当前位置:网站首页>Shader common functions
Shader common functions
2022-06-24 08:04:00 【Kenight_】
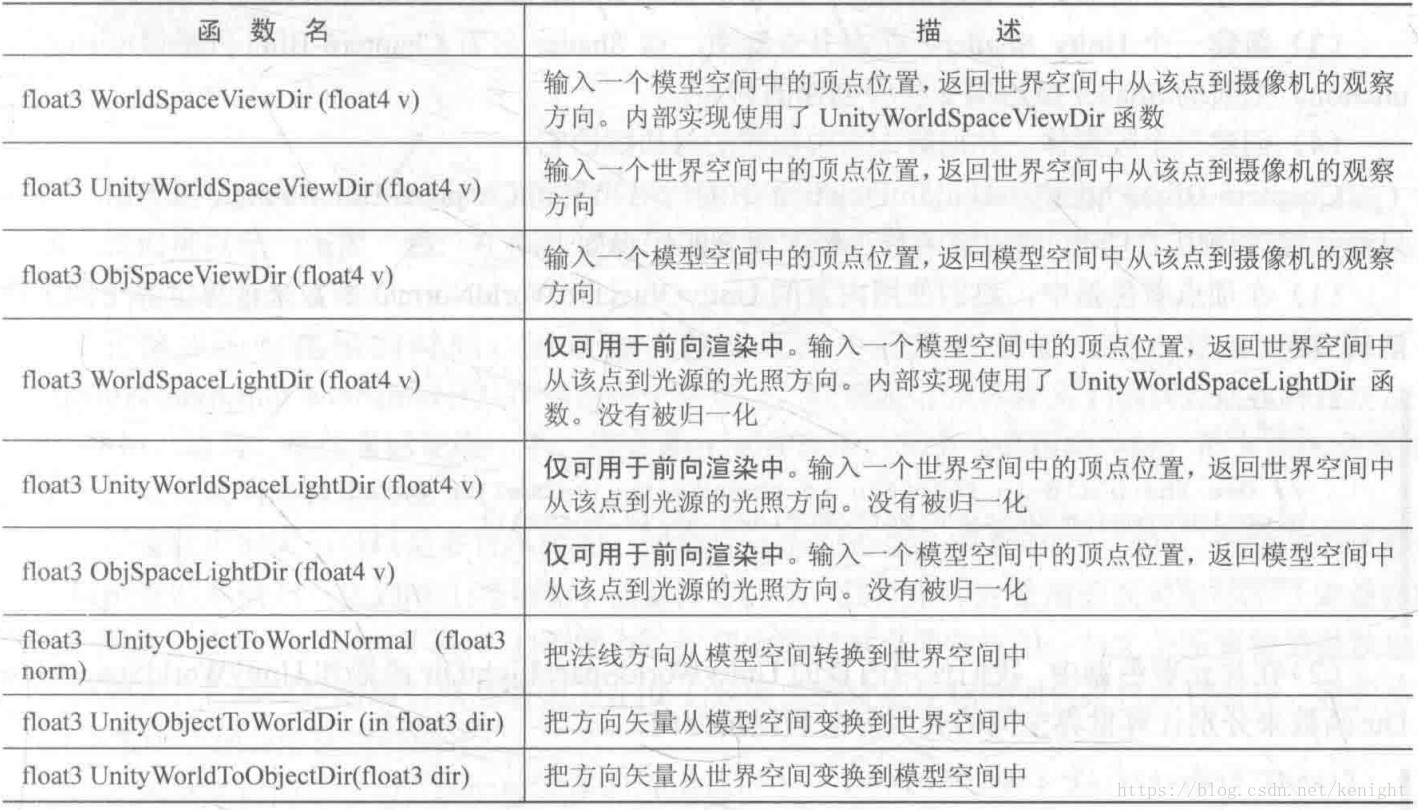
- Transform the direction vector from model space to world space
float3 UnityObjectToWorldDir(float3 dir)
// amount to
float3 normalize(mul((float3x3)unity_ObjectToWorld, dir));To change the direction, just multiply float3x3 matrix , This is because of the direction vector w Coordinate for 0 [x,y,z,0] And the vertex w by 1 [x,y,z,1], Change direction if and float4x4 matrix multiplication , The translation amount of the fourth column in the matrix will not affect the transformation .
- Transform vertices from model space to world space
// Compared with changing direction , Transforming vertices requires float4x4 matrix
float3 mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;- Transform vertices from model space to observation space
// Returns only the xyz coordinate , And z It's negative ( The field of vision is the right hand system )
float3 UnityObjectToViewPos(float3/float4 pos)- Transform normal vector from model to world space
float3 UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal)
// Internal implementation details
#ifdef UNITY_ASSUME_UNIFORM_SCALING // In case of uniform scaling , Then the matrix of changing direction can be used directly
return UnityObjectToWorldDir(norm);
#else // In case of non-uniform scaling , You need to right multiply the inverse transpose matrix of the matrix in the transformation direction
// mul(IT_M, norm) => mul(norm, I_M) => {dot(norm, I_M.col0), dot(norm, I_M.col1), dot(norm, I_M.col2)}
// Parse the uplink comment : Right multiply inverse transpose matrix => Left multiply inverse matrix => The column of the inverse matrix of point multiplication ( The dot multiply column is equivalent to the row after dot multiply transpose )
// According to the above equation , The result can be obtained by left multiplying the inverse matrix of the transformation direction matrix (I_M equivalent unity_WorldToObject)
return normalize(mul(norm, (float3x3)unity_WorldToObject));
#endifIf the model is non uniformly scaled, such as Scale(1,2,1), If you use a matrix with the same transform vertices to transform normals , Then the transformed normal cannot maintain the original verticality . According to the operation of the matrix , The meaning of left multiplication is equivalent to right multiplication of the transposed matrix of the matrix .
- Transform normal vector from model to observation space
// According to the above normal transformation to world space , Non uniform scaling , You need to right multiply the inverse transpose matrix
// Unity This inverse transpose matrix is provided directly UNITY_MATRIX_IT_MV
float3 mul((float3x3)UNITY_MATRIX_IT_MV, v.normal);- The direction of sight in world space ( The vertex faces in the direction of the camera )
float3 UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(float3 worldPos)
// amount to ( Note that the result is not normalize)
return _WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - worldPos;
// General usage :
float3 normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(worldPos))- Transformation matrix from model space to tangent space
// Built in macro , Output rotation matrix , The variable name is fixed to rotation
TANGENT_SPACE_ROTATION
// Implementation details
// v.tangent.w Determine the direction of the sub tangent
float3 binormal = cross( normalize(v.normal), normalize(v.tangent.xyz) ) * v.tangent.w;
float3x3 rotation = float3x3( v.tangent.xyz, binormal, v.normal ) // This is the row vector matrix The matrix from tangent space to model space is composed of tangents 、 Sub tangent line 、 The order of normals is Column arrangement You can get , Then according to the properties of orthogonal matrix , The inverse of a matrix with only rotation and translation is equal to its transpose matrix . So put the tangent line 、 Sub tangent line 、 Normal press Row arrangement Then we can get the inverse matrix .
- Transformation matrix from tangent space to world space
// Get vertex normals 、 Tangent line 、 Representation of sub tangent in world space
fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
fixed3 worldTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.tangent.xyz);
fixed3 worldBinormal = cross(worldNormal, worldTangent) * v.tangent.w;
