当前位置:网站首页>The context of virtual memory technology (Part 1)
The context of virtual memory technology (Part 1)
2022-07-23 13:08:00 【liyinuo2017】
1. Introduction to virtual memory
Every modern computer system is equipped with high-speed random access memory , Called primary memory 、 Physical memory or directly called memory . Memory is the hardware used to store code and data , It is the storage space that the processor can address directly , Memory is made of semiconductor devices , It is characterized by fast access rate .
Before the program is executed, the program needs to be put into memory before it can be CPU Handle , The program we usually use , Such as : operating system 、 Office software 、 Game software, etc , It is usually installed on external memory such as hard disk , Software needs runtime , They have to be run in memory , Can be really implemented .
The bearing entity of memory is usually random access memory (RAM),CPU Can be directly related to RAM Exchange data .RAM In working condition , You can write from any specified address at any time ( Deposit in ) Or read out ( Take out ) Information .
efficient Memory management system Is one of the important functions of the operating system , Modern operating systems provide a memory management technology : Virtual memory . Virtual memory is one of the most important concepts in computer systems , It involves almost all levels of computer system , At the hardware level , Compiler level , Document level , The process level plays an important role .
Virtual memory Is the operating system with hardware implementation , It works automatically , No programmer intervention is required . Virtual memory gives applications powerful capabilities , Applications can create and destroy memory slices , Applications can map memory slices to disk files , Applications can share memory with other processes .
2. Physical addressing and virtual addressing
2.1 Physical addressing
The memory of the computer system is organized into a N An array of contiguous byte units , Each byte has and only has a unique physical address (PA). The physical address of the first byte is 0, The physical address of the next byte is 1, The physical address of the next byte is 2, And so on .CPU The most natural way to access memory is to use physical addresses , This access method is called physical addressing .
In the early PC Use physical addressing , At present, digital signal processors , Embedded microcontrollers ( Single chip microcomputer ) Continue to use this addressing method . The figure below shows a Examples of physical addressing :
The above figure shows an example of a load instruction , It reads the physical address 4 At the beginning of 4 byte . When the processor executes this load instruction , The processor will generate a physical address 4, Memory bus will physical address 4 Address port passed to memory , Take out the physical address from the memory 4 Continuity at 4 Bytes of data are output to the memory data bus , Pass to processor , The processor will send this 4 Byte data is stored in registers .
2.2 Virtual addressing
Physical addressing is the most direct , Efficient , But this addressing method has obvious disadvantages : It is not supported to run applications with larger capacity than physical ; Writing machine independent code is not supported , The code needs to correspond to the physical memory configuration . Modern computer systems use an addressing method called virtual addressing .
The addressing process of virtual addressing is :CPU Usually generate a Virtual address (VA) To access main memory , Before this virtual address is loaded into memory , You need to convert it into a physical address first (PA), Final CPU Indirectly accessed the physical address of the memory (PA). The process of converting virtual addresses into physical addresses is called address translation .CPU There is a chip called Memory management unit (MMU) Dedicated hardware for , The memory management unit uses the query table to dynamically complete the address translation .
The following figure shows an example of physical addressing :
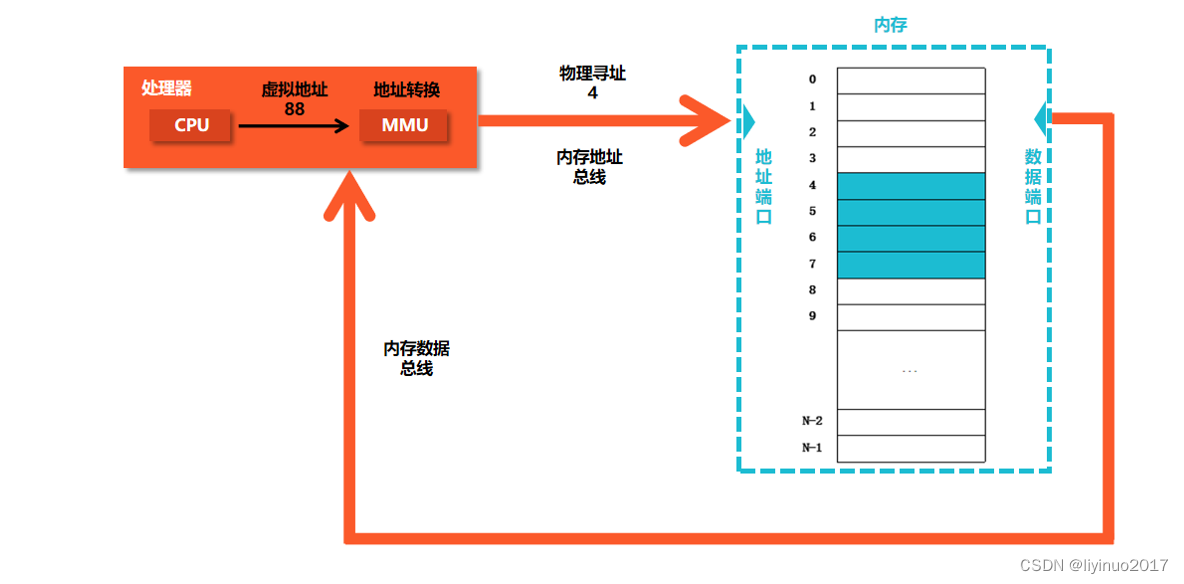
The above figure shows an example of a load instruction , It reads the virtual address 88 At the beginning of 4 byte . When the processor executes this load instruction , The processor will generate a virtual address 88 to MMU,MMU Look up the table to get the virtual address 88 Corresponding physical address 4, Memory bus will physical address 4 Address port passed to memory , Take out the physical address from the memory 4 Continuity at 4 Bytes of data are output to the memory data bus , Pass to processor , The processor will send this 4 Byte data is stored in registers .
3. Memory management technology development
3.1 Manual operation
The earliest computers had no operating system , Instead, the task is handled manually . Programmers will use machine language Written programs and data . Stored in by punching Paper tape On , Then load the perforated paper tape into the input machine of the machine , Then start the program through the console switch . After the calculator finishes the calculation , Output the calculation results through the printer . After the operator removes the results and removes the paper tape , To start the next program ( paper bag ).
Paper bag recognition principle : The collector is a group of probes and a group of corresponding probe seats , The paper tape passes through the probe set , Where there are holes, the probe will contact and conduct , Where there is no hole, there will be no conduction , Drag the tape at a constant speed so that the computer can recognize the tape code , And then calculate .
There are two types of probes : Signal probe and Synchronous probe . The signal probe reads program code and data , Synchronous probe is to generate synchronous signal , The function of synchronous signal is similar to that of clock signal in modern computer , Each synchronization signal will trigger the computer to execute an instruction .
The disadvantages of manual operation are very obvious :
1、 There is a huge contradiction between the high speed of computer and the low speed of manual operation , The man-machine speed is extremely uncoordinated , The waste of resources is serious .
2、 One program monopolizes the whole machine , Resulting in low utilization of resources .
characteristic : The earliest electronic computers had no operating system , no memory , There is no memory management , Manual operation .
3.2 Single channel batch processing mechanism
20 century 50 Late S , In order to overcome the contradiction between the slow speed of manual operation and the high speed of computer , There is Single channel batch processing system , That is, on the computer Load a system software , Under the control of the system software, the computer can Automatically 、 Batch processing jobs for one or more users .
The purpose of single pass batch processing system is to reduce the manual operation during the conversion between jobs , Thereby reducing CPU The waiting time of . Batch processing is to group jobs according to their nature ( Or in batches ), Then submit to the computer system one by one , The result will be output after it is automatically completed by the computer , So as to reduce the time waste in the process of job establishment and completion . This working mode is like an assembly line in a factory .

