当前位置:网站首页>MySQL learning summary
MySQL learning summary
2022-06-26 09:54:00 【Ma cute's Ma cute】
1. Common databases 
2.MySQL grammar
(1)SQL classification
《1》DDL(Data Definition Language) Data definition language : Used to define database objects , Such as a database 、 surface 、 Column, etc. , There are keywords create、drop、alter etc. .
《2》DML(Data Manipulation Language) Data operation language : Used to add to tables in the database 、 Delete 、 Change , There are keywords update、delete、insert etc. .
《3》DQL(Data Query Language) Data query language : Used to query the records of tables in the database , There are keywords select、where etc. .
《4》DCL(Data Control Language) Data control language : It is used to define the access rights and security level of the database , And create users , There are keywords grant、revoke etc. .
3.DDL( Operating the database 、 surface )
(1) database
《1》 Query all database names :show databases ;
Query the character set corresponding to a database :show create database xxx;
《2》 Create database
create database xxx ; However, if the database already exists, an error will be reported if it is created again , So use create database if not exists xxx; # Create if it does not exist , There is no error report . Set up the character set to create the database :create database xxx character set utf8; Of course, the above two can be combined into one statement ( Create a database to determine whether there is , There is no way to create and set up its character set ):create database if not exists xxx character set utf8;
《3》 modify the database
alter database xxx character set Character set ;
《4》 Delete database
drop database xxx; First judge whether there is , Exist and delete :drop database if exists xxx;
《5》 Using a database
Using a database :use xxx;
Query which database is currently in use :select database();
(2) Data sheet
《1》 Query the names of all data tables in a database :show tables;
Query table structure :desc Table name ;
The character set of the query table :show create table xxx;
《2》 Create table
careate table Table name (
Field 1 data type ,
Field 2 data type ,
...........
Field n data type
); Note that there is no need to add... To the last column “,”.
Copy the same table :create table The new name of the table like Table name ;
《3》 Delete table
drop table xxx;
First determine the existence and then delete :drop table if exists xxx;
《4》 Modify table
Modify the name of the table :alter table The old name of the table rename to The new name of the table ;
Modify the character set of the table : alter table Table name character set utf8;
Add a column :alter table Table name add Field name data type ;
Modify the field name and data type : alter table Table name change Original field The new fields New data types ;
ALTER TABLE route CHANGE r_name r_name VARCHAR(30) CHARACTER SET utf8; # Modify the coding format of the fields in the table
Only modify the field data type : alter table Table name modify Old fields New data types ;
Delete a field :alter table Table name drop Field name ;
4.DML( Add / delete data in the table )
《1》 Add data
Insert a piece of data :insert into Table name ( Field 1, Field 2..... Field n)values( value 1, value 2... value n);
Insert multiple data :insert into Table name ( Field 1, Field 2..... Field n)values( value 1, value 2... value n),( value 1, value 2... value n),( value 1, value 2... value n).........
Of course, for the self increasing type id It can also be removed directly
insert into `user` (name,age,emil) VALUES
('malong',21,'[email protected]'),
('malong1',22,'[email protected]'),
('malong2',23,'[email protected]'),
('malong3',24,'[email protected]');
If you want to interpolate all the fields , You can omit the field directly , But the back values It includes id Corresponding value Can't be omitted
insert into `user` VALUES
(9,'malong',21,'[email protected]'),
(10,'malong1',22,'[email protected]'),
(11,'malong2',23,'[email protected]'),
(12,'malong3',24,'[email protected]');
You can also add some fields to it , If you add values to all fields , You can omit the fields after the table name and directly write all the values in the table corresponding to the fields , It assigns values to all fields by default
replace Use
replace into tablaname values(id,xx,xx,....)
above replace into At the same time insert into and update The function of .replace It's replacement Existing lines . If replace Medium id Existed before , Then its function is equivalent to update, Information used to update data in the database . But if id It didn't exist before . Then its function is equivalent to insert into, That is, insert a piece of data into the data table .
《2》 Delete data
Delete on condition :delete from Table name where Conditions ;
Delete all data :delete from Table name ; The auto increment field after deletion is deleted from the id Start , Not from 1 Start , And how many pieces of data will be deleted , The efficiency value is relatively low ;
however truncate table Table name ; After deletion, the entire table can still be deleted from the 1 From the beginning ; amount to drop table xxx, Then create a table as like as two peas.
It can also be directly truncate Table name ;
《3》 Modifying data
update Table name set Field 1= value 1, Field 2= value 2....... where Conditions ;
In the actual development, if no condition is added, all the values under this field will be modified by default
5.DQL( Query the records in the table )
New add
Query requirement : The name and gender of the female employee in the query table , requirement sex by 1 Show as male when ,sex by 0 It is shown as female ( It's actually a sex The value of the column is determined by 0 and 1 Revised as female and male respectively , Same as sex The fate of the column is also shown as gender )

