当前位置:网站首页>MySQL must master 4 languages!
MySQL must master 4 languages!
2022-06-26 02:18:00 【Junhong's road of data analysis】
This article mainly introduces to you MySQL Commonly used 4 Languages :

One 、DDL
DDL,data defination language, refer to Data definition language , Its main function is to create a database , Delete and modify the structure of the library table .
Access to database
mysql -uroot -p -- In this way , Next you need to enter the password . Password is secret
mysql -uroot -p123456 -- The password can be directly 123456 Put it in the parameter p Behind , unsafe Parameter interpretation :
u: Designated user
p: Specified password

All orders
1. Database operation
show databases; // Show all databases
use school; // Use school database
create database school; // Create database
drop database school; // Delete a database
2. Table operations
-- Create table
create table user( Field 1, Field 2,..., Field n);
-- View the SQL sentence
show create table user;
-- View the structure of the table
desc user;
-- Delete table
drop table user;
-- Modify the name of the table
alter table user rename to users;Database operation
show databases; // Show all databases
use school; // Use school database
create database school; // Create database
drop database school; // Delete a database
mysql> show databases; // Display database
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| peter |
| school |
| sys |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> use school; // Choose to use the database
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -ATable operations
// 1、 Create table
create table user( Field 1,
Field 2,
...,
Field n
); // The last semicolon must not be forgotten
// 2、 Look at all the tables
show tables;
// 3、 View the structure of the table
desc user;
// 4、 View the SQL sentence
show create table user;
// 5、 Delete table
drop table user;
// 6、 Modify the name of the table
alter table user rename to users; # Change table name to users;to Omission The last semicolon must not be forgotten
mysql> use school; // Use a database
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables; // Look at all the tables in the database
+------------------+
| Tables_in_school |
+------------------+
| course |
| score |
| student |
| teacher |
| total |
+------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)Create table
Primary key
primary keyandauto_incrementMust be used togetherWriting norms : The statement of each field should be written separately , Easy to check
The last semicolon must not be forgotten
# establish user surface :6 Species field +1 Primary keys
create table user( id int(10) unsigned not null auto_increment comment "user_id", // take id A primary key
name varchar(20) not null comment "user_name",
email varchar(50) not null comment "user_email",
age tinyint unsigned not null comment "user_age",
fee decimal(10,2) not null default 0.00 comment "user_fee",
createTime timestamp not null comment "user_time",
primary key(id)
); // Remember the semicolon 
View table structure
mysql> desc user;
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| fee | decimal(10,2) | NO | | 0.00 | |
| createTime | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
6 rows in set (0.02 sec) View the SQL sentence
show create table user;
Field operations
The key word is alter, First select the table to be operated .
modify: modifychange: Change the nameadd: Add fields
The default is the end
Add... At the specified location
// Modify field information
alter table user modify name varchar(50) not null; # Change the field name from 20 Change it to 50 Characters
// Modify field name
alter table user change email user_email varchar(50) not null; # take email Change to user_email
// Add a field at the end
alter table user add password char(30) not null comment "user_password"; # increase password Field
// Specify the location to add the field
alter table user add password1 char(30) not null comment "user_password1" after user_name; # stay name Add... To the back password1 Field
// Delete field
alter table user drop password1; # Delete field password1
// The original table information
mysql> desc user;
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| fee | decimal(10,2) | NO | | 0.00 | |
| createTime | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# Modify field information
mysql> alter table user modify name varchar(50);
# Modify field name
mysql> alter table user change email user_email varchar(50) not null;
# Add fields , At the end of
mysql> alter table user add password char(30) not null comment "user_password";
# Specify the location to add the field
mysql> alter table user add password1 char(30) not null comment "user_password1" after name;
mysql> desc user;
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| password1 | char(30) | NO | | NULL | |
| user_email | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| fee | decimal(10,2) | NO | | 0.00 | |
| createTime | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
| password | char(30) | NO | | NULL | |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)Two 、DML
DML,data manipulation language, refer to Data operation language . It is mainly the language for operating the table records in the database , Contains inserting data into the table 、 Update of data in the table 、 Deletion of tables, etc
Insert data into the table
The data in the table is updated
Delete table
Insert data into the table
-- Match the field name to the field value one by one , You can just insert some fields
-- omitted id and createtime Field
mysql> insert into user(
name,
email,
age,
fee,
password)
values("xiaoming",
"[email protected]",
20,
56.56,
Password("xiaoming") // Password here to use the function Password()
);
-- Contains all field information
insert into user values(10, "nanan", "[email protected]", 38, 89.19, 2019-10-02, Password("nanan"));String fields must be enclosed in quotation marks
The password requires the use of a function
Password()Add a semicolon at the end of the statement
Use insert only partial fields
You can leave out the field name , At this point, we need to add
id, And you have to fill in all the fields , You can't just add some data

