1 background
As a long-term in the first-line belt group Owner And the old trial Officer , Our interview targets are basically front-line developers . Start from the technology stack of the server , The scope of the problem is mainly around the development language (Java、Go) And so on 、 Database technology 、 Cache technology 、 Message middleware 、 The use of the microservice framework .
MySQL As the mainstream data storage configuration of large factories , Of course, the most frequently asked , The key area is the use and optimization of indexes .
2 Optimization steps of index
2.1 The principle of efficient indexing
- Correctly understand and calculate the discrimination of index field , Here are the calculation rules , High resolution index , You can quickly locate data , The distinction is too low , Can't use index effectively , You may need to scan a large number of data pages , It's no different than not using an index . When we create an index , Try to select highly differentiated columns as indexes .
selecttivity = count(distinct c_name)/count(*)
- Correctly understand and calculate the field length of prefix index , Here are the rules of judgment , The appropriate length should ensure high discrimination and the most appropriate index storage capacity , Only when you are at your best , It is the index that ensures high efficiency . The length of the next cloth is 6 Is at its best .
select count(distinct left(c_name , calcul_len)) / count(*) from t_name;
mysql> SELECT
count(DISTINCT LEFT(empname, 3)) / count(*) AS sel3,
count(DISTINCT LEFT(empname, 4)) / count(*) AS sel4,
count(DISTINCT LEFT(empname, 5)) / count(*) AS sel5,
count(DISTINCT LEFT(empname, 6)) / count(*) AS sel6,
count(DISTINCT LEFT(empname, 7)) / count(*) AS sel7
FROM
emp;
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| sel3 | sel4 | sel5 | sel6 | sel7 |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| 0.0012 | 0.0076 | 0.0400 | 0.1713 | 0.1713 |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
1 row in set
- Union index pays attention to the leftmost matching principle : Match from left to right ,MySQL The index is matched to the right until a range query is encountered (>、<、between、like) And then stop matching . Such as depno=1 and empname>'' and job=1 , If set up (depno,empname,job) Index of order ,empname and job There is no index .
- Strategy on demand , When looking up records , Don't use it as soon as you come up *, Just take the data you need , If possible, use only index coverage , It can reduce the operation of returning table , Improve efficiency .
- Judge whether to use union index correctly ( Strategy chapter The section on the use of joint indexes describes the judgment rules ), We can also further analyze the index push down (IPC), Reduce the return operation , Improve efficiency .
- The principle of avoiding index invalidation : Disable the use of functions... On index fields 、 Operator operation , Will invalidate the index . This is actually the field corresponding to the index ” Cleanliness “.
- Avoid unnecessary type conversions , When string fields are compared with numeric values, the index will be invalid .
- Fuzzy query '%value%' Will invalidate the index , Change to full scan , Because it's impossible to determine the scan range , however 'value%' The index can be used effectively .
- Index override sort field , This reduces the sorting steps , Improve query efficiency
- Expand the index as much as possible , There is no need to create a new index . Let's say it's already in the table a The index of , Now want to add (a,b) The index of , All you need to do is change the original index .
- There is no need to force index order , such as establish (depno,empno,jobno) Index of order , You can be empno = 1 and jobno = 2 and depno = 8. because MySQL The query optimizer of will optimize the order according to the actual index situation , So the sequence consistency is not enforced here . But under the same conditions, they are arranged in order , clearer , And save the processing of query optimizer .
2.2 Query optimization Analyzer - explain
explain The order should be familiar to all of you , Please refer to the official website for specific usage and field meaning explain-output, It needs to be emphasized here rows It's the core indicator , most rows Small statements must execute very quickly , Because the scanning content base is small .
So the optimization statement is basically in the optimization to reduce rows value .
2.2.1 Explain Output field
| Column | JSON Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| id select_id | The SELECT | identifier |
| select_type | None | The SELECT type |
| table table_name | The table for the output row | |
| partitions | partitions | The matching partitions |
| type | access_type | The join type |
| possible_keys | possible_keys | The possible indexes to choose |
| key | key | The index actually chosen |
| key_len | key_length | The length of the chosen key |
| ref | ref | The columns compared to the index |
| rows | rows | Estimate of rows to be examined |
| filtered | filtered | Percentage of rows filtered by table condition |
| Extra | None | Additional information |
2.2.2 select_type enumeration
Note several core key parameters :possible_keys、key、rows、select_type, It is very meaningful for optimization guidance .