// These three terms are equivalent to the representation of the coordinate axis of the subspace in the parent space , The transformation matrix from tangent space to world space can be obtained by directly constructing the matrix by column
o.TtoW0 = float3(worldTangent.x, worldBinormal.x, worldNormal.x); // The first row of the matrix
o.TtoW1 = float3(worldTangent.y, worldBinormal.y, worldNormal.y); // The second row of the matrix
o.TtoW2 = float3(worldTangent.z, worldBinormal.z, worldNormal.z); // The third row of the matrix Use multiple variables to build a matrix , Freely arrange by column vector or row vector . Use float3x3 Variables are matrices arranged by row vectors .
// give an example : Use this matrix to transform the vector stored in the tangent space normal map into world space
fixed3 bump = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.BumpUv));
fixed3 normal = normalize(half3(dot(i.TtoW0, bump), dot(i.TtoW1, bump), dot(i.TtoW2, bump)));According to the definition of matrix multiplication , Just by bump Point multiplication Column matrices To get the corresponding component
- Obtain the screen space sampling coordinates corresponding to the vertex
// The purpose is , obtain [0,1] Coordinates of the screen texture that can be sampled
// actually , The function itself will only xy Change to [0,w] (zw unchanged ), You need to perform perspective division in the slice function to get the final [0,1]
// among z Is to observe space z After zooming and panning ( Projection matrix transformation ) Non linear value after
// and w Is the depth value of the observation space ( Correct ), namely view space's -z
// Be careful : Parameters received are clip space position
float4 ComputeScreenPos (float4 clipPos)
// for sampling a GrabPass texure ( Cross platform processing of sampling coordinates )
float4 ComputeGrabScreenPos (float4 clipPos)Why not do the perspective division directly in the function ? Because the interpolation process from vertex function to slice function will lead to incorrect results .
- Sample the normal map and get the correct normal information
fixed3 UnpackNormal(fixed4 packednormal) // packednormal = tex2D(_BumpMap, i.BumpUv)
// Implementation details :
#if defined(UNITY_NO_DXT5nm) // If the texture is not compressed , Directly restore to [-1,1] Between
return packednormal.xyz * 2 - 1;
#else // otherwise ( After compression ), adopt xy The components are calculated z component
return UnpackNormalmapRGorAG(packednormal);
// UnpackNormalmapRGorAG Function implementation details
packednormal.x *= packednormal.w; // This do the trick
fixed3 normal;
normal.xy = packednormal.xy * 2 - 1;
normal.z = sqrt(1 - saturate(dot(normal.xy, normal.xy)));
return normal;When the normal texture Texture Type The label is normal map When you can let Unity Compress the normal texture according to different platforms , After compression, the texture saves only two channels , The third channel can be derived from the other two ( The normal is the unit vector , And in tangent space z The component is always positive ).
// A technique for controlling the degree of unevenness : The zoom xy The components are recalculated z
fixed3 bump = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.BumpUv));
bump.xy *= _Scale;
bump.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(bump.xy, bump.xy)));- Get vertex depth
// Get the observation space depth value ( Take a positive value , Itself is negative )
// Mode one : Use macros , And output the result to o (o.screenPos.z) in
o.screenPos = ComputeScreenPos(o.vertex);
COMPUTE_EYEDEPTH(o.screenPos.z);
// Mode two : In fact, that is COMPUTE_EYEDEPTH(o) Internal implementation
float -UnityObjectToViewPos( v.vertex ).z
// Mode three : Know by projection matrix , In homogeneous coordinates w value , Is to observe space z Positive value
o.screenPos.w
// get [0,1] Depth value between
// _ProjectionParams.w is 1/FarPlane
float -UnityObjectToViewPos(v.vertex).z * _ProjectionParams.w
// Equate to
float -mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MV, v.vertex).z * _ProjectionParams.w- Get and use depth maps
// Get depth map
// Delay rendering , Production depth 、 Normal cache , stay shader Can be obtained by directly using variables in