Data update
Data update update The most used is where sentence , Specify a condition to execute ; If not where, All fields will be changed ( Be careful )
Appoint
idNumberSpecify the specific value of the field
Multiple fields are allowed , Separated by commas
mysql> update user set name="nangying" where id=6; // adopt id Appoint
mysql> update user set fee=88.76 where fee=56.90; // Specify directly by field name
mysql> update user set email="[email protected]", age=54 where id=7; // Modify multiple values at the same time
mysql> update user set fee=88.88 where id in(2,4,6); // in Usage of
mysql> update user set fee=66.66 where id between 2 and 6; // between ... and ...Delete
There are two ways to delete a table :
delete: Delete table , insert dataFrom the last timeOfidWe're going to start inserting ; Deleted records still existtruncate: Clear the table , Reinsert dataidfrom 1 Start ; No memory space
delete table user;
truncate table user;Delete
deleteA record in a table
delete from user where id=7; // Delete record
insert into user (name,email,age,fee,password) values("lisi","[email protected]", 36, 81.17, Password("lisi")); // id Is to increase from the original basis 

About truncate
# Delete data
mysql> truncate table user;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
# Reinsert data
mysql> insert into user (user_name, user_email, user_age, password, fee) values ("peter", "[email protected]", 27, password("101010"), 28.87);
Query OK, 1 row affected, 2 warnings (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
+----+-----------+-----------------+----------+--------------------------------+-------+
| id | user_name | user_email | user_age | password | fee |
+----+-----------+-----------------+----------+--------------------------------+-------+
| 1 | peter | [email protected] | 27 | *C3BC3E91915DCAE22014892F9827D | 28.87 |
+----+-----------+-----------------+----------+--------------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)3、 ... and 、DCL
data control language,DCL, It refers to data control language , It is mainly a language to control the login in the database and the user's permission , contain
The user login
MySQLdatabaseHow to change the user password and forget the password
Create common users and authorizations
Revoke authority
revokeView permissions and delete users
All orders
1. View users and information in the database
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
use mysql;
show tables;
select user, host, passord from user; # All the users are user In the table
2. Create a new user 、 to grant authorization 、 Revoke permissions and delete
-- establish
create user "test"@"192.168.2.10" identified by"password"; # Designated user test、ip And password password
flush privileges; # Refresh the permissions
mysql -utest -h192.168.2.10 -p # use test The user login
-- to grant authorization
grant select, insert, delete on shop.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10"; # shop It's the database ,test Is the table in the database
flush privileges; # Refresh the permissions
systemctl restart mysql; # restart mysql
-- Authorization while creating users
grant select, insert, delete on shop.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10" identified by"password";
-- View permissions
show grants for "test"@"192.168.2.10"\G # \G Parameters are used to output good-looking
-- Revoke authority
revoke delete on shop.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10"; # revoke shop In the database test User delete jurisdiction
flush privileges; # Refresh the permissions
systemctl restart mysql; # restart mysql
-- Delete user
drop user "test"@"192.168.2.10";
-- Prudent operation
grant all privileges on *.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10" # Give all permissions to all databases
3. Change user password
-- The user's original password is known , Be able to log in
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
use mysql;
show tables;
select user, host, password from user; # All the users are user In the table
update user set password=PASSWORD("123456admin") where user="test"; # take test Change the user's password to 123456admin
flush privileges;
-- Forget the original password : With the help of the jump permission table , Restart the daemons
mysql skip-grant-tables # Jump permission table
mysql # Re enter mysql
show databases;use mysql;show tables;
select user, host, password from user; # All the users are user In the table
update user set password=PASSWORD("123456admin") where user="test"; # take test Change the user's password to 123456admin
flush privileges;
4. see mysql service
-- window
Go directly to the task manager
-- linux
netstat -an # find 3306 port About root Account
By default ,MySQL Database means to allow root Account login and login on this computer .
-urootExpressrootAccount-pIndicates that a password is requiredNo,
-hIndicates that the default is locallocalhostperhaps127.0.0.1Sign in

Log in to view your account
MySQL The service port number of the database is 3306, By means of mysql Database user View the login database user information in the table :
mysql> show databases; # View all databases
mysql> use mysql; # choice mysql database
mysql> show tables; # Look up all the tables in the database
mysql> select user, host from user; # Look at... In this table user and host Information 
Delete user
It should be noted that the permission must be refreshed after deleting a user :
mysql> delete from user where host="%"; # Delete host by % Users of
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> flush privileges; # Refresh the permissions
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)Be careful : When in actual development projects , The project and the database server are not in the same place , You can specify ip Connect to access
mysql> update user set host="192.168.1.10" where user="root";
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select user,host from user;
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
When to exit mysql Re enter , You need to specify the IP Address , It's the one set up above IP:

