当前位置:网站首页>ADC acquisition noise and comparison between RMS filter and Kalman filter
ADC acquisition noise and comparison between RMS filter and Kalman filter
2022-06-26 00:51:00 【To, violet】
For a while, the author was doing a PT100 The conditioning circuit of thermal resistance adopts , Use a constant current source to measure the resistance of the thermal resistance . For the convenience of collection , take 0.3mA The current of is connected PT100 Put... Directly ADC The input terminal is connected to PT100 Both ends . When the temperature is output later, the data is very chaotic . Access to information is inspired , Use to find the effective value of the signal ( Root mean square value ) Method to filter .
ADC sampling 、 Constant current source
ADC It uses STM32F10x Inside the series 12 position ADC. The current value of the constant current source is 0.3mA.
PT100 Thermal resistance
PT100 It's below zero , The resistance value is 100Ω Thermal resistance of , The temperature characteristic curve is shown in the figure 1

chart 1:PT100 Temperature characteristic curve
Basically, in -200—600 There is a linear relationship between temperature and resistance . Therefore, measurement PT100 One way to measure resistance is to give PT100 Connect a constant current source , Then measure the voltage at both ends and then calculate PT100 Resistance value .
Noise analysis
Power on the circuit ( The power supply adopts two sections 18650 Series connection ,AMS1115-3.3V Voltage reduction and stabilization ) Connect both ends of the thermal resistance to the oscilloscope ( Input impedance 1MΩ) Pictured 2.Single once , Then, all the sampling data in the interface are processed FFT( The fast Fourier transform ) Get the picture 3、 chart 4. It is not difficult to see that the noise mainly comes from 1Mhz And some Gaussian white noise .

chart 2: The original signal

chart 3:FFT

chart 4:FFT
Root mean square noise removal

To find the root mean square value of a signal is actually to find the effective value of the signal (RMS) That is, the mean square of the signal is redistributed .ADC Sampling frequency is 10Khz. Every time 100 Data to calculate . The calculated data is output by the serial port , See the picture :6、 chart 7.(C See the program for the code 1)
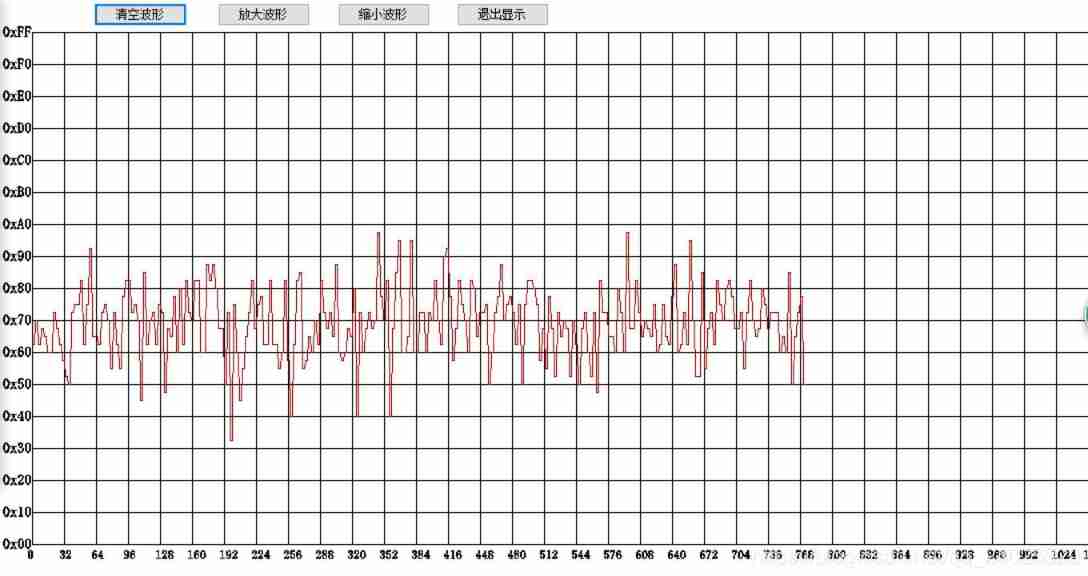
chart 5: Serial port outputs raw data