(1) Basic query
《1》 Query all the information in a table select * from Table name ;
Query the information under certain fields in a table select Field 1, Field 2, Field 3.... from Table name ;
Query one of the fields , Then remove the same weight , For example, the student's address may be repeated , So we need to get rid of the repetition :select distinct adress from Table name ;
《2》 Calculate all... In a table math and english The sum of our achievements :

select name,math,english,math+english from Table name ;
However, if a field or multiple fields to be searched in one piece of data are empty , You need to do this ( As above math Results and english achievement ):
select name,math,english,ifnull(math achievement ,0)+ifnull(english achievement ,0) from Table name ;
The meaning above is if math The result is null, It will be assigned as 0, If it is not empty, it can be calculated according to the parameter number
《3》 names ( Tables and fields can be aliased ) You can add keywords before aliases as Or you can skip it as
select name full name ,math mathematics ,english English ,ifnull(math achievement ,0)+ifnull(english achievement ,0) Total score from Table name Alias ;
(2) Conditional query and fuzzy query
《1》 Basic operators , stay where Then use (where Field Operator Numbers Such as where age > 20)
、=、<、<=、>=、<> stay sql Is not equal to ,mysql It can also be expressed as !=
between…and Such as between 20 and 50, Inquire about 20 To 50 Between , Both include 20 It also includes 50
in( aggregate ) A collection represents multiple values , Separated by commas
like "% Zhang ” Fuzzy query
is null Query a column as null Value , Cannot be written as =null
and or &&( It is not recommended to use )
or or ||( It is not recommended to use )
not or !
《2》 Examples of use
Inquiry age is not equal to 30 year :select * from Table name where age!=30;
select * from Table name where age <>30;
The age of inquiry is 20 To 30 Between :select * from Table name where age between 20 and 30;
select * from Table name where age >=20 and age <=30;
You can also use it java Medium &&, But it is not recommended
Inquire about 20、19 perhaps 25 A man of years old :select * from surface where age=19 or age = 20 or age =25; Express choice , You can also use java Medium ||, But not recommended
select * from surface where age in(19,20,25);
Check the students who have passed the English test : select * from surface where english is not null;
instead of select * from surface where english=null, Such queries have no results
《3》 Fuzzy query
Station symbol :
_ : Represents any one character
% : Express 0 One or more arbitrary characters
select * from surface where name=“% Horse %” # The query name contains the name of the horse
select * from surface where name=“ Horse %” # Query for names that begin with horses
select * from surface where name=“__” # Query for three word names
select * from surface where name=“_ Horse %” # The second name in the query is the name of the horse
(3) Sort query
select * from surface order by math asc ,english asc; # First of all, math Ascending row , If math There are two students who have the same grades , Then the English scores of the same two students will be ranked in ascending order ,desc It is in descending order , If you don't write a sort condition , Then sort in the default ascending order
(4) Aggregate functions 

select count( Field )from surface ;# Count the number of entries in this field
( Excluded fields are null Value ) Solutions for :
select count(*) from surface ; # It is not recommended to use
select count(id) from surface ; # id It must not be empty
Same as before , If there is a null value under the field corresponding to a piece of data . In this way , Because it treats the null value under the field corresponding to a piece of data as invalid , That is, no statistics , But there is no value in this field except for this piece of data , Other fields of this data are worth it , So use select count(ifnull (enliglish,0))from surface , The meaning is the same as the previous usage of calculating the sum of math and English grades
select avg(math) from surface ; # Statistical mathematical mean
select max( math) from surface ; The maximum in statistical mathematics
select min(math) from surface ; # Statistical mathematical minimum
(5) Group query
where and having The difference between :where Use in group by Previously limited to , If the conditions are not met, they will not participate in the grouping ;having Use in group after , If the conditions are not met, the query will not be displayed on the page ;
where After that, you can't follow the aggregation function ,having Then you can judge with the aggregate function
(6) paging
select * from surface limit 0,3; # first page
select * from surface limit 3,3; # The second page , The first parameter represents the starting index , The second represents the number of data pieces displayed on each page
The formula : Index started =( The current page number -1)* Number of data pieces displayed per page
(7) Learn to supplement
“SELECT distinct Field FROM surface ” This sentence , If not distinct Will find duplicate data



