当前位置:网站首页>Notes to nodejs (II)
Notes to nodejs (II)
2022-06-23 22:47:00 【Qiu Qiu Qiu YF】
I have been studying books recently Explain profound theories in simple language nodejs , Some notes written casually , Share with you ~ If there is a mistake , Welcome to correct ~
Memory control
With node The development of ,js It is no longer limited to the browser side . But when running on the server side for a long time , Memory control is very important , To serve a large number of users , We have to make efficient use of all resources .
V8 Garbage collection mechanism and memory control
1. V8 Memory limit of
64 Bit system is about 1.4G, 32 About 0.7G. Such restrictions will lead to Node Can't directly manipulate large memory objects , For example, you can't put a 2G File read into memory for string analysis . The reason for this problem is Node be based on V8 structure , therefore Node Use js Objects are passed V8 To manage the distribution . This form is more than enough on the browser side , But in node It limits developers . The following is described first V8 Strategies on memory usage
2. V8 Object allocation of
js Objects are allocated through the heap , When we declare objects in code , The memory of the object used is allocated in the heap . If the requested heap free memory is not enough to allocate new objects , Will continue to request heap memory , Until the size of the heap exceeds V8 Limit .
V8 The underlying reason for limiting the size of the heap is V8 The limitation of garbage collection mechanism .( According to the official statement , With 1.5G Garbage collection heap memory for example , V8 Do a small garbage collection needs 50ms above , Doing an incremental garbage collection even requires 1s above .) This is caused by garbage collection js Thread pause time , Is not very acceptable . So limiting heap memory is a good choice .
3. V8 Garbage collection mechanism
Multiple garbage collection algorithms . Because in practical application , The lifetime of an object varies , Different algorithms can only have the best results for specific situations . Therefore, modern garbage collection algorithms divide the garbage collection of memory into different generations according to the exclusive lifetime ( The new generation , Old generation ) Then use more efficient algorithms for different generations .
V8 Memory generation based on
It is mainly divided into the new generation and the old generation . The objects in the new generation are the ones with shorter survival time , The old generation is a long-lived or resident object .
V8 The overall size of the heap is the memory space used by the new generation plus the old generation .( stay node It can be set manually at startup )
64 Bit system The Cenozoic era is about 32M, Old students take the place of 1400M
32 The Cenozoic generation in the system is about 16M, Old students take the place of 700M
Scavenge Algorithm
Algorithms used by objects in the new generation . In fact, it is a kind of garbage collection algorithm implemented by copying . It splits the memory into two , Every part of space is called semispace. In two semispace Only one clock is in use (From Space ), The other is idle (To Space ). When we assign objects, we start with From Middle distribution . Check when garbage collection begins From Living objects in space , The surviving object will be copied to To In the space ( In fact, before that, there is a step to check whether the object needs to be promoted ), The space occupied by non living objects will be released . Once the copy is done , The two spatial roles are interchanged . In short , Is to put the surviving objects in two semispace Copy between spaces .
The disadvantage is that only half of the heap memory can be used . Because only surviving objects are copied , For the scene at the end of the life cycle, there are only a few surviving objects , So it has excellent performance in efficiency . A typical sacrificial space for time algorithm , Suitable for the new generation . When an object is still alive after multiple copies , Will be considered a long-lived object , Then it is moved to the old generation to adopt the new algorithm , This process is called promotion . There are two main conditions for promotion , One is whether the object has experienced Scavenge Recycling , One is To The memory proportion of space exceeds the limit (25%, Because after this To It becomes From, If the share is too high , Will affect subsequent memory allocation ).
Mark-Sweep & Mark-Compact
For the old generation, if we still use Scavenge The algorithm has two problems : One is that there are many survivors , It leads to inefficient replication ; The other is to waste half the space . Therefore, CAITONG Mark-Sweep & Mark-Compact Garbage collection in a combined way .
Mark-Sweep It means to clear the mark , It is divided into two stages, marking and clearing .
And Scavenge The copy object is different ,Mark-Sweep Traverse all objects in the heap during the marking phase , And mark the living , In the subsequent cleanup phase, objects that are not marked are purged . The dead are only a few in the old generation , So it is more efficient .
Mark-Sweep The biggest problem is that memory discontinuities will occur after a clear mark ( Memory fragments ). This will cause problems for subsequent memory allocation , Because it is very likely that a large object cannot be allocated , And trigger garbage collection in advance , But this recycling is actually unnecessary .
In order to solve the problem of memory fragmentation ,Mark-Compact It was brought up . Mark-Compact The meaning of mark arrangement , Based on mark removal . The difference lies in After the object is marked dead , During the process of sorting, the live objects will be moved to one end , Clean up the memory outside the boundary after moving . The disadvantage is that Due to the need to move objects , The execution speed will decrease .
The final choice ,V8 The main use of Mark-Sweep, Only when there is insufficient space to allocate the objects promoted from the new generation Mark-Compact.
Increment mark