- select_type: Represents each... In the query select The type of clause (Simple、Primary、Depend SubQuery)
- possible_keys : Pointed out that MySQL Which index can be used to find records in the table , If there is an index on the field involved in the query , Then the index will be listed , But not necessarily used by queries
- key:key Columns show MySQL Actually decide which key to use ( Indexes ), Index not taken yes null
- rows: Express MySQL According to table statistics and index selection , Estimate the number of rows to scan
Basic steps of slow query optimization
- Run it first to see the actual time consumption , Judging whether it's really slow ( Pay attention to the settings SQL_NO_CACHE).
- High priority strategy :where Check the list of conditions , Conditions for locking the minimum return record table .
It's a query statement where The table with the smallest number of records returned in the table starts to look up , Each field of a single table is queried separately , See which field has the highest discrimination . The fields with high discrimination are arranged forward . - explain View execution plan , Whether or not 1 The expectations are the same ( Start with a table with fewer locked records )
- order by limit Formal sql Statement to give priority to the sorted table
- Understand the usage scenarios of the business side , Adjust according to the use scenario .
- When adding index, refer to the ten principles of building index above
- Observations , Do not meet expectations, continue to analyze from the first step
2.3 Query case analysis
The following examples explain in detail how to analyze and optimize slow queries .
Analysis of complex query conditions
Generally speaking, we write SQL The way to do it is to It's about realizing the function , On the basis of realizing the function, guarantee MySQL The efficiency of implementation is also very important , This requires us to be right MySQL Have a very clear understanding of the execution plan and indexing rules of , Analyze the following case :
1 mysql> select a.*,b.depname,b.memo from emp a left join
2 dep b on a.depno = b.depno where sal>100 and a.empname like 'ab%' and a.depno=106 order by a.hiredate desc ;
3 +---------+---------+---------+---------+-----+---------------------+------+------+-------+------------+----------+
4 | id | empno | empname | job | mgr | hiredate | sal | comn | depno | depname | memo |
5 +---------+---------+---------+---------+-----+---------------------+------+------+-------+------------+----------+
6 | 4976754 | 4976754 | ABijwE | SALEMAN | 1 | 2021-01-23 16:46:24 | 2000 | 400 | 106 | kDpNWugzcQ | TYlrVEkm |
7 ......
8 +---------+---------+---------+---------+-----+---------------------+------+------+-------+------------+----------+
9 744 rows in set (4.958 sec)
All in all 744 Data , But it cost 4.958 Time for , Let's take a look at the existing indexes in the current table and the analysis of index usage
1 mysql> show index from emp;
2 +-------+------------+---------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
3 | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
4 +-------+------------+---------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
5 | emp | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 4952492 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
6 | emp | 1 | idx_emo_depno | 1 | depno | A | 18 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
7 +-------+------------+---------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
8 2 rows in set
9
10 mysql> explain select a.*,b.depname,b.memo from emp a left join
11 dep b on a.depno = b.depno where sal>100 and a.empname like 'ab%' and a.depno=106 order by a.hiredate desc ;
12 +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+--------+-----------------------------+
13 | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
14 +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+--------+-----------------------------+
15 | 1 | SIMPLE | a | ref | idx_emo_depno | idx_emo_depno | 3 | const | 974898 | Using where; Using filesort |
16 | 1 | SIMPLE | b | ref | idx_dep_depno | idx_dep_depno | 3 | const | 1 | NULL |
17 +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+--------+-----------------------------+
18 2 rows in set
It can be seen that , Currently in emp There is only one index on the table except the primary key idx_emo_depno , In the department number field , The goal of the index is to filter out data under specific department numbers .
adopt explain The analyzer can see where After the condition is gone idx_emo_depno Indexes , But it also compares 97W The data of , This shows that the discrimination of this field is not high , According to the principle of high discrimination priority , We calculate the discrimination of the three query fields in this table .
