当前位置:网站首页>Index +sql exercise optimization
Index +sql exercise optimization
2022-06-27 07:44:00 【Fairy wants carry】
Catalog
Insert 100w How to achieve the fastest data
1. Create a function ( Randomly generate numbers and random names )
The execution of multi field index is shown in the figure
Small conclusion of association query :
The impact of indexes on grouped queries
Sorting and grouping optimization
There is also a very optimized point ( Overlay index ):
Homework (sql practice + Optimize )
Advantages and disadvantages
Improve data retrieval efficiency through indexing , Reduce IO cost , But using indexes will also reduce the efficiency of updating , Each modification will cause the information in our index file to change , And memory consumption up

An index can also be understood as a table , The index fields inside point to entity table records
When to use the index

Frequently used as query criteria 、 Associated query 、 Group sorted 、 The only index
Expain Performance analysis
effect :
Use Explain Keywords can simulate the optimizer ( It's the one before Optimizer Optimizer ) perform SQL Query statement , obtain mysql How to deal with sql Of the statement , Analyze ( View execution plan )
Use :

Analysis field :
id Represents an independent query , One sql The less you lie down, the better 

select_type

type
The most important three :range、index、all

key and key_len and rows
key_len How to calculate index length

EXTRA

Purpose : Reduce full table scanning , Increase performance
Subquery (SUBQUERY):
Range queries (DEPENDENT SUBQUERY)
Unavailable cache queries :
sql Not hit ,sql Dissimilarity ——> When a variable appears ,sql It must be different ;
All problem :
All table scan, Traverse the entire table to find the matching rows ;
index Indexes
appear index yes sql Index is used but not filtered by index , Generally, the overlay index is used or the index is used for sorting and grouping ;
Range queries :
group by Sort first and then group
After using the index, it is found that the speed is 100 times optimized (reset cache)
Two tables are associated with , Associated fields should be indexed
where The field after the condition is indexed
Statistical quantity count(*):MyISAM Words , He counted the amount of data in the table ,InnoDB No statistics will really open the table for scanning
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t_deptField analytical :
id It refers to the execution sequence ,type It refers to the yellow, red and black warnings ,key_len refer to where Condition field length ( The longer the length , The easier it is to hit ),rows The number of rows for the value ( Number of lines scanned physically , The less the better, the faster ),Extra Additional fields are generally viewed group by,other by, Relational query ;
Insert 100w How to achieve the fastest data
1. We can 100w Insert statements to splice , Turn him into a sentence , It must be faster
2. We can cancel mysql Automatic submission of , because 100w Data submission 100w Times and submissions 1 Time
It must be different ;
3. Using multithreading
mysql Master-slave replication of
The master slave uses a binlog, There are common functions

