当前位置:网站首页>How to process large volume xlsx/csv/txt files?
How to process large volume xlsx/csv/txt files?
2022-06-23 03:51:00 【Sojson Online】
In the development process , There may be such a need , We need to get from the local Excel or CSV And so on , This information may be clock in records , It could be calendar information , It may also be the recent bill flow . But their common feature is that there are many and complicated data , The workload of manual input is huge and easy to make mistakes , It takes a lot of time . Is there any way to automatically parse files and get useful information ?

When the amount of data in this file is not very large , There are many front-end tools to choose from . for example SheetJS, From Excel、CSV There are many ways to use information , It is very convenient .
When the amount of data is only a few thousand , There are many choices , But once the data size increases , Processing becomes complicated . If XLSX/CSV The amount of data reached 100w+ strip ,Office、WPS I want to open it and have a look , It will take a long time .
Then how to get from such a large volume Excel/CSV/TXT Analyze the data in the ?
background
Let's pass a hypothetical requirement , To tell the whole process of understanding . Suppose our demand is from local Excel、CSV、TXT( Or some other format ) Parse the data from the file , After cleaning, it is stored in the local database file . But the volume of these files may be 5M、50M、500M Even larger . So how to upload in the browser environment ?Node How to parse in the environment ?
First , What we need to know is the browser Web How to upload large volume files on the page ?
Web How to upload large volume files on the page ?
Web Pages can also upload large files , But there is a problem . If the data to be uploaded is large , The whole upload process will be so long , Plus the uncertainties in the upload process , Once it fails , Then the whole upload will start from scratch , It takes a long time .
Face the problem , We can divide a large file into several small files , Only upload one copy at a time to solve . So even if a request fails , There's no need to start from scratch , Just upload the failed one again .
If you want to use this method , We need to meet the following needs :
- Large volume files support slicing and uploading
- You can continue transmission at breakpoint
- You can know the upload progress
First, let's take a look at how to cut large files .Web Pages are basically through <input type='file' /> To get the of local files . And by input Of event.target.files Acquired file, It's actually a File Class , yes Blob Subclasses of classes .
Blob Object represents an immutable 、 Class file object of original data . Its data can be read in text or binary format , It can also be converted into ReadableStream For data manipulation . A simple understanding of oneness will Blob Think of it as a binary container , Indicates that a large binary file is stored .Blob Object has a very important method :slice(), What needs to be noted here is Blob Object is immutable ,slice Method returns a new one Blob, Represents the binary file to be cut .
slice() Method accepts three parameters , Starting offset , End offset , There are also options mime type . If mime type , No settings , So new Blob Object's mime The type is the same as the parent . and File Interface based on Blob,File Objects also contain slice Method , The results include active Blob Data in the specified range in the object .
function sliceInPiece(file, piece = 1024 * 1024 * 5) { let totalSize = file.size; // Total file size let start = 0; // Start byte of each upload let end = start + piece; // End bytes per upload let chunks = [] while (start < totalSize) { // The length of each upload is based on the need // File Object inherited from Blob object , So it contains slice Method let blob = file.slice(start, end); chunks.push(blob) start = end; end = start + piece; } return chunks} Get the array after file cutting , You can call the interface one by one and upload it to the server .
let file = document.querySelector("[name=file]").files[0];const LENGTH = 1024 * 1024 * 0.1;let chunks = sliceInPiece(file, LENGTH); // Split the slice first chunks.forEach(chunk=>{ let fd = new FormData(); fd.append("file", chunk); post('/upload', fd)})After uploading, send it to the server to splice the slice file into a complete file , Give Way FileReader Objects from Blob Read data from .
Of course, there are two problems here , One is to face a pile of sliced files uploaded , If the server knows their correct order ? The second is if multiple large files are uploaded at the same time , How can the server determine which slice belongs to which file ?
The question of sequence , We can construct sliced FormData Add parameters to handle . For example, use parameters ChunkIndex Indicates the order of the current slice .
