当前位置:网站首页>Interview MySQL
Interview MySQL
2022-06-22 19:00:00 【LXMXHJ】
List of articles
- review
- MySQL summary
- database Basic operation
- data type
- Data sheet Basic operation
- operation Table data
- View
- Indexes
- Talk about your understanding of index ?
- What data structure is used at the bottom of the index ?
- Talk to you about B+ Trees The understanding of the ?
- To cluster index 、 Sparse index The understanding of the ?
- Understanding of hash index ?
- Understanding of overlay indexes ?
- Classification of indexes ?
- Understanding of the leftmost prefix principle ?
- How to know if the created index has been used ? Or how can we know the reason why this statement runs so slowly ?
- When the index will fail ? That is, the query does not go through the index ?
- Business
- Storage index
- constraint
review
Database mind map
MySQL Mind mapping
MySQL summary
Oracle and MySQL difference
All two are
| difference | MySQL | Oracle |
|---|---|---|
| company | The Swedish MySQL AB company Has been sun Acquisition Has been Oracle Acquisition | Oracle |
| type | Small and medium databases | Large databases |
| cost | Free open source | charge |
| Default port number | 3306 | 1521 |
| Database and user relationship | One user to one or more databases | One database corresponds to multiple users |
| Field auto increment | Set field to auto increment | Create sequence sequence, add to The sequence of .nextval() |
| character | varchar | varchar2 |
| Numeric type | smallint(2 byte ) int(4 byte ) integer(int A synonym for ) bigint(8 byte ) | number |
| Pagination | select * from table limit(start-1)*limit,limit start Page number ,limit It's the number of bars per page | Use pseudo Columns rownum |
Yes MySQL Understanding of the framework ?
MySQl Can be divided into Server layer and Storage engine Two parts .
- Server layer :
cover MySQL Most of the core functions of , And all the built-in functions , All cross engine functions are implemented at this layer ; - Storage engine :
Data storage and extraction .
Components are plug-in . The storage engine has InnorDB、MyISAM、memory;
MySQL5.5.5 The default is InnorDB, Can pass engine = MyISAM To specify the storage engine ;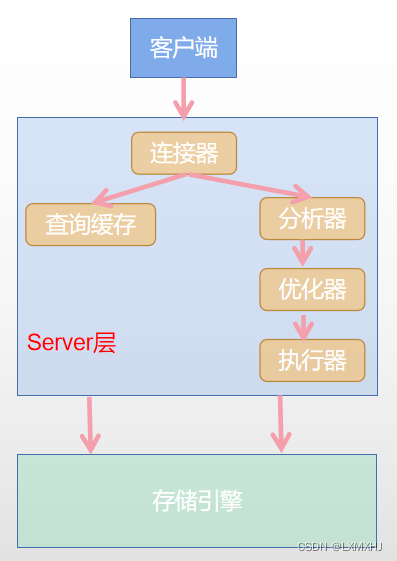
Server Introduction to layer components :
| member | effect |
|---|---|
| The connector | Manage connections , Authority verification |
| The query cache | If hit, the result will be returned directly |
| analyzer | Lexical analysis 、 Syntax analysis |
| Optimizer | Execution plan generation , Index selection |
| actuator | Operate the engine , Return results |
One SQL Statement execution flow in the database framework ?
Execution process :
- The application puts the query SQL Statement is sent to the server for execution ;
- Check whether the query exists in the cache . There is , Returns the result in the cache ; otherwise , Perform the next step ;
- Conduct SQL Parsing 、 Syntax checking and preprocessing , Then the optimizer generates the corresponding execution plan ;
- MySQL According to the execution plan , Call the interface of storage engine to query ;
- Finally, the query result is returned to the client .
What are the three paradigms of a database ?
| name | meaning | explain |
|---|---|---|
| First normal form (1NF) | All domains should be atomic Each column is indivisible Each column of a database table is an indivisible atomic data item , It's not a collection 、 Array 、 Records and other non atomic data items | When an attribute of an entity has multiple values , Must be split into different properties |
| Second normal form (2NF) | Non primary key columns are completely dependent on primary key columns , Not dependent on other non primary keys | It is required that each instance or record in the database table can be uniquely distinguished |
| Third normal form (3NF) | Any non primary attribute does not depend on other non primary attributes | It is required that one relationship does not contain the non primary key word information already contained in other relationships give an example : Department information table , Primary key = Department number , Other information includes the name of the Department 、 Department profile, etc ; After the department number is listed in the employee information table , No longer list Department names 、 Department indirect information |
Professional term or key word
DB:Database database
DBMS:Database Management System Database management system
RDBMS:Relative Database Management System Relational database management system
database : Is a collection of tables , With relevant data ;
surface : A table is a matrix of data ;
Column ( Field ): One column ( data elements ) Contains the same type of data ;
That's ok ( Record ): A set of relevant data ;
database Basic operation
see 、 establish 、 modify 、 Delete database .
Understanding of horizontal and vertical segmentation ?
- Database splitting principle :