1. Create a function ( Randomly generate numbers and random names )

2. Create stored procedures and insert data ( Use the above two functions to get the random number and name )
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`deptName` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,
ceo INT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `emp` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`empno` INT NOT NULL ,
`name` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` INT(3) DEFAULT NULL,
`deptId` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
#CONSTRAINT `fk_dept_id` FOREIGN KEY (`deptId`) REFERENCES `t_dept` (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
# Enable the user-defined function configuration
SET GLOBAL log_bin_trust_function_creators=1;
# Randomly generated string function
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION rand_string(n INT) RETURNS VARCHAR(255)
BEGIN
DECLARE chars_str VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFJHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
DECLARE return_str VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i < n DO
SET return_str =CONCAT(return_str,SUBSTRING(chars_str,FLOOR(1+RAND()*52),1));
SET i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
RETURN return_str;
END $$
USE mydb
# Used to randomly generate number to number
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION rand_num (from_num INT ,to_num INT) RETURNS INT(11)
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
SET i = FLOOR(from_num +RAND()*(to_num -from_num+1)) ;
RETURN i;
END$$
# If you want to delete
#drop function rand_num;
# If you want to delete
#drop function rand_string;
# Insert 500000 pieces of data
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE insert_emp( START INT , max_num INT )
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
#set autocommit =0 hold autocommit Set to 0, Turn off auto submit
SET autocommit = 0;
REPEAT
SET i = i + 1;
INSERT INTO emp (empno, NAME ,age ,deptid ) VALUES ((START+i) ,rand_string(6) , rand_num(30,50),rand_num(1,10000));
UNTIL i = max_num
END REPEAT;
COMMIT;
END$$
# Delete
# DELIMITER ;
# drop PROCEDURE insert_emp;
# Execute stored procedures , Go to dept Add random data to table
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `insert_dept`( max_num INT )
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
SET autocommit = 0;
REPEAT
SET i = i + 1;
INSERT INTO dept ( deptname,address,ceo ) VALUES (rand_string(8),rand_string(10),rand_num(1,500000));
UNTIL i = max_num
END REPEAT;
COMMIT;
END$$
# Delete
# DELIMITER ;
# drop PROCEDURE insert_dept;
# Insert 1w Data
# Execute stored procedures , Go to dept Table to add 1 Ten thousand data
DELIMITER ;
CALL insert_dept(10000);
# Execute stored procedures , Go to emp Table to add 50 Ten thousand data
DELIMITER ;
CALL insert_emp(100000,500000);
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM emp;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM dept;

Like so much data , We need an index to query , We're going to do the next sql To delete the current sql The index of
technological process :
need mysql Acknowledge the string you extracted

1. Look at the index in the table
SHOW INDEX FROM t_emp;
2. Our index is also a table , stay information In the database , The name is STATISTICS
Look at the index table , The primary key index cannot be deleted

3. Create index
Single field
Let's check , Find out explain Estimate 49w Multiple lines
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.`age`=30;

CREATE INDEX idx_age ON emp(age);
After index creation , Only 4w All right , Speed up

0.03->0.007
Multiple fields
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 AND deptid=4 AND emp.name = 'abcd';
CREATE INDEX idx_age_deptid_name ON emp(age,deptid,NAME);

Speed by 0.082-> negligible
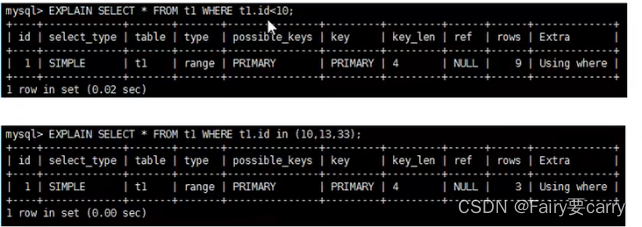
The execution of multi field index is shown in the figure
Best left prefix : Execute from left to right in order , Otherwise it will disconnect
If the system often appears sql as follows :
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 AND emp.name = 'abcd'
perhaps
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.deptid=1 AND emp.name = 'abcd'
The original idx_age_deptid_name Whether it can be used normally ?The second one cannot be executed normally , Not following the order from left to right , Ring hit is required ——> At the same time, it also reflects the full value matching , Fields must correspond to indexes