The second problem can be solved by adding parameters, such as sourceFile etc. ( The value can be the full path of the current large volume file or more strictly the path of the file hash value ) To mark the source of the original file . In this way, when the server obtains the data , You can know which slices come from which file and the sequence between slices .
If it is not convenient to construct by yourself for the time being , You can also consider using cloud services , For example, cloud storage supports large file upload and breakpoint continuation . such as :
Breakpoint continuation
When uploading large files or files on the mobile terminal , Because the network quality 、 Upload failed due to long transmission time and other reasons , You can use breakpoints to continue . Specially , The picture uploaded by breakpoint continuation does not support preprocessing . Specially , Files uploaded by breakpoint continuation cannot be overwritten by other upload methods , If you need to cover , The file must be deleted first .
Name concept
The file is partitioned : Directly cut binary files into small pieces . The block size is fixed to 1M. Except for the last block .
Upload phase : Use x-upyun-multi-stage The parameters of the continuation phase indicate . It is divided into the following three stages : initate( Upload initialization ), upload( Uploading ), complete( End of upload ). Each stage is carried out in turn .
Piece number : Use x-upyun-part-id Parameter to indicate the current slice serial number , The serial number from 0 Start up .
Sequential upload : For the same breakpoint, continue the transmission task , Only sequential upload is supported .
Upload logo : Use x-upyun-multi-uuid Parameter to uniquely identify an upload task , Type is string , The length is 36 position .
Upload cleanup : Resume incomplete files at breakpoint , Will save 24 Hours , Beyond , The file will be deleted .
You can see , Cloud storage is realized through fragment serial number x-upyun-part-id And upload logo x-upyun-multi-uuid It solves the two problems we mentioned earlier . It should be noted here that these two data are not generated by the front end itself , Instead, after the initial upload, it passes responseHeader Back to .

What I said earlier is to use Web How to upload large files on the page . So let's see NodeJS How to parse 、 Dealing with such large files ?
NodeJS Parsing large volume files
First of all, we need to define a concept NodeJS Not in it File object , But there are fs( file system ) modular .fs The module supports standard POSIX Functional modeling interacts with the file system .
POSIX It's a portable operating system interface Portable Operating System Interface of UNIX Abbreviation . Simply speaking POSIX It is to provide a unified calling interface under the operating systems provided by different kernels , For example linux Open the file and in widnows Next, open the file . Maybe the way the kernel provides is different , But because fs It's supporting POSIX The standard , So for program apes, no matter what the kernel provides , Directly in Node Li Diao fsPromises.open(path, flags[, mode]) Method can be used .
It's easy to use here Vue Illustrate with examples .Vue For example, in different environments Web The page or Weex The way of generating page elements is different . For example Web Under the createElement It's like this :
export function createElement (tagName: string, vnode: VNode): Element { const elm = document.createElement(tagName) if (tagName !== 'select') { return elm } // false or null will remove the attribute but undefined will not if (vnode.data && vnode.data.attrs && vnode.data.attrs.multiple !== undefined) { elm.setAttribute('multiple', 'multiple') } return elm}export function createElement (tagName: string): WeexElement { return document.createElement(tagName)} In the above two cases createElement It's different . Empathy , There are many other ways to create modules or elements , But for different platforms ,Vue Provides the same patch Method , To update or create components .
import * as nodeOps from 'web/runtime/node-ops'import { createPatchFunction } from 'core/vdom/patch'import baseModules from 'core/vdom/modules/index'import platformModules from 'web/runtime/modules/index'// the directive module should be applied last, after all// built-in modules have been applied.const modules = platformModules.concat(baseModules)// nodeops Encapsulates a series of DOM Operation method .modules The implementation of hook function of some modules is defined export const patch: Function = createPatchFunction({ nodeOps, modules })△ Web Under platform conditions
import * as nodeOps from 'weex/runtime/node-ops'import { createPatchFunction } from 'core/vdom/patch'import baseModules from 'core/vdom/modules/index'import platformModules from 'weex/runtime/modules/index'// the directive module should be applied last, after all// built-in modules have been applied.const modules = platformModules.concat(baseModules)export const patch: Function = createPatchFunction({ nodeOps, modules, LONG_LIST_THRESHOLD: 10})△ weex Under platform conditions
such , Whether the internal implementation of the running environment is different or not , Just call the same patch The method can . and POSIX The idea is the same as the case illustrated above .