chart 6: Filter data

chart 7: to PT100 Heating temperature
First order low pass filter
y(n) = q*x(n) + (1-q)*y(n-1)
in Y(n) For export ,x(n) For input . among Q take 0.5 The input waveform is shown in Figure 8.(C See the program for the code 2)
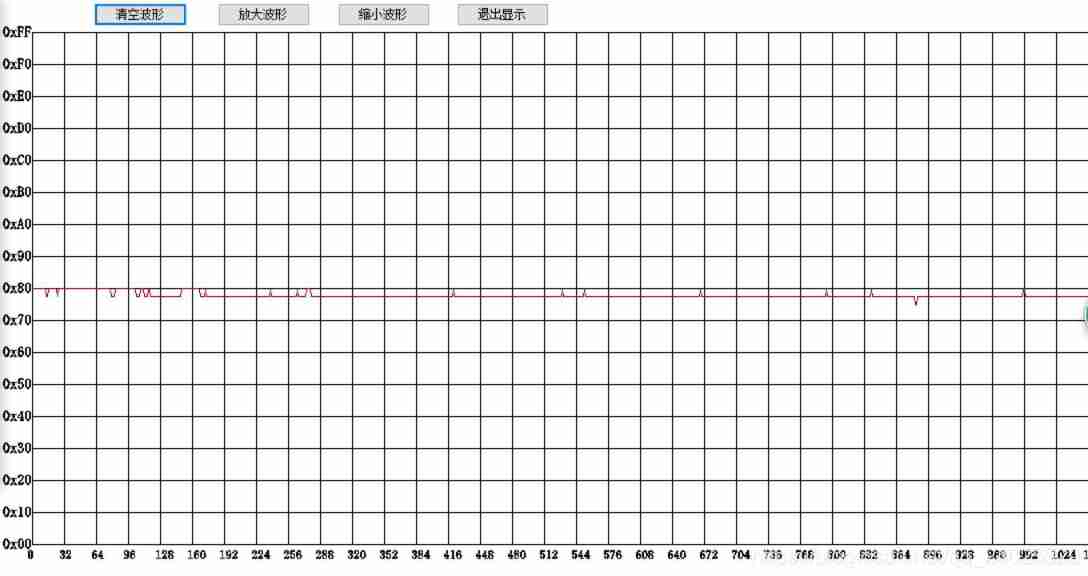
chart 8: Add the first-order low-pass filter serial port output
kalman wave filtering
The first step is to import the data MATLAB, Draw the raw data curve . See the picture 9.. Make the data as Kalman filter observation matrix . Put the data of t-2 To t The mean value of the time is used as the speculative matrix ( See additional code for details ). Finally, the Kalman output is made into a moving average . Kalman output model ( Blue ) See the picture 10.(matlab See the program for the code 3)

