当前位置:网站首页>Dark horse shopping mall ---8 Microservice gateway and JWT token
Dark horse shopping mall ---8 Microservice gateway and JWT token
2022-06-25 11:53:00 【Shuaijie it God】
Learning goals
- Master the system construction of microservice gateway
- Understand what a microservice gateway is and what it does
- Master the construction of micro service in the system center
- Master user password encryption storage bcrypt
- understand JWT Introduction to authentication
- master JWT Use of authentication
- Master the use of gateway JWT check
- Master gateway current limiting
1 Microservice gateway
1.1 Overview of microservice gateway
Different microservices usually have different network addresses , External clients may need to call multiple service interfaces to fulfill a business requirement , If the client is allowed to directly communicate with various microservices , There will be the following questions :
- Clients will request different microservices multiple times , Increased client complexity
- There are cross domain requests , It is relatively complex to deal with in a certain scenario
- Authentication is complex , Each service requires independent authentication
- Difficult to reconstruct , As the project iterates , Microservices may need to be redistributed . for example , It is possible to merge multiple services into one or split one service into multiple . If the client communicates directly with the microservice , Then refactoring will be difficult to implement
- Some microservices may use firewalls / Browser unfriendly protocol , Direct access will be difficult
These problems can be solved by gateway .
Gateway is the middle layer between client and server , All external requests go first The gateway layer . in other words ,API More consideration of business logic in the implementation of , And security 、 performance 、 Monitoring can be handed over to Gateway to do , This improves both business flexibility and security , The typical architecture is shown in the figure :

Advantages as follows :
- Security , Only the gateway system is exposed to the outside world , Microservices can be hidden in the intranet , Protect through firewalls .
- Easy to monitor . Monitoring data can be collected at the gateway and pushed to an external system for analysis .
- Easy to authenticate . Can authenticate on the gateway , Then forward the request to the back-end microservice , Without authentication in every microservice .
- Reduce the number of interactions between clients and various microservices
- Easy to unify Authorization .
summary : Microservice gateway is a system , By exposing the microservice gateway system , It is convenient for us to carry out relevant authentication , safety control , Log unified processing , Easy to monitor related functions .
1.2 Microservice Gateway Technology
There are many technologies to implement microservice gateway ,
- nginx Nginx (engine x) Is a high-performance HTTP and Reverse proxy web The server , It also provides IMAP/POP3/SMTP service
- zuul ,Zuul yes Netflix One of the products is based on JVM Load balancer on Routing and server side .
- spring-cloud-gateway, yes spring Produced be based on spring Gateway project for , Integrated circuit breaker , The path to rewrite , Performance ratio Zuul good .
We use gateway This gateway technology , Seamlessly connect to based on spring cloud The development of micro services .
gateway Official website :
https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-gateway
2 Gateway system uses
2.1 Demand analysis
Because of the system we developed There are front-end and back-end systems , The background system For administrators . Then we also need to call various microservices , So we aim at System management builds a gateway system . The analysis is as follows :

2.2 Build the background gateway system
2.2.1 Construction analysis
From above we can know , because Multiple gateways are required , So for the convenience of Management . Let's create a new project , The packing method is pom, You can set up various gateway system modules inside . As shown in the figure :

2.2.2 Project construction
(1) Introduce dependencies
modify changgou-gateway engineering , The packing method is pom
pom.xml as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>changgou-parent</artifactId> <groupId>com.changgou</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>changgou-gateway</artifactId> <packaging>pom</packaging> <modules> <module>changgou-gateway-web</module> </modules> <!-- Gateway depends on --> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
stay changgou-gateway In Engineering , establish changgou-gateway-web engineering , The gateway is mainly used to perform a call operation on the background micro service , Concatenate multiple microservices .
pom.xml:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>changgou-gateway</artifactId> <groupId>com.changgou</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>changgou-gateway-web</artifactId> <description> Ordinary web Request gateway </description> </project>
(2) Boot class
stay changgou-gateway-web Create a boot class in com.changgou.GatewayWebApplication, The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient public class GatewayWebApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(GatewayWebApplication.class,args); } }
(3)application.yml To configure
stay changgou-gateway-web Of resources Create application.yml, The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18spring: application: name: gateway-web server: port: 8001 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka instance: prefer-ip-address: true management: endpoint: gateway: enabled: true web: exposure: include: true
2.3 Cross domain configuration
occasionally , We need to process all microservice cross domain requests , Can be in gateway Cross domain support in . modify application.yml, Add the following code :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12spring: cloud: gateway: globalcors: cors-configurations: '[/**]': # Match all requests allowedOrigins: "*" # Cross domain processing Allow all domains allowedMethods: # Supported methods - GET - POST - PUT - DELETE
The final documents are as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29spring: cloud: gateway: globalcors: cors-configurations: '[/**]': # Match all requests allowedOrigins: "*" # Cross domain processing Allow all domains allowedMethods: # Supported methods - GET - POST - PUT - DELETE application: name: gateway-web server: port: 8001 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka instance: prefer-ip-address: true management: endpoint: gateway: enabled: true web: exposure: include: true
2.4 Gateway filtering configuration

