当前位置:网站首页>Review the SQL row column conversion, and the performance has been improved
Review the SQL row column conversion, and the performance has been improved
2022-06-23 04:06:00 【It bond】
hello ! Hello everyone , I am a 【IT bond 】, Jianghu people jeames007,10 year DBA Work experience
A highly motivated 【 Bloggers in big data field 】!
China DBA union (ACDU) member , Currently engaged in DBA And program programming ,B Station and Tencent classroom lecturer , Live broadcast volume breaking 10W
Good at mainstream data Oracle、MySQL、PG Operations and development , Backup recovery , Installation migration , performance optimization 、 Fault emergency treatment, etc .
If there is a pair of 【 database 】 Interested in 【 Cutie 】, Welcome to your attention 【IT bond 】
️️️ Thank you, big and small !️️️
List of articles
Preface
Recently, all the questions raised by fans have something to do with row column switching , So I made a summary of the related knowledge of the row and column conversion , I hope so We can help , What's wrong at the same time , Please point out , I also learn in the process of writing , Let's study togetherThere are six cases of row and column switching :
- Column turned
- Transfer line column
- Multiple columns converted to strings
- Multiple lines into strings
- String into multiple columns
- String to multiple lines
One 、 Column turned
In short, the column name in the original table is used as the content of the converted table , That's column to row
1.1 UNION ALL
create table TEST_JEM
(
NAME VARCHAR2(255),
JANUARY NUMBER(18),
FEBRUARY NUMBER(18),
MARCH NUMBER(18),
APRIL NUMBER(18),
MAY NUMBER(18)
);
insert into TEST_JEM(NAME, JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY)
values (' longevity ', 58, 12, 26, 18, 269);
insert into TEST_JEM(NAME, JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY)
values (' Bishan ', 33, 18, 17, 16, 206);
insert into TEST_JEM(NAME, JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY)
values (' Yang Jiaping ', 72, 73, 79, 386, 327);
insert into TEST_JEM(NAME, JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY)
values (' Wuxi ', 34, 9, 7, 21, 33);
insert into TEST_JEM(NAME, JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY)
values (' Fengdu ', 62, 46, 39, 36, 91);
insert into TEST_JEM(NAME, JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH, APRIL, MAY)
values (' Wulong ', 136, 86, 44, 52, 142);
commit;
SELECT * FROM TEST_JEM;

️ Row to column
SELECT *
FROM (SELECT t.name, 'january' MONTH, t.january v_num
FROM TEST_JEM t
UNION ALL
SELECT t.name, 'february' MONTH, t.february v_num
FROM TEST_JEM t
UNION ALL
SELECT t.name, 'march' MONTH, t.march v_num
FROM TEST_JEM t
UNION ALL
SELECT t.name, 'april' MONTH, t.april v_num
FROM TEST_JEM t
UNION ALL
SELECT t.name, 'may' MONTH, t.may v_num FROM TEST_JEM t)
ORDER BY NAME;

1.2 insert all into … select
First, create the tables you need , test_row
create table test_row
(
NAME VARCHAR2(255),
MONTH VARCHAR2(8),
V_NUM NUMBER(18)
);
SQL> desc test_row

Then perform the following sql sentence :
Be careful : Inquire about test_jem To insert into the table
insert all
into test_row(NAME,month,v_num) values(name, 'may', may)
into test_row(NAME,month,v_num) values(name, 'april', april)
into test_row(NAME,month,v_num) values(name, 'february', february)
into test_row(NAME,month,v_num) values(name, 'march', march)
into test_row(NAME,month,v_num) values(name, 'january', january)
select t.name,t.january,t.february,t.march,t.april,t.may from test_jem t;
commit;
select * from test_row;
1.3 MODEL
CREATE TABLE t_col_row(
ID INT,
c1 VARCHAR2(10),
c2 VARCHAR2(10),
c3 VARCHAR2(10));
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (1, 'v11', 'v21', 'v31');
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (2, 'v12', 'v22', NULL);
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (3, 'v13', NULL, 'v33');
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (4, NULL, 'v24', 'v34');
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (5, 'v15', NULL, NULL);
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (6, NULL, NULL, 'v35');
INSERT INTO t_col_row VALUES (7, NULL, NULL, NULL);
COMMIT;
SELECT * FROM t_col_row;

SELECT id,
cn,
cv
FROM t_col_row
MODEL RETURN
UPDATED ROWS PARTITION BY(ID)
DIMENSION BY(0 AS n)
MEASURES('xx' AS cn, 'yyy' AS cv, c1, c2, c3)
RULES UPSERT ALL(cn[1] = 'c1', cn[2] = 'c2', cn[3] = 'c3', cv[1] = c1[0],
cv[2] = c2[0], cv[3] = c3[0])
ORDER BY ID,cn;

Two 、 Transfer line column
Row to column is to use row data content as column name
CREATE TABLE t_row_col AS
SELECT id, 'c1' cn, c1 cv
FROM t_col_row
UNION ALL
SELECT id, 'c2' cn, c2 cv
FROM t_col_row
UNION ALL
SELECT id, 'c3' cn, c3 cv FROM t_col_row;
SELECT * FROM t_row_col ORDER BY 1,2;

