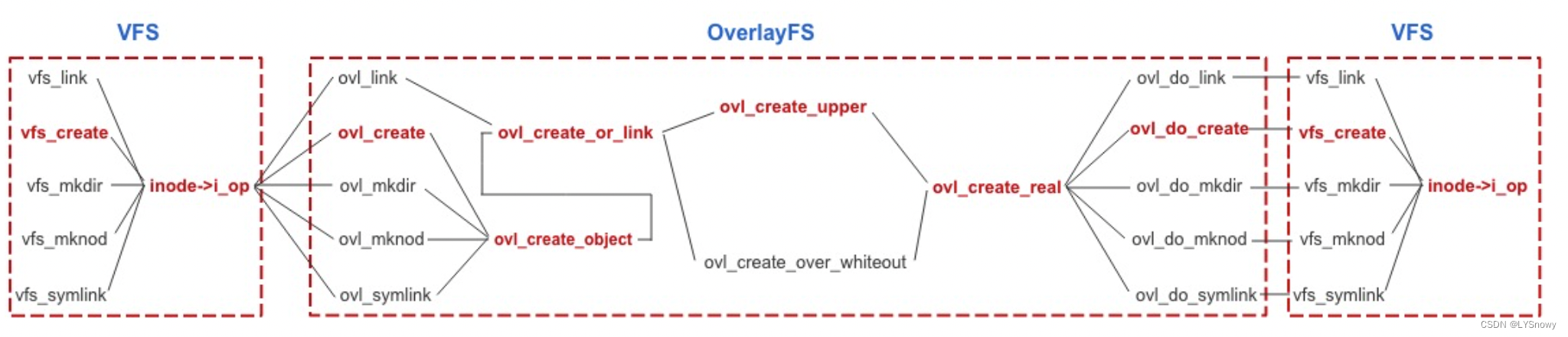
static int ovl_create(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, umode_t mode, bool excl)
{
return ovl_create_object(dentry, (mode & 07777) | S_IFREG, 0, NULL);
}
Be careful , Inside dentry It should correspond to the newly created file dentry, in other words , Before that, we did some initialization , such as d_parent etc. , But specific and overlayfs The relevant has not been assigned .
static int ovl_create_object(struct dentry *dentry, int mode, dev_t rdev, const char *link)
{
int err;
err = ovl_want_write(dentry);// Get right upper Write access of mount point
if (!err) {
err = ovl_create_or_link(dentry, mode, rdev, link, NULL);
ovl_drop_write(dentry);
}
return err;
}
static int ovl_create_or_link(struct dentry *dentry, int mode, dev_t rdev, const char *link, struct dentry *hardlink)
{
...
struct inode *inode;
struct kstat stat = {
.mode = mode,
.rdev = rdev,
};
...
/* stay OverlayFS Next, assign a to the newly created file inode*/
inode = ovl_new_inode(dentry->d_sb, mode, dentry->d_fsdata);
...
/* The parent directory may be lower Layer Directory , So we have to cow-on-write operation */
// dentry->d_parent Namely merged Catalog
err = ovl_copy_up(dentry->d_parent);
...
/* according to dentry Of opaque Value determines which function to call */
if (!ovl_dentry_is_opaque(dentry)) {
err = ovl_create_upper(dentry, inode, &stat, link, hardlink);
} else {
...
err = ovl_create_over_whiteout(dentry, inode, &stat, link,
hardlink);
...
}
...
}
- call ovl_new_inode() stay OverlayFS Assign a... To the newly created file in inode
- Because the parent directory may be a lower Layer Directory , Therefore, call the parent directory ovl_copy_up() perform copy_up operation , Copy the parent directory to upper layer
- According to the newly created file opaque Attribute in upper Create the actual file in the layer :
- If not set opaque attribute , Call ovl_create_upper() function . In this case , This function will be called :
dentry->d_parent Find the parent directory of the newly created file dentry. In this case , The parent directory is OverlayFS Root directory
Call function ovl_dentry_upper() According to the hierarchical information of the parent directory ( Other blogs have introductions ), Find the parent directory corresponding upper Layer directory dentry And inode, In this example, the parent directory corresponds to upper The layer directory is upper Catalog . stay upper The directory corresponds to dentry Find out whether there is a file with the same name as the new file dentry, Create if it does not exist . call ovl_create_real() function , Pass in the last step dentry, as well as upper The directory corresponds to inode. Functions call different functions to create files according to the type of files :
If it is a general document , call ovl_do_create(), This function further calls vfs_create(), Transfer control to VFS,vfs_create() The function will inode The index to the inode operation , And then call inode In operation create() Function to complete the creation of the file . In this case , Will follow this path
If it's a catalog , Call ovl_do_mkdir(), This function further calls vfs_mkdir(), Transfer control to VFS,vfs_mkdir() The function will also be based on the passed inode The index to the inode operation , And then call inode In operation mkdir() Function to complete the creation of the directory
… - If set opaque attribute , Call ovl_create_over_whiteout() Letter . root ovl_create_upper() The function is different from ,ovl_create_over_whiteout() use workdir, Put the above steps in workdir Next finish , Then call a rename operation , take workdir Rename the file created under to upper layer
Inside opaque Attributes refer to the attributes of the created file , That is, whether to create a real file or a fake file .
static int ovl_create_upper(struct dentry *dentry, struct inode *inode,
struct kstat *stat, const char *link,
struct dentry *hardlink)
{
struct dentry *upperdir = ovl_dentry_upper(dentry->d_parent);//dentry Of the parent directory upper Catalog items
struct inode *udir = upperdir->d_inode;// Parent directory upper Directory entries correspond to inode
struct dentry *newdentry;
int err;
mutex_lock_nested(&udir->i_mutex, I_MUTEX_PARENT);
newdentry = lookup_one_len(dentry->d_name.name, upperdir,
dentry->d_name.len);// In the parent directory upper Search under the directory dentry
err = PTR_ERR(newdentry);
if (IS_ERR(newdentry))
goto out_unlock;
err = ovl_create_real(udir, newdentry, stat, link, hardlink, false);
if (err)
goto out_dput;
ovl_dentry_version_inc(dentry->d_parent);
ovl_dentry_update(dentry, newdentry);// Set up dentry Of upper The directory entry is newdentry
ovl_copyattr(newdentry->d_inode, inode);
d_instantiate(dentry, inode);
newdentry = NULL;
out_dput:
dput(newdentry);
out_unlock:
mutex_unlock(&udir->i_mutex);
return err;
}
Delete file
static int ovl_do_remove(struct dentry *dentry, bool is_dir)
{
enum ovl_path_type type;
int err;
...
/* The deleted file may be a lower Layer files , So you need to set the parent directory first copy_up*/
err = ovl_copy_up(dentry->d_parent);
...
type = ovl_path_type(dentry);// Get the path type of the deleted file
if (OVL_TYPE_PURE_UPPER(type)) {
//(type) & __OVL_PATH_PURE
err = ovl_remove_upper(dentry, is_dir);//1. If the file only exists upper layer
} else {
...
err = ovl_remove_and_whiteout(dentry, is_dir);
...
}
...
}
- If the deleted file only exists in upper layer , Call function ovl_remove_upper() Implement delete operation :