In order to avoid js Inconsistency between application logic and garbage collector , The application logic needs to be suspended during garbage collection , Recover after garbage collection , This is called “ A complete pause ”(stop-the-world). stay V8 In the generational garbage collection of , A small garbage collection only collects the new generation , Because the default configuration of the new generation is small , And there are few surviving objects , So even a full pause has little effect . But the whole pause caused by the old generation is terrible and needs to be improved .
In order to reduce the pause time caused by garbage collection ,V8 Start with the tag , Change the action that should be completed in one breath to Increment mark (incremental marking), That is, split into many small steps , Let's go with each step js The application logic executes for a while , Alternate until the marking phase is complete . After this improvement , The maximum pause time of garbage collection can be reduced to the original 1/6 about . Later, deferred cleanup and incremental cleanup were introduced , I won't repeat .
Efficient use of memory
- Active release of variables If the variable is a global variable , You must wait until the process exits to release , This will cause the object to reside in the old generation , Can pass delete Or assign it to null To get the object out of reference , Let him be recycled by the garbage collection mechanism .
- Less closures var foo = function() { var bar = function() { var local = 'local var'; return functoin() { return local; } } var baz = bar() console.log(baz()); } /* generally speaking , stay bar() After the function is executed , local variable local Will be recycled as the scope is destroyed . But note that the feature here is that the return value is an anonymous function , And this function has access to local Conditions . Although in the subsequent implementation , It is still not directly accessible in the external scope local, But to access it , Just pass this intermediate function . This is the closure , But his problem is , Once a variable references this intermediate function , This winning function will not release , At the same time, the original scope will not be released , The memory footprint generated by the scope will not be released . */
Out of heap memory
adopt process.memoryUsage() We can see that , The amount of memory in the heap is always less than the resident memory of the process , It means Node Memory usage in is not always through V8 The distribution of . We will not pass V8 Is called out of heap memory . For example, using Buffer() The application for memory fails V8 Distribute ( The reason is that the operation string in the browser can meet most requirements , But in node You also need to process network stream files in I/O flow , The operation string is far from meeting the performance requirements )
The main limitations of the garbage collection mechanism are V8 Heap memory for .
Memory leak
- cache Once an object is used as a cache , It means that the old generation will live forever , The more keys stored, the more long-lived objects , This causes the garbage collection mechanism to scan and sort , Do useless work . In addition, strict caching has a perfect expiration mechanism , But ordinary objects don't .( Policies can be added to limit cache wireless growth ) Be careful with ! You can use third-party , Such as LRU. Solution : Use similar Redis, Memcached etc. .
- Queue consumption is not timely production - Consumption model Once the consumption rate is lower than the production rate , Will form a pile
- Scope not released
Large memory applications
stay nodo It is inevitable to operate large files in .Node Provides stream Modules are used to process large files . for example fs Medium createReadStream and createWriteStream Method to realize the operation of large files by stream .pipe Methods can help with more concise coding . If you don't need string level operations , You can try to use Buffer operation , This will not be affected by V8 Heap memory limits .
Asynchronous programming
difficulty
difficulty 1 exception handling
asynchronous I/O The implementation of is mainly composed of two stages : Submit requests and process results . There is event cycle scheduling between these two stages , They're not related to each other . Asynchronous methods usually return immediately after the request is submitted in the first phase , Therefore, exceptions do not usually occur in this and stage ,try/catch The effect of does not work ( Only exceptions within the current event loop can be caught , Yes callback Exceptions thrown during execution are powerless ).
Node A convention has been formed on exception handling , Return the exception as the first argument , If it is empty, no exception is thrown .
We also need to follow this principle when we write our own asynchronous methods : The callback passed in by the caller must be executed , Correctly pass the exception to the caller .
difficulty 2 Function nested too deep
Generally, asynchronous operations have dependencies , Such as traversing the directory
difficulty 3 Blocking code
How to block code implementation in other languages sleep The effect of ( It is highly discouraged to use while Big loop to simulate similar situations )
Solution ( Books were published earlier , at that time es6 Not yet )
- Event publishing / A subscription model
- Promise/Deferred Pattern
- Process control library
Now? ES6 Medium Promise, async await It can be used to solve , I won't repeat .
边栏推荐
- In the eyes of the universe, how to correctly care about counting East and West?
- C language picture transcoding for performance testing
- Implement sequence restriction on memory operations
- Six supervised learning methods: classification of poisonous mushrooms
- You must like these free subtitle online tools: Video subtitle extraction, subtitle online translation, double subtitle merging
- Intelligent storage | high speed HD media processing capability
- 蚂蚁集团自研TEE技术通过国家级金融科技产品认证
- SAP mm initial service purchase order
- First talk about the necessary skills of Architecture
- The article "essence" introduces you to VMware vSphere network, vswitch and port group!
猜你喜欢