1 mysql> select count(distinct empname)/count(*),count(distinct depno)/count(*),count(distinct sal)/count(*) from emp;
2 +----------------------------------+--------------------------------+------------------------------+
3 | count(distinct empname)/count(*) | count(distinct depno)/count(*) | count(distinct sal)/count(*) |
4 +----------------------------------+--------------------------------+------------------------------+
5 | 0.1713 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
6 +----------------------------------+--------------------------------+------------------------------+
7 1 row in set
This is the result of the calculation ,empname The highest discrimination , Therefore, it is reasonable to establish a joint index containing these three fields , Order as follows :empname、depno、sal;
And the query conditions are reordered , In line with the leftmost matching principle ; On the other hand, strategies based on needs , hold b.memo The fields are removed .
1 mysql> select a.*,b.depname from emp a left join
2 dep b on a.depno = b.depno where a.empname like 'ab%' and a.depno=106 and a.sal>100 order by a.hiredate desc ;
3 +---------+---------+---------+---------+-----+---------------------+------+------+-------+------------+
4 | id | empno | empname | job | mgr | hiredate | sal | comn | depno | depname |
5 +---------+---------+---------+---------+-----+---------------------+------+------+-------+------------+
6 | 4976754 | 4976754 | ABijwE | SALEMAN | 1 | 2021-01-23 16:46:24 | 2000 | 400 | 106 | kDpNWugzcQ |
7 ......
8 +---------+---------+---------+---------+-----+---------------------+------+------+-------+------------+
9 744 rows in set (0.006 sec)
Here's another question , The union index is based on the leftmost matching principle : Must match from left to right ,MySQL The index is matched to the right until a range query is encountered (>、<、between、like) And then stop matching .
So in the sentence Execute to a.empname Field , Because of the use of like, No more indexing . In this scenario , independent empname The efficiency of index on field is similar to that of joint index .
In addition, sort fields hiredate You can also consider covering the index , It will increase efficiency accordingly .
Analysis of invalid index
There is a need , Using the user table userinfo And consumption schedules salinvest , The purpose is to make 2020 Each user in four category levels in the year (A1、A2、A3、A4) The amount of consumption on the Internet , So we have the following script :
1 select (@rowNO := @rowNo+1) AS id,bdata.* from
2 (
3 select distinct a.usercode,a.username,
4 @A1:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A1'
5 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A1,
6 @A2:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A2'
7 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A2,
8 @A3:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A3'
9 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A3,
10 @A4:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A4'
11 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A4,
12 ,(@[email protected][email protected][email protected]) as allnum
13 from userinfo a
14 inner JOIN `salinvest` b on a.usercode = b.usercode
15 where b.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'
16 order by allnum desc
17 ) as bdata,(SELECT @rowNO:=0) b;
This query seems to be ok , Although compound query is used 、 Subquery , But if the index is done right , There won't be any problem . Let's take a look at the index , There is a joint index , In line with our leftmost matching principle and high discrimination priority principle :
1 mysql> show index from salinvest;
2 +------------+------------+------------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
3 | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
4 +------------+------------+------------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
5 | lnuminvest | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | autocode | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
6 | lnuminvest | 1 | idx_salinvest_complex | 1 | usercode | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
7 | lnuminvest | 1 | idx_salinvest_complex | 2 | gravalue | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
8 | lnuminvest | 1 | idx_salinvest_complex | 3 | logdate | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
9 +------------+------------+------------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
10 4 rows in set
Let's look at the efficiency of its implementation :
mysql> select (@rowNO := @rowNo+1) AS id,bdata.* from
(
select (@rowNO := @rowNo+1) AS id,bdata.* from
(
select distinct a.usercode,a.username,
@A1:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A1'
and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A1,
@A2:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A2'
and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A2,
@A3:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A3'
and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A3,
@A4:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A4'
and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A4,
,(@[email protected][email protected][email protected]) as allnum
from userinfo a
inner JOIN `salinvest` b on a.usercode = b.usercode
where b.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'
order by allnum desc
) as bdata,(SELECT @rowNO:=0) b;
+----+------------+---------+------+------+------+------+------+--------+
| id | usercode | username | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |allnum
+----+------------+---------+------+------+------+------+------+--------+
| 1 | 063105015 | brand | 789.00 | 1074.50 | 998.00 | 850.00 |
......
