当前位置:网站首页>Summary of JS methods for obtaining data types
Summary of JS methods for obtaining data types
2022-06-22 16:31:00 【Dumiyue】
Catalog
1. typeof
(1) Introduce
typeof The operator returns a string , Represents the type of uncomputed operand .
typeof It's the operator , The return value is a lowercase string .
(2) grammar
typeof(operand) or typeof operand
Parameters :operand : An expression that represents an object or original value , Its type will be returned .
(3) example :
console.log('1 As the result of the : ' + typeof 1);
console.log(' "1" As the result of the : ' + typeof '1');
console.log('undefined As the result of the : ' + typeof undefined);
console.log('null As the result of the : ' + typeof null);
console.log('NaN As the result of the : ' + typeof NaN);
console.log('1n As the result of the : ' + typeof 1n);
console.log('Symbol(1) As the result of the : ' + typeof Symbol(1));
console.log('true As the result of the : ' + typeof true);
console.log('function() {} As the result of the : ' + typeof function() {
});
console.log("[1, '1'] As the result of the : " + typeof [1, '1']);
console.log("{a: 1} As the result of the : " + typeof {
a: 1});
console.log(" The result of the date is : " + typeof new Date());
console.log(" The regular result is : " + typeof /\d/);
Output :
(4) shortcoming
(1)typeof For most simple data types , The reference data type cannot be detected . Such as arrays 、 date 、 Regular 、 The results detected by the object are object, But it can be judged that function.
(2)typeof null Returns the object
2. instanceof
(1) Introduce
instanceof Operator is used to detect the prototype Whether the attribute appears in the prototype chain of an instance object . That is, the detection object A Is it an object B Example . But I can't judge A What data type is it ,B Object type required .
instanceof Returns a Boolean value .
(2) grammar
object instanceof constructor
Parameters :
object: An instance object constructor: Some constructor
(3) principle
see B Object's prototype Whether the prototype object pointed to by the property is in A On the prototype chain , If there is a return true, Otherwise return to false.
example :
function Fruit (name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
function Apple (shape) {
this.shape = shape;
}
Apple.prototype = new Fruit(' Red Fuji ', 'red'); // Inherit
let newApple = new Apple(' Round ');
console.log(newApple);
console.log(newApple instanceof Apple); //true
console.log(newApple instanceof Fruit); //true
console.log(newApple instanceof Object); //true
Output :
Prototype chain :newApple —(–proto–)—> Apple.protoType —(–proto–)—> Fruit.protoType —(–proto–)—> Object.protoType —(–proto–)—> null
It should be noted that , If the expression newApple instanceof Fruit return true, Does not mean that the expression will always return true, because Fruit.prototype The value of the property may change , It is very likely that the changed value does not exist in newApple On the prototype chain , Then the value of the original expression will become false. In another case , The value of the original expression will also change , It's about changing objects newApple The prototype chain of , Although at present ES Specification , We can only read the prototype of the object and not change it , But with the help of nonstandard __proto__ Pseudo attribute , It can be realized . Such as execution newApple.__proto__ = {} after ,newApple instanceof Fruit It will return false 了 .
(4) example
console.log('1 yes number Type ? ');
console.log(1 instanceof Number);
console.log('new Number(1) in 1 yes number Type ? ');
console.log(new Number(1) instanceof Number);
console.log(' "1" String ? ' );
console.log( '1' instanceof String);
console.log('new String(1) in 1 yes String Type ? ' );
console.log( new String(1) instanceof String);
console.log('true Is it Boolean ? ' );
console.log(true instanceof Boolean);
console.log('new Boolean(true) in 1 yes Boolean Type ? ' );
console.log( new Boolean(true) instanceof Boolean);
console.log('undefined yes Object Do you ? ' );
console.log(undefined instanceof Object);
console.log('null yes Object Do you ? ' );
console.log(null instanceof Object);
console.log('Symbol yes Symbol Type ? ' );
console.log(Symbol() instanceof Symbol);
console.log('Object(Symbol()) yes Symbol Type ? ' );
console.log(Object(Symbol()) instanceof Symbol);
console.log('1n yes BigInt Type ? ' );
console.log(1n instanceof BigInt);
console.log('Object(1n) yes BigInt Type ? ' );
console.log(Object(1n) instanceof BigInt);
console.log('function yes Function Type ? ' );
console.log((function() {
}) instanceof Function);
console.log('[] yes Array Type ? ' );
console.log([] instanceof Array);
console.log('new Date() yes Date Type ? ' );
console.log(new Date() instanceof Date);
console.log('/regex/ yes RegExp Type ? ' );
console.log(/regex/ instanceof RegExp);
console.log('{} yes Object Type ? ' );