The routing filter allows the incoming... To be modified in some way HTTP Requested or communicated HTTP Respond to . Path filters are limited to specific paths . Spring Cloud Gateway Contains many built-in GatewayFilter factory . Pictured above , Route to different micro services according to the request path , This one can be used Gateway The routing filtering function of .
filter Yes 20 Multiple Realization class , Include Head filter 、 route class filter 、 Hystrix filter and change request URL Of filter , also Parameters and state code etc. other type Of filter .
The built-in filter factory has 22 Implementation classes , Include Head filter 、 Path filter 、Hystrix filter 、 request URL Change filter , There are other types of filters such as parameters and status codes . According to the purpose of the filter factory , It can be divided into the following :Header、Parameter、Path、Body、Status、Session、Redirect、Retry、RateLimiter and Hystrix.
2.4.1 Host route
Such as user request cloud.itheima.com When , Requests can be routed to http://localhost:18081 Service handling , The following configuration :

The configuration shown in the figure above is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: http://localhost:18081 predicates: - Host=cloud.itheima.com**
The test request http://cloud.itheima.com:8001/brand, The effect is as follows :

Be careful : At this point, you want cloud.itheima.com Access local computer , You want to configure C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts file , The mapping configuration is as follows :
127.0.0.1 cloud.itheima.com
2.4.2 Path matching filter configuration
We can also implement the corresponding route filtering operation according to the request path , For example, the request is marked with /brand/ Path start request , All directly to http://localhost:180801 Service handling , The following configuration :

The configuration shown in the figure above is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: http://localhost:18081 predicates: - Path=/brand/**
The test request http://localhost:8001/brand, The effect is as follows :

2.4.3 PrefixPath Filter configuration
Every time a user requests a path , We can add a uniform prefix to the real request , For example, user requests http://localhost:8001 When we ask it to ask for the real address http://localhost:8001/brand, The following configuration :

The configuration shown in the figure above is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: http://localhost:18081 predicates: #- Host=cloud.itheima.com** - Path=/** filters: - PrefixPath=/brand
The test request http://localhost:8001/ The effect is as follows :

2.4.4 StripPrefix Filter configuration
Many times there will be such a request , The user request path is /api/brand, And the real path is /brand, At this time, we need to get rid of /api Is the real path , You can use SttripPrefix Function to realize the path filtering operation , The following configuration :

The configuration shown in the figure above is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: http://localhost:18081 predicates: #- Host=cloud.itheima.com** - Path=/** filters: #- PrefixPath=/brand - StripPrefix=1
The test request http://localhost:8001/api/brand, The effect is as follows :

2.4.5 LoadBalancerClient Routing filter ( Client load balancing )
The above routing configuration will send the request to the specified server every time URL Handle , But if in the future production environment , When the amount of concurrency is large , We need to judge the load balancing operation according to the name of the service , have access to LoadBalancerClientFilter To achieve load balancing, call .LoadBalancerClientFilter Will act on url With lb The first route , And then use it loadBalancer To get the service instance , Construct goals requestUrl, Set to GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR Properties of the , for NettyRoutingFilter Use .
modify application.yml The configuration file , The code is as follows :

The configuration shown in the figure above is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10routes: - id: changgou_goods_route #uri: http://localhost:18081 uri: lb://goods predicates: #- Host=cloud.itheima.com** - Path=/** filters: #- PrefixPath=/brand - StripPrefix=1
Test request path http://localhost:8001/api/brand

2.5 Gateway current limiting
Gateway can do a lot of things , such as , Current limiting , When our system When asked frequently , It is possible. Crush the system , therefore To solve this problem , It is necessary to do flow limiting operation in each microservice , But if you have a gateway , Then we can limit the current in the gateway system , Because all requests need to go through the gateway system before they can be routed to the micro service .
2.5.1 Thought analysis

2.5.2 Token bucket algorithm
Token bucket algorithm is one of the most common current limiting algorithms , Here's a general description :
1) All requests need to get an available token before they can be processed ;
2) According to the current limit , Set to add tokens to the bucket at a certain rate ;
3) Bucket set maximum token limit , When the bucket is full 、 The newly added token is discarded or rejected ;
4) After the request arrives, first get the token in the token bucket , Take the token to carry out other business logic , After processing the business logic , Delete the token directly ;
5) Token bucket has a minimum of , When the token in the bucket reaches the minimum limit , The token will not be deleted after the request is processed , So as to ensure sufficient current limiting
Here's the picture :