practice
# Execution deletion
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","emp");
# Query the specified index in the index table ( Non primary key )
SELECT index_name FROM information_schema.`STATISTICS` WHERE TABLE_NAME='t_emp'
AND TABLE_SCHEMA='mydb' AND INDEX_NAME <>'PRIMARY' AND SEQ_IN_INDEX=1;
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.`age`=30; #0.03 0.007
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 AND deptid=4
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 AND deptid=4 AND emp.name = 'abcd';
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_age ON emp(age);
CREATE INDEX idx_age_deptid_name ON emp(age,deptid,NAME);
SHOW INDEX FROM emp;
# Fuzzy query
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.`name` LIKE 'abc%';#0.8->0.016
# This can lead to index invalidation , Don't use functions
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE LEFT(emp.`name`,3)='abc';#0.8
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON emp(NAME);
# Execution deletion
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","emp");
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","dept");
# Range queries , The field index on the right side of the range is invalid ( The right side is judged according to the index )
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp #0.5->0.052,type:range
WHERE emp.age=30 AND emp.deptId>20 AND emp.name = 'abc' ; # Optimal efficiency 0.004
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_age_deptid_name ON emp(age,deptid,NAME);
CREATE INDEX idx_age_deptid_name ON emp(age,NAME,deptid);
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.`name` <> 'abc';
# Create index , For the above failure != Can cause indexes to fail
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON emp(NAME);
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age IS NULL #0.2->0.001
# This is not It's going to fail
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age IS NOT NULL;#0.04->0.009, Index failure ,type by ALL
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_age ON emp(age);
# Our index structure of the balanced tree is based on a-z, If the initials are uncertain , The index will fail
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.`name` LIKE '%abc%';#0.329->0.274
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON emp(NAME);
# Execution deletion
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","emp");
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","dept");
# Type conversion can also cause index invalidation
# If you have several fields, you can index them How the index finds the data
matters needing attention
Be careful sql To write , Prevent index invalidation

A small summary
1. Remember the best left front rule
2. You can't use functions :abs,max,<>....
3. Out-of-service like Prefix %xxx wildcard
4.is not null no way
5. Nor can type conversion

Some suggestions
1. When selecting a composite index , We can put the fields with good filtering performance in the front of the index fields , Because it is filtered out to the next tree , Maybe there are fewer nodes , Even for 1, More efficient ;
2. When selecting Composite Index , Try to include where More fields after
3. Try to avoid index invalidation
Relational query
scene :
When two tables have no associated fields , And then it makes the association query , Both tables will be scanned globally , So the Cartesian product
How they relate to :
In the associated query scenario , We associate queries -> First, the data in the first row of the drive table will be scanned , Then scan the driven table according to the first row of data , The found data is combined into a row of data ;
Conclusion :
1. The drive table must be scanned globally , Driven tables are not necessarily , So we build the index on the driven table , The drive table must be completely scanned, so it doesn't matter whether the index is built or not ;
2. To improve efficiency , Our relatively small amount of data is best used as the driving table
3. in addition ,inner join and left join Not quite the same. , stay inner join Next mysql Will automatically select the driven table , Rather than their relative position , yes According to the small result set as the driving table ;

