当前位置:网站首页>Compilation and preprocessing
Compilation and preprocessing
2022-07-23 13:17:00 【Er Mu】
List of articles
One 、 The environment of the program
stay ANSI C In any implementation of , There are two different environments .
- The first 1 One is the translation environment , In this environment, source code is converted into executable machine instructions .
- The first 2 One is the execution environment , It's used to actually execute code .
Two 、 compile + link
1. Translation environment
- Each source file constituting a program is converted into object code through the compilation process (object code).
- Each target file is linked by a linker (linker) Tied together , Form a single and complete executable program .
- Linkers also introduce standards C Any function in the function library used by the program , And it can search individual programmers
The library of , Link the functions it needs to the program .

2. Each stage of compilation
sum.c
int g_val = 2016;
void print(const char *str)
{
printf("%s\n", str);
}
test.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
extern void print(char *str);
extern int g_val;
printf("%d\n", g_val);
print("hello world.\n");
return 0;
}
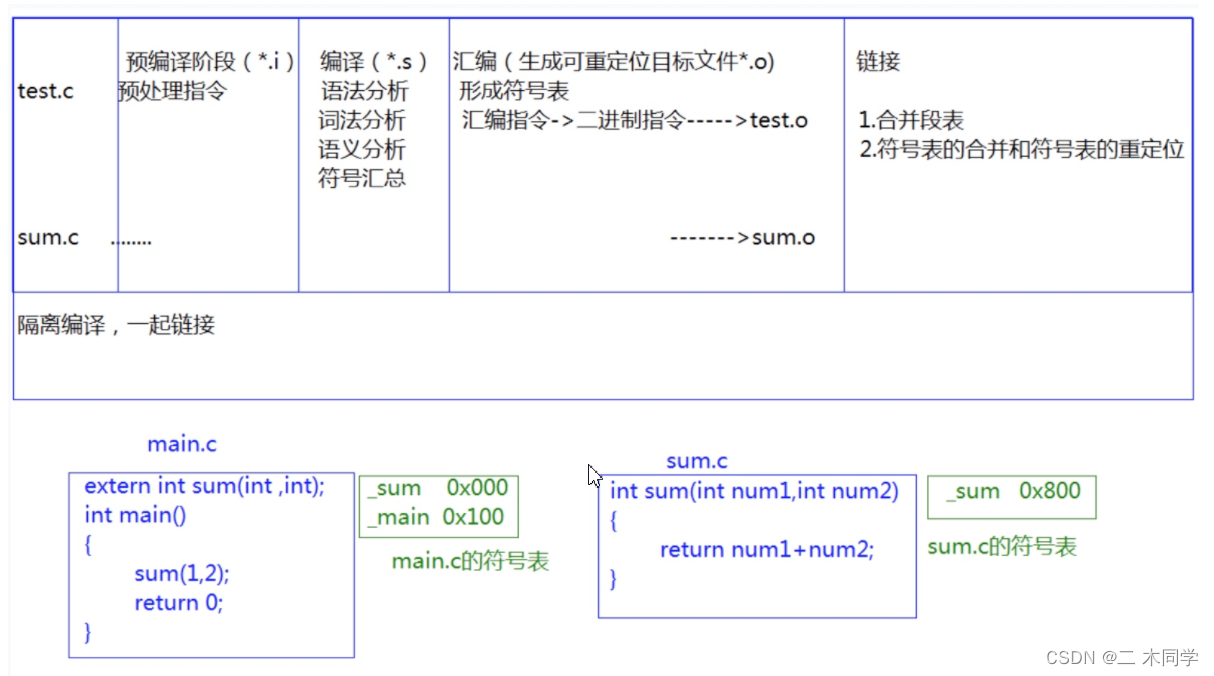
How do I see what happens at each step of the compilation process ?
- Preprocessing gcc -E test.c -o test.i
Stop after the pretreatment is complete , All the results after pretreatment are put in test.i In file . - compile gcc -S test.c
- Stop when the compilation is complete , The results are stored in test.s in .
- assembly gcc -c test.c
Stop when the assembly is finished , The results are stored in test.o in .
3. Running environment
The process of program execution :
- The program must be loaded into memory . In an operating system environment : This is usually done by the operating system . In an independent environment , The loading of the program must be arranged manually , It can also be done by putting executable code into read-only memory .
- The execution of the procedure begins . And then I call main function .
- Start executing program code . At this point, the program will use a runtime stack (stack), Store function local variables and return address . Programs can also use static (static) Memory , Variables stored in static memory are stored throughout the execution of the program Keep their values all the time .
- To terminate the program . Normal termination main function ; It could be an accidental termination .
3、 ... and 、 Preprocessing
1. Preprocessing symbols
__FILE__ // Source files to compile
__LINE__ // The current line number of the file
__DATE__ // The date the file was compiled
__TIME__ // When the file was compiled
__STDC__ // If the compiler follows ANSI C, Its value is 1, Otherwise, it is not defined
These predefined symbols are built into the language .
example :
printf("file:%s line:%d\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);