The characteristic of single channel batch processing system is that only one job is allowed to be stored in memory , That is, only the currently running job can reside in memory , The order of operation is first in, first out , That is, execute in order . In this model, user processes are always loaded into the same fixed memory address to run , The address used by the user process is the physical address .
This system has two fatal disadvantages :
1、 The system can only run applications with less capacity than physical memory , It is not supported to run applications with larger capacity than physical .
2、 The system can only run one application , Running multiple applications is not supported .
The next computer history , It is the history of computer pioneers overcoming these two problems step by step . In this section, let's take a look at how computer pioneers conquered these two BOOS Of .
3.2 Multi channel batch processing mechanism
Because in the single channel batch processing system , A job enters memory alone and monopolizes system resources , The next job cannot enter the memory until the end of the run , When the operation is in progress I/O In operation ,CPU Can only be in a waiting state , therefore CPU Low utilization .
until 20 century 60 The mid - , Multiprogramming technology appears , Officially enter the stage of multi-channel batch processing system . 1964 year ,IBM Produced the first small-scale integrated circuit computer IBM 360, Developed for this machine OS/360 The operating system is the first batch processing system that can run multiple programs .
Multiprogramming technology can put multiple programs into memory at the same time , And allow them to alternate between CPU Run in , Share all kinds of hardware in the system 、 Software resources . When a procedural cause I/O( Input / Output ) Request and suspend the runtime ,CPU Then immediately switch to run another program . Multi channel batch processing does not run multiple programs at the same time , Instead, multiple programs are ready to run in memory , Only when the program is running for some reason ( such as , Wait for output or output data ) And temporarily unable to continue running , The system will automatically start another program to run .
That is, there can be several jobs in memory at the same time , There is no strict correspondence between the order of job execution and the order of entering memory , Because these jobs are used through certain job scheduling algorithms CPU Of . An assignment is waiting I/O When dealing with ,CPU Schedule another job to run , therefore CPU The utilization rate of has been significantly improved .

