当前位置:网站首页>Simulation Implementation of string
Simulation Implementation of string
2022-06-22 15:57:00 【Stock god.】
String Required members
string This type uses 4 Member variables and several member functions are encapsulated .
The member variables are :
- char* _str: This member variable is used to point to the opened string
- size_t _size: Indicates the size of the string
- size_t _capacity: indicate string The space occupied , To work with size This member distinguishes ,_size Indicates the actual size of the string , and _capacity Indicates the amount of space occupied ,
_capacity >= _size - static const size_t npos: yes string A built-in member variable , The value is -1, This variable is static Of , It belongs to the whole class
string Class constructor
1、_capacity+1 Because _str Is pointing to the space of the string , And the string has "\0", As an end sign , therefore _str The space pointed to should be one byte larger .
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str)),
_capacity(_size)// no need +1
{
_str = new char[_capacity+1];// Only here +1
strcpy(_str, str);
}
string Destructor of class
Destructor needs to release _str Point to space , And will _size and _capacity Set as 0
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
Copy structure
1、 Use the constructor to construct a temporary object tmp, Reuse swap Function exchange tmp Content of
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
// Modern writing of deep copy
string(const string& s)
:_str(nullptr),// This must be initialized to a null pointer . If null pointer is not initialized , It's a random value , In exchange for tmp after ,tmp Out of scope , Destroy call destruct , Destroy the space of random values , There is a wild pointer problem
_size(0),
_capacity(0)
{
string tmp(s._str);//tmp Is a temporary object , Out of scope destroy , because tmp The content and content of this Swap , So there is no memory to destroy .s._str It's one by one char*, And this char* Refers to parameters s String , This sentence is equivalent to string tmp=(” A string “), This sentence calls string Constructor for
swap(tmp);
}
Assignment operator overload
1、 Because it is value transfer and parameter transfer , So the copy construct is called , Construct a temporary object tmp, Call again swap Function exchange tmp The content of . Out of scope ,tmp This object will call the destructor to destroy .
string& operator=(string tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
c_str()、size()、[] Operator overloading
c_str(): It's used to return to c Interface of formal string
size(): Returns the size or length of a string
operator[]: This interface has a normal version and const Version of
const char* c_str() const// Don't worry about why const char* ,c_str The return is c Formal string , and c This is the type of string
{
return _str;
}
size_t size() const // This const This is to enable ordinary objects to call ,const Objects can also call , If you don't write , You have to const Object to write another function .
{
return _size;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);// Forget to write this sentence
return *(_str + pos);
//return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos)const// the last one const modification this The pointer , Composition function overload ( The return value does not constitute a function overload ), Give Way const Object call
{
assert(pos < _size);
return *(_str + pos);
}
reserve(): Expansion function
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp,_str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
resize(): Set the size and initialize
Set size n Yes 3 Medium condition :1、n<=_size 2、n>_size, however n<=capacity 3、n>capacity
The default initialization character is 0
When setting the n To be less than _size when , Directly subscript n Output setting "\0", As the end of a string , There is no need to reduce the space .
When setting the n Be greater than _capacity, Need to expand
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
memset(_str+_size,ch,n-_size);
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
insert(): stay pos Insert a character or string at the subscript
Insert a character : When the length of the string equals the capacity , Need to expand ; Then you need to move the data , stay pos To insert the character ch; Subscript end The point is \0 Next to
string& insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end ] = _str[end-1];
end--;
}
_str[end] = ch;
++_size;
return *this;
}
Insert a string :
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* s)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(s);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end >= pos + len)
{
_str[end ] = _str[end-len];
end--;
}
strncpy(_str+pos, s,len);//strncpy There is no need to duplicate \0;
_size += len;
return *this;
}
erase: from pos Position start , Delete len A string of length