+----+------------+---------+------+------+------+------+------+--------+
6217 rows in set (12.745 sec)
I've omitted the query results here , In fact, the result output 6000 Multiple data , In about 50W Statistics and consolidation of the data , Output 6000 Multiple data , It cost nearly 13 second , This is obviously unreasonable .
Let's analyze the reasons :
1 mysql> explain select (@rowNO := @rowNo+1) AS id,bdata.* from
2 (
3 select distinct a.usercode,a.username,
4 @A1:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A1'
5 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A1,
6 @A2:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A2'
7 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A2,
8 @A3:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A3'
9 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A3,
10 @A4:=IFNULL((select sum(c.ltimenum) from `salinvest` c where c.usercode=a.usercode AND c.gravalue='A4'
11 and c.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'),0) as A4,
12 ,(@[email protected][email protected][email protected]) as allnum
13 from userinfo a
14 inner JOIN `salinvest` b on a.usercode = b.usercode
15 where b.logdate between '2020-01-01' and '2020-12-31'
16 order by allnum desc
17 ) as bdata,(SELECT @rowNO:=0) b;
18 +----+--------------------+------------+------------+--------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-----------------------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
19 | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
20 +----+--------------------+------------+------------+--------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-----------------------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
21 | 1 | PRIMARY | <derived8> | NULL | system | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100 | NULL |
22 | 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100 | NULL |
23 | 8 | DERIVED | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | No tables used |
24 | 2 | DERIVED | b | NULL | index | idx_salinvest_complex | idx_salinvest_complex | 170 | NULL | 5 | 20 | Using where; Using index; Using temporary; Using filesort |
25 | 7 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | c | NULL | ALL | idx_salinvest_complex | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 20 | Using where |
26 | 6 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | c | NULL | ALL | idx_salinvest_complex | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 20 | Using where |
27 | 5 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | c | NULL | ALL | idx_salinvest_complex | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 20 | Using where |
28 | 4 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | c | NULL | ALL | idx_salinvest_complex | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 20 | Using where |
29 +----+--------------------+------------+------------+--------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+-----------------------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
30 9 rows in set
Look at the last four data , Look at him possible_key and Actually key, It's going to be idx_salinvest_complex Indexes , In fact, the index is empty , Why is this ? Look at the front select_type Field , The value is DEPENDENT SUBQUERY, It's clear .
The official response to DEPENDENT SUBQUERY Explanation : First in subquery SELECT, Depends on external queries .
What does that mean ? It means two steps :
First step ,MySQL according to select distinct a.usercode,a.username Get a big result set t1, That's what we've shown above 6000 user .
The second step , The big result set above t1 Each record in , Equivalent to subquery SQL Compose a new query statement : select sum(c.ltimenum) from salinvest c where c.usercode in (select distinct a.usercode from userinfo a) .
in other words , Each subquery needs to compare 6000 Time , Hundreds of thousands of data …… Even if the index is used in both steps of the query , But it's going to be slow .
In this case , The execution efficiency of subquery is limited by the number of records of outer query , It's better to split it into two independent queries and execute them sequentially .
This slow query solution , There are a lot of solutions on the Internet , The most common method is to replace subqueries with union queries , You can check it yourself .
3 Appropriate sub database and sub table
Physical server CPU、 Memory 、 The storage device 、 Limited resources such as connections , A large number of connections perform operations at the same time in a certain period of time , It will cause the database to encounter performance bottleneck in processing . To solve this problem , Industry pioneers have fully carried forward the idea of division and rule , Split the large database table ,
Then implement better control and management , Using multiple machines at the same time CPU、 Memory 、 Storage , Provide better performance . There are two ways to achieve divide and conquer : Split vertically and horizontally .
3.1 Vertical sub database
Vertical database is a simple logical partition , For example, establish an independent commodity Library in the database Products、 Order Library Orders, Integral Library Scores etc. .