Password problem
1、 Change Password
You also need to enter mysql Database user In the table
mysql>update user set password=PASSWORD("admin") where user="root"; # take root The password of the account is changed to admin
mysql> flush privileges; # update operation
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)2、 Forget the password
If you forget the password , You need to enter the configuration file
[email protected]:~$ vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnfFind the in the figure below
skip-grant-tables, Ahead of # Get rid of , Just uncomment : Cancel authority authentication , Open a new process in the background to avoid secret entryMySQL
restart
MySQLservice :systemctl restart mysqladopt
MySQLGo straight into :

Then follow the above steps to reset the password
mysql> show databases;
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> select user, password from user;
# Next, reset the password 
Four 、DQL
DQL(data query language), refer to Data query language , The main function is to query the data in the database , It is also the most common and important function .
There are many ways to query : The joint query 、 Group query 、 Inline query 、 Subquery etc. , just so so Limit the number of queries etc. , Here are some common queries
Format :
select
column1,
column2,... # Fields to query
from table_name # Table name
where Conditions Simple query
select
name,
age
from user
where id=4;
where id in(1,3,5,7);
where name = "xiaoming";Filter query
The keywords for filtering queries are distinct, Remove duplicate values from the field
-- Filter duplicate fields
select distinct(password) from user; # password Is a duplicate
select distinct password from user; # Brackets can be omitted 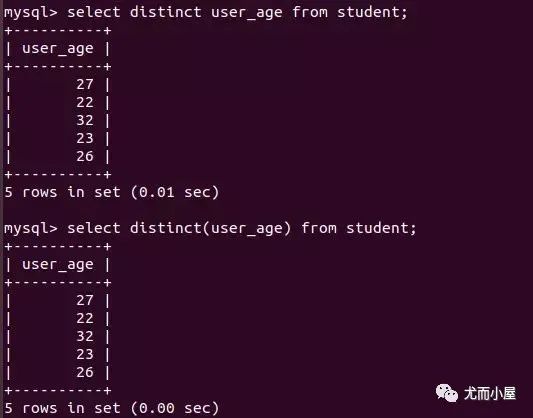
Link query
The keyword of connection query is concat
Directly use the default connection mode of the system , Connect the original fields with underscores
Use
concat...as...,asLater, I specify the new field name of the connectionQueries with a join symbol
concat_ws("+", Name 1, Name 2); among "+" Is to specify the connector
select concat(name, email) from user; # The result shows concat(name_email)
select concat(name, email) as nameEmail from user; # Use the new field name with nameEmail To express 


Fuzzy query
The key word of fuzzy query is like, Chinese translation into image :
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "peter"; # image peter
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "%e"; # % Express arbitrarily , Indicates the name with e ending
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "%e%"; # Indicates that the name contains eSort query
Ascending the records in the table asc Or descending order desc Permutation , The default is ascending asc, At the same time, we need to use order by keyword :
Ascending :
asc, By defaultDescending :
desc
select * from student order by user_age asc; # The ascending order of age
select * from student order by user_age desc; # The descending order of age 
Aggregate functions
select count(*) from student; # General record
select sum( Name ) from student; # The sum of the
select avg( Name ) from student; # Average
select max/min( Name ) from student; # Maximum / Small value Limit query results
To limit the number of queries, use limit keyword
Use it directly
limitUse
limit ... offset ...: Specify where to start displaying , How many lines are displayedAbbreviation :
limit 5, 4: Says from the first 5 OK, let's start , Show 4 Row data
select name, age from user limit 5; -- Display only 5 Row data
select name, age from user limit 5 offset 4; -- From 4(offset) Line start display 5(limit) Row data
select name, age from user limit 4, 5 ; -- The effect same as above : Before the comma is offset The content of , After the comma is limit Content - END -边栏推荐
- ARM流水线如何提高代码执行效率
- Keda 2.7.1 brief analysis of scaledjob code
- Implementation of image binary morphological filtering based on FPGA -- Corrosion swelling
- socket demo01
- Calibration...
- .NET7之MiniAPI(特别篇) :Preview5优化了JWT验证(下)
- Redis6.0新特性——ACL(权限控制列表)实现限制用户可执行命令和KEY
- @Query 疑难杂症
- Markov decision process (MDP): gambler problem
- Is the securities account recommended by qiniu safe?
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
云答题不显示第三方登陆按钮是什么情况
【缺陷检测】基于matlab GUI印刷电路板自动缺陷检测【含Matlab源码 1912期】
其他代码,,vt,,,k
Small ball bouncing against the wall
Scala 基础 (二):变量和数据类型
图的深度优先遍历
It's better to finish one than start thousands of times (reprinted from Douban)
树莓派 + AWS IoT Greengrass
初识Opengl
Depth first traversal based on adjacency table
哪个证券公司手机股票开户更好更安全?
[JS] free API to judge holidays, working days, Saturdays and Sundays
vs2015+PCL1.8.1+qt5.12-----(1)
Keda 2.7.1 brief analysis of scaledjob code
How to efficiently complete daily tasks?
Shell curl execution script, with passed parameters and user-defined parameters
Three factors affecting personal growth
Redis linked list
The first intimate contact of caching technology
socket demo01