Group query

having Must be with group by In combination with , And follow group by Behind

Link query








nested queries
The following example is an unrelated subquery



all Represents all values , use all To decorate subqueries , The specified expression must be compared with each value in the sub query result set . The true value is returned only when the expression satisfies the comparison relationship with each value , Otherwise return false value .any Represents some or some value , When a query expression satisfies a comparison relationship with a value in a subquery , Return the true value .
Related sub queries are as follows
demand : On the student list student And student transcript grade Find out who participated in “ Fundamentals of computer ” Course and score at 80 All student information above grade .
select t.sno,t.sname,t.sage,t.sgentle,t.sbirth,sdept from student t where 80<=(select f.score from grade f where f.sno=t.sno and f.cname=' Fundamentals of computer ')
The execution process of this sub query :
1、 Query from parent first student Take the first record from the table sno value , Enter the subquery , Compare them where Condition of clause “where f.sno=t.sno and f.cname=’ Fundamentals of computer ’”, If yes, return score achievement .
2、 Return the parent query , Judge the parent query where Clause condition 80<= Back to score, If the condition is true, Then go back to 1 Bar record .
3、 From the parent query student Take the second from the table 2 Data , Repeat the above operation , Until all the records in the table in the parent query are retrieved .
————————————————
Copyright notice : This paper is about CSDN Blogger 「 Struggling young people _」 The original article of , follow CC 4.0 BY-SA Copyright agreement , For reprint, please attach the original source link and this statement .
Link to the original text :https://blog.csdn.net/mascf/article/details/50288199

Data manipulation



6. constraint
(1) Non empty constraint : Value cannot be empty
There are two ways to create non empty constraints :
《1》 When creating a table, you can directly add not null;
《2》 Use... After creating the table alter add to , Such as :
How to delete non empty constraints :`alter table Table name modify Field name Field type ; `
(2) Unique constraint : All values under the field name cannot be duplicate , But you can have two values null
There are two ways to create unique constraints :
《1》 Add... When creating a table unique;
《2》 Use... After creating the table alter, Such as :
How to delete a unique constraint ( The index is used here , Because it can't be repeated , There are rules , So use the index ):
instead of :
Can run successfully , However, you cannot add duplicate values when adding
(3) Primary key constraint : Non empty and unique
There are two ways to create a primary key
《1》 Add... When creating a table primary key
《2》 After creating the table , Use alter, Such as :
How to delete a primary key ( Because the primary key is unique in a table , So you don't need to add field names ):
Instead of the following way :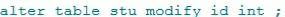
(4) Primary key constraint - Automatic growth
There are two ways to create automatic primary key growth
《1》 When you create a primary key, you add... After the primary key auto_increment
《2》 Use... After creating the table alter, Such as :
Delete the method of automatic growth type 
(5) Foreign key constraints
《1》 Add foreign keys when creating the main table 
《2》 After creating the main table, use alter To add foreign keys 
《3》 Delete foreign key 
(6) Foreign key constraints - Cascade operation ( Cascade update and cascade delete can be set at the same time , It can also be set separately )
Cascading deletions and cascading updates require caution , Especially in the actual development, you should think clearly whether to set cascading deletion
7. Multi table relation 
** For one-on-one , There is no need to , Just add it directly to a table **
Design examples :



8. Database design paradigm
(1) First normal form : Each column is an indivisible atomic item of data 
The above is against the first paradigm , So there's a problem with building tables like this , It should be done 
The above follows the first paradigm , But there are also the following problems in this way 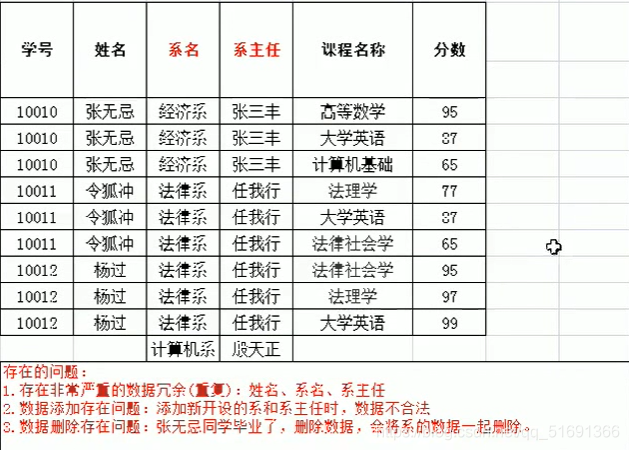
(2) To solve the above problems, we need to use the first paradigm , The premise of using the first paradigm is to build on the first paradigm , The concept of the second paradigm is as follows :
Several concepts in the second paradigm :
Third normal form :
Principles of table building :
Is an atomic term - Eliminate some functional dependencies - Eliminate delivery dependency
9. Multi-table query
(1) Query statement 
(2) Internal connection query ( Only when the conditions on both sides are equal at the same time will all the information queried be displayed )
《1》 Implicit inner join : Use where Conditions eliminate useless data ( The following tables have been built in advance )