在宇宙的眼眸下,如何正确地关心东数西算?

游戏安全丨喊话CALL分析-写代码

Ant won the finqa competition champion and made a breakthrough in AI technology of long text numerical reasoning
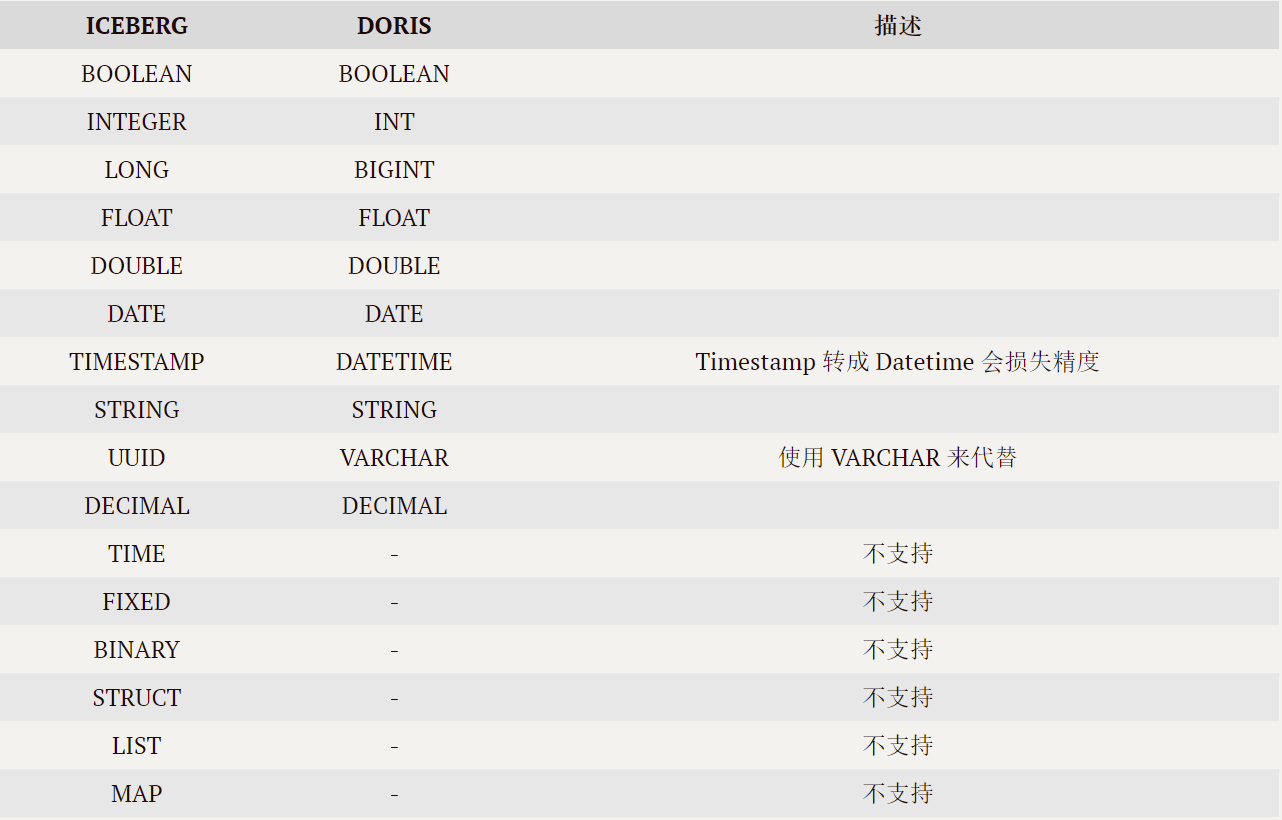
Application practice | Apache Doris integrates iceberg + Flink CDC to build a real-time federated query and analysis architecture integrating lake and warehouse
Hackinglab penetration test question 8:key can't find it again

Save: software analysis, verification and test platform

Game security - call analysis - write code

混沌工程,了解一下

为什么你的数据图谱分析图上只显示一个值?

SLSA: 成功SBOM的促进剂
随机推荐
Huawei hardware configuration command, recommended collection
Chaos engineering, learn about it
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] insert data example (TDR table)
Detailed explanation of GC principle
0day1- (cve-2021-44228) log4j2 rce recurrence
2008R2 CFS with NFS protocol
[technical dry goods] the technical construction route and characteristics of zero trust in ant Office
Advantages of micro service registry Nacos over Eureka
Performance test - LoadRunner obtains the return value and user-defined parameters (parameter operation)
【技术干货】蚂蚁办公零信任的技术建设路线与特点
Flush cache clear
Is the website under construction because there is no FTP upload? Can I upload without FTP
What are the operation and maintenance advantages of Fortress machine web application publishing server? Two outstanding advantages
What server is used for website construction? What is the price of the server
Remember a compose version of Huarong Road, you deserve it!
Detailed explanation of bitmap optimization
What are the application flow restrictions of API gateway framework?
Consequences of website construction without SSL authentication are websites without SSL authentication reliable
WordPress plugin smart product review 1.0.4 - upload of any file
FTP server setup setting website information can I set up FTP myself