The implementation of this algorithm , There's a lot of Technology ,Guaua Is one of them ,redis The client also has its implementation .
2.5.3 Use token bucket to limit the number of requests
spring cloud gateway By default redis Of RateLimter Current limiting algorithm to achieve . So if we want to use it, we need to introduce redis Dependence
(1) introduce redis rely on
stay changgou-gateway Of pom.xml Introduction in redis Dependence
1 2 3 4 5 6<!--redis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive</artifactId> <version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
(2) Definition KeyResolver
stay Applicatioin Add the following code to the bootstrap class ,KeyResolver Used to calculate the current limit of a certain type KEY in other words , Can pass KeyResolver To specify current limiting Key.
We can use IP To limit the flow , Like every one of them IP Only one request per second , stay GatewayWebApplication Definition key Acquisition , Get the client IP, take IP As key, The following code :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16/*** * IP Current limiting * @return */ @Bean(name="ipKeyResolver") public KeyResolver userKeyResolver() { return new KeyResolver() { @Override public Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange) { // Get the remote client IP String hostName = exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress().getAddress().getHostAddress(); System.out.println("hostName:"+hostName); return Mono.just(hostName); } }; }
(3) modify application.yml Configuration item in , Specify the configuration for limiting traffic and REDIS Configuration of , Pictured
The modification is shown in the figure below :

The configuration code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47spring: cloud: gateway: globalcors: corsConfigurations: '[/**]': # Match all requests allowedOrigins: "*" # Cross domain processing Allow all domains allowedMethods: # Supported methods - GET - POST - PUT - DELETE routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: lb://goods predicates: - Path=/api/brand** filters: - StripPrefix=1 - name: RequestRateLimiter # The number of requests is limited Names can't be written casually , Use default facatory args: key-resolver: "#{@ipKeyResolver}" redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 1 application: name: gateway-web #Redis To configure redis: host: 192.168.211.132 port: 6379 server: port: 8001 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka instance: prefer-ip-address: true management: endpoint: gateway: enabled: true web: exposure: include: true
explain :
redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate Is how many requests you want to allow users to execute per second , Without dropping any requests . This is the rate at which the token bucket is filled
redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity Is the capacity of the command card bucket , The maximum number of requests allowed to complete in one second , Setting this value to zero will block all requests .
key-resolver: “#{@ipKeyResolver}” Used by SPEL Expression to specify which one to use KeyResolver.
The above configuration :
Express One second , allow A request goes through , The fill rate of the token bucket is also one token added per second .
Maximum emergency Only allowed There's a request in a second , It can be adjusted according to the business .
Multiple requests can lead to the following

3 The user login
There are 2 An important role , Administrator and user respectively , In the following chapters, we will realize shopping order and payment , If the user is not logged in, he cannot place an order or pay , So we need to implement a login function here .
3.1 Table structure Introduction
changgou_user The table is as follows :

User information sheet tb_user
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24CREATE TABLE `tb_user` ( `username` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT ' user name ', `password` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT ' password , Encrypted storage ', `phone` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Register mobile number ', `email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Sign up for email ', `created` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT ' Creation time ', `updated` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT ' Modification time ', `source_type` varchar(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Member source :1:PC,2:H5,3:Android,4:IOS', `nick_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' nickname ', `name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Real name ', `status` varchar(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Using a state (1 normal 0 abnormal )', `head_pic` varchar(150) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Head portrait address ', `qq` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'QQ number ', `is_mobile_check` varchar(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Whether the mobile phone is verified (0 no 1 yes )', `is_email_check` varchar(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Whether the mailbox is detected (0 no 1 yes )', `sex` varchar(1) DEFAULT '1' COMMENT ' Gender ,1 male ,0 Woman ', `user_level` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Membership level ', `points` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' integral ', `experience_value` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Empirical value ', `birthday` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Date of birth ', `last_login_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Last login time ', PRIMARY KEY (`username`), UNIQUE KEY `username` (`username`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT=' User table ';
3.2 User micro service creation
Before creating the project , First, use the code generator to generate the corresponding business code .
(1) public API establish
stay changgou-service-api Created in changgou-service-user-api, And will pojo Copy to project , Here's the picture :

stay changgou-service Created in changgou-service-user Microservices , And introduce the generated business logic code , Here's the picture :