Association query instance
Query the two tables by association ->extra There are no associated fields between the two tables , Very slow to check , Descartes appears
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM class LEFT JOIN book ON class.`card`=book.`card`;
# Create index , Here we usually index the driven table
CREATE INDEX Y ON book(card);
# Execution deletion
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","book");
DROP INDEX Y ON book;
DROP INDEX X ON class;
# Create index
ALTER TABLE class ADD INDEX X (card);
#inner join,mysql Choose which is the driven table ——> Judge according to the index , Whoever has an index is driven
# Small data is the driving table , Short scanning time to improve efficiency
# Please all dept Corresponding CEO name
#1. Here you will find that it is a query ,mysql5.7 An optimization of ,c The table is the driving table , Our driven table is ab Virtual table
# Virtual tables cannot create indexes , So an optimization opportunity will be wasted ,5.7 Where the update is
EXPLAIN SELECT c.`name`,ab.name ceoname FROM t_emp c LEFT JOIN
(SELECT b.`id`,a.`name` FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`)ab
ON c.`deptld`=ab.id;
# obtain dept The leader of
SELECT b.`id`,a.`name` FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`
#2. First, check the name and CEO
SELECT ab.name,c.`name` ceoname FROM
(SELECT a.`name`,b.`CEO` FROM t_emp a LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`) ab
LEFT JOIN t_emp c ON ab.ceo=c.`id`;
#3. The fastest , Directly related , You don't need to subquery to connect to the sect leader twice at a time ( Get the user's information for the first time , The second is based on CEO Screening )
EXPLAIN SELECT a.`name`,c.`name` ceoname FROM t_emp a
LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`
LEFT JOIN t_emp c ON b.`CEO`=c.`id`;Small conclusion of association query :
1. We need to ensure that the driven table join And indexed
2.left join when , Select the small table as the driver
3.inner join: The small result set is used as the driving table
4. Subqueries should not be placed in the driver table , because 5.7 Pre virtual tables cannot be indexed , Will lead to reduced efficiency
5. If it can be directly related, it can be directly related
Correlation optimization test
There is obviously not The index cannot be used , Optimize -> Use left join Make association query , Then filter according to the conditions
# At least two non leader sects ( The leader number first , Then, according to the leader's number, you can go to t_emp Intermediate investigation )
SELECT * FROM t_emp a WHERE a.id NOT IN
(SELECT b.CEO FROM t_dept b WHERE b.CEO IS NOT NULL);
# Optimize ( Get all the leaders first (left join), Then the bar filter )
SELECT * FROM t_emp a LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.id = b.CEO
WHERE b.id IS NULL;
The impact of indexes on grouped queries
summary :
1. Group query order by Whether the field after can use the index -> It depends on whether the filter conditions are followed , If so, the index will take effect
2.order by The following sequence is very important , The order is different, the result is different , So it will not be optimized
3. If the fields are in ascending or descending order, the result will not be affected , If there is any inconsistency, it will affect the occurrence of using filesort
# Execution deletion
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","emp");
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","dept");
# Group query
CREATE INDEX idx_age_deptid_name ON emp (age,deptid,NAME)
CREATE INDEX idx_age_deptid_empno ON emp (age,deptid,empno);
# Whether the following indexes can be used , Can you get rid of it? using filesort ,(order by If you want to use the index, you must filter the conditions )
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp ORDER BY age,deptid;
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp ORDER BY age,deptid LIMIT 10;
# No filtering No index
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age=45 ORDER BY deptid;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age=45 ORDER BY deptid,NAME;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age=45 ORDER BY deptid,empno;
#deptid The field needs to be name front , This order is not optimized , Because the result will be affected ,order by The order of the following fields is very important
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age=45 ORDER BY NAME,deptid;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE deptid=45 ORDER BY age;
# Wrong order , No sorting is required , It can be in descending or ascending order , In this case , Changing the order will not affect the result
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age=45 ORDER BY deptid DESC, NAME DESC ;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE age=45 ORDER BY deptid ASC, NAME DESC ;
# In the opposite direction No sorting is required , One rise and one fall cannot be indexed :Using filesort
Sorting and grouping optimization
mysql The index selection will be optimized , Choose an index that you think is the fastest
If the field is not on the index column ,filesort There are two algorithms
1. Two way sorting : Just scan the disk twice , First, scan everything and put it on the disk , After scanning, sort the contents of the disk ( That is, read the line pointer and order by Column ), Scan the disk twice ,IO Very time consuming
2. One way sorting : Read the index column of the query from disk , And then according to order by The query , He puts the contents of each read into memory , Less IO Loss of