- Just like file creation , First, you will find the directory corresponding to the file you want to delete upper Layer directory inode and dentry
What you got in the last step upper Layer directory dentry Search for deleted files dentry. If it is not found, an error will be returned
Depending on whether the deleted file is a directory, call different functions to transfer control to VFS:
If the deleted file is a directory , Call vfs_rmdir()
If the deleted file is not a directory , Call vfs_unlink()
vfs_rmdir() or vfs_unlink() According to the above upper Layer directory inode, The index to the inode operation , And then call upper Layer file system rmdir() or unlink() Hand over control upper Layer file system , Finish deleting the file - If the deleted file exists lower layer , Call function ovl_remove_and_whiteout() Implement delete operation . This function will also find the directory where the deleted file is located upper Layer corresponding to the directory inode and dentry. And files only exist upper Different layers , If the file exists lower layer , You need to in work Under the directory whiteout The file was finally renamed to upper Layer to hide lower Layer files .
Read and write files
read / write directory
This has been introduced before ,ls Even a kind of reading directory , I won't introduce it here , To emphasize again is Open the directory and finally get ovl_inode Of , And that makes sense , Because directly merge Reading and writing really need now merge Of overlayfs To establish inode, Then it is written to upper layer , therefore , about merge The first thing you get from directory operations is ovl_inode!
read / Writing documents
In fact, there is no special need to add , If it's in lower and upper The operation under the folder is actually similar to overlayfs It doesn't matter , Only need ls Update it when you need it , Because the operation is ext4 file system , It's equivalent to changing the lamp inode Information , however overlayfs Is stored in inode The pointer to , So it doesn't matter .
If it's in merge Now read and write files , You just need to choose the exact upper Of inode still lower Of inode, Because this needs to be accurate , Because even if upper and lower All have merge It is definitely upper Of course. , So there is no need to merge like a directory , Because in merged The operation of files under the folder will never be the same as lower Related ( Unless it is lower The only files under ), So we need to give it accurately lower Or is it upper Of inode.
So we need to choose inode,inode The choice of depends mainly on ovl_d_select_inode function .
First, choose to complete the previous function slightly
int vfs_open(const struct path *path, struct file *file, const struct cred *cred)
{
// Select a inode return
struct inode *inode = vfs_select_inode(path->dentry, file->f_flags);
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return PTR_ERR(inode);
file->f_path = *path;
// Open the returned inode
return do_dentry_open(file, inode, NULL, cred);
}
static int do_dentry_open(struct file *f, struct inode *inode, int (*open)(struct inode *, struct file *), const struct cred *cred)
{
...
f->f_inode = inode;
f->f_mapping = inode->i_mapping;
...
f->f_op = fops_get(inode->i_fop);
...
if (!open)
open = f->f_op->open;
if (open) {
error = open(inode, f);
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
}
...
}
You can see it ,do_dentry_open Function just uses inode Inside open Function to open , So the point is inode The choice of .
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
static inline struct inode *vfs_select_inode(struct dentry *dentry, unsigned open_flags)
{
struct inode *inode = d_inode(dentry);//dentry->d_inode
// call inode What it has select function
if (inode && unlikely(dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_SELECT_INODE))
inode = dentry->d_op->d_select_inode(dentry, open_flags);
return inode;
}
struct inode *ovl_d_select_inode(struct dentry *dentry, unsigned file_flags)
{
int err;
struct path realpath;
enum ovl_path_type type;
// If it's a directory , As mentioned above, return inode that will do
if (d_is_dir(dentry))
return d_backing_inode(dentry);
// If not one dir, The following code is executed
type = ovl_path_real(dentry, &realpath);// Get the real path
if (ovl_open_need_copy_up(file_flags, type, realpath.dentry)) {
err = ovl_want_write(dentry);
if (err)
return ERR_PTR(err);
if (file_flags & O_TRUNC)
err = ovl_copy_up_truncate(dentry);
else
err = ovl_copy_up(dentry);
ovl_drop_write(dentry);
if (err)
return ERR_PTR(err);
ovl_path_upper(dentry, &realpath);
}
if (realpath.dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_SELECT_INODE)
return realpath.dentry->d_op->d_select_inode(realpath.dentry, file_flags);
return d_backing_inode(realpath.dentry);
}
If it is a general document , According to the opening flag and the corresponding upper or lower The directory entry of the layer file determines whether to execute copy-up operation . For example , If it's a lower General file of layer , Open in read-write mode , This file will be copied to upper layer . If it is opened in read-only mode , You don't need to . Then according to the final upper Layer or lower Layer of the directory entry of the corresponding file d_flags Field determines whether further calls are needed d_select_inode() function . If not, return upper Layer or lower Layer corresponding file inode
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