(2) rely on
stay changgou-service-user Of pom.xml Introduce the following dependencies :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>changgou-service</artifactId> <groupId>com.changgou</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>changgou-service-user</artifactId> <!-- rely on --> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.changgou</groupId> <artifactId>changgou-service-user-api</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
(3) Start class creation
stay changgou-service-user Create a startup class in the microservice com.changgou.UserApplication, The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @MapperScan("com.changgou.user.dao") public class UserApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(UserApplication.class,args); } }
(4)application.yml To configure
stay changgou-service-user Of resources Created in application.yml To configure , The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19server: port: 18089 spring: application: name: user datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.211.132:3306/changgou_user?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123456 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka instance: prefer-ip-address: true feign: hystrix: enabled: true
3.3 Sign in
When logging in , Password verification is required , Here we use BCryptPasswordEncoder To encrypt , It is necessary to transfer the BCrypt Import to common In Engineering , among BCrypt.checkpw(“ Plaintext ”,“ Ciphertext ”) Used to compare whether passwords are consistent .
modify changgou-service-user Of com.changgou.user.controller.UserController Add login method , The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13/*** * The user login */ @RequestMapping(value = "/login") public Result login(String username,String password){ // Query user information User user = userService.findById(username); if(user!=null && BCrypt.checkpw(password,user.getPassword())){ return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK," Login successful !",user); } return new Result(false,StatusCode.LOGINERROR," Wrong account or password !"); }
Be careful : Here the password is encrypted .
Use Postman Test the following :

3.4 Gateway Association

In our daily work , It will not directly expose microservices , Generally, the gateway is used for docking , Implement a protection function for microservices , Pictured above , When users access /api/user/ Then we call the specified method of the user microservice according to the user's request . Of course , except /api/user/ also /api/address/、/api/areas/、/api/cities/、/api/provinces/ All need to be done by user Microservice processing , Modify the gateway project changgou-gateway-web Of application.yml The configuration file , The following code :

The above code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54spring: cloud: gateway: globalcors: corsConfigurations: '[/**]': # Match all requests allowedOrigins: "*" # Cross domain processing Allow all domains allowedMethods: # Supported methods - GET - POST - PUT - DELETE routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: lb://goods predicates: - Path=/api/goods/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 - name: RequestRateLimiter # The number of requests is limited Names can't be written casually , Use default facatory args: key-resolver: "#{@ipKeyResolver}" redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 1 # User microservices - id: changgou_user_route uri: lb://user predicates: - Path=/api/user/**,/api/address/**,/api/areas/**,/api/cities/**,/api/provinces/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 application: name: gateway-web #Redis To configure redis: host: 192.168.211.132 port: 6379 server: port: 8001 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka instance: prefer-ip-address: true management: endpoint: gateway: enabled: true web: exposure: include: true
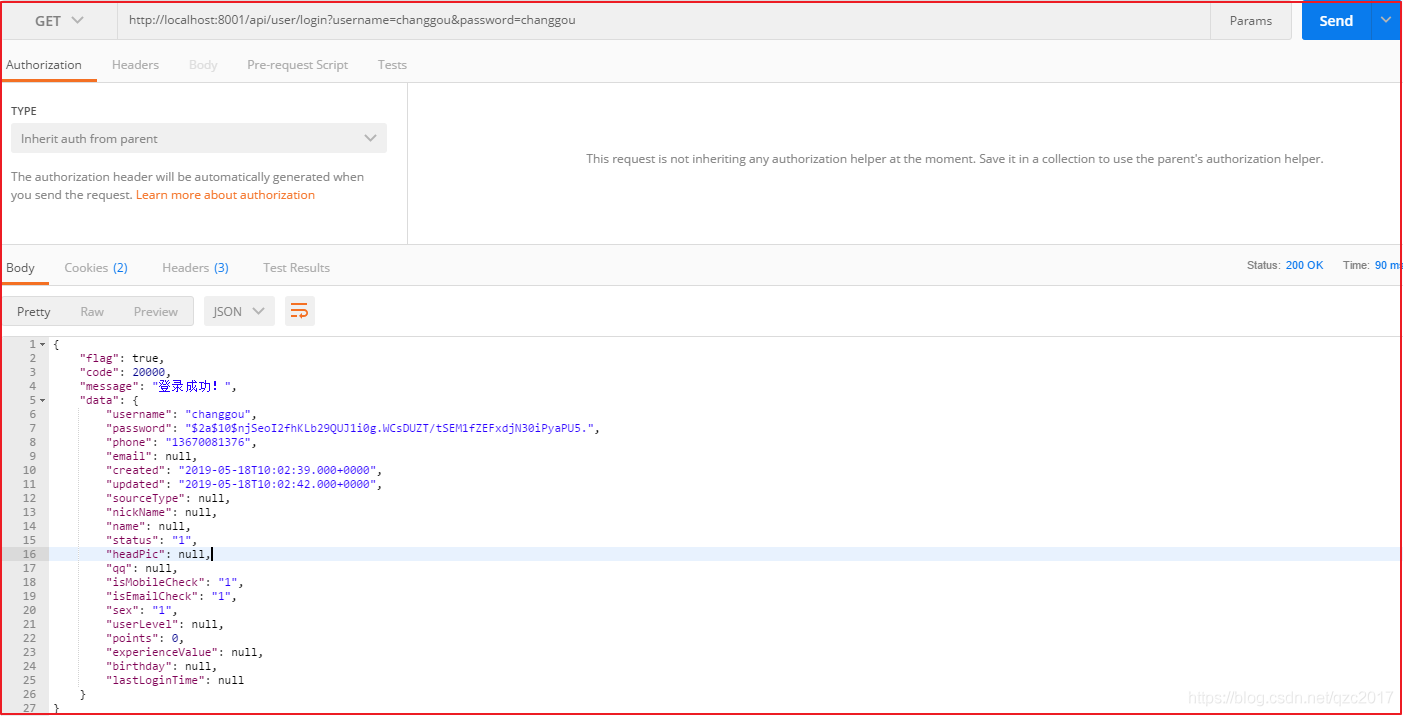
Use Postman visit http://localhost:8001/api/user/login?username=changgou&password=changgou, The effect is as follows :
4 JWT Explain
4.1 Demand analysis
We have built a gateway before , Using the gateway is more suitable for permission verification in the gateway system .