Through certain conditions , According to a certain dimension , Distribute the data in the same database to multiple databases ( host ), So as to achieve decentralized single database ( host ) Effect of load ; - Split mode :
vertical ( The longitudinal ) Split 、 Horizontal split .
Split Vertically : It's special for the special warehouse
| Introduce | explain |
|---|---|
| Concept | Classify the table by business , Distributed to different databases |
| Problem solving | Reduce the load on a single node database |
| Can't solve the problem | Shrinkage table , That is, the amount of data in each database has not changed |
| advantage | After the split, the business is clear , The split rules are clear Integration or expansion between systems is easy Data maintenance is simple |
| shortcoming | Some business tables cannot join, Only through interface , Increased system complexity There is a single library performance bottleneck due to different restrictions of each business , Not easy to expand data and improve performance . The transaction is complex |
Horizontal split : Sub database and sub table
- Concept :
Split the same table into different databases ;
It's not about classifying tables , It's distributed to multiple libraries according to certain rules of a field , Each table contains some data ;
Simple understanding = According to the segmentation of data rows , Splitting some rows into other databases ; - misunderstand :
The data table sliced horizontally must be saved in different places MySQL Node ;
In fact, the data table from horizontal segmentation can also be saved in a MySQL Node ; - Why does horizontal segmentation not necessarily require multiple MySQL Node ?
MySQL It comes with a data partition technology , You can put the data of a table , According to special rules , Sharding is stored in different directories .
If given Linux The host is attached with multiple hard disks , You can use MySQL Partition technology , The data of a table is partitioned and stored on multiple hard disks .
In this way, the original hard disk is limited IO Ability , Upgraded to multiple disk enhanced IO.
data type
value type 、 String type 、 Escape character 、 date / Time 、 Binary type 、 Variable .
char and varchar The difference between ?
| difference | char | varchar |
|---|---|---|
| length | Fix char(10) character string "abc" Storage 10 Bytes , among 7 One is a space | variable varchar(10) character string "abc" Only three bytes |
| efficiency | Higher | The lower |
| Save a space | – | Than char Save a space |
| Storage type | – | varchar yes oracle Developed data types Industry standards can store empty strings ;oracle It can also store NULL value |
varchar(10) and varchar(20) The difference between ?
varchar(10) Put at most 10 Characters , therefore varchar(10) and varchar(20) Storage 10 And 10 Less than characters occupy the same space ;
But the latter consumes more memory when sorting , because order by col use fixed_length Calculation col length .
fixed_length Fixed length ;
Data sheet Basic operation
establish 、 see 、 Modify data table structure .
operation Table data
Inquire about 、 increase 、 modify 、 Delete 、 Clear the table record .
How to optimize query performance ?
Reduce the amount of data requested
Only necessary columns are returned : Avoid using select * sentence ;
Just go back to the necessary lines : Use limit Statement to limit the data returned ;
Cache data from repeated queries ;Reduce the number of lines scanned by the server
Overwriting queries by index ;
sql tuning
- Create index :
Try to avoid full scan , Consideration should be given where or order by - Avoid using calculations on indexes
stay where In the sentence , If the index column is part of a calculation or function ,DBMS The optimizer will not use indexes but full table queries - Use precompiled queries
The program is usually executed dynamically according to the user's input SQL, Use parameterization as much as possible SQL, You can avoid SQL Inject holes ;
The database will parameterize SQL Precompile , You can directly use the precompiled results in the future . - adjustment where Join order in clause
DBMS It is generally analyzed from top to bottom where Clause ; - Try to put as many as possible sql The statement is compressed into one sql in
Every time you execute sql You have to go through the following process : Set up a network connection 、 Verify authority 、 Conduct SQL Statement query optimization 、 Send the execution result
This process is very time consuming . - use where Clause substitution Having Clause
Avoid using having, because having The result set is filtered only after all records are retrieved , and where Is before the aggregation ;
If you can use where Reduce the number of records , You can reduce the cost ; - Use the alias of the table
sql Join multiple tables , Use the alias of the table It can reduce the parsing time And reduce the syntax ambiguity of column names with the same name in different tables - use union all Replace union
- use varchar/nvarchar Replace char / nchar