When the deleted length is npos or pos+len When the length of is greater than the length of the string , Description to delete pos Location ( Include pos Location ) All the following strings .
If it is not , You need to _str + pos + len The following string under position is copied to pos Under the position .
//erase Will change _size, But it won't change _capacity
string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;// Don't think , When this is the case , The length of the description string is pos individual
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);//strcpy( Purpose , Source )
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
clear(): Clear all strings
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
push_back(): Trailing character
void push_back( char ch)//ch no need const Modification of , because ch It's not quoting ( Because if it is a quotation , The character has... In the constant field const Properties of ), The value copy is passed , no need const receive
{
Method 1
//if (_size == _capacity)
//{
// reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
//}
//_str[_size] = ch;
//++_size;
//_str[_size] = '\0';
// Method 2
insert(_size , ch);
}
append(): Trailing string
void append(const char* str)
{
Method 1
//size_t len = strlen(str);
//if (_size+len > _capacity)
//{
// reserve(_size + len);
//}
//strcpy(_str + _size, str);
//_size += len;
// Method 2
insert(_size, str);
}
Operator overloading +=:+= A character or a string
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
find(): Find a character or string , Found return subscript , No return found npos
npos It's a built-in static Member variables of , Value to -1; If function returns -1 Indicates that... Was not found
size_t find(char ch)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* s,size_t pos=0)
{
const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, s);//strstr Is a string comparison function
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return ptr - _str;// The return is the subscript
}
}
iterator
string The essence of an iterator is a char Pointer to type , Is a public member variable ( Public is used outside the class )
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()// Returns the beginning of a string
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()// Returns the end of a string
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _str + _size;
}
Operator overloading ==、 <= 、<、> 、>=、!=
bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
Method 1
//size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
//while (i1 < s1.size() && i2 < s2.size())
//{
// if (s1[i1] < s2[i2])
// {
// return true;
// }
// else if(s1[i1] > s2[i2])
// {
// return false;
// }
// else
// {
// ++i1;
// ++i2;
// }
//
//}
//return i2 < s2.size() ? true : false;
// Method 2
return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) < 0;
}
bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) == 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2; } bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2) && !(s1 == s2);
//return !(s1 <= s2); The teacher's method
}
bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 > s2 || s1 == s2;
//return !(s1 < s2); The teacher's method
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
Operator overloading <<: Output string type
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
Method 1
//for (auto ch : s)
//{
// out << ch;
//}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
out << s[i];
}
//out << s.c_str(); // You can't write that , It can be used in most cases . With this line of code , encounter \0 Stop printing , When
// Some strings have \0 when , The following characters cannot be printed . The above code is based on string Of
//_size To print the string .
return out;// This type is returned so that multiple strings can be output consecutively
}
Operator overloading >>: towards string Type object input string data
call c.clear(): It's for emptying s Because of the data in . For example, when s There are strings , If you call this operator again at this time to overload the function , We will insert the string we entered after the original string .
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();//test6 Have a show , To add clean Why .
char ch = in.get();//get() and getchar() almost ,get yes istream The inside of the class
while (ch != ' ' || ch != '\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
边栏推荐
- Quick sort_ sort
- 84. (cesium chapter) movement of cesium model on terrain
- C # implements insertion sorting
- C语言学习-18-makefile文件编写例子以及如何生成、调用动态库
- [Newman] postman generates beautiful test reports
- Jenkins automatically triggers compilation by checking code submissions
- Discourse 的信任级别
- C language learning -18-makefile file writing examples and how to generate and call dynamic libraries
- Scala language learning-05-a comparison of the efficiency of recursion and tail recursion
- 阿里云中间件的开源往事
猜你喜欢