So we can use JWT To realize authentication and verification .
4.2 What is? JWT
JSON Web Token(JWT) It's a very light standard . This specification allows us to use JWT Deliver secure information between users and servers .
4.3 JWT The composition of the
One JWT It's actually a string , It consists of three parts , Head 、 Loads and signatures .
Head (Header)
The head is used to describe about the JWT The most basic information , For example, its type and the algorithm used for signature . It can also be expressed as a JSON object .
{"typ":"JWT","alg":"HS256"}
In the header, it indicates that the signature algorithm is HS256 Algorithm . We carry out BASE64 code http://base64.xpcha.com/, The encoded string is as follows :
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9
Little knowledge :Base64 It's based on 64 A representation of binary data that represents three printable characters . because 2 Of 6 The second power equals 64, So every 6 Each bit is a unit , Corresponds to some printable character . Three bytes have 24 A bit , Corresponding to 4 individual Base64 unit , namely 3 You need to use 4 Three printable characters .JDK Provides a very convenient **BASE64Encoder** and **BASE64Decoder**, Using them can be very convenient based on BASE64 Code and decode
load (playload)
The load is where the payload is stored . The name seems to refer to the goods carried on the plane , The valid information consists of three parts
(1) A statement registered in the standard ( Recommended but not mandatory )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7iss: jwt Issuer sub: jwt Target users aud: receive jwt On the side of exp: jwt The expiration time of , The expiration time must be greater than the issuing time nbf: Define before what time , The jwt They're not available . iat: jwt Issued on jti: jwt Unique identity of , Mainly used as a one-off token, To avoid replay attacks .
(2) Public statement
Public statements can add any information , Generally add relevant information of users or other necessary information required by business . But it's not recommended to add sensitive information , Because this part can be decrypted on the client side .
(3) Private statement
A private statement is a statement defined by both the provider and the consumer , It is generally not recommended to store sensitive information , because base64 It's symmetric decryption , It means that this part of information can be classified as clear text information .
This refers to custom claim. For example, in the following face structure example admin and name It's all self determined claim. these claim Follow JWT standard-specified claim The difference lies in :JWT Stipulated claim,JWT The receiver is getting JWT after , We all know how to deal with these standards claim To verify ( I don't know if I can verify ); and private claims No validation , Unless the receiving party is explicitly told to claim Validation and rules .
Define a payload:
{"sub":"1234567890","name":"John Doe","admin":true}
And then it's done base64 encryption , obtain Jwt Part two .
eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9
visa (signature)
jwt The third part of the is a visa information , This visa information consists of three parts :
header (base64 After )
payload (base64 After )
secret
This part needs base64 Encrypted header and base64 Encrypted payload Use . String of connections , And then through header Adding salt in the encryption method stated in secret Combination encryption , And then it forms jwt Part three .
TJVA95OrM7E2cBab30RMHrHDcEfxjoYZgeFONFh7HgQ
Use these three parts with . Connect to a complete string , The final jwt:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9.TJVA95OrM7E2cBab30RMHrHDcEfxjoYZgeFONFh7HgQ
Be careful :secret It's stored on the server side ,jwt The signature generation of is also on the server side ,secret It's used to do jwt And jwt Validation of the , therefore , It is the private key of your server , It should not be revealed in any scene . Once the client knows this secret, That means that the client can issue itself jwt 了 .
4.4 JJWT Introduction and use of
JJWT Is an end-to-end JWT Create and verify Java library . Always free and open source (Apache License, edition 2.0),JJWT It's easy to use and understand . It is designed as a smooth interface centered on Architecture , Hides most of its complexity .
Official documents :
4.4.1 establish TOKEN
(1) Depend on the introduction of
stay changgou-parent In the project pom.xml Add dependency to :
1 2 3 4 5 6<!-- authentication --> <dependency> <groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId> <artifactId>jjwt</artifactId> <version>0.9.0</version> </dependency>
(2) Create the test
stay changgou-common Of /test/java Create a test class , And set the test method
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16public class JwtTest { /**** * establish Jwt token */ @Test public void testCreateJwt(){ JwtBuilder builder= Jwts.builder() .setId("888") // Set unique number .setSubject(" The small white ") // Set the theme It can be JSON data .setIssuedAt(new Date()) // Set issue date .signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS256,"itcast");// Set signature Use HS256 Algorithm , And set up SecretKey( character string ) // structure And return a string System.out.println( builder.compact() ); } }
Run print results :
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiI4ODgiLCJzdWIiOiLlsI_nmb0iLCJpYXQiOjE1NjIwNjIyODd9.RBLpZ79USMplQyfJCZFD2muHV_KLks7M1ZsjTu6Aez4
Run again , You will find that the results of each run are different , Because our load contains time .
4.4.2 TOKEN analysis
We have just created token , stay web In the application, this operation is performed by the server and then sent to the client , The client needs to carry this when sending a request to the server next time token( It's like holding a ticket ), The server is connected to this token It should be resolved that token Information in ( For example, users id), According to this information, query the database and return the corresponding results .
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12/*** * analysis Jwt Token data */ @Test public void testParseJwt(){ String compactJwt="eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiI4ODgiLCJzdWIiOiLlsI_nmb0iLCJpYXQiOjE1NjIwNjIyODd9.RBLpZ79USMplQyfJCZFD2muHV_KLks7M1ZsjTu6Aez4"; Claims claims = Jwts.parser(). setSigningKey("itcast"). parseClaimsJws(compactJwt). getBody(); System.out.println(claims); }
Run print effect :
{jti=888, sub= The small white , iat=1562062287}
Try to token Or tamper with the signature key , You will find that an error will be reported when running , So parsing token That's validation token.
4.4.3 Set expiration time
A lot of times , We don't want to issue token It's permanent , So we can do it for token Add an expiration time .
4.4.3.1 token Expiration settings