console.log({
} instanceof Object);
Output :
(5) shortcoming
(1)instanceof Be able to check object、date、array、function And so on , But it can't be checked number、boolean、string Basic data type .
(2) Because the Boolean value returned , So you can't see the data type directly .
3. constructor( Not recommended )
(1) Introduce
View the constructor corresponding to the object .constructor Under the prototype of its corresponding object , It's generated automatically . When we write a constructor , The program will automatically add : Constructor name .prototype.constructor = Constructor name
(2) example :
var str = '1';
console.log(str.constructor === String); //true
var bool = true;
console.log(bool.constructor === Boolean); //true
var num = 1;
console.log(num.constructor === Number); //true
//null and undefined It's an invalid object , No, constructor
// var nul = null;
// console.log(nul.constructor == Object); // Report errors
// var und = undefined;
// console.log(und.constructor == Object); // Report errors
var newDate = new Date();
console.log(newDate.constructor === Date); //true
var newObject = {
};
console.log(newObject.constructor === Object); //true
var arr = [];
console.log(arr.constructor === Array); //true
var reg = /\d/;
console.log(reg.constructor === RegExp); //true
var newfunction = function(){
};
console.log(newfunction.constructor === Function); //true
var error = new Error();
console.log(error.constructor === Error); //true
Output :
(3) shortcoming
constructor Attributes can be modified , It will lead to incorrect results .
example :
function A(){
}
A.prototype.constructor = A; // Write a constructor A, The program automatically adds ,A The constructor for points to A
function B(){
}
A.prototype.constructor = B; // hold A The constructor for points to B 了
console.log(A.construtor === A); //false
Output :
therefore , Not recommended .
4. Object.prototype.toString.call() ( recommend )
(1) Introduce
The data type can be accurately determined .
(2) grammar
Object.prototype.toString.call(param)
(3) principle
Object There are two on toString Method , In a Object In itself , The other is Object.prototype On prototype object .Object.prototype Upper toString() Method has the function of judging the data type . By default ,toString() The method is each Object Object inheritance . If this method is not overridden in the custom object ,toString() return “[object type]”, among type It's the type of object . in other words ,Object In itself toString() Methods are rewritten after inheriting the methods on the prototype .Array,function And so on Object Example , It's all rewritten toString() Method , Call the rewritten directly when calling toString() Method .
Only Object.prototype Upper toString It has the function of judging the data type , So we use it to determine the data type call Method change this Point to .
Principle example :
let arr = [1, '1']
console.log(Object.prototype.toString(arr));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arr));
Output :
explain : No addition call(),this Pointer to object, So the data type is object,
added call(),this Point to arr, Called the overridden of the array toString() Method , The result is Array type .
(4) example
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(1));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call('1'));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(true));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call({
}));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([]));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(function(){
}));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date()));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(/\d/));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(1n));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol()));
Output :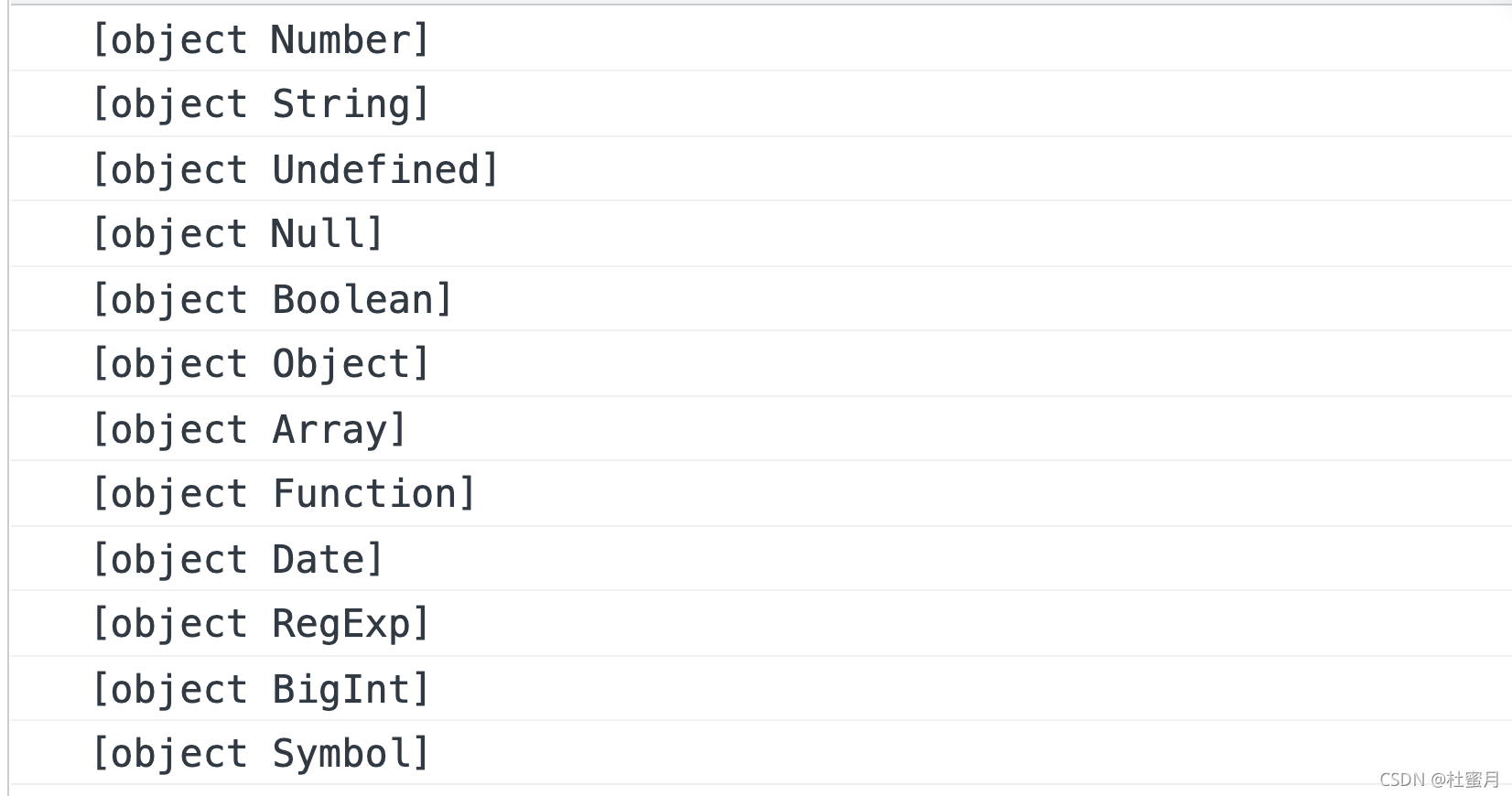
5. isArray()
(1) Introduce
Array.isArray() Used to determine if the value passed is a Array. Returns a Boolean value .
(2) grammar
Array.isArray(obj)
Parameters :obj: The values that need to be detected .
(3) example
let arr = [1, '1'];
let obj = {
a: 1};
console.log(Array.isArray(arr));
console.log(Array.isArray(obj));
Output :
Reference resources :
- MDN Official website
- instanceof principle
- Judge js Four methods of data type , And their advantages and disadvantages // Refer to the constructor to determine the type
- Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) The understanding of the
边栏推荐
- 学习量子纠缠的可解释表示,该深度生成模型可直接应用于其他物理系统
- SAP ABAP 中 OpenSQL和Native SQL-05 本教程的目的不是教您 SQL 或数据库概念
- Ironsource Luna offers a limited time discount for Apple search ads and enjoys 3 months of free service upon registration
- phantomJs使用总结
- SAP script tutorial: se71, se78, SCC1, vf03, so10-013
- SAP ABAP 报告编程-08
- nio使用可写事件处理一次性写不完情况
- Static assertion static_ assert
- 解决mysql远程登录报权限问题
- 什么是RESTful,REST api设计时应该遵守什么样的规则?
猜你喜欢