Have a brief understanding of POSIX, We go back to fs modular .fs The module provides many ways to read files , for example :
- fs.read(fd, buffer, offset, length, position, callback) Read file data . To manipulate files , You have to open the file first , This method is fd, It's called fs.open File descriptor returned .
- fs.readFile(path[, options], callback) Read all the contents of the file asynchronously . You can view it as fs.read Further encapsulation .
The usage scenario is as follows :
import { readFile } from 'fs';readFile('/etc/passwd','utf-8', (err, data) => { if (err) throw err; console.log(data);});because fs.readFile Function to buffer the entire file , If the file to be read is small, it's OK , However, if the file size is large, it will put pressure on the memory . Is there a way to read files with less memory ?
yes , we have , Our leading role today stream Stream on stage .
stream
stream Stream is used in Node.js Abstract interface for processing stream data in . stream The module provides a method for implementing the flow interface API. Streams can be readable 、 Writable 、 Or both .
fs There is a... In the module fs.createReadStream(path[, options]) Method , It returns a readable stream , The default size is 64k, That is, buffering 64k. Once the internal read buffer reaches this threshold , The stream will temporarily stop reading data from the underlying resource , Until the current buffered data is consumed .
The method of consumption data can be to adjust pipe() Method , It can also be consumed directly by events .
// pipe consumption readable.pipe(writable)// perhaps // Event consumption readable.on('data', (chunk) => { writable.write(chunk);});readable.on('end', () => { writable.end();});Except for readable streams , There are also writable streams fs.createWriteStream(path[, options]), You can write data to a file .
Okay , The required pre knowledge is basically introduced , Back to the point . Suppose we have a folder , There are dozens of XLSX/CSV file , And each volume exceeds 500M. How to read information from these files , And write it into the database file ?
Batch parsing CSV file
Suppose we already know the file path we need to parse , You can get the file through the path , Then store these paths in an array and name them needParseArr, We need to parse these one by one in order CSV、XLSX file information , Clean and write to the database .
First , Is the logic of reading one by one (readOneByOne).
async readOneByOne () { try { for (let i = 0; i < needParsePathArr.length; i++) { const filePath = needParsePathArr[i] console.log(` Resolve to the second ${i} File , file name :${filePath}`) await streamInsertDB(filePath) } } catch (err) { }}async function streamInsertDB (filePath) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const ext = path.extname(filePath) // Determined the file type if (ext === '.csv') { // analysis csv parseAndInsertFromCSV(filePath, resolve, reject) } else if (ext === '.xlsx') { // Self executing functions (async function getName () { try { // First convert to csv. You can also not convert , Direct analytical xlsx, This will be explained in detail later . const csvFileName = await convertXlsx2Csv(filePath) // Reuse resolution csv The logic of parseAndInsertFromCSV(csvFileName, resolve, reject) } catch (error) { reject(`error: ${error.message || error}`) } })() } })}parseAndInsertFromCSV Is the main position to use the knowledge points we mentioned earlier . Let's briefly introduce each function :
- chardet: This function is used to monitor CSV The encoding format of the file , After all, not everyone CSV All are UTF-8 code , With Chinese CSV The encoding type may be GBK perhaps GB18030、GB18031 wait , This format is read directly without processing , Chinese will be displayed as garbled . So the function that needs to perform the conversion iconv Change my .
- pipe: Can be used to build pipe chains , It can be understood as pipe It acts like a pipe , You can read and write to the target stream , Here we are decoding and recoding .
