当前位置:网站首页>Principle of skip table
Principle of skip table
2022-06-23 07:20:00 【51CTO】
Skip list
Jump lists are based on linked lists , A multi-layer index structure is added to the linked list .
The special data result of jump table is Willam Pugh Invented . First appeared in 1990 A paper published in 1987 《Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees》
There is a description in the paper :
Skip lists are a data structure that can be used in place of balanced trees.
Skip lists use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing and as a result the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
- 1.
- 2.
To put it simply , Jump table is a table based on probability .
Let's first look at the structure of an ordinary ordered linked list :

If you want to find 23 Then at least we need to compare 2 Time , lookup 43 Compare 4 Time , lookup 59 Compare 6 Time . Is there any way to solve this problem ? It's easy to think of binary search .
Adopt hierarchical linked list structure , Take some nodes as indexes ,


such as , Extracted 14 34 50 72 As a linked list , lookup 59 When , You can compare 14 24 50 59 common 5 Times found 59 To reduce the number of lookups .
If you add a layer , Basically, you can use the similar dichotomy method to search
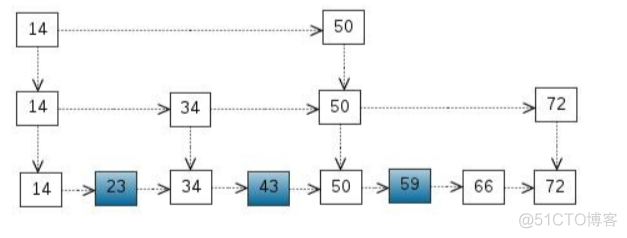

Now look at the complete The process of inserting a new element into a fast watch :

Reference code :
public class SkipList {
private static class SkipListNode {
int data;
SkipListNode[] next;
SkipListNode(int d, int level) {
data = d;
next = new SkipListNode[level + 1];
}
}
private int maxLevel;
SkipListNode header;
private static final int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
SkipList(int maxLevel) {
this.maxLevel = maxLevel;
header = new SkipListNode(0, maxLevel);
SkipListNode sentinel = new SkipListNode(INFINITY, maxLevel);
for (int i = 0; i
<
=
maxLevel;
i++)
header.next[i] =
sentinel;
}
public
boolean
find(int
key)
{
SkipListNode
current =
header;
for
(int
i =
maxLevel;
i
>= 0; i--) {
SkipListNode next = current.next[i];
while (next.data
<
key)
{
current =
next;
next =
current.next[i];
}
}
current =
current.next[0];
if
(current.data =
=
key)
return
true;
else
return
false;
}
public
void
insert(int
searchKey,
int
newValue)
{
SkipListNode[]
update =
new
SkipListNode[maxLevel
+
1];
SkipListNode
current =
header;
for
(int
i =
maxLevel;
i
>= 0; i--) {
SkipListNode next = current.next[i];
while (next.data
<
searchKey)
{
current =
next;
next =
current.next[i];
}
update[i] =
current;
}
current =
current.next[0];
if
(current.data =
=
searchKey)
current.data =
newValue;
else
{
int
v =
generateRandomLevel();
SkipListNode
node =
new
SkipListNode(newValue,
maxLevel);
for
(int
i =
0;
i
<= v; i++) {
node.next[i] = update[i].next[i];
update[i].next[i] = node;
}
update = null;
}
}
private int generateRandomLevel() {
int newLevel = 0;
while (newLevel
<
maxLevel
&&
Math.random()
< 0.5)
newLevel++;
return newLevel;
}
public boolean delete(int searchKey) {
SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[maxLevel + 1];
SkipListNode current = header;
for (int i = maxLevel; i >= 0; i--) {
SkipListNode next = current.next[i];
while (next.data
<
searchKey)
{
current =
next;
next =
current.next[i];
}
update[i] =
current;
}
current =
current.next[0];
if
(current.data =
=
searchKey)
{
for
(int
i =
0;
i
<= maxLevel; i++) {
if (update[i].next[i] == current) {
update[i].next[i] = current.next[i];
current.next[i] = null;
} else
current.next[i] = null;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
Official account :【 Programmer development community 】

边栏推荐
- yolov5检测小目标(附源码)
- Mysql事务隔离级别
- MySQL (VIII) - explain
- In depth learning series 46: face image super score gfp-gan
- 如何优雅的快速下载谷歌云盘的大文件 (二)
- 315. 计算右侧小于当前元素的个数
- Akamai-1.75 version-_ Abck parameter generation JS reverse analysis
- 407-栈与队列(232.用栈实现队列、225. 用队列实现栈)
- 897. incremental sequential search tree
- Spock sub piling
猜你喜欢

User mode and kernel mode

Learning and using quartz scheduling framework

GINet

100 GIS practical application cases (79) - key points of making multi plan integrated base map

MySQL(八) — 执行计划(Explain)详解

Deep learning series 47: Super sub model real esrgan

U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation

UNET code implementation

初始化层实现
都是硬盘分区 C盘和D盘到底有什么区别?
随机推荐
U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Arthas-thread命令定位线程死锁
MySQL Niuke brush questions
Several characteristics of MySQL database
Don't look for [12 super easy-to-use Google plug-ins are here] (are you sure you want to take a look?)
Deep learning series 47: Super sub model real esrgan
20220620 uniformly completely observable (UCO)
Ldconfig command
The List
'Latin-1' codec can't encode characters in position 103-115: body ('string of Chinese ') is not valid Latin-1
别找了诸位 【十二款超级好用的谷歌插件都在这】(确定不来看看?)
898. subarray bitwise OR operation
313. 超级丑数
Project_ Filter to solve Chinese garbled code
MySQL(四) — MySQL存储引擎
Heterogeneous transaction scenario interaction process and consistency assurance
[AI practice] data normalization and standardization of machine learning data processing
启发式的搜索策略
In depth learning series 47:stylegan summary
MySQL summary