2. #define
#define Define identifier :
#define name stuff
example :
#define MAX 1000
// by register This keyword , Create a short name
#define reg register
// Replace an implementation with a more vivid symbol
#define do_forever for(;;)
// Writing case Automatically put break write
#define CASE break;case
notes :
stay define When defining identifiers , Don't add... At the end ;
3. #define Defining macro
#define The mechanism includes a provision , Allow parameters to be replaced with text , This implementation is often called a macro (macro) Or define macro (define macro)
How macros are declared :
#define name( parament-list ) stuff
example :
#define SQUARE( x ) x * x

This macro takes a parameter x. If after the above statement , hold SQUARE( x )
Put in the program , The preprocessor will use 10*10 This expression replaces the above expression .
Be careful :
There is a problem with this macro :
Look at the following code snippet :
int a = 3;
printf("%d\n" ,SQUARE( a + 1) );
At first glance , You might think this code will print 16 This value .
in fact , It will print 7

When replacing text , Parameters x Replaced with a + 1, So this statement actually becomes :
printf ("%d\n",a + 1 * a + 1 );
So it's clear , The expression resulting from the substitution does not evaluate in the expected order .
Add two parentheses to the macro definition , This problem is easily solved
#define SQUARE(x) (x) * (x)
There is such a macro :
#define DOUBLE(x) (x) + (x)
What will the following code print ?
int a = 5;
printf("%d\n" ,10 * DOUBLE(a));
it seems , It's like printing 100, But in fact, it's printed 55
After replacement :
printf ("%d\n",10 * (5) + (5));
The solution to this problem is to add a pair of parentheses around the macro definition expression
#define DOUBLE( x) ( ( x ) + ( x ) )
So the macro definitions used to evaluate numeric expressions should be bracketed in this way , Avoid unexpected interactions between operators in parameters or adjacent operators when using macros .
4. #define Replacement rules
Extend... In a program #define When defining symbols and macros , There are several steps involved :
- When calling a macro , First, check the parameters , See if it contains any information from #define Defined symbols . If it is , They are replaced first .
- The replacement text is then inserted into the program at the location of the original text . For macros , Parameter names are replaced by their values .
- Last , Scan the result file again , See if it contains any information from #define Defined symbols . If it is , Just repeat Describe the process .
Be careful :
- Macro parameters and #define Other... Can appear in the definition #define Defined symbols . however Recursion cannot occur for macros .
- When the preprocessor searches #define When defining symbols , The contents of string constants are not searched .
5. # and ##
How to insert parameters into a string ?
char* p = "hello ""world\n";
printf("hello"" world\n");
printf("%s", p);
The output here is hello world
We found that Strings have the characteristics of automatic connection .
We can write code like this :
#define PRINT(FORMAT, VALUE) printf("the value is "FORMAT"\n", VALUE);
PRINT("%d", 10);


Another way is :
- Use #, Change a macro parameter into the corresponding string .
such as :