3.2 Vertical sub table
Comparison is applicable to tables with more fields , Suppose we have a table with 100 A field , Analyze the current business execution SQL sentence , Yes 20 Fields are frequently used , And the other 80 Fewer fields to use . hold 20 Fields in the main table , Let's create another auxiliary table , Store in addition 80 A field .
3.3 Sub table in the warehouse
Split a single large capacity table according to certain policies .
3.4 Sub database and sub table
The sub database and sub table are based on the sub table in the database , Move the divided tables to different hosts and databases . Can make full use of other hosts CPU、 Memory and IO resources .
4 A complete index knowledge system
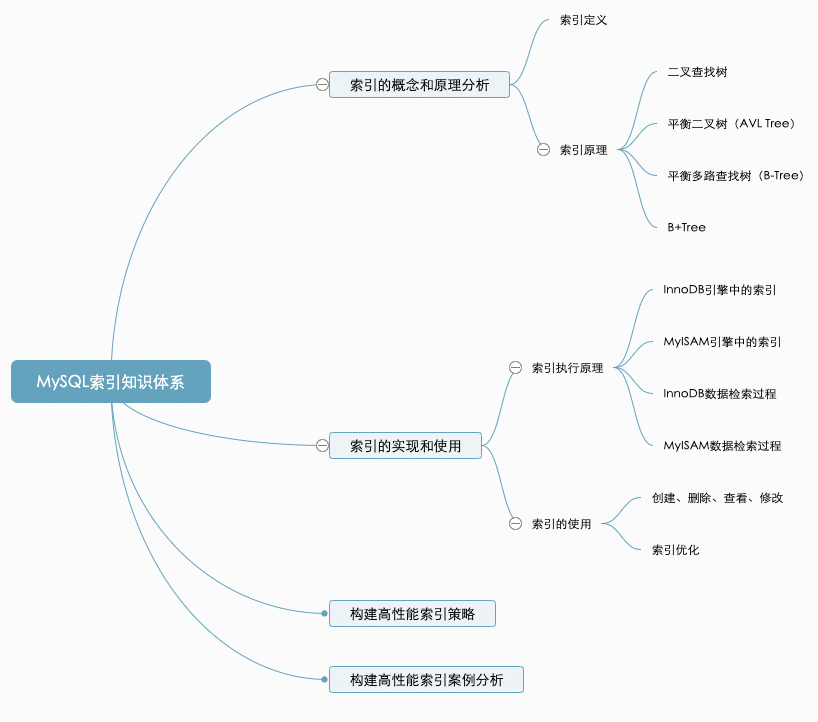
Refer to the four indexes written by the author before + There are two sub databases and tables
MySQL Break down altogether 22: Introduction and principle analysis of index
MySQL Break down altogether 23:MySQL Index implementation and use
MySQL Break down altogether 24: Building high performance indexes ( Strategy chapter )
MySQL Break down altogether 25: Building high performance indexes ( Case analysis )
MySQL Break down altogether 28: Sub database and sub table
MySQL Break down altogether 29: Sub library sub table Partition Function details
Database Series :MySQL Index optimization summary ( Comprehensive Edition ) More articles about
- mysql Database optimization course ---17、mysql Index optimization
mysql Database optimization course ---17.mysql Index optimization One . summary One sentence summary : Some index fields may fail , such as like,or etc. 1.check What is the usage scenario of table monitoring ? View The view is built on two tables , Deleted ...
- Explain profound theories in simple language Mysql Index optimization topic sharing | Interview cycle
Article outline The article combines 18 Hand drawn legend ,21 individual SQL Classic case . near 10000 word , take Mysql The experience of index optimization is summarized , You can decide whether to continue reading according to the outline , It will probably take 25-30 minute , Believe that your persistence is not bad for time ...
- Mysql Database knowledge -Mysql Index summary mysql mysql database mysql function
mysql Database knowledge -Mysql Index summary : Indexes (Index) Help MySQL Data structure for efficient data acquisition . The following is my own materials and my own learning summary ,, Make a summary . One . Is it really necessary to use indexes ? Not every performance ...