Variable length fields have small storage space , You can save storage space ;
For queries , Searching in a relatively small field is efficient ;
View
establish 、 see 、 modify 、 Delete view .
Indexes
Create index instance 、 General index 、 unique index 、 primary key 、 Composite index 、 Full-text index .
Talk about your understanding of index ?
effect :
Index appears to improve query efficiency , It is equivalent to the directory of the database ;
It is the most effective way to optimize query performance ;Concept :
stay MySQL Also known as “ key ”, It is a data structure used by the storage engine to quickly find records ;principle :
Filter out the final desired results by constantly narrowing the range of data you want to obtain , At the same time, it turns random events into sequential events ;classification :
hash Index of type : Quick to query a single item , Range query is slow ;
b-tree Index of type :b+ Trees , The more layers , Exponential growth in data volume ;shortcoming :
Creating and maintaining indexes takes time ;
Add to data 、 Delete 、 Change time , Indexes also need to be maintained dynamically , Reduce the speed of data maintenance ;
As the amount of data increases , The more physical space an index needs to occupy ;Establish principles :
Frequently queried fields :where In clause ;
In the grouped fields : That is to say group by In clause ;
Joint query between dependent child table and parent table , Primary key or foreign key field ;
Set unique integrity constraint fields ;Not suitable for indexing :
Columns that are rarely used in queries perhaps Columns with more duplicate values , It's not good to index ;
Some special data types , It's not good to index . such as : The text field (text) etc. .
What data structure is used at the bottom of the index ?
The data structure of the index and Specific storage engine The realization of ;
MySQL The indexes used more often in are Hash Indexes 、B+ Trees Index, etc. ;
Then the underlying layer of the corresponding index is Hash surface 、 B + Trees ;
Talk to you about B+ Trees The understanding of the ?
Icon :
| explain | The root node | Branch nodes Grubbing node 、 Leaf node | Leaf node |
|---|---|---|---|
| The number of sons | Yes M A son has m Elements | Yes M A son has m Elements | – |
| Store content | keyword ( Indexes )、 The pointer | keyword ( Indexes )、 The pointer | keyword 、 data |
| Storage | – | – | All root nodes 、 Branch nodes exist in child nodes , Is the maximum or minimum value |
| – | – | Include all keywords 、 A pointer to a data record Leaf nodes themselves are linked in descending order according to keywords |
effect :
advantage 1 = More efficient single element lookup .
To cluster index 、 Sparse index The understanding of the ?
- Cluster index :
It is to reorganize the actual data on the disk , According to the specified value of one or more columns Sorting algorithm .
The feature is that the order of storing data is consistent with the order of index .
In general, the primary key creates a clustered index by default , And only one cluster index is allowed in a table .
Cluster index and Nonclustered index ( Sparse index ) difference :
Cluster index : That is, the leaf node contains all complete row records , The leaf node contains the index and all other field information , That is, the data node ;InnoDB Storage engine built with primary key index B+tree That is, the cluster index ,
Nonclustered index : The others are sparse indexes ; The leaf node is still the index node ;
- Sparse index :
Secondary indexes 、 Joint index 、MyISAM The indexes of the storage engine are all sparse indexes .
Understanding of hash index ?
Understanding of overlay indexes ?
Classification of indexes ?
Understanding of the leftmost prefix principle ?
How to know if the created index has been used ? Or how can we know the reason why this statement runs so slowly ?
When the index will fail ? That is, the query does not go through the index ?
Business
Storage index
MyISAM、InnoDB、Memory.
Why? InnorDB The storage index adopts B+ Trees instead of B Trees ?
InnoDB and MyISAM Comparison ?
constraint
Primary key constraint 、 Foreign key constraints 、 Unique constraint 、 Check constraint 、 Non empty constraint 、 Default constraint .
20 Which three threads are involved in master-slave replication ?
边栏推荐
- Custom database connection pool class: requirement: enclose the collection class of a collection object
- 问下 cdc 2.2.1监控sqlServer是不支持监控多库的吗?
- Binary tree practice the second bullet
- Five practical tips for power Bi (complimentary books at the end of the article)
- std::enable_shared_from_this 错误:error: expected template-name before ‘<’ token
- [OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 build
- Exness sorted out three problems to be solved in Musk's acquisition of Twitter
- Nuxt - Universal(SSR / SSG)/ Single Page App(渲染模式)
- Filebeat collects log data and transfers it to redis. Different es indexes are created based on log fields through logstash
- Jenkins configuration project integration pin notification
猜你喜欢

