当前位置:网站首页>Thread pool
Thread pool
2022-06-23 16:03:00 【weixin_ forty-three million seven hundred and sixty-six thousan】
Thread pool
1. Thread pool summary

public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//======================== Fixed length ==========================
ExecutorService ftp = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//newFixedThreadPool The constructor used
/* public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
//======================== Caching ==========================
ExecutorService ctp = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//newCachedThreadPool The constructor used
/* public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
//======================== timing ==========================
ScheduledExecutorService stp = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
//newScheduledThreadPool The constructor used
/* public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); }*/
//======================== Single case ==========================
ExecutorService ste = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//newSingleThreadExecutor The constructor used
/*public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }*/
}
2. Blocking and non blocking queues

//============================== Non blocking queues ===============================
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> clq = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
// The team
clq.add("a");
clq.add("b");
clq.add("c");
// View queue headers
String peek = clq.peek();
System.out.println("peek = " + peek);//a
System.out.println("clq.size() = " + clq.size());//3
// Out of the team
String poll = clq.poll();
System.out.println("poll = " + poll);//a
System.out.println("clq.size() = " + clq.size());//2
System.out.println("=================================");
//====================== Blocking queues =======================================
BlockingQueue<String> bq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2);
// bq.add("a");
//bq.add("b");
// bq.add("c");//java.lang.IllegalStateException: Deque full
//todo:offer and add The same is to join the team , however offer You can wait a certain time to see if you can insert
bq.offer("a");
bq.offer("b");
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll());
// Blocking 3 second , Let's see if we can handle it c Put it in line
bq.offer("c",3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll());
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll());
// Blocking 5 second , Wait to see if there are any elements that can be extracted
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll(5,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
2. Thread pool principle
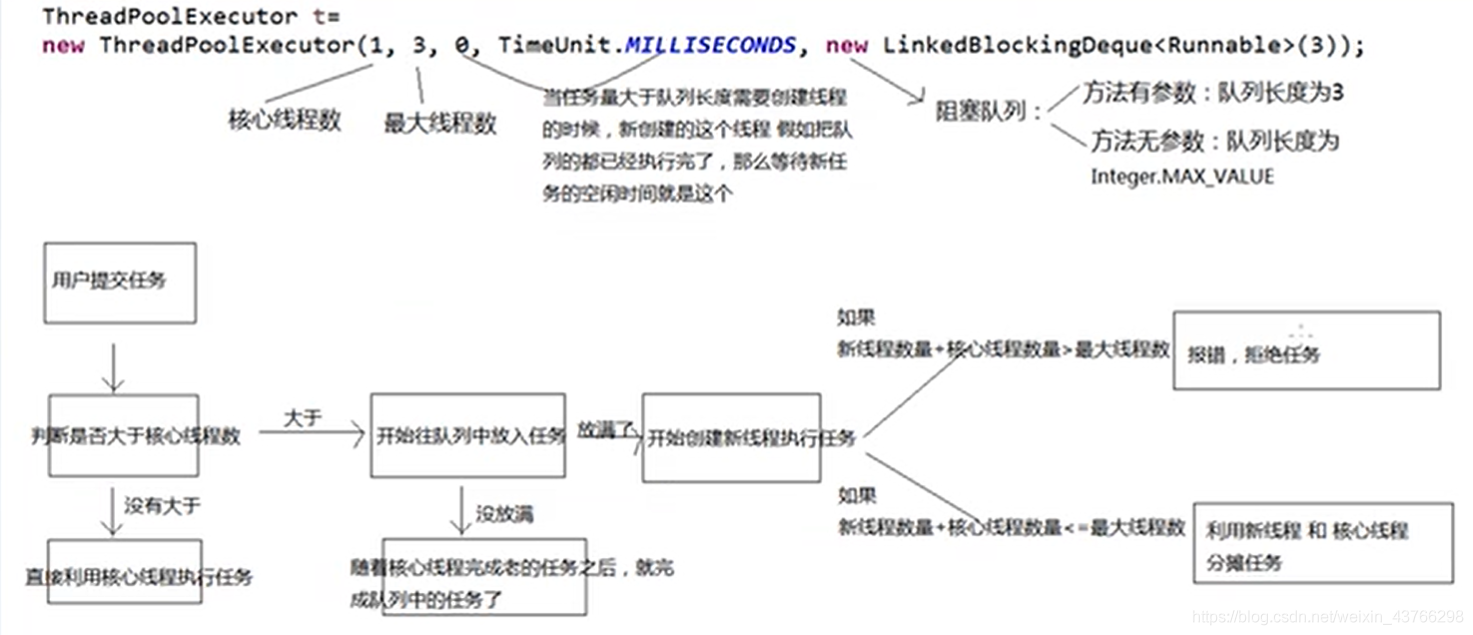
3. Thread pool testing and analysis
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// Using a borderless queue , Let's create a thread with a task
/* Create threads as needed , But the thread pool of previously constructed threads will be reused when available . These pools typically improve the performance of programs that perform many short-term asynchronous tasks . call execute ( If available ) The previously constructed threads are reused . If no existing thread is available , A new thread will be created and added to the pool . Unused 60 Seconds of thread will terminate and be removed from the cache . So keep it idle long enough that the pool doesn't consume any resources */
/* public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
es.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
es.shutdown();
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
/* Create a thread pool , The thread pool can reuse a fixed number of threads , Operate on a shared borderless queue . At any time , most {nThreads} Threads will be active processing tasks . If other tasks are submitted while all threads are active , Then they will wait in the queue , Until the thread is available . If any thread terminates before shutting down due to a failure during execution , If a new thread is required, it will perform subsequent tasks instead . Threads in the pool will exist , Until clearly shutdown*/
/*public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
fixedThreadPool.shutdown();
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
/* Create a thread pool , This thread pool can schedule commands to run after a given delay or execute periodically . @param corePoolSize Number of threads to keep in the pool even when idle */
/*public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//delay(3): Delay three seconds to execute the task
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()),3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//initialDelay(2) : Delay time before the first execution period(1) The time interval between successive executions
//scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()),2,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
scheduledThreadPool.shutdown();
ExecutorService singlePool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
/* Create one using a single worker Thread operation the executor of an unbounded queue . ( But please note , If the single thread terminates due to a failure in the execution process before the shutdown , If follow-up tasks are required , There will be a new replacement .) The task of is to ensure the sequential execution of , And no more than one task will be active at any given time . Equivalent to others newFixedThreadPool(1) The returned execution guarantees that there is no need to reconfigure to use other threads .*/
/* public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
singlePool.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
singlePool.shutdown();
}
边栏推荐
- Redis集群操作的方法
- Important knowledge of golang: mutex
- [openharmony] USB gadget configuration HDC function cfg file interpretation
- 进阶开发- 泛型入门基础类测试
- Analysis of TCP three-time handshake and four-time handshake
- 规避这六大难点,成功实施MES系统
- 他山之石 | 微信搜一搜中的智能问答技术
- Memory consistency and cache consistency
- Thymeleaf——学习笔记
- 【TcaplusDB知识库】Tmonitor单机安装指引介绍(二)
猜你喜欢