In code #VALUE Preprocessor processing is :"VALUE"
## The role of
- ## You can combine the symbols on both sides of it into one symbol .
- It allows macro definitions to create identifiers from detached pieces of text .
#define ADD_TO_SUM(num, value) sum##num += value;
ADD_TO_SUM(5, 10);// Role is : to sum5 increase 10.
Such a connection must produce a legal identifier
6. Macro parameters with side effects
When macro parameters appear more than once in the macro definition , If the parameter has side effects , Then when you use this macro, you may
There is danger , Lead to unpredictable consequences . The side effect is the permanent effect of expression evaluation .
example :
x+1;// No side effects
x++;// With side effects
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX(a, b) ( (a) > (b) ? (a) : (b) )
int main()
{
int x = 5;
int y = 8;
int z = MAX(x++, y++);
printf("x=%d y=%d z=%d\n", x, y, z);// What is the result of the output ?
return 0;
}
After preprocessor processing :
z = ( (x++) > (y++) ? (x++) : (y++));
Output results :
x=6 y=10 z=9
7. Comparison between macros and functions
Macros are usually used to perform simple operations .
For example, find the larger of the two numbers .
#define MAX(a, b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
Then why not use functions to accomplish this task ?
reason :
- The code used to call and return from the function may take more time than actually performing this small computation .
therefore Macros are better than functions in terms of program size and speed . - More importantly, the parameters of a function must be declared as specific types .
So functions can only be used on expressions of the right type . On the contrary, how can this macro be applied to shaping 、 Long integer 、 Floating point type can be used for > To compare the types of .
Macros are type independent .
The disadvantages of macro :
- Every time you use a macro , A macro defined code will be inserted into the program . Unless the macro is short , Otherwise, the length of the program may be greatly increased .
- Macros can't be debugged
- Macro is type independent , It's not rigorous enough .
- Macros can cause operator priority problems , It is easy for Cheng to make mistakes .
Macros can sometimes do things that functions can't do .
such as : Macro parameters can have types , But functions can't do it .
#define MALLOC(num, type) (type *)malloc(num * sizeof(type))
// Use
MALLOC(10, int);// Type as parameter
// After preprocessor replacement :
(int *)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
Comparison between macros and functions :
| attribute | macro | function |
|---|---|---|
| Code length | Every time I use it , Macro code is inserted into the program . Except for very small macros , The length of the program will increase significantly | Function code only appears in one place ; Every time you use this function , Call the same code in that place |
| Execution speed | faster | There is an extra cost of calling and returning functions , So it's relatively slow |
| Operator priority | Macro parameters are evaluated in the context of all surrounding expressions , Unless you put parentheses , Otherwise, the priority of adjacent operators may have unpredictable consequences , Therefore, it is recommended that macros be written with more parentheses . | Function parameters are evaluated only once when the function is called , Its result value is passed to the function . The evaluation of expressions is easier to predict . |
| Parameters with side effects | Parameters may be replaced at multiple locations in the macro body , Therefore, parameter evaluation with side effects may produce unpredictable results . | Function parameters are evaluated only once when passing parameters , The result is easier to control . |
| Parameter type | Macro parameters are type independent , As long as the operation on parameters is legal , It can be used for any parameter type . | The arguments to the function are type dependent , If the type of parameter is different , You need different functions , Even if they perform the same tasks . |
| debugging | Macros are inconvenient to debug | Functions can be debugged statement by statement |
| recursive | Macros cannot be recursive | Functions can be recursive |
8. Conditional compilation
When compiling a program, if we want to translate a statement ( A set of statements ) It's convenient to compile or discard . Because we have conditional compilation instructions .
for instance :
Debugging code , It's a pity , Reservation is in the way , So we can Selective compilation .
example :
#include <stdio.h>
#define __DEBUG__
int main()
{
int i = 0; int arr[10] = {
0 }; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
#ifdef __DEBUG__
printf("%d\n", arr[i]);// To see if the array assignment is successful .
#endif //__DEBUG__
}
return 0;
}
- Common conditional compilation instructions :
1.
#if Constant expression
//...
#endif
// Constant expressions are evaluated by the preprocessor .
Such as :
#define __DEBUG__ 1
#if __DEBUG__
//..
#endif
2. Conditional compilation of multiple branches
#if Constant expression
//...
#elif Constant expression
//...
#else
//...
#endif
3. Judge whether it is defined
#if defined(symbol)
#ifdef symbol
#if !defined(symbol)
#ifndef symbol
4. Nested instruction
#if defined(OS_UNIX)
#ifdef OPTION1
unix_version_option1();
#endif
#ifdef OPTION2
unix_version_option2();
#endif
#elif defined(OS_MSDOS)
#ifdef OPTION2
msdos_version_option2();
#endif
#endif
9. File contains
We already know ,#include Instruction can cause another file to be compiled . It's like it actually appears in #include Where the order is equally .
It's a simple alternative :
The preprocessor first removes this instruction , And replace... With the contents of the containing file .
Such a source file is contained 10 Time , So it's actually compiled 10 Time .
- The local file contains
#include "filename"
Search strategy :
First, find the source file in the directory , If the header file is not found , The compiler looks up the header file in a standard location just like it looks up the header file of a library function .
If no compilation error is found .
- The library file contains
#include <filename>
Look up the header file and go directly to the standard path , If no compilation error is found .
Is it possible to say , For library files, you can also use “” The form of includes ?
The answer is yes , Sure .
But this is less efficient , Of course, it is not easy to distinguish between library files and local files .
- Prevent header files from repeatedly containing
#ifndef __TEST_H__
#define __TEST_H__
// Content of header file
#endif //__TEST_H__
or
#pragma once
That's all for this article , If there is a mistake , Please correct me. .
边栏推荐
- 根据不同时间统计不同类型的数据(存储过程)
- Li Kou 729. My schedule I
- 功能测试转自动化测试,十年自动化测试经验分享
- 当输入网址后,到网页显示,期间发生了什么
- 谈谈学习和工作——钱学森
- 倍福PLC和C#通过ADS通信传输bool类型变量
- 倍福PLC--C#ADS通信以通知的方式读取变量
- Quelle est la raison pour laquelle la plate - forme easygbs ne peut pas lire l'enregistrement vidéo et a un phénomène de streaming répété rtmp?
- 倍福PLC和C#通过ADS通信传输String类型
- 虚拟内存技术的来龙去脉(上)
猜你喜欢