explain :
.setExpiration(date)// Used to set the expiration time , Parameter is Date Type data
function , The printing effect is as follows :
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiI4ODgiLCJzdWIiOiLlsI_nmb0iLCJpYXQiOjE1NjIwNjI5MjUsImV4cCI6MTU2MjA2MjkyNX0._vs4METaPkCza52LuN0-2NGGWIIO7v51xt40DHY1U1Q
4.4.3.2 analysis TOKEN
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12/*** * analysis Jwt Token data */ @Test public void testParseJwt(){ String compactJwt="eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiI4ODgiLCJzdWIiOiLlsI_nmb0iLCJpYXQiOjE1NjIwNjI5MjUsImV4cCI6MTU2MjA2MjkyNX0._vs4METaPkCza52LuN0-2NGGWIIO7v51xt40DHY1U1Q"; Claims claims = Jwts.parser(). setSigningKey("itcast"). parseClaimsJws(compactJwt). getBody(); System.out.println(claims); }
Printing effect :

The current time exceeds the expiration time , May be an error .
4.4.4 Customize claims
Our example just now just stores id and subject Two messages , If you want to store more information ( For example, characters ) You can define custom claims.
Create test class , And set the test method :
establish token:

Run print effect :
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiI4ODgiLCJzdWIiOiLlsI_nmb0iLCJpYXQiOjE1NjIwNjMyOTIsImFkZHJlc3MiOiLmt7HlnLPpu5Hpqazorq3nu4PokKXnqIvluo_lkZjkuK3lv4MiLCJuYW1lIjoi546L5LqUIiwiYWdlIjoyN30.ZSbHt5qrxz0F1Ma9rVHHAIy4jMCBGIHoNaaPQXxV_dk
analysis TOKEN:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12/*** * analysis Jwt Token data */ @Test public void testParseJwt(){ String compactJwt="eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiI4ODgiLCJzdWIiOiLlsI_nmb0iLCJpYXQiOjE1NjIwNjMyOTIsImFkZHJlc3MiOiLmt7HlnLPpu5Hpqazorq3nu4PokKXnqIvluo_lkZjkuK3lv4MiLCJuYW1lIjoi546L5LqUIiwiYWdlIjoyN30.ZSbHt5qrxz0F1Ma9rVHHAIy4jMCBGIHoNaaPQXxV_dk"; Claims claims = Jwts.parser(). setSigningKey("itcast"). parseClaimsJws(compactJwt). getBody(); System.out.println(claims); }
Running effect :