On the routing tree of gin

英国考虑基于国家安全因素让Arm在伦敦上市

建议自查!MySQL驱动Bug引发的事务不回滚问题,也许你正面临该风险!
![[leetcode] 9. Palindromes](/img/58/1817b072949458f9652c144ac4ec0e.png)
[leetcode] 9. Palindromes
数字人民币可以买理财产品了!建行APP在试点地区上线服务专区,实测体验如何?

C语言学习-18-makefile文件编写例子以及如何生成、调用动态库

Application of mongodb in Tencent retail premium code

小白操作Win10扩充C盘(把D盘内存分给C盘)亲测多次有效

壹连科技冲刺深交所:年营收14亿 65%收入来自宁德时代
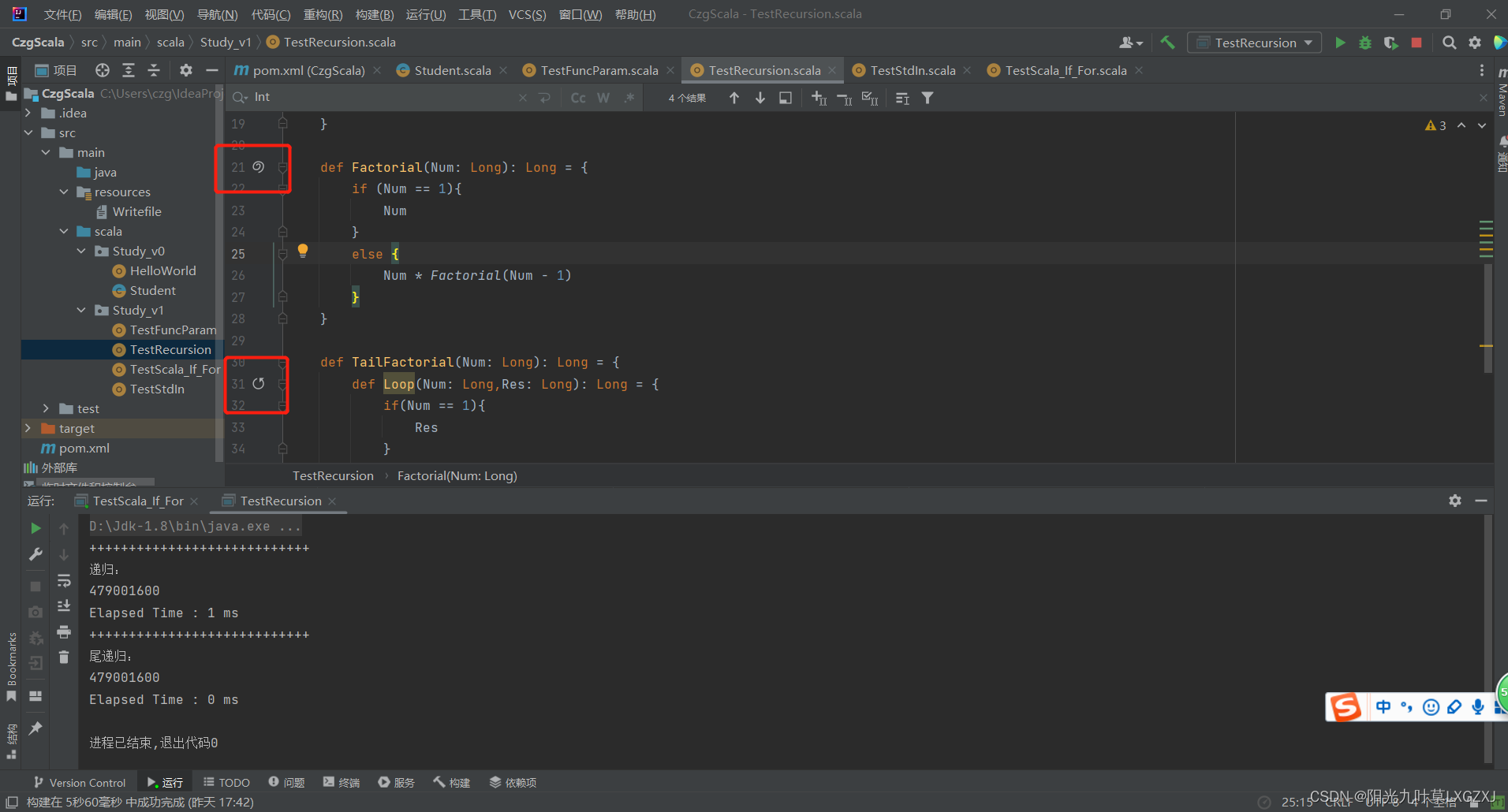
Scala语言学习-05-递归和尾递归效率对比
随机推荐
js中const定义变量及for-of和for-in
社区文章|MOSN 构建 Subset 优化思路分享
校企联合在路上!华为云GaussDB又来高校啦
Yilian technology rushes to Shenzhen Stock Exchange: annual revenue of RMB 1.4 billion, 65% of which comes from Ningde times
The IPO of Tian'an technology was terminated: Fosun and Jiuding were shareholders who planned to raise 350million yuan
Is pioneer futures reliable? How to open a futures account safely?
大佬们 2.2.1cdc 监控sqlsever 只能拿到全量的数据 后期增量的数据拿不到 咋回事啊
C language learning -18-makefile file writing examples and how to generate and call dynamic libraries
模板特例化 template<>
标准化、最值归一化、均值归一化应用场景的进阶思考
鸿世电器冲刺创业板:年营收6亿 刘金贤股权曾被广德小贷冻结
84. (cesium chapter) movement of cesium model on terrain
How safe is the new bond
Discourse 的信任级别
多年亿级流量下的高并发经验总结,都毫无保留地写在了这本书中
Recommend several AI Intelligent Platforms
新版负载均衡WebClient CRUD
天安科技IPO被终止:曾拟募资3.5亿 复星与九鼎是股东
[Shangshui Shuo series] day three - VIDEO
【LeetCode】9、回文数