- insertInBlock: This function is to obtain a certain amount of data ( In this case, it is from CSV Resolve in 3 When there are about 10000 pieces of data ), Pause and do something , For example, write to the database or filter the data in it 、 Processing and so on , According to the actual needs .
- csv: This function is used to read out the specific data in the stream .
The specific logical explanation can be seen in the notes .
const chardet = require('chardet');const csv = require('fast-csv'); // Faster parsing csv Speed tools const iconv = require('iconv-lite');const arrayFromParseCSV = [] // Store the parsed lines csv Data let count = 0 // Count // resolve, reject It's from an external function , Used to judge the state of function execution , In order to correctly carry out subsequent logical processing function parseAndInsertFromCSV (filePath, resolve, reject) { const rs = fs.createReadStream(filePath) // Create a readable stream // The anti shake and Coriolis here const delayInsert = debounce((isEnd, cb = () => {}) => insertInBlock(isEnd, cb, rs, resolve, reject), 300) /// sampleSize: 5120 Indicates that the value is before reading the file 5120 Bytes of data , You can judge the encoding type of the file , You don't need to read all chardet.detectFile(filePath, { sampleSize: 5120 }).then(encoding => { // If not UTF-8 code , Convert to utf8 code if (encoding !== 'UTF-8') { rs.pipe(iconv.decodeStream(encoding)) .pipe(iconv.encodeStream('UTF-8')) .pipe(csv.parse({ header: false, ignoreEmpty: true, trim: true })) // analysis csv .on('error', error => { reject(` analysis csv error: ${error}`) }) .on('data', rows => { count++ // Count , Because we have to read and operate in blocks arrayFromParseCSV.push(rows) // When you read it, push it to the array if (count > 30000) { // Have read 30000 That's ok , We're going to take this 3w OK, get rid of , Avoid using too much memory . rs.pause() // Pause the read stream delayInsert(false) // false It's not over yet . Be careful : Even if rs.pause, The reading of the stream is not suspended immediately , So you need anti shake . } }).on('end', rowCount => { console.log(` The analysis is finished ${filePath} The documents are ${rowCount} That's ok `) delayInsert(true, () => { rs.destroy() // Destroy stream resolve('ok') // A file has been read }) }) } })} The logic of cleaning data and subsequent operations is insertInBlock in .
function insertInBlock (isEnd, cb, filePath, resolve, reject) { const arr = doSomethingWithData() // There may be some data cleaning operations // If our subsequent demand is to write data into the database const batchInsert = () => { batchInsertDatabasePromise().then(() => { if (cb && typeof cb === 'function') cb() !isEnd && rs.resume() // The data of this fragment is written , You can resume the stream and continue reading }) } const truely = schemaHasTable() // For example, judge whether there is a table in the database , Write if you have . No table is created before writing . if (truely) { // batchInsert() } else { // Create tables or other operations , And then write doSomething().then(() => batchInsert()) }} such , The process of parsing and writing is completed . Although a lot of business code has been simplified , But the implementation is generally similar to this process .
Batch parsing XLSX file
Turn it into CSV?
In the previous code example , We take advantage of writable streams fs.createWriteStream take XLSX File conversion to CSV The file is then reused and parsed CSV . What needs to be noted here is , Writing data to CSV Format file , To write at the beginning bom head \ufeff. It can also be used xlsx-extract Of convert function , take XLSX File conversion to TSV.
const { XLSX } = require('xlsx-extract')new XLSX().convert('path/to/file.xlsx', 'path/to/destfile.tsv') .on('error', function (err) { console.error(err); }) .on('end', function () { console.log('written'); })Some might wonder , No CSV Well , How to convert it into TSV Well ?
Actually tsv and CSV The only difference is that the separators of field values are different ,CSV Separate values with commas (Comma-separated values), and TSVA Use tabs to separate values (Tab-separated values). We used it to quickly parse CSV Of documents fast-csv The tool is to support the selection of tabs \t As a separator for values .
import { parse } from '@fast-csv/parse';const stream = parse({ delimiter: '\t' }) .on('error', error => console.error(error)) .on('data', row => console.log(row)) .on('end', (rowCount: number) => console.log(`Parsed ${rowCount} rows`));Direct analytical ?