图像处理1:RGB888_YCbCr444
![[laser principle and application -7]: semiconductor refrigeration sheet and Tec thermostat](/img/c8/e750ff7c64e05242eac7b53b84dbae.png)
[laser principle and application -7]: semiconductor refrigeration sheet and Tec thermostat

Connaissance détaillée du GRE, du mgre; Connaissance de la configuration de base de l'OSPF

Creo 9.0 如何快速修改CAD坐标系?
iQOO 10 Pro和小米12 Ultra哪个好 哪个值得买 两者配置对比

rtx3080ti和3090差距 rtx3080ti和3090哪个性价比高

赛扬n5095处理器怎么样 英特尔n5095核显相当于什么水平

数千个数据库、遍布全国的物理机,京东物流全量上云实录 | 卓越技术团队访谈录

考研题库小程序中如何实现打开考研思维导图pdf

sdf折射反射效果记录
随机推荐
Image processing 6: top level file
使用Stream流来进行分类展示。
ERP生产作业控制
rtx3090ti什么水平 rtx3090ti显卡什么级别 rtx3090ti显卡怎么样
FPGA:ov7725摄像头通过VGA/HDMI显示RGB565格式的图像
[understanding of opportunity-50]: Guiguzi - the twelfth Rune chapter - the art of being a good leader: keep your position, observe the four directions, cave in danger, talk widely, empty advice, set
Comment creo 9.0 modifie - t - il rapidement le système de coordonnées Cao?
NR Modulation 5
Elephant Swap的LaaS方案优势分析,致eToken表现强势
MGRE comprehensive experiment
考研题库小程序中如何实现打开考研思维导图pdf
Common mouse events and keyboard events
KingbaseES DENSE_RANK 函数用法
机器学习入门难?说说我是如何快速开始机器学习入门的!
常用的鼠標事件和鍵盤事件
iQOO 10 Pro和小米12 Ultra哪个好 哪个值得买 两者配置对比
静态综合实验(HCIA)
图像处理1:RGB888_YCbCr444
How to open the thought map pdf of postgraduate entrance examination in the small program of postgraduate entrance examination question bank
《乔布斯传》英文原著重点词汇笔记(十五)【 chapter fourteen】