4.5 Authentication processing
4.5.1 Thought analysis

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 81. The user invokes the microservice by accessing the microservice gateway , At the same time, carry the header file information 2. Intercept at the microservice gateway , After interception, obtain the path that the user wants to access 3. Identify whether the path accessed by the user needs to be logged in , if necessary , Identify whether the user's identity can access the path [ Here you can design a set of permissions based on the database ] 4. If you need permission to access , The user has logged in , The release 5. If you need permission to access , And the user is not logged in , Prompt the user to log in 6. Users access user microservices through the gateway , Do login verification 7. After the verification is passed , The user micro service will issue a token to the gateway , The gateway encapsulates the user information into a header file , And respond to the user 8. The next time the user visits , Carry the token information in the header file to identify whether to log in
4.5.2 The user logs in and signs TOKEN
(1) Generate token tool class
stay changgou-common Create class in entity.JwtUtil, Mainly auxiliary generation Jwt The token information , The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65public class JwtUtil { // Valid for public static final Long JWT_TTL = 3600000L;// 60 * 60 *1000 An hour //Jwt The token information public static final String JWT_KEY = "itcast"; public static String createJWT(String id, String subject, Long ttlMillis) { // Specified algorithm SignatureAlgorithm signatureAlgorithm = SignatureAlgorithm.HS256; // Current system time long nowMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); // Token issuing time Date now = new Date(nowMillis); // If the token is valid for null, The validity period is set by default 1 Hours if(ttlMillis==null){ ttlMillis=JwtUtil.JWT_TTL; } // Token expiration time setting long expMillis = nowMillis + ttlMillis; Date expDate = new Date(expMillis); // Generate secret key SecretKey secretKey = generalKey(); // encapsulation Jwt The token information JwtBuilder builder = Jwts.builder() .setId(id) // Unique ID .setSubject(subject) // The theme It can be JSON data .setIssuer("admin") // Issuer .setIssuedAt(now) // The issuance of time .signWith(signatureAlgorithm, secretKey) // Signature algorithm and key .setExpiration(expDate); // Set expiration time return builder.compact(); } /** * Generate encryption secretKey * @return */ public static SecretKey generalKey() { byte[] encodedKey = Base64.getEncoder().encode(JwtUtil.JWT_KEY.getBytes()); SecretKey key = new SecretKeySpec(encodedKey, 0, encodedKey.length, "AES"); return key; } /** * Parse token data * @param jwt * @return * @throws Exception */ public static Claims parseJWT(String jwt) throws Exception { SecretKey secretKey = generalKey(); return Jwts.parser() .setSigningKey(secretKey) .parseClaimsJws(jwt) .getBody(); } }
(2) User login successful be Issue TOKEN, Modify the login method :

The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20/*** * The user login */ @RequestMapping(value = "/login") public Result login(String username,String password){ // Query user information User user = userService.findById(username); if(user!=null && BCrypt.checkpw(password,user.getPassword())){ // Set token information Map<String,Object> info = new HashMap<String,Object>(); info.put("role","USER"); info.put("success","SUCCESS"); info.put("username",username); // To generate the token String jwt = JwtUtil.createJWT(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), JSON.toJSONString(info),null); return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK," Login successful !",jwt); } return new Result(false,StatusCode.LOGINERROR," Wrong account or password !"); }
4.5.3 Gateway filter intercepts request processing
Copy JwtUtil To changgou-gateway-web in

4.5.4 Custom global filter
establish Filter class , As shown in the figure :

AuthorizeFilter The code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67@Component public class AuthorizeFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered { // Token header name private static final String AUTHORIZE_TOKEN = "Authorization"; /*** * Global filter * @param exchange * @param chain * @return */ @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) { // obtain Request、Response object ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse(); // Obtain requested URI String path = request.getURI().getPath(); // If it's login 、goods And other open micro services [ there goods Partially open ], Then direct release , There is no complete demonstration here , The complete demonstration needs to design a set of permission system if (path.startsWith("/api/user/login") || path.startsWith("/api/brand/search/")) { // release Mono<Void> filter = chain.filter(exchange); return filter; } // Get the token information in the header file String tokent = request.getHeaders().getFirst(AUTHORIZE_TOKEN); // If there is no... In the header file , Get... From the request parameters if (StringUtils.isEmpty(tokent)) { tokent = request.getQueryParams().getFirst(AUTHORIZE_TOKEN); } // If it is empty , The error code is output if (StringUtils.isEmpty(tokent)) { // The setting method is not allowed to be accessed ,405 Error code response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED); return response.setComplete(); } // Parse token data try { Claims claims = JwtUtil.parseJWT(tokent); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); // Parse failure , Respond to 401 error response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED); return response.setComplete(); } // release return chain.filter(exchange); } /*** * Filter execution order * @return */ @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } }
4.5.5 Configure filtering rules
Modify the of the gateway system yml file :

