当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree part I
Binary tree part I
2022-06-24 09:50:00 【Herding】
List of articles
- Binary tree
- Concept ( important )
- Tree representation
- 2、 Binary tree
- 3、 Binary tree storage
- The creation of binary tree
- Traversal of binary tree ( a key )
- 1. Code to achieve preorder traversal
- Program traversal
- Finally came 4 Problem end The first part is the binary tree
Binary tree

A tree structure
Tree is a kind of nonlinear data structure , It is from n(n>=0) Finite nodes make up a set with hierarchical relations . It's called a tree because it looks like an upside down tree , That is to say, it is root up , And leaf down .
It has the following characteristics : There's a special node , Called the root node ,
The root node does not have a precursor node Except for the root node ,
The remaining nodes are divided into M(M > 0) Disjoint sets T1、T2、…、Tm, And every set of them Ti (1 <= i<= m) Another subtree similar to a tree .
The root node of each subtree has and has only one precursor , There can be 0 One or more successors
Trees are defined recursively .

Concept ( important )

got it Concept that how Express Trees ???

Tree representation
Tree structure is more complex than linear table , It's more troublesome to store and represent , In fact, there are many representations of trees , Such as : Parenting ,
Child representation 、 Child brother notation and so on . Let's briefly understand the most commonly used ** The child's brother said 
2、 Binary tree
A binary tree is a finite set of nodes , The set is either empty , Or a root node plus two binary trees called left subtree and right subtree
Tree composition .
Characteristics of binary trees :
Each node has at most two subtrees , In other words, the degree of nonexistence of binary tree is greater than 2 The node of .
The subtree of a binary tree has left and right branches , The order of its subtrees cannot be reversed , So a binary tree is an ordered tree .
( Orderly No Ordered in size It is The order )

Two special binary trees
Concept :
- Full binary tree : A binary tree , If the number of nodes in each layer reaches the maximum , Then this binary tree is full of binary trees . in other words , If
The number of layers of a binary tree is K, And the total number of nodes is , Then it's full of binary trees . - Perfect binary tree : A complete binary tree is an efficient data structure , A complete binary tree is derived from a full binary tree . For a depth of K Of , Yes n
A binary tree of nodes , If and only if each of its nodes has a depth of K From the full binary tree of 1 to n When the nodes of are one-to-one corresponding, it is called complete
Binary tree . It should be noted that a full binary tree is a special kind of complete binary tree .

Binary tree nature



After reading the properties of binary trees, let's take a look at the storage of binary trees 
3、 Binary tree storage
The storage structure of binary tree is divided into : Sequential storage and chain storage similar to linked list
Here we are Main understanding Chain store And the order Storage be Will be commonly used in the heap
The chain storage of binary tree is referenced by nodes one by one , The common expressions are binary and trigeminal , As follows :
// Child representation
class Node {
int val; // Data fields
Node left; // Left child's quote , It often represents the whole left sub tree rooted by the left child
Node right; // Right child's quote , It often represents the whole right subtree with the right child as the root
}
// The expression of children's parents
class Node {
int val; // Data fields
Node left; // Left child's quote , It often represents the whole left sub tree rooted by the left child
Node right; // Right child's quote , It often represents the whole right subtree with the right child as the root
Node parent; // The root node of the current node
}
The creation of binary tree
here We Create a binary tree Will use A very, very guy How it was created
No real How it was created , Let's do this first establish To understand the once Properties of binary trees 

Attach code
class BTNode {
public char val;
// Left child quotes
public BTNode left;
// The right child
public BTNode right;
public BTNode (char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
public BTNode root; // The root node of a binary tree
public BTNode createTree() {
BTNode A = new BTNode('A');
BTNode B = new BTNode('B');
BTNode C = new BTNode('C');
BTNode D = new BTNode('D');
BTNode E = new BTNode('E');
BTNode F = new BTNode('F');
BTNode G = new BTNode('G');
BTNode H = new BTNode('H');
A.left = B;
A.right = C;
B.left = D;
B.right = E;
C.left = F;
C.right = G;
E.right = H;
return A;
}
}
Traversal of binary tree ( a key )
3 Ergodic ways ( The time to access the binary tree is different )
1. The former sequence traversal ( First root through

2. In the sequence traversal

3. Subsequent traversal

summary
Finished learning Binary tree Of Three traversals The way Find out they yes Follow a route Of , It's just printing Of opportunity It's just different
practice