2.1 max+decode
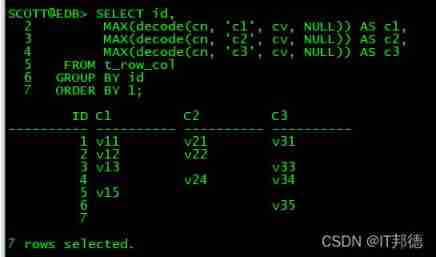
SELECT id,
MAX(decode(cn, 'c1', cv, NULL)) AS c1,
MAX(decode(cn, 'c2', cv, NULL)) AS c2,
MAX(decode(cn, 'c3', cv, NULL)) AS c3
FROM t_row_col
GROUP BY id
ORDER BY 1;
SELECT t.name,
MAX(decode(t.month, 'may', t.v_num)) AS may,
MAX(decode(t.month, 'april', t.v_num)) AS april,
MAX(decode(t.month, 'february', t.v_num)) AS february,
MAX(decode(t.month, 'march', t.v_num)) AS march,
MAX(decode(t.month, 'january', t.v_num)) AS january
FROM test_row t
GROUP BY t.name;

If we want to realize the statistics of different intervals , be :
SELECT * FROM test_row t ORDER BY t.name, t.month;

SELECT t.name,
CASE
WHEN t.v_num < 100 THEN
'0-100'
WHEN t.v_num >= 100 AND t.v_num < 200 THEN
'100-200'
WHEN t.v_num >= 200 AND t.v_num < 300 THEN
'200-300'
WHEN t.v_num >= 300 AND t.v_num < 400 THEN
'300-400'
END AS grade,
COUNT(t.v_num) count_num
FROM test_row t
GROUP BY t.name,
CASE
WHEN t.v_num < 100 THEN
'0-100'
WHEN t.v_num >= 100 AND t.v_num < 200 THEN
'100-200'
WHEN t.v_num >= 200 AND t.v_num < 300 THEN
'200-300'
WHEN t.v_num >= 300 AND t.v_num < 400 THEN
'300-400'
END;

3、 ... and 、 Multiple columns converted to strings
CREATE TABLE t_col_str AS
SELECT * FROM t_col_row;
This is simpler , use || or concat Functions can be implemented :
SELECT concat('a','b') FROM dual;
SELECT ID,
c1 || ',' || c2 || ',' || c3 AS c123
FROM t_col_str;

Four 、 Multiple lines into strings
CREATE TABLE t_row_str(
ID INT,
col VARCHAR2(10)
);
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(1,'a');
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(1,'b');
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(1,'c');
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(2,'a');
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(2,'d');
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(2,'e');
INSERT INTO t_row_str VALUES(3,'c');
COMMIT;
SELECT * FROM t_row_str;

4.1 ROW_NUMBER + LEAD
SELECT id, str
FROM (SELECT id,
row_number() over(PARTITION BY id ORDER BY col) AS rn,
col || lead(',' || col, 1) over(PARTITION BY id ORDER BY col) ||
lead(',' || col, 2) over(PARTITION BY id ORDER BY col) ||
lead(',' || col, 3) over(PARTITION BY id ORDER BY col) AS str
FROM t_row_str)
WHERE rn = 1
ORDER BY 1;

Everybody likes it 、 Collection 、 Focus on 、 Comments WeChat official account
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

【机器学习】 吴恩达机器学习作业 ex2逻辑回归 Matlab实现

1058 multiple choice questions (20 points)

Talk about memory model and memory order

怎么用好MySQL索引

How to process large volume xlsx/csv/txt files?
![[machine learning] wuenda's machine learning assignment ex2 logistic regression matlab implementation](/img/eb/0d4caf0babbe14f51f4dbf1b9ae65d.png)
[machine learning] wuenda's machine learning assignment ex2 logistic regression matlab implementation

如何处理大体积 XLSX/CSV/TXT 文件?

Insérer le tri directement

Using jhipster to build microservice architecture
![[two points] leetcode1011 Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days](/img/fd/c6f31a44ebaf41bd5ab2a342f10d06.png)
[two points] leetcode1011 Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
随机推荐
移动端城市列表排序js插件vercitylist.js
innodb_ruby 视角下 MySQL 记录增删改
数据交易怎样实现
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] [list table] example code for deleting the data at the specified location in the list
How to solve the problem that the web page fails to log in after the easycvr service is started?
仿360桌面悬浮球插件
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] [list table] delete all data sample codes in the list
What is the digital "true" twin? At last someone made it clear!
What if the self incrementing IDs of online MySQL are exhausted?
HAProxy的编译安装及全局配置段说明
The tax software exits when it detects that it is a virtual machine. How to solve this problem?
What is the difference between the poll () method and the remove () method?
How to save the model obtained from sklearn training? Just read this one
Flutter怎么实现不同缩放动画效果
d重载嵌套函数
January 17, 2022: word rule II. Give you a pattern and a character
聊聊内存模型和内存序
Select sort method
APM 工具 SkyWalking 是什么
怎么用好MySQL索引