chart 9:MATLAB Import raw data

chart 10: Raw data and filtered data
summary :
A large part of the reason for the noise is that the digital and analog are not separated when drawing the circuit board .Kalman Filtering algorithm is a filtering algorithm based on time domain . The author thinks that the Gaussian white noise in this circuit mainly comes from the interference of power supply and digital signal to analog signal . As far as this circuit is concerned, it is an effective method to find the root mean square value of the signal . The author has limited knowledge , If there are mistakes, please correct them .
Program 1
unsigned int disposePT100v()
{
unsigned char i;
double dData[100];
double dSum;
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
dData[i] = g_iADC[0];// obtain ADC data
dSum +=pow(dData[i],2);// Do the sum of squares
delay_us(100);
}
dSum /= 100;// Calculating mean
dSum = sqrt(dSum);// prescribing
return (unsigned int)dSum*3300/4096;//mv Voltage value
}Program 2
unsigned int lowV(unsigned int com)
{
static unsigned int iLastData;
unsigned int iData;
double dPower=0.5;
iData = (com*dPower)+(1-dPower)*iLastData;// Calculation
iLastData = iData;//jilu
return iData;// Return the data
}Program 3
clear
clc
ydata=textread('a123.txt','%s');%% Import data
cData = hex2dec(ydata);% Convert to 10 Hexadecimal data
%t-1 The output of the time is taken as the estimated value of the system at this time Optimal deviation ( initial value )g_zer Speculative error ( initial value )g_ter Measured value deviation ( initial value )g_cer
% Measurement results ( matrix ) ner1 Conjecture ( matrix )ner2 (end)
g_zer = 5;%% Initial value of optimal deviation
g_ter = 3;%% Guess the initial value of deviation
g_cer = 2;%% Measure the initial value of deviation
kdata = 0;
for i=1:5792%% iteration 5000 Time
ner1 = cData(i);
if i>3
ner2 = (cData(i-2)+cData(i-1)+cData(i))/3;%%t-2 Moment to t The average value of time is taken as t The estimated value of time
else
ner2 = kdata;
end
if g_zer>g_ter
g_er = sqrt((g_zer^2)-(g_ter^2));% Calculate this error
else
g_er = sqrt((g_ter^2)-(g_zer^2));% Calculate this error
end
kk = sqrt((g_er^2)/((g_er^2)+(g_cer^2)));% Calculate Kalman gain
kdata = ner1+kk*(ner2-ner1);% Update Kalman output
g_zer = ((1-kk)*g_ter^2)^0.5;% Calculate the optimal deviation
cKdata(i) = kdata;
end
%%%%%%% moving average %%%%%%%%%%
t = 1:5792;
a = 0;
b = 0;
pKdata = zeros(1,5792);
for i=1:5700
for j=1:50
a = a + cKdata(i+j);
end
b = a/50;%% Averaging
a = 0;
pKdata(i)=b;
end
plot(t,cData,'R',t,cKdata,'G',t,pKdata,'B');
边栏推荐
- 简单 deepclone
- 每日一问:线程和进程的区别
- Atlas200dk brush machine
- 随便画画的
- Flink reports error: a JNI error has occurred, please check your installation and try again
- Understanding of prototypes and prototype chains
- mtb13_Perform extract_blend_Super{Candidate(PrimaryAlternate)_Unique(可NULL过滤_Foreign_index_granulari
- How to deliver a shelter hospital within 48 hours?
- Methods to realize asynchrony
- 鼠标拖拽围绕某个物体旋转展示
猜你喜欢

Is camkiia the same as gcamp6f?

使用VS2022编译Telegram桌面端(tdesktop)

Explain from a process perspective what happens to the browser after entering a URL?
![[TSP problem] solving traveling salesman problem based on Hopfield neural network with matlab code](/img/a9/4fbe82fc77712f2e10119aacb99143.png)
[TSP problem] solving traveling salesman problem based on Hopfield neural network with matlab code
![Final review [machine learning]](/img/63/d617a95592b1499cff0161bd5c3e9e.png)
Final review [machine learning]
Post ordered clue binary tree

86. (cesium chapter) cesium overlay surface receiving shadow effect (gltf model)

Leetcode 513. Find the value in the lower left corner of the tree

【图像检测】基于高斯过程和Radon变换实现血管跟踪和直径估计附matlab代码

Preorder and middle order traversal of forest
随机推荐
2021-04-28
1-11solutions to common problems of VMware virtual machine
Ssl/tls, symmetric and asymmetric encryption, and tlsv1.3
Comprehensive introduction to Simulink solver
Send mail tool class
Web学习之TypeScript
213. house raiding II
Why do we need to make panels and edges in PCB production
1-10vmware builds customized network architecture
How to bypass SSL authentication
CaMKIIa和GCaMP6f是一样的嘛?
Precautions for cleaning PCBA board in SMT chip processing
Performance leads the cloud native database market! Intel and Tencent jointly build cloud technology ecology
基于OpenVINOTM开发套件“无缝”部署PaddleNLP模型
Flex & Bison 开始
"Method not allowed", 405 problem analysis and solution
11.1.2 overview of Flink_ Wordcount case
Mining pit record of modified field information in Dameng database
Analyze the five root causes of product development failure
论文中英文大小写、数字与标点的正确撰写方式