Can it not be converted into CSV, Direct analytical XLSX What about the documents ? In fact, it is also feasible .
const { xslx } = require('xlsx-extract') // Stream parsing xlsx File tools // parser: expat, Additional installation required node-expat, It can improve the parsing speed .new XLSX().extract(filePath, { sheet_nr: 1, parser: 'expat' }) .on('row', function (row) { // When each row of data is obtained, it can trigger }).on('error', function (err) { // error });But this approach has one drawback , Once parsing starts , You can't pause the process of data reading .xlsx-extract Encapsulates the sax, There is no way to pause and resume .
If we directly use the readable stream to read XLSX What happens to the file ?
const readStream = fs.createReadableStream('path/to/xlsx.xlsx')You can see that the data in the stream is now buffer There is a form of . But because of xlsx The format is actually a zip Compressed format of archive , Stored XML Text information of structure . So readable streams cannot be used directly , You need to decompress it first .
Decompression can use npm package unzipper .
const unzip = require('unzipper')const zip = unzip.Parse();rs.pipe(zip) .on('entry', function (entry) { console.log('entry ---', entry); const fileName = entry.path; const { type } = entry; // 'Directory' or 'File' const size = entry.vars.uncompressedSize; // There is also compressedSize; if (fileName === "this IS the file I'm looking for") { entry.pipe(fs.createWriteStream('output/path')); } else { entry.autodrain(); } })Now we have unzipped the file .
Mentioned earlier ,xlsx-extract yes Encapsulates the sax, and sax Itself is used to analyze XML Textual , Then we can also use sax To process the readable stream .
sax The parsed source code can be seen here , Roughly judge the content of each character 、 Line break 、 Start 、 End and so on , Then trigger the corresponding event .
const saxStream = require('sax').createStream(false);saxStream.on('error', function (e) { console.error('error!', e);});saxStream.on('opentag', function (node) { console.log('node ---', node);});saxStream.on('text', (text) => console.log('text ---', typeof text, text)); Finally, combine the two :
const unzip = require('unzipper');const saxStream = require('sax').createStream(false);const zip = unzip.Parse();saxStream.on('error', function (e) { console.error('error!', e);});saxStream.on('opentag', function (node) { console.log('node ---', node);});saxStream.on('text', (text) => { console.log('text ---', typeof text, text)});rs.pipe(zip) .on('entry', function (entry) { console.log('entry ---', entry); entry.pipe(saxStream) }) Use local XLSX After file test , The console prints out the following information :

This information corresponds to XLSX This part of the information in the document .Node Printed in ST SI, Represents the xml The label of .

such , In fact, we also got XLSX The data in , But these data still need to be cleaned 、 Summary 、 One-to-one correspondence . At the same time, because we operate directly on the readable stream , Naturally, it can be pause、resume flow , To realize the logic of block reading and other operations .
summary
For smaller XLSX、CSV file , basic SheetJS It can meet the parsing requirements of various format files , But once the document is large , So slice 、 Streaming reading and writing will become an essential way .
Through the previous examples and code decomposition , We can understand the solutions to such problems , It can also expand different solutions to similar needs . Once we can have a certain concept and understanding of block processing of large volume files , So when you encounter similar problems , You know where the realization idea is .
Article from Cloud again contribute
边栏推荐
- Easygbs service is killed because the user redis is infected with the mining virus process. How to solve and prevent it?