畅享高性能计算!天翼云HPC解决方案来了

什么是 SAP ABAP? 类型、ABAP 完整形式和含义
![Consumption monitoring of Prometheus monitoring [consult exporter]](/img/9e/8547b2c38143ab0e051c1cf0b04986.png)
Consumption monitoring of Prometheus monitoring [consult exporter]

10款超牛Vim插件,爱不释手了

让pycharm项目里面的文本模板支持jinjia2语法
User exit and customer exit in SAP ABAP -015

SAP ABAP 表控制与示例-07

SAP ABAP 中的用户出口和客户出口-015
SAP ABAP internal tables: create, read, populate, copy and delete-06

CUMT study diary - quick notes of digital image processing examination
随机推荐
SAP ABAP 表控制与示例-07
SAP ABAP table control and example-07
SAP abap 数据类型,操作符和编辑器-02
大话局部性原理
SAP ABAP 中的模块化:宏、子程序和功能模块 -04
Unity game optimization (version 2) learning record 8
天翼云乘风新基建,构建数字化转型“4+2”能力体系
[Shanda conference] establishment of webrtc tools for multi person video call
Reddit对LaMDA模型的探讨:并非无状态,采用双重过程,相比它编辑维基百科的方式,有没有感情并不重要
3.抽象类(shape)
SAP ABAP 内部表:创建、读取、填充、复制和删除-06
SAP web service 无法使用 SOAMANAGER 登陆到SOA管理页面
数睿数据受邀参与南通企业数字化转型研讨会
执行逻辑大同小异的实现类使用模板模式
Swift -- 保存打印日志到沙盒
让pycharm项目里面的文本模板支持jinjia2语法
Cmake tutorial series-00-introduction
Deploy odoo to the server and configure it as a service
Prometheus监控之Consul监控 [consul-exporter]
Pod type