group by And other by The difference is that :
group by You can use indexes without restrictions ,other by No filtering, no indexing
There is also a very optimized point ( Overlay index ):
Fuzzy queries did not appear before like %xx、is not、other by xxx All these will lead to index invalidation , We can restrict the content of the query , No more select * , Instead, fields limit , In this way, the index can be matched according to the field , To improve efficiency ;
CREATE INDEX idx_id_age_deptid ON emp(id,age,deptid);
# The query contents can be indexed
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE NAME FROM emp WHERE age IS NOT NULL;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE NAME LIKE '%abc';
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE id,age,deptid FROM emp WHERE NAME LIKE '%abc';
# Look at the index
SHOW INDEX FROM emp;Homework (sql practice + Optimize )
Be careful :Group by After setting the field of , front select The field of can only contain Group by Content of and function content , Otherwise, an error will be reported
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE age =30 AND empno <101000 ORDER BY NAME ;#0.729
# Execution deletion
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","emp");
CALL proc_drop_index("mydb","dept");
# Index , First priority idx_age_empno The index of ,mysql Will choose the best index
CREATE INDEX idx_age_empno ON emp(age,empno);
CREATE INDEX idx_age_name ON emp (age,NAME);
CREATE INDEX idx_age ON emp(age);
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON emp(NAME);
CREATE INDEX idx_id_age_deptid ON emp(id,age,deptid);
# The query contents can be indexed
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE NAME FROM emp WHERE age IS NOT NULL;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM emp WHERE NAME LIKE '%abc';
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE id,age,deptid FROM emp WHERE NAME LIKE '%abc';
# Look at the index
SHOW INDEX FROM emp;
#1. Ask for information that my younger brother is younger than the sect leader
SELECT a.name FROM t_emp a
LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.id
LEFT JOIN t_emp c ON b.CEO=c.`id`
WHERE c.`age`<a.`age`;
# Optimize
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE a.`name`,a.`age`,c.`name`,c.`age` FROM emp a
LEFT JOIN dept b ON a.`deptId`=b.`id`
LEFT JOIN emp c ON b.`ceo`=c.`id`
WHERE c.`age`<a.`age`;
#2. List those who are younger than the average age of the guild ( Get the personnel information of the Department group first )
SELECT c.`name`,c.`age` FROM t_emp c INNER JOIN
(SELECT a.`deptld`,AVG(a.`age`) avgage FROM t_emp a WHERE a.`deptld` IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY a.`deptld`)aa
ON c.`deptld`=aa.deptld
WHERE c.`age`<aa.avgage;
# Optimize , Use this subquery as the driver table
# Because subquery 5.7 You cannot have an index before the version , So we use it as a driver table , In this way, the non driven table can be indexed
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE c.`name`,c.`age`,aa.avgage FROM emp c
INNER JOIN
(SELECT a.deptId,AVG(a.age)avgage FROM emp a WHERE a.deptId IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY a.deptId)aa
ON c.`deptId`=aa.deptId
WHERE c.`age`<aa.avgage;
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_deptId ON emp(deptId);
CREATE INDEX idx_deptId_age ON emp(deptId,age);
#3. List at least 2 Age >40 Year old members of the sect (select Get the quantity , Must be group by 了 )
#( First, group according to the sect -> Then filter to get >40 Number of employees aged —> Finally, make a judgment )
SELECT b.`deptName`,b.`id`,COUNT(*) FROM t_emp a
INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`
WHERE a.`age`>40
GROUP BY b.`deptName`,b.`id`
HAVING COUNT(*)>=2;
# Optimize
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE b.`deptName`,b.`id`,COUNT(*) FROM dept b
STRAIGHT_JOIN emp a ON a.`deptId`=b.`id`
WHERE a.`age`>40
GROUP BY b.`deptName`,b.`id`
HAVING COUNT(*)>=2;
# Index
CREATE INDEX idx_deptName ON dept(deptName);
CREATE INDEX idx_deptId_age ON emp(deptId,age);
#4. Non leader ( First, check all the gangs with gangs , Then extract CEO, then not in)
SELECT * FROM t_emp a WHERE a.`id` NOT IN
(SELECT b.`CEO` FROM t_dept b WHERE b.`CEO` IS NOT NULL)
;
SELECT * FROM t_emp
SELECT * FROM t_dept
# Optimize :(1. Get the information of non leader sect members , Use left outer Association query , If there is no match in the sect table, you will null, So we need to b.id is null)
SELECT * FROM t_emp a
LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`
WHERE b.`id` IS NULL;
SELECT c.deptName,c.id,COUNT(*)
FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept c ON a.`deptld`=c.id
LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`
WHERE b.`id` IS NULL
GROUP BY c.deptName,c.id
HAVING COUNT(*)>=2
;
#5. Get all the members of the gang -> Get the name of the local gang and id-> In association once , Remove the leader , Leave the information of non leader ( Using the property of left outer )
# To get the quantity , So grouping
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE c.`deptName`,c.`id`,COUNT(*) FROM emp a
INNER JOIN dept c ON a.`deptId`=c.`id`
LEFT JOIN dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`
WHERE b.`id` IS NULL
GROUP BY c.`deptName`,c.`id`
HAVING COUNT(*)>=2;
# Create index
CREATE INDEX idx_deptName ON dept(deptName);
CREATE INDEX idx_deptId ON emp(deptId);
CREATE INDEX idx_CEO ON dept(CEO);
#6. List all people , And add a column to indicate whether it is the leader , If it is a remark, it is ——>case when Judge
# Then we use the left outer property b Of id->is null then xxx Judge
SELECT a.`name`,a.`age`,b.`deptName`,(CASE WHEN b.id IS NULL THEN ' no ' ELSE ' yes ' END)' Is it the leader '
FROM t_emp a
LEFT JOIN t_dept b ON a.`id`=b.`CEO`;
#7. List all sects , And note , Average age >50 Old bird , Otherwise, it will be a rookie
SELECT b.`deptName`,b.`id`,IF(AVG(a.`age`)>50,' veteran ',' rookie ')' veteran or rookie '
FROM t_emp a
INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.`id`
GROUP BY b.`deptName`,b.`id`;
#8. Show the oldest person of each sect (-> First get the maximum age and group according to the sect -> Then we can get the oldest person by associating the character table )
SELECT c.`name`,c.`age`,aa.maxage FROM t_emp c INNER JOIN
(SELECT a.`deptld`,MAX(a.`age`)maxage
FROM t_emp a WHERE a.`deptld` IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY a.`deptld`)aa
ON c.`deptId`=aa.deptld AND c.`age`=aa.maxage;
#9. Ask the third oldest person of each sect (w Write the wrong )
SELECT a.`age`,a.`name`,a.`deptld` FROM t_emp a ORDER BY a.`age` DESC
LEFT JOIN(
SELECT a.`id` FROM t_emp a INNER JOIN t_dept b ON a.`deptld`=b.id
)aa ON a.`deptld`=aa.id;# Here is the wrong grouping , Group the original plan and then limit complete
边栏推荐
- JS output all prime numbers between 1-100 and calculate the total number
- Use uview to enable tabbar to display the corresponding number of tabbars according to permissions
- JDBC操作Mysql示例
- Testing network connectivity with the blackbox exporter
- Coal crusher
- 【11. 二维差分】
- 什么是期货反向跟单?
- 游戏六边形地图的实现
- js用switch语句根据1-7输出对应英文星期几
- JS use the switch statement to output the corresponding English day of the week according to 1-7
猜你喜欢