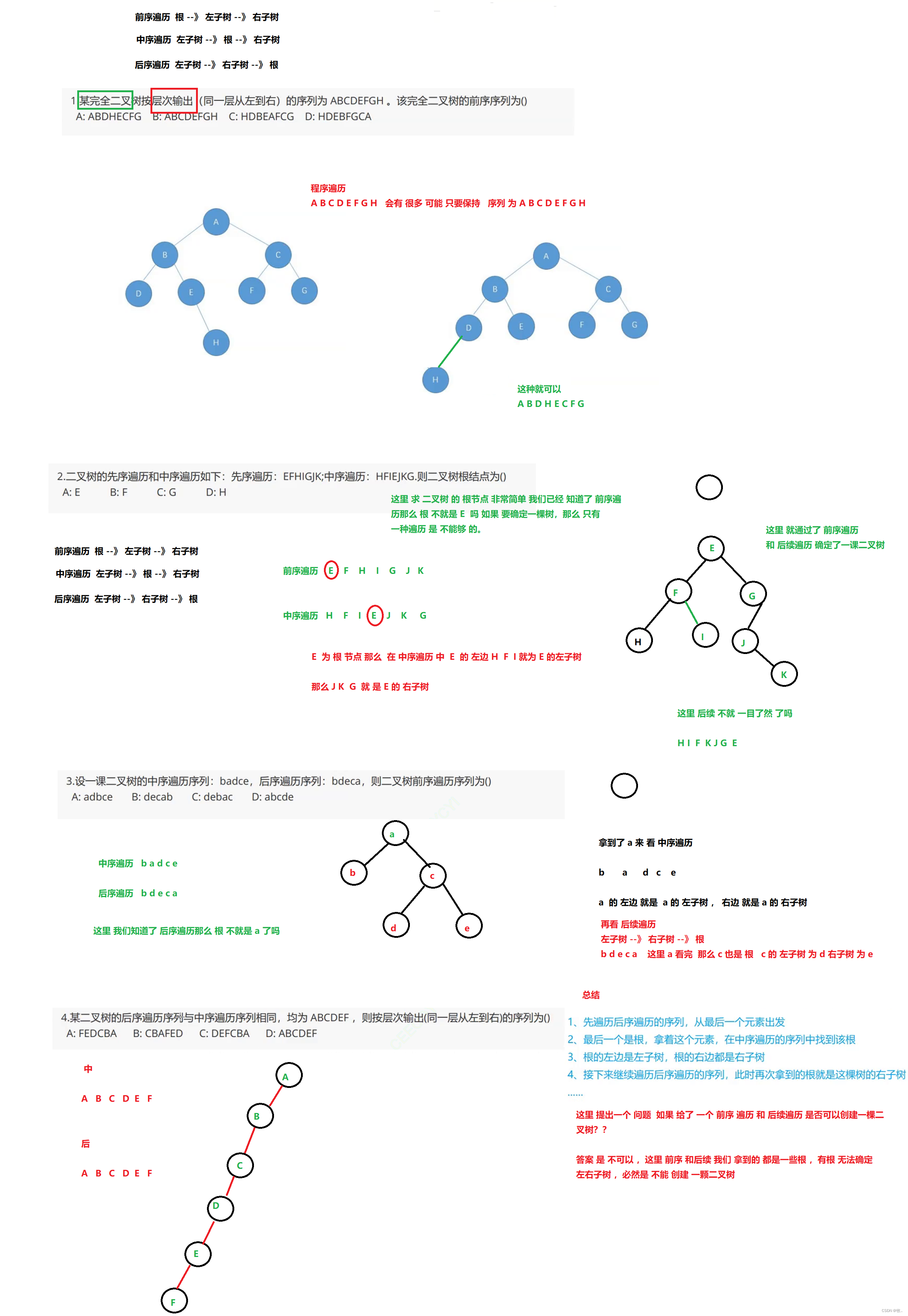
1. Code to achieve preorder traversal
1. The former sequence traversal root --》 The left subtree --》 Right subtree
// adopt recursive Realize preorder traversal
void preOrder(BTNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}


got it Before the order Traverse that We directly To do it The former sequence traversal Of oj topic 
Preorder traversal of two tree
Method 1 : Traverse Ideas
class Solution {
// here Guarantee 了 list all Only One copy
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
list.add(root.val);
preorderTraversal(root.left);
preorderTraversal(root.right);
return list;
}
}
Method 2 : Sub problem ideas
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
list.add(root.val);
List<Integer> leftTree = preorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(leftTree);
List<Integer> rightTree = preorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(rightTree);
return list;
}
}