- How to get started with apiccloud app and multi terminal development of applet based on zero Foundation
- [tcapulusdb knowledge base] [list table] example code of batch deleting data at specified location in the list
- 【曾书格激光SLAM笔记】Gmapping基于滤波器的SLAM
- Insérer le tri directement
- January 17, 2022: word rule II. Give you a pattern and a character
- [leetcode] flip linked list II
- 【贪心】leetcode991. Broken Calculator
- [two points] leetcode1011 Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
- Insert sort directly
猜你喜欢
![[two points] leetcode1011 Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days](/img/fd/c6f31a44ebaf41bd5ab2a342f10d06.png)
[two points] leetcode1011 Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
![[OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 build 2: test unit construction and operation](/img/b0/4ea8069a88ce19ca7dbfa67ac9fcba.png)
[OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 build 2: test unit construction and operation

mysql存储引擎之Myisam和Innodb的区别
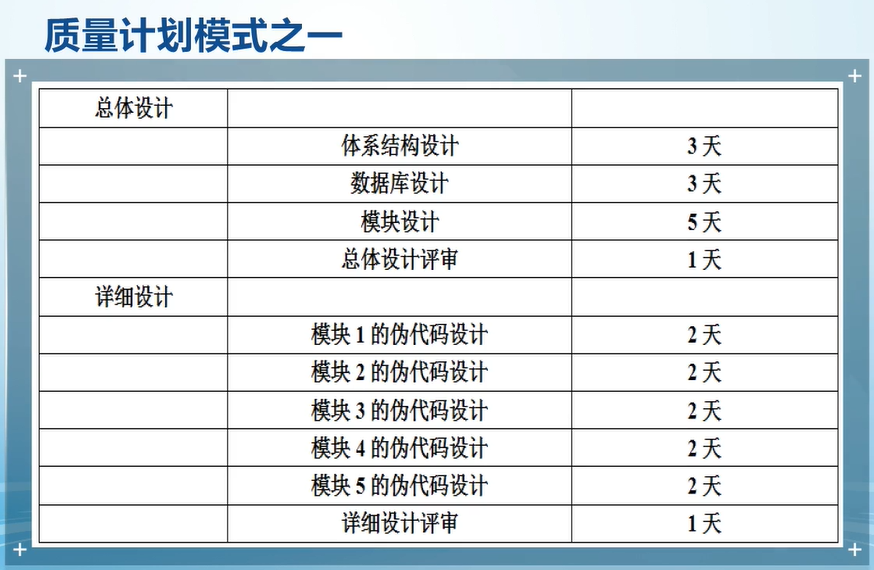
Software project management 8.4 Software project quality plan

Hierarchical attention graph convolution network for interpretable recommendation based on knowledge graph

Detailed discussion on modular architecture design of MCU firmware

Google Earth Engine(GEE)——长时间序列逐月VCI数据提取分析和面积计算(墨西哥为例)

第一批00后下场求职:不要误读他们的“不一样”

1-1 introduction to VMWare
One of the touchdesigner uses - Download and install
随机推荐
1-1 introduction to VMWare
1058 multiple choice questions (20 points)
【owt】owt-client-native-p2p-e2e-test vs2017构建 4 : 第三方库的构建及链接p2pmfc.exe
How to solve the problem that the web page fails to log in after the easycvr service is started?
Easygbs service is killed because the user redis is infected with the mining virus process. How to solve and prevent it?
The first batch of job hunting after 00: don't misread their "different"
数据加密技术之源代码加密
The new version of Kali switches the highest account
第一批00后下场求职:不要误读他们的“不一样”
d重载嵌套函数
Troubleshooting and resolution of asydss virtual live broadcast status synchronization and service downtime
Simple analysis of easygbs compatible with old version HLS streaming address method [with code]
Adobe international certification 𞓜 how IIT Madras brings efficiency and accessibility to scholars through Adobe e Acrobat
折半查找法
Which insurance company is the most cost-effective for purchasing serious illness insurance?
Is LinkedList a one-way linked list or a two-way linked list?
Apicloud native module, H5 module and multi terminal component tutorial
【LeetCode】翻转链表II
[OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 build 3: no test unit comparison, manually generate vs projects
One of the touchdesigner uses - Download and install