2. QT components used in the project

索引+sql练习优化

Common operation and Principle Exploration of stream

Basic knowledge | JS Foundation

Win10 how to manage startup items?

What is the difference between volatile and synchronized?

js中判断成绩是否合格,范围在0-100,否则重新输入

【批处理DOS-CMD命令-汇总和小结】-环境变量、路径变量、搜索文件位置相关指令——set、path、where,cmd命令的路径参数中有空格怎么办

【10. 差分】

JS print 99 multiplication table
随机推荐
[Software Engineering] software engineering review outline of Shandong University
1-4 decimal representation and conversion
js例题打印1-100之间所有7的倍数的个数及总和
什么是浮选机?
js来打印1-100间的质数并求总个数优化版
hutool对称加密
Stream常用操作以及原理探索
期货反向跟单靠谱吗?
碎煤机crusher
JS use the switch statement to output the corresponding English day of the week according to 1-7
2、项目使用的QT组件
1-4 进制表示与转换
JS print 99 multiplication table
Win10 how to manage startup items?
JS performance reward and punishment examples
R language analyzing wine data
How to add data to the back-end database in the form of Excel file on the web page
JS output all prime numbers between 1-100 and calculate the total number
Basic knowledge | JS Foundation
【c ++ primer 笔记】第3章 字符串、向量和数组