· Know the preface Traverse that In the sequence traversal and Subsequent traversal that No, it is. Adjust the recursive Order
2. In the sequence traversal The left subtree --》 root --》 Right subtree
// In the sequence traversal
// The left subtree --》 root --》 Right subtree
void inOrderTraversal(BTNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
inOrderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrderTraversal(root.right);
}
Middle order traversal of binary trees
Method 1 : Traversal ideas
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
inorderTraversal(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inorderTraversal(root.right);
return list;
}
}
Method 2 : Sub problem ideas
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
List<Integer> leftTree = inorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(leftTree);
list.add(root.val);
List<Integer> rightTree = inorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(rightTree);
return list;
}
}
3. After the sequence traversal The left subtree --》 Right subtree --》 root
// After the sequence traversal
// Right subtree --》 The left subtree --》 root
void postOrderTraversal(BTNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
inOrderTraversal(root.left);
inOrderTraversal(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}
Postorder traversal of binary trees
Method 1 : Ergodic thought
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
postorderTraversal(root.left);
postorderTraversal(root.right);
list.add(root.val);
return list;
}
}
Method 2 : Sub problem ideas
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
List<Integer> leftTree = postorderTraversal(root.left);
list.addAll(leftTree);
List<Integer> rightTree = postorderTraversal(root.right);
list.addAll(rightTree);
list.add(root.val);
return list;
}
}
Come here One idea Shortcut key Overall change Variable life shift Add f6
Program traversal
Let the level of the root node of the binary tree be 1, Sequence traversal starts from the root node of the binary tree , First visit the root node of the first layer , And then from
From left to right, visit page 2 Nodes on the layer , Then there are the nodes of the third layer , And so on , From top to bottom , The process of accessing the nodes of the tree layer by layer from left to right is
Sequence traversal .
Finally came 4 Problem end The first part is the binary tree


边栏推荐
- 如何解决独立站多渠道客户沟通难题?这款跨境电商插件一定要知道!
- 新手怎么选择投资理财产品的等级?
- 转:三星电子CEO:一切决策都要从认清自己开始
- When should gridfs be used?
- 关于thinkphp5 使用模型save()更新数据提示 method not exist:think\db\Query-&gt; 报错解决方案
- P6698-[balticoi 2020 day2] virus [AC automata, DP, SPFA]
- How do novices choose the grade of investment and financial products?
- CICFlowMeter源码分析以及为满足需求而进行的修改
- 使用Live Chat促进业务销售的惊人技巧
- Oracle数据库监听文件配置
猜你喜欢

Why is LNX of e equal to X

Reasons for the failure of digital transformation and the way to success

PTA猴子选大王(约瑟夫环问题)

实战剖析:app扫码登陆实现原理(app+网页端详细逻辑)附源码
Learning Tai Chi Maker - esp8226 (XIII) OTA

In depth analysis of Apache bookkeeper series: Part 3 - reading principle

LeetCode: 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II

PTA monkey chooses King (Joseph Ring problem)

居家办公如何管理数据中心网络基础设施?

In depth study paper reading target detection (VII) Chinese English Bilingual Edition: yolov4 optimal speed and accuracy of object detection
随机推荐
Seekbar with text: customize progressdrawable/thumb: solve incomplete display
[GDB debugging tool] | how to debug under multithreading, multiprocessing and running programs
PostgreSQL
[custom endpoint and implementation principle]
In depth analysis of Apache bookkeeper series: Part 3 - reading principle
如何管理海量的网络基础设施?
数组无缝滚动demo
198. house raiding
LeetCode: 137. Number II that appears only once
SQL-统计连续N天登陆的用户
Why is LNX of e equal to X
tp5 使用post接收数组数据时报variable type error: array错误的解决方法
P6698-[balticoi 2020 day2] virus [AC automata, DP, SPFA]
Ora-28000 error after upgrading Oracle 12C to 19C
Inspiration from reading CVPR 2022 target detection paper
正则匹配手机号
最新Windows下Go语言开发环境搭建+GoLand配置
Turn to: CEO of Samsung Electronics: all decisions should start from recognizing yourself
ByteDance Interviewer: talk about the principle of audio and video synchronization. Can audio and video be absolutely synchronized?
百度AI模板 获取知识理解