Because multiple programs can be used alternately CPU, Improved CPU And other system resources , At the same time, it also improves the efficiency of the system . The disadvantage of multi-channel batch processing system is to prolong the turnover time of jobs , Users cannot intervene directly , Lack of interactivity , It is not conducive to program development and debugging .
The advantages of multi-channel batch processing system are also obvious :
The system can accommodate multiple jobs at the same time . These assignments are in external storage , Form a backup line , According to a certain scheduling principle, the system selects one or more jobs from the backup job queue to run in memory , End of run job 、 Exit operation and backup operation are automatically realized by the system , In order to form an automatic transfer in the system 、 Continuous job flow .
The disadvantages of multi-channel batch processing system are also obvious :
During the operation of the system , Users are not allowed to interact with their jobs , That is, once the job enters the system , Users cannot directly interfere with the running of their jobs .
3.3 Coverage mechanism
Multi channel batch processing system solves the problem of running multiple applications , However, the system still does not support running applications with larger capacity than the physical , This restriction produces a Coverage mechanism .
The coverage mechanism covers the address space that the application no longer needs , To achieve the purpose of reusing memory . for example , Once the system is loaded and running , The code memory initialized by the system can be recycled to the program , This software coverage mechanism requires application developers to do additional programming operations . Coverage technology frees up useless code space , Increase the available memory space .
Generally speaking, coverage technology is Divide the program into segments , The segments that are often executed are placed in Fixed area , After transfer in, unless the operation ends , Otherwise, it will not be called out . And not commonly used is placed in Coverage area , Only when it is needed can it be loaded into memory , Otherwise, it will be called out and covered by other programs .
As shown in the figure below , If we had a program A,8k Of main It is often executed , Then the memory will allocate one 8k Fixed area of . And for B、C These two commanders were A Where segments are occasionally called , The memory will take the maximum value of these two segments, that is 10k As the coverage area of these two sections .DEF Empathy . It can be seen that coverage technology only uses 30k Of memory space , It's solved 52k The problem of loading the program into memory .
3.4 Exchange mechanism
Memory can hold a few processes at the same time , Each process is loaded into a continuous physical memory , The system provides time-sharing services for these processes in memory . If you want to run other processes , The system needs to choose a process in memory to exchange , The system will copy the selected process to a specific swap partition on the disk . Then load other programs that need to be run into memory to run .

When exchanging a process , The operating system will guarantee the size of memory exchanged , When saving the process , Not only save the data of the process , At the same time, it also saves the running state of the processor , When the saved process is restored , The process will continue from where it was suspended .
Exchange mechanism , Make the physical memory capacity “ Bigger ”, The memory available to the system can be much larger than the capacity of physical memory .
Memory becomes bigger and stronger 
3.5 On demand paging mechanism
The on-demand paging mechanism needs to be completed by the operating system and paging hardware . In the on-demand paging system , The physical memory and the address space of the process are divided into fixed size pages , Data is loaded and released in pages . Pages in physical memory are usually called page boxes or physical pages .
Multiple processes can be active in memory at any time , But each process may only have some pages in physical memory , The address of the process is virtual , Virtual addresses contain page numbers and intra page offsets . With the cooperation of the operating system and hardware , The virtual address of the program is converted into a physical address , And access the corresponding physical memory . In the on-demand paging mechanism , All pages are loaded into memory when needed .

