当前位置:网站首页>Guess Tongyuan B
Guess Tongyuan B
2022-06-25 12:37:00 【haoming Hu】
Tongyuan B review
au:haomingHu
ut:2021/06/09
1、 Performance indicators : Effectiveness and reliability
Analog communication system : effectiveness –> Bandwidth utilization reliability –> Signal-to-noise ratio
Digital communication system : effectiveness –> Bandwidth utilization ( Transmission rate per unit bandwidth ) reliability –> Bit error rate
2、 Advantages of digital communication system :
① The transmitted signal is discrete or digital ;
② Strong anti-interference ability , Digital signals can be regenerated , So as to eliminate noise accumulation ;
③ Transmission errors can be controlled ;
④ It is convenient to use modern digital signal processing technology to process digital signals ;
⑤ Easy to encrypt , High reliability ;
⑥ It is convenient to realize the comprehensive transmission of various information .
3、 Reuse : Frequency division multiplexing (FDM)、 Time division multiplexing (TDM) And code division multiplexing (CDM)
4、 white Gaussian noise : Gaussian white noise is a common channel noise in communication systems .“ gaussian ” Refer to : The probability density is Gaussian ;“ white ” Refer to : Power spectral density Is uniform ( Within the frequency range studied ).
5、 Narrow band stationary Gauss
envelope : Rayleigh distribution phase : Uniform distribution
6、0 Mean sine narrowband Gauss
envelope : rice distribution ( Big SNR–> Gaussian distribution Small SNR–> Rayleigh distribution )
7、 If the white noise in the question is bilateral power spectrum , Calculate by 2 Is the correct calculation of noise power
8、 Channel classification
Narrow channel : Narrow sense channel can be divided into wired channel and wireless channel . Narrow sense channel can be divided into constant parameter channel and random parameter channel . Constant parameter channel refers to channel transmission The input parameters are constant ( Time does not change ) Channel of . The parameter dependent channel refers to the channel whose transmission parameters change randomly with time .
Generalized channel : There are modulation channel and coding channel Be clear about the starting positions of the two channels
9、 Constant parameter channel —》 Linear time invariant network Be clear about its amplitude 、 phase 、 Characteristics of group delay
The distortion :
Amplitude frequency distortion : simulation –》SNR falling , Numbers : Code string ( The bit error rate increases )
Phase frequency distortion : Code string
10、 Random channel :
characteristic : attenuation 、 Time delay varies with time 、 Multipath propagation
Multipath effect : Rayleigh fading 、 frequency dispersion 、 Frequency selective fading ( It belongs to fast decline )
reason : The signal reaches the receiving end through several paths , And the length of each path ( Time delay ) And decay over time .
measures : Reduce RB
11、 Channel capacity : The channel capacity is the maximum value of the information rate when the channel can transmit without error . Three points need to be noted : One is the condition : Error free transmission ; Second, channel capacity refers to information rate , Because the unit is bit/s; Third, it is the maximum , But the theoretical limit , Or an ideal indicator , The actual system cannot exceed .
Shannon formula C=Blog2(1+S/N) Is the channel capacity of a continuous channel , On the condition that : The signal is Gaussian , The noise is additive Gaussian white noise . Shannon formula points out the existence of theoretical limit ,
increase C :① Increase signal power S; ② Reduce noise power spectral density no.
12、 Definition of amplitude modulation : Amplitude modulation is to control the amplitude of high frequency carrier wave by modulated signal , The process of making it change linearly with the modulated signal .
13、 Performance summary of analog modulation system
In terms of bandwidth savings :SSB best ,AM/DSB second ,FM The worst ;
In terms of signal-to-noise ratio improvement :FM best ,SSB/DSB second ,AM The worst ;
In terms of power utilization :FM best ,SSB/DSB second ,AM The worst ;
In terms of equipment complexity :AM best ,FM/DSB second ,SSB The worst .
14、 Incoherent demodulation ( Envelope detection ) There is a threshold effect . What is the threshold effect ?
15、AM DSB SSB PM FM The bandwidth of the 、 Institutional gain 、 Carson formula calculates bandwidth 、


