当前位置:网站首页>The basis of C language grammar -- pointer (multidimensional array, function, summary) learning
The basis of C language grammar -- pointer (multidimensional array, function, summary) learning
2022-06-26 09:50:00 【Tanzanian auduvi Canyon expert】
Normal pointer :
Two dimensional array , Generally, there are several rows and columns ;
If more than one ordinary pointer is defined , This pointer only represents the address of the row , Instead of an element address , such as :
int a[3][3]={
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int *p;
p=a; //
printf("%d\n",*p); // 1 The element values of the first row and the first column
p=a+1;
printf("%d\n",*p); // 4 The element values in the first column of the second row
You can define a pointer to a specified address :
int a[3][3]={
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int *p;
p=&a[1][1]; // The address of the element in the second row and the second column
printf("%d\n",*p); // 5 The element values of the first row and the first column
p++;
printf("%d\n",*p); // 6 The element values in the second row and the third column
p=a+1; // The second line
printf("%d\n",*p); // 4 The element values in the first column of the second row


int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
/* 1 2 1 3 2 1 4 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 */
int a[5][5];
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
for(j=0;j<5;j++){
// a[i][j]=i-j+1; // Non pointer version
*(a[i]+j)=i-j+1; // Pointer version
*(*(a+i)+j)=i-j+1; // Pointer version
if(i>=j){
// printf(" %d", a[i][j]); // Non pointer version
// printf(" %d", *(a[i]+j)); // Pointer version
printf(" %d", *(*(a+i)+j)); // Pointer version
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Array pointer :
Define line pointer ( Array pointer ): You can use *(*(p+i)+j, Otherwise, the report will be wrong , Only use *(*(a+i)+j
int a[3][3]={
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int (*p)[3]; // Array row pointer

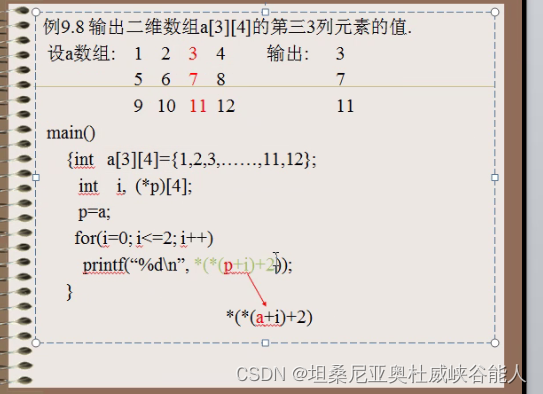
Several pointer operations on arrays :

Notice the commas in the figure , The execution order is from right to left , If it is a comma, change it to a multiplication sign , It's from left to right
int a[]={
1,2,3},y,*p=&a[2];
y=*--p;
y Value : 2
Logic :p The initial pointing subscript is 2 The address of , First --, Move to subscript 1, then * Value , The table below for 1 The address of , The value is 2
int a[]={
1,2,3,4,5,6},*p=a;
*p++ * *++p The value of is :3
Logic : Multiplication sign , From left to right , First *p=1, Then add the pointer 1, In execution ++p, The pointer is adding 1, And then take *++p=3 , Last 1*3=3
A function pointer :
int max(int a, int b){
}
int (*p)()
max(a,b) --> (*p)(a,b)
Pointer array :
Definition :
Each subscript variable is a pointer variable , It's an address , It is mainly used to handle variable length multiple strings .
understand : Pointer array is not the same concept as the previous array pointer , Pointer arrays are special in that all elements are an address
style :
int *b[3]={ a,&a[1] }
Pointer summary :

// Area of circle
double area(int r){
return 3.14*r*r;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
double (*p)(); // Note that the type must be consistent with the function type , If the function is double, Here is int, The result will be 4199728.00000
p=area;
int i=2;
double result;
result=(*p)(i);
printf("%f",result); // 12.560000
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- LeetCode 0710. Random numbers in the blacklist - preprocessing implementation o (1) value
- Use recursion or a while loop to get the name of the parent / child hierarchy
- Record a time when the server was taken to mine
- Test instructions - common interface protocol analysis
- Industrial and enterprise patent matching data (hundreds of thousands of data) 1998-2014
- Badge series 5: use of codecov
- How to create an IE tab in edge browser
- 软件测试---如何选择合适的正交表
- The 100000 line transaction lock has opened your eyes.
- 安装 新版本cmake & swig & tinyspline
猜你喜欢

做测试需要知道的内容——url、弱网、接口、自动化、

How does flutter transfer parameters to the next page when switching pages?

2021-11-29 轨迹规划五次多项式

How to create an IE tab in edge browser

The first techo day Tencent technology open day, 628

Specific implementation comparison between different programming languages

Mysql database field query case sensitive setting
CVPR:Refining Pseudo Labels with Clustering Consensus over Generations for Unsupervised Object Re-ID

install realsense2: The following packages have unmet dependencies: libgtk-3-dev

逻辑英语结构【重点】
随机推荐
Opencv depthframe - > pointcloud causes segmentation fault!
Leetcode connected to rainwater series 42 (one dimension) 407 (2D)
Teach you to use shell script to check whether the server program is running
thinkphp6.0的第三方扩展包,支持上传阿里云,七牛云
节流,防抖,new函数,柯里化
Badge series 5: use of codecov
halcon 光度立体
LeetCode 498. 对角线遍历
Why do some functions in the go standard library have only signatures but no function bodies?
install opencv-contrib-dev to use aruco code
js---获取对象数组中key值相同的数据,得到一个新的数组
[trajectory planning] testing of ruckig Library
How to correctly open the USB debugging and complete log functions of Huawei mobile phones?
Industrial and enterprise patent matching data (hundreds of thousands of data) 1998-2014
PHP extracts TXT text to store the domain name in JSON data
Speed test of adding, deleting, modifying and querying 5million pieces of data in a single MySQL table
install realsense2: The following packages have unmet dependencies: libgtk-3-dev
Meaning of go runtime
欧冠比赛数据集(梅西不哭-离开巴萨也可能再创巅峰)
LeetCode 958. Completeness checking of binary tree