MySQL series: storage engine

MySQL series: overview of the overall architecture

12 BeautifulSoup类的初始化

Leetcode 450.删除二叉搜索树中的结点

Important knowledge of golang: detailed explanation of context
![生成二叉搜索平衡树[利用树递归特性]](/img/b3/f8edf45bdfdced7c3698088dbf7d84.png)
生成二叉搜索平衡树[利用树递归特性]

嵌入式软件架构设计-程序分层

5 minutes to quickly launch web applications and APIs (vercel)
513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value

Matlab| sparse auxiliary signal denoising and pattern recognition in time series data
随机推荐
B. AND 0, Sum Big-Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2)
要买的理财产品年限长,划算吗?
MATLAB中iscellstr函数的使用
The running rabbit fell
服务器的部署及使用说明
OpenResty 基础
FPGA 常用缩写及单词在工程领域内的意义
MES在流程和离散制造企业的15个差别(上)
Personal summary of system design and Analysis Course Project
15 differences between MES in process and discrete manufacturing enterprises (Part I)
Why can a high pass filter become a differentiator?
B. Integers Shop-Hello 2022
为什么高通滤波器也能变成微分器?
Important knowledge of golang: atomic atomic operation
Six programming insights in these five years!
window远程桌面连接互传文件加速小技巧
Redis集群操作的方法
Important knowledge of golang: sync Cond mechanism
MySQL series: storage engine
Important knowledge of golang: timer timer