16、 What is reuse 、 What is the purpose ?
17、AMI HDB3 Differential code Differential biphase code transformation 
18、NRZ RZ Signal power spectrum ? Whether there is a timing component 、 Discrete spectrum 、 Continuum spectrum ?
AMI code 、HDB3 Code and bipolar RZ There is no bit timing information in the code waveform , At this point, they only need to be rectified into unipolarity RZ code , Bit synchronization information can be extracted .
19、 Code string judgment
B Station links https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1RD4y1D7xv?from=search&seid=10136544546335783507
20、 The time-frequency conditional expression of no code string 

21、 Nyquist bandwidth 、 rate ?
22、 How to calculate the cosine roll off coefficient 、 Maximum frequency band utilization without inter symbol crosstalk ?

23、 AMI characteristic
advantage :①0、1 There is no direct current at any time ;② Low frequency components near zero frequency are small ;③ After rectification, it is RZ code ;④ The encoding and decoding circuit is simple and easy to observe the error code .
shortcoming : even 0 A long yard ,AMI Rectified RZ Code link 0 Many , It is not conducive to extracting high-quality bit synchronization signals ( Bit synchronization jitter is large ).
24、 Common forms of digital baseband signals are : Unipolar code 、 Bipolar code 、 Return to zero for unipolarity 、 Bipolar zeroing 、 Differential codes and multicode codes .
25、ASK The digital signal controls the carrier amplitude
Expressions and waveforms ?
The generation method : Analog modulation method ( Multiplication ) And keying .
Demodulation method : Incoherent demodulation ( Envelope detection ) And coherent demodulation
26、2FSK Digital signal controls carrier frequency
Expressions and waveforms ?
The generation method : Analog frequency modulation and keying .
Demodulation method : Incoherent demodulation ( Envelope detection ) And coherent demodulation
27、2PSK Digital signal controls carrier phase
Expressions and waveforms
The generation method : Analog modulation method ( Multiplication ) And keying .
Demodulation method : Coherent demodulation
characteristic : There is phase ambiguity —— pour The phenomenon , so 2PSK Unpractical , And use 2DPSK.
28、2DPSK
Expressions and waveforms
The generation method : Analog modulation method ( Multiplication ) And keying .
Demodulation method : Coherent demodulation ( Polarity comparison method ) And differential coherent demodulation ( Delay coherent demodulation , Phase comparison method )
2DPSK Signals and 2PSK The difference between the signals lies only in differential coding , Their signal expressions 、 Power spectrum 、 Same bandwidth .
29、 Performance comparison *****
Bit error rate calculation formula ?
30、 Calculation : bandwidth 、 Bandwidth utilization 、 drawing


31、 M-ary modulation 
32、 Block diagram of matched filter receiving circuit 、 Relevant receiving and transmitting block diagram ?
33、 Bit error rate 、 Symbol energy calculation ( Definite integral calculation ), The correlation coefficient ?
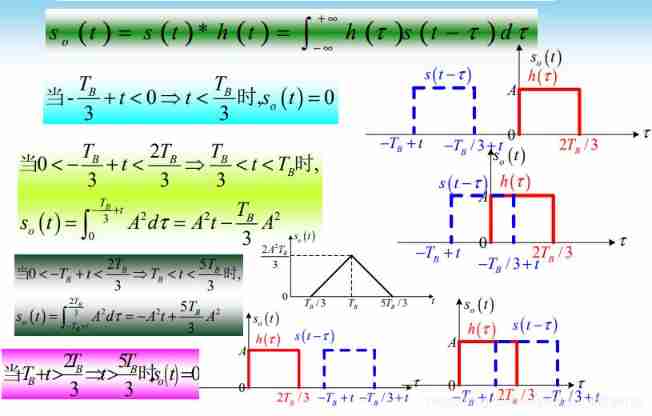
34、 How to convolute signals , Graphic method , Draw the output waveform 
35、 Impulse response of matched filter 、 The maximum output signal-to-noise ratio time and signal-to-noise ratio of the matched filter ?