3.6 Virtual memory mechanism
Memory virtualization technology is not a single new technology , It is a technology formed by combining a variety of technologies . Virtual address technology used by memory virtualization , Paging mechanism , Exchange mechanism .
Virtual memory mechanism is a comprehensive memory management technology .
4. Virtual memory solves the problem
Virtual memory is one of the most important parts of computer system , Virtual memory can realize the following functions :
1、 Run programs larger than physical memory . Such as 64 Bit computer system has 256T Virtual memory , Theoretically, it can run about 256T The size of the program , Today's mainstream 64 The physical memory size of a bit computer is about 4G. Therefore, using virtual memory can ideally run programs of any size .
2、 When the program runs, it only needs to load some . Because virtual memory uses paging mechanism , The program is divided into segments , Reduced program startup time , Reduced physical memory usage .
3、 Support multiple programs to run in memory at the same time . Only part of each program is in physical memory , So that the physical memory can accommodate multiple programs at the same time .
4、 The support code is machine independent , There is no correspondence between code and physical memory .
5、 Programs that support relocation , The relocation program can be stored anywhere in memory , And the position can be changed during execution .
6、 Support memory sharing .
7、 Programmers who do not need applications are directly involved in the allocation and management of physical memory
5. Virtual memory model
Virtual memory is a hardware exception , Hardware address translator , Main memory , disk , The kernel software cooperates to realize .

To be continued …
It's not easy to create. I hope my friends will like it , forward , Comment on , Focus on .
What do you like , forward , Comment on , Attention will be my driving force for continuous renewal
author : Li Wei
Github:liyinuoman2017
CSDN:liyinuo2017
Today's headline : Program ape Li Wei 
边栏推荐
- [untitled]
- DNS domain name resolution service
- Static routing principle and configuration
- Jenkins deployment
- C randomly generate a score to judge its grade (excellent, good, medium, poor, failed)
- Vmware虚拟机和主机之间复制、粘贴内容、拖拽文件
- HCIA----03 eNSP使用、DHCP、路由器
- Rk3588 compilation problem set
- 0 backtracking / dynamic programming medium leetcode526. Beautiful arrangement
- Hcia---04 route static extension, VLAN
猜你喜欢

【离线语音专题④】安信可VC离线语音开发板二次开发语音控制LED灯
![Build FRPC client in NAS [super brainless]](/img/02/bc150ab6cec73b9142d0e3c3532417.png)
Build FRPC client in NAS [super brainless]

踩坑electron渲染进程renderer,解决require is not defined的问题
Solution rapide: xshell ne peut pas glisser dans un dossier ou un paquet

vlan配置实例学习记录

CORTEX-A系列处理器

4D毫米波雷达硬件系统架构

信号完整性(SI)电源完整性(PI)学习笔记(三十一)电源分配网路(三)

Frame relay network configuration example learning record

信号完整性(SI)电源完整性(PI)学习笔记(三十二)电源分配网路(四)
随机推荐
NFS service deployment notes
Helm installing rancher
C#输入一个字母,判断其大小写
用户与组的管理、文件的权限
RIP 配置实例学习记录
Square root cube root
Jupyter notebook添加已存在的虚拟环境
RHCSA--文件内容浏览、cut、uniq、sort、.tr命令使用
Jenkins deployment
快速解决:Xshell拖不進去文件夾或者軟件包的問題
Real questions required for Niuke interview [algorithm] summary of high-frequency TOP200 questions
2020-09-20
HCIA----07 ACL-Net
Single arm routing configuration instance learning record
DHCP 配置实例学习记录
ACL——net
【无标题】
Three layer switching configuration example learning record
TI单芯片毫米波雷达代码走读(二十五)—— 角度维(3D)处理流程
2020-09-22