// Forward rendering , It is necessary to set the camera to obtain manually ( The underlying layer is replaced with a shader , And use ShadowCaster Pass Get the depth )
Camera.depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.Depth
Camera.depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals // depth + normal
// stay shader The variable of
sampler2D _CameraDepthTexture
sampler2D _CameraDepthNormalsTexture
// sampling _CameraDepthTexture
// The way 1, Generally used for post screen effects
// uv come from Graphics.Blit Produced full-screen quad
fixed4 d = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture, i.uv)
// adopt MVP After the transformation , The value in the obtained depth texture is a nonlinear high-precision value ( Mainly after the transformation of projection matrix Z The value is nonlinear )
// LinearEyeDepth Convert back to the linear depth value of the observation space (+Z)
// Linear01Depth The switch to [0,1] Linear depth value of
float linearDepth = Linear01Depth(d)
// The way 2, Used when a single object needs depth information
float4 d = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_PROJ(_CameraDepthTexture, i.screenPos);
float linearDepth = Linear01Depth(d);
// sampling _CameraDepthNormalsTexture
fixed4 d = tex2D(_CameraDepthNormalsTexture, i.uv);
float depth; // Accept decoded depth , yes [0,1] The linear value of
float3 normal; // Accept viewing space normals , Range [-1,1]
// Decode the depth and observe the space normal
DecodeDepthNormal(d, depth, normal);- Shader Calculate the distance of a space vertex in
// It's actually finding the module of a vector ( length / size )
float sqrt(dot(float3 pos, float3 pos))The above function is equivalent to :pos.x2+pos.y2+pos.z2−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√ p o s . x 2 + p o s . y 2 + p o s . z 2 , That is, dot times the same vertex ( vector ) We'll start again .
// Some use cases :
// The attenuation value of the sampled light texture , Distance used ( model ) The square of , Avoid the cost of prescribing .
// dot(lightCoord, lightCoord) And... In the script lightCoord.SqrMagnitude It means the same thing
fixed atten = tex2D(_LightTexture0, dot(lightCoord, lightCoord).rr).UNITY_ATTEN_CHANNEL;
// UnpackNormal Middle computation z component
normal.z = sqrt(1 - saturate(dot(normal.xy, normal.xy)));- CG Common geometric functions
// Two vector Distance between
float distance(x, y)
// vector The mold
float length(x)
// The reflection vector is obtained by the incident ray and the surface normal
vector reflect(i, n) // Be careful i Is the direction to the vertex
// Usually used :
o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz; // Get the vertex in world space
o.worldViewDir = UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(o.worldPos); // The vertex points in the direction of the camera's line of sight
o.worldRefl = reflect(-o.worldViewDir, o.worldNormal); // Reflection vector
// The refraction vector is obtained by the incident ray and the surface normal (i,n Must be a normalized vector )
vector refract(i, n, float(x)) // i Is pointing to the vertex ,x Is the ratio of the refractive index of the incident medium to that of the refractive medium
// Usually used :
o.worldRefr = refract(-normalize(o.worldViewDir), normalize(o.worldNormal), _RefractRatio);Common built-in functions Official documents
Shader Property attributes and drawers
// Attributes recognized by Unity:
[HideInInspector]
[NoScaleOffset]
[Normal]
[HDR]
[Gamma]
[PerRendererData]// Drawers:
// Will set "_INVERT_ON" shader keyword when set [Toggle] _Invert ("Invert?", Float) = 0 // Will set "ENABLE_FANCY" shader keyword when set. [Toggle(ENABLE_FANCY)] _Fancy ("Fancy?", Float) = 0 // Also will set "JUSTOUTLINE_ON" shader keyword when set. [MaterialToggle] JustOutline ("JustOutline", Float) = 1Attributes View details Property attributes and drawers, more Drawers Please check out MaterialPropertyDrawer
边栏推荐
- OpenGauss数据库在 CentOS 上的实践,配置篇
- Review of postgraduate English final exam
- [008] filter the table data row by row, jump out of the for cycle and skip this cycle VBA
- Atguigu---16-custom instruction
- Atguigu---15- built in instruction
- Vulnhub target: boredhackerblog: social network
- 闲谈:3AC到底发生了什么?
- Ke Yi fallible point
- Smart pointer remarks
- Notes on the use of date and time base
猜你喜欢
Svn actual measurement common operation record operation