- Mysql Index optimization analysis
MySQL Index optimization analysis Why did you write sql Slow query ? Why do your indexes often fail ? Through the content of this chapter , You will learn to MySQL The reason for the performance degradation , Introduction to index , Principles of index creation ,explain Use of commands , as well as explain Output word ...
- Knowledge point :Mysql Index Optimization Practice (3)
Knowledge point :Mysql The principle of indexing is completely manual (1) Knowledge point :Mysql The principle of indexing is completely manual (2) Knowledge point :Mysql Index Optimization Practice (3) Knowledge point :Mysql Database Index Optimization Practice (4) Review of indexing principles The nature of index ...
- MySQL This article is enough for index optimization !
It is necessary to read this article 5 minute . source :cnblogs.com/songwenjie/p/9410009.html This article mainly discusses MySQL Part of the knowledge of index . Will be from MySQL Index basis . Index optimization and database index ...
- mysql Index optimization is much faster than ordinary query
mysql Index optimization is much faster than ordinary query One . summary One sentence summary : General query, full table query , Slower , Index optimization, then take space for time , Pierce to the heart of the matter , So it's a lot faster . Index optimization is much faster Space for time 1. Optimizing database query at software level ...
- mySql Index optimization analysis
MySQL Index optimization analysis Why did you write sql Slow query ? Why do your indexes often fail ? Through the content of this chapter , You will learn to MySQL The reason for the performance degradation , Introduction to index , Principles of index creation ,explain Use of commands , as well as explain Output word ...
- DB2 Database performance tuning and optimization ( The first 2 edition )
<DB2 Database performance tuning and optimization ( The first 2 edition )> essential information author : Niuxinzhuang Press. : tsinghua university press ISBN:9787302325260 Shelf time :2013-7-3 Publication date :2013 year 7 month open ...
- Speak true ,MySQL This article is enough for index optimization
This article mainly discusses MySQL Part of the knowledge of index . Will be from MySQL Index basis . Index Optimization Practice and data structure behind database index , Let's expand one by one . One .MySQL—— Index basis First , We'll start with the basics of indexing ...
Random recommendation
- Nginx-Lua The execution sequence of the modules
One .nginx Execution steps nginx In processing every user request , They are all dealt with according to several different stages in turn , It has nothing to do with the order on the configuration file , The details can be read < In depth understanding of nginx: Module development and architecture analysis > This book , ...
- v-show and v-if The difference between
v-show and v-if The difference between
- obj-c Noun
class : Class (description/template for an object) example : Instance (manifestation of a class) news : Message ...
- Rewrite step by step CodeIgniter frame (7) —— Controller At the time of execution Model The obtained data is transferred into View in , Realization MVC
1. Implementation process 1) The last section talked about View View loading process , It's in Loader Class , And pass Include Statement to contain . So in order to View Pass variables in , Only need include The sentence is ...
- In personal projects WCF Use
I have nothing to do today , Let me share with you one of my projects WCF Use . My project uses Silverlight, The same is true for other types of use . 1. Build a Silverlight belt Web Project solution . 2. stay w ...
- UWP--MVVM Simple calculator
namespace LBI.DataBinding { /// <summary> /// It can be used for itself or to navigate to Frame Blank pages inside . /// </summary> pub ...
- The box model bug And trigger bfc
One .margin Merge css classic bug Two block level elements Set separately margin-bottom and margin-top It can not achieve the expected effect <style> .up{ width: 200 ...
- How to verify Certificate Pinning?
Some friends of mine they worry about the risk of Man-in-the-middle so they ask me how to verify the ...
- 【 The third day of training · Crazy training 】 Oh , By the way manacher
It's crazy training, though , But I didn't write many questions , I'm familiar with the operation of stretching the tree ,ac 了 5 A title . There's nothing to make complaints about all day. , In addition to a friend who played games in the computer room yesterday, he talked to the coach after rollover 2333 Go ahead .. 1.BZOJ1208 H ...
- Linux0.11 The boot process
Power up from Startup , To carry out main Procedure before function ok , There should be execution 3 An assembly file , But I don't know much about . Embarrassed from main function , To start OK( You can respond to user actions ) This step is done 3 thing : Create a process 0, Make it in the Lord ...