《2》 Explicit inner connection ( The result is the same as the above query )
Internal join query considerations :
(3) External connection
《1》 The left outer join ( Queries all the data in the left table regardless of whether the data in the right table is complete , Even if the data in the right table is incomplete, the query and display of the left table will not be affected )
Such as :


《2》 Right connection ( Queries all the data in the right table regardless of whether the data in the left table is complete , All the data in the right table are displayed , The data in the left table shows , No, it's empty )

(4) Subquery ( Nested query in query , Call nested queries word queries )
《1》 Subqueries are single row and single column 
《2》 Subqueries are multi row, single column 
《3》 Subqueries are multi row and multi column 

10.(1) Business : If a business operation contains multiple steps , Managed by transactions at the same time , So these operations are either successful at the same time , Or fail at the same time , That is to prevent exceptions :




(2) The four characteristics of affairs :
(3) Isolation level of data 
11.DCL
(1) Manage users 
If you forget mysql All operations in the password , Everything involves newly opened cmd window , It is better to open as an administrator
(2) Query the user 
(3) Rights management 
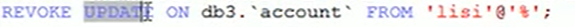
12. View
1. Definition of view
The view is to protect the security of the information in the original database table, and specially select some unique data from the data table that you want to show to the outside world , Instead of showing the whole database information to the outside world . So the view is only used by developers at lower levels to operate the data table and complete the whole project . This is to prevent the exposure of important information in the database .
2. View creation
create or replace view viewname as select * from tablename;
The above program code will tablabname All fields in and information records in fields are selected as view tables , That is, the so-called virtual table .
3. Query the virtual tables in the database
show table status where commment='view';
4. For view query 、 Change 、 Delete 、 The operations of adding and deleting view tables are the same as those of real tables in the database .
Here is the view 、 Detailed description of real table and query table
边栏推荐
- 调用api接口生成不同颜色的微信小程序二维码
- Test instructions - common interface protocol analysis
- 安装 新版本cmake & swig & tinyspline
- Teach you to use shell script to check whether the server program is running
- What you need to know to test -- URL, weak network, interface, automation
- Redis notes (12) - single thread architecture (non blocking IO, multiplexing) and multiple asynchronous threads
- Druid data source for background monitoring
- Wechat official account reported error 10003
- The basis of C language grammar -- function definition learning
- logback
猜你喜欢

Day 3 array, pre post, character space, keyword and address pointer
![[trajectory planning] testing of ruckig Library](/img/c7/51c0f6dc3bf7c7fa4528118a4c32fa.png)
[trajectory planning] testing of ruckig Library

Single sign on logic

Champions League data set (Messi doesn't cry - leaving Barcelona may reach another peak)

Notes on sports planning on November 22, 2021

jz2440---使用uboot烧录程序

VI summary of common commands
WGCLOUD的web ssh服务端口是多少

#云原生征文# 在 Google Kubernetes Cluster 上使用 HANA Expression Database Service

Mysql database field query case sensitive setting
随机推荐
国际化配置
2021-11-12 vrep视觉传感器配置
The basis of C language grammar -- learning of local variables and storage categories, global variables and storage categories, and macro definitions
Various errors encountered by tensorflow
逻辑英语结构【重点】
WIN10系统实现Redis主从复制
mysql 数据库字段查询区分大小写设置
Detailed explanation of the network security competition questions (2) of the 2021 national vocational college skills competition (secondary vocational group)
c语言语法基础之——指针( 多维数组、函数、总结 ) 学习
install ompl.sh
调用api接口生成不同颜色的微信小程序二维码
pcl install
SQL 函数
The basis of C language grammar -- pointer (multidimensional array, function, summary) learning
cento7.7安装ELK简单记录
自动化测试——pytest本身及第三方模块介绍及使用
online trajectory generation
Leetcode connected to rainwater series 42 (one dimension) 407 (2D)
Learning and understanding of thread pool (with code examples)
2021-11-22 运动规划杂记