Specify IP when calling feign interface

GPU is not used when the code is running

SVN实测常用操作-记录操作大全

What kind of experience is it when the Institute earns 20000 yuan a month!
![[run the script framework in Django and store the data in the database]](/img/6b/052679e5468e5a90be5c4339183f43.png)
[run the script framework in Django and store the data in the database]

Cold thinking on the hot track: multiplier effect is the fundamental requirement of East West calculation

Vulnhub target: boredhackerblog: social network

2022 PMP project management examination agile knowledge points (1)

火线,零线,地线,你知道这三根线的作用是什么吗?
随机推荐
Atguigu---15- built in instruction
Error:Kotlin: Module was compiled with an incompatible version of Kotlin. The binary version of its
调用Feign接口时指定ip
解决 These dependencies were not found: * core-js/modules/es6.array.fill in xxx 之类的问题
Opencvsharp binary image anti color
闲谈:3AC到底发生了什么?
Examples of corpus data processing cases (reading multiple text files, reading multiple files specified under a folder, decoding errors, reading multiple subfolder text, batch renaming of multiple fil
Oracle advanced SQL qualified query
研究生英语期末考试复习
Baidu map, coordinate inversion, picking coordinate position
[test development] first knowledge of software testing
Common array encapsulation
Echart 心得 (一): 有关Y轴yAxis属性
Cloud development who is the source code of undercover applet
解决笔记本键盘禁用失败问题
These dependencies were not found: * core JS / modules / es6 array. Fill in XXX
Chrono usage notes
软件工程导论——第三章——需求分析
Specify IP when calling feign interface
Graphmae ---- quick reading of papers