The above code is as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54spring: cloud: gateway: globalcors: corsConfigurations: '[/**]': # Match all requests allowedOrigins: "*" # Cross domain processing Allow all domains allowedMethods: # Supported methods - GET - POST - PUT - DELETE routes: - id: changgou_goods_route uri: lb://goods predicates: - Path=/api/album/**,/api/brand/**,/api/cache/**,/api/categoryBrand/**,/api/category/**,/api/para/**,/api/pref/**,/api/sku/**,/api/spec/**,/api/spu/**,/api/stockBack/**,/api/template/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 - name: RequestRateLimiter # The number of requests is limited Names can't be written casually , Use default facatory args: key-resolver: "#{@ipKeyResolver}" redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 1 # User microservices - id: changgou_user_route uri: lb://user predicates: - Path=/api/user/**,/api/address/**,/api/areas/**,/api/cities/**,/api/provinces/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 application: name: gateway-web #Redis To configure redis: host: 192.168.211.132 port: 6379 server: port: 8001 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka instance: prefer-ip-address: true management: endpoint: gateway: enabled: true web: exposure: include: true
Test access http://localhost:8001/api/user/login?username=changgou&password=changgou, The effect is as follows :

Test access http://localhost:8001/api/user, The effect is as follows :

Refer to the official manual :
4.6 Conversation retention
Every time a user requests , We all need to get token data , How many methods , It can be submitted every time , Submit data to header file , You can also store data in Cookie in , Each time from Cookie Check data in , The token data can also be submitted to the gateway in the form of parameters each time , It uses Cookie It's easier to implement .
4.6.1 Login encapsulation Cookie
modify user Microservices , Every time I log in , Add token information to Cookie in , modify changgou-service-user Of com.changgou.user.controller.UserController Of login Method , The code is as follows :

4.6.2 The filter gets token data
Every time in the gateway, get through the filter Cookie The token in , Then analyze the token data , Modify the microservice gateway changgou-gateway-web Medium AuthorizeFilter, The code is as follows :

Post login test , Can identify the user , Unrecognized without login . Visit http://localhost:8001/api/user Will carry token data :

4.6.3 add to Header Information
We can still do that Gateway Add request header information to the global filter of , For example, you can add token information to the request header , Get header information in microservice , The following code :
Modify the in the microservice gateway AuthorizeFilter filter , Add the token to the request header in the token information verification block , The following code :

stay changgou-service-user Micro service UserController Of findAll Method to get the request header test , The code is as follows :

The background output token data is as follows :
边栏推荐
- The service layer reports an error. The XXX method invalid bound statement (not found) cannot be found
- .Net Core 中使用工厂模式
- Design and implementation of university laboratory goods management information system based on SSH
- JSON format processing
- quarkus saas动态数据源切换实现,简单完美
- Why distributed IDS? What are the distributed ID generation schemes?
- Simple use of stream (II)
- Thingspanel releases Internet of things mobile client (multiple pictures)
- Explain websocket protocol in detail
- 依概率收敛
猜你喜欢

芯片的发展史和具体用途以及结构是什么样的

记一次给OpenHarmony提交代码的过程

Spark history server and event log details

黑马畅购商城---8.微服务网关Gateway和Jwt令牌
Research on parallel computing architecture of meteorological early warning based on supercomputing platform

Why can't the form be closed? The magic of revealing VFP object references

Countdownlatch source code analysis

为什么要分布式 id ?分布式 id 生成方案有哪些?

Actual combat summary of Youpin e-commerce 3.0 micro Service Mall project

牛客网:分糖果问题
随机推荐
黑马畅购商城---6.品牌、规格统计、条件筛选、分页排序、高亮显示
The service layer reports an error. The XXX method invalid bound statement (not found) cannot be found
TCP如何处理三次握手和四次挥手期间的异常
Real software developers will use this method to predict the future
Spark history server and event log details
文献之有效阅读
Share 7 immortal wallpaper websites, let the new wallpaper give you a little joy, and don't fall into the repetition year after year.
quarkus saas动态数据源切换实现,简单完美
Evaluating the overall situation of each class in a university based on entropy weight method (formula explanation + simple tool introduction)
Use of JSP sessionscope domain
Very important very important very important very important very important very important very important very important very important
WebRTC Native M96 基础Base模块介绍之实用方法的封装(MD5、Base64、时间、随机数)
TCP如何處理三次握手和四次揮手期間的异常
开哪家证券公司的账户是比较好,比较安全的
交易期货沪镍产品网上怎么开户
Niuke.com: Candy distribution
Translation of meisai C topic in 2022 + sharing of ideas
Spark runs wordcount (case 1)
Comment TCP gère - t - il les exceptions lors de trois poignées de main et de quatre vagues?
Spark Tuning common configuration parameters