太空射击 Part 2-3: 子弹与敌人碰撞处理

Redis如何实现持久化?详细讲解RDB的三种触发机制及其优缺点,带你快速掌握RDB
Opencv image processing (Part 2): edge detection + template matching + Hough transform

互联网时代下,如何精细化用户运营?
使用vscode进行远程编辑和调试

com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.MysqlDataTruncation: Data truncation: Truncated incorrect DOUBLE value:

4D毫米波雷达硬件系统架构

The unity model is displayed in front of the UI, and the UI behind it jitters

The context of virtual memory technology (Part 1)
第十天笔记
随机推荐
行业现状令人失望,工作之后我又回到UC伯克利读博了
Harbor deployment
Common CMD commands to quickly open programs
Software testing jobs saturated? Automated testing is a new generation of 'offer' skills
力扣 729. 我的日程安排表 I
[offline voice topic ④] Anxin VC offline voice development board secondary development voice control LED light
HCIA----02
迷茫、工作没动力? 职业发展没希望? 看这篇文章就够了
国信证券软件开户是安全吗?信息会不会泄露?
【JZOF】08 二叉树的下一个结点
Common scheduled cron expressions for scheduled tasks
When using fastjson to parse and assign JSON data, the order of JSON fields is inconsistent
软件测试岗位饱和了?自动化测试是新一代‘offer’技能
Record a reptile question bank
Numpy: quick start to basic operations
雷达导论PART VII.4 SAR系统设计
Pod topology constraints
Hcia---03 ENSP usage, DHCP, router
Why build a local Yum warehouse?
Outlook tutorial, how to switch calendar views and create meetings in outlook?