36、 What is absolute phase shift ? What is relative phase shift ? What's the difference between them ?
answer : Absolute phase shift is to use the phase of the carrier to directly represent the symbol ; Relative phase shifting is to use the relative carrier phase values of the adjacent symbols before and after to represent the digital information . Relative phase shift signal can be regarded as a sequence of digital information ( The absolute value ) Transform to relative code , Then it is formed by absolute phase shifting according to the relative code .
37、A/D Transformation includes sampling 、 quantitative 、 There are three steps to coding
38、 Sampling includes impulse sampling 、 Natural sampling 、 Flat top sampling .
39 、A Law 13 discount PCM a key
key word :
seek C1~C8
Coding output level
Decoding output level
Quantization error
Uniformly quantized 11 Bit code
Decoding error
bandwidth
Bit rate 

40、 What is quantification ? Why quantify ?
answer : Quantization is to transform a continuous signal into a discrete value in the value domain , Make the signal take one of the finite quantization levels . The purpose of quantization is to approximate the amplitude of the original signal with finite discrete values , At the receiving end, the original signal is recovered from these finite discrete values , Thus, the information of sampling value can be transmitted by digital transmission system .
41、 In non-uniform quantization , Why compress and expand ?
answer : In non-uniform quantization , Using compression and expansion can improve the signal-to-noise ratio of small signals , Thus, it is equivalent to expanding the dynamic range of the input signal .
42、 Concept and implementation of carrier synchronization ( qualitative )
43、 Concept and implementation of symbol synchronization ( qualitative )
44、 frame ( Group ) The concept and implementation of synchronization ( qualitative )
45、 Network synchronization

边栏推荐
- Set the transparency of the picture to gradient from left to right
- Figure explanation of fiborache sequence
- Tp6 exception handling try catch writing method
- mysql FIND_ IN_ Set function
- Disconnected: No supported authentication methods available (server sent: )
- Wait for the end of the network request in the uniapp Onshow method before executing the subsequent code content
- How can we differ LEFT OUTER JOIN vs Left Join [duplicate]
- VIM common commands and shortcut keys
- ECSHOP product attribute color specification size stock item No. automatic combination
- Mind mapping video
猜你喜欢

Uncover gaussdb (for redis): comprehensive comparison of CODIS

Go from 0 to 1. Obtain the installation package, get, post request, params, body and other parameters

Installation and removal of MySQL under Windows
MySQL common interview questions

Happy shopkeeper source code -- Introduction to happy shopkeeper system development mode

Rank sum ratio comprehensive evaluation method for common models in mathematical modeling

Today, I will explain to you what is DFI and its development prospects

The server reported an error 503 service unavailable:the system returned: (71) protocol error

Explain AHP in human language (very detailed principle + simple tool implementation)

Zhangxiaobai's road to penetration (7) -sql injection detailed operation steps -union joint query injection
随机推荐
Ubuntu uninstalling PHP
Découvrir gaussdb (pour redis): une comparaison complète avec Codis
Installation and removal of MySQL under Windows
Spicy food advertising e-commerce system development function and spicy food advertising e-commerce app system development source code sharing
Node child processes and threads
Go defer little knowledge
揭秘GaussDB(for Redis):全面对比Codis
PHP files running online
Development with courtesy -- share the source code of the secondary development of the app system of the imitation shopping mall
Disconnected: No supported authentication methods available (server sent: )
Go from 0 to 1. Obtain the installation package, get, post request, params, body and other parameters
2022 meisai D topic ideas sharing + translation
Today, I will explain to you what is DFI and its development prospects
High performance + million level Excel data import and export
Navicat premium view password scheme
The source code of the hottest online disk money making system in 2022 imitates Lanzou online disk / Chengtong online disk / sharing money making cloud disk system / online disk VIP Download System
thinkphp3.2.5 GIF. class. php for php7.4
2022 meisai e topic ideas sharing + translation
The server reported an error 503 service unavailable:the system returned: (71) protocol error
How can we make an annual income of onemillion yuan by making our own media video?