Alibaba cloud cannot find the account security group id problem during the account transfer

RSPS2022 Finalist | Dr. Yang Bai 简介

Nuxt - Universal(SSR / SSG)/ Single Page App(渲染模式)

今天19:30 | 科普大佬说,带大家探寻AI如何激发人类的创造力
Set of redis data structure

Explain the startup process of opengauss multithreading architecture in detail

第四届青年生命科学论坛 | 第一轮通知

At 19:30 today, the science popularization leader said that he would take you to explore how AI can stimulate human creativity

c# sqlsugar,hisql,freesql orm框架全方位性能测试对比之sqlserver

详解openGauss多线程架构启动过程
随机推荐
直播预告 | 12位一作华人学者开启 ICLR 2022
Excuse me, when cdc2.0 reads mysql, there should be no table lock. An error was just reported, access D
大一女生废话编程爆火!懂不懂编程的看完都拴Q了
Activity跳转到Fragment的方法(Intent)
plsql变量赋值问题
China's two meteorological "new stars" data products are shared with global users
2022焊工(初级)特种作业证考试题库模拟考试平台操作
Pytorch——报错解决:“torch/optim/adamw.py” beta1, UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘beta1‘
Plan and change of continuous repair
@“齐鲁多娇”幸运用户,山东5A景区喊你免费游园啦!
sqlserver保存时遇到这个页面怎么回事啊
Nuxt - create nuxt app
在循环中动态改变标签元素的样式
各位大佬,第一次使用flink mysql cdc, 现在程序启动 没报错 新增数据没有打印出来
2022年T电梯修理复训题库及答案
SystemVerilog(十二)-$unit声明空间
Behind the fall of the first Seberg: the extreme race between technology and frostbite
JVM quick start
Jenkins installation and upgrade
c# sqlsugar,hisql,freesql orm框架全方位性能测试对比之sqlserver
