当前位置:网站首页>Isn't this another go bug?
Isn't this another go bug?
2022-06-24 00:45:00 【Insect catching master】
hello, Hello, everyone , I'm a small building .
Recently, I wrote another article by once again BUG, An online service is deadlocked , But thanks to a new service , No big impact .
What's wrong is Go Read and write lock of , If you write Java Of , No need to row away , Let's take a look at this article , The focus of this paper is Java and Go Read / write lock comparison , Even after reading it, you will have a faint feeling :Go Is there a read-write lock for BUG?
Fault playback
The background is simply abstracted : One server service (Go Language implementation ), Provides a http Interface , Another one client Service to invoke this interface , The overall architecture is very simple , You can understand it even without a easel .
These two services have been running online for some time without any problems , And then one day client Call this server All the interfaces of have timed out .
We have this kind of problem , Check the log and monitor at the first time ,client The end is full of timeout logs ,server There is no exception in the end log , Even the requested monitoring was not reported , as if client The request from the end did not arrive server The same .
So I went to server The server manually requested an interface , As a result, the card owner does not move , This rule out client, It must be server Something went wrong with the end .
This kind of stuck problem is actually very easy to check , Direct use pprof You can basically draw a conclusion by looking at the location of the synergy card ( and Java Of jstack Similar tools ), But this service is not enabled pprof, Can only change the code to open pprof Re release , Wait for the next problem to recur .
Good luck ,2 The problem came out days later , use pprof Look where the program card is :

It turns out that you are stuck in a place where you can judge whether the cluster or service is a small traffic , This interface will accept a parameter of cluster name or service name , Then judge whether the cluster or service is a small traffic cluster , And then do a series of things , It doesn't matter what you did . Small traffic clusters are configured in the configuration center .
I'll take this code out ( The figure shows the branch of the judgment cluster , The following code is explained in a simpler service branch , The bottom layer is consistent ). To avoid voids , Here I will briefly explain the logic of the program :
- First, the configuration of small traffic defines a read / write lock (sync.RWMutex), And the rules of which services need grayscale are kept in memory (scopesMap)

- Called when the configuration changes reset Refresh this scopesMap, Write lock , The following logic is omitted

- Determine whether it is grayscale service , First, add a read lock to see if the rule exists :

- Add a lock to determine whether the service hit the rule :

Circle the key points in this way , You may see the problem at a glance , Read the lock twice , The second time is not necessary , It's a mistake . exactly , Delete the second code that adds a read lock . If things end here , There is no need to write this article , Let's analyze why the deadlock occurs .
Why is deadlock
See the result , My first reaction was Go The lock of Reentrant problem .
be familiar with Java My classmates are no strangers to lock reentry , In case some readers don't understand the reentry of the lock , I want to sum it up in one sentence :
Reentrant lock It's a lock that can be accessed repeatedly , Also called Recursive lock .
Java There is one of them. ReentrantLock, Such as this , There is no problem with locking repeatedly :

but Go The lock inside is not reentrant :

I've stepped on this pit too , This is a Go The realization of . If you will , use Java It can also realize non reentrant lock , but Java Most of them use reentrant locks , Because it's more convenient to use .
as for Go Why not implement a reentrant lock , You can refer to this article of fried fish boss 《Go Why not support reentrant locks ?》, The reason can be summed up as Go The designers of the re-entry lock think the re-entry lock is a bad design , So I didn't adopt . But I think the comments in this article are more wonderful :

Speaking of this , You might say , The problem above is obviously a read-write lock (sync.RWMutex), What are the characteristics of read-write locks ?
- Reading and reading are not mutually exclusive
- Read and write 、 Write and write are mutually exclusive
Since read locks are not mutually exclusive , That is, you can add a read lock twice , Then reading locks must be Reentrant Of . We write a demo Under test :

As we expected , By the way, let's take a look at the logic of adding read locks :
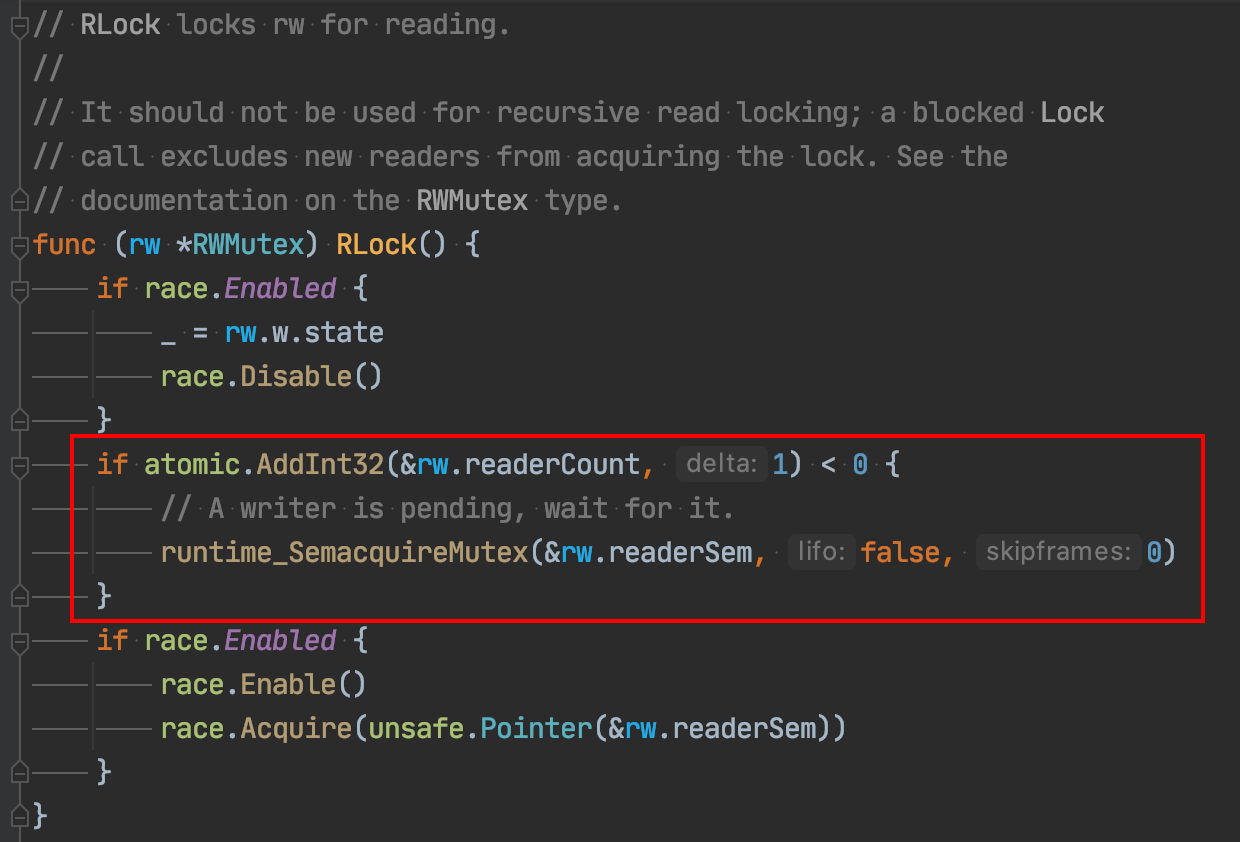
Look at the code I framed , If there is a write lock waiting , Read lock needs to wait for write lock !

What's the logic ?
If a coroutine has obtained the read lock , Another coroutine tries to add a write lock , It should not be added at this time , No problem . If the lock reading process goes to get the lock , Need to wait for write lock , This is a deadlock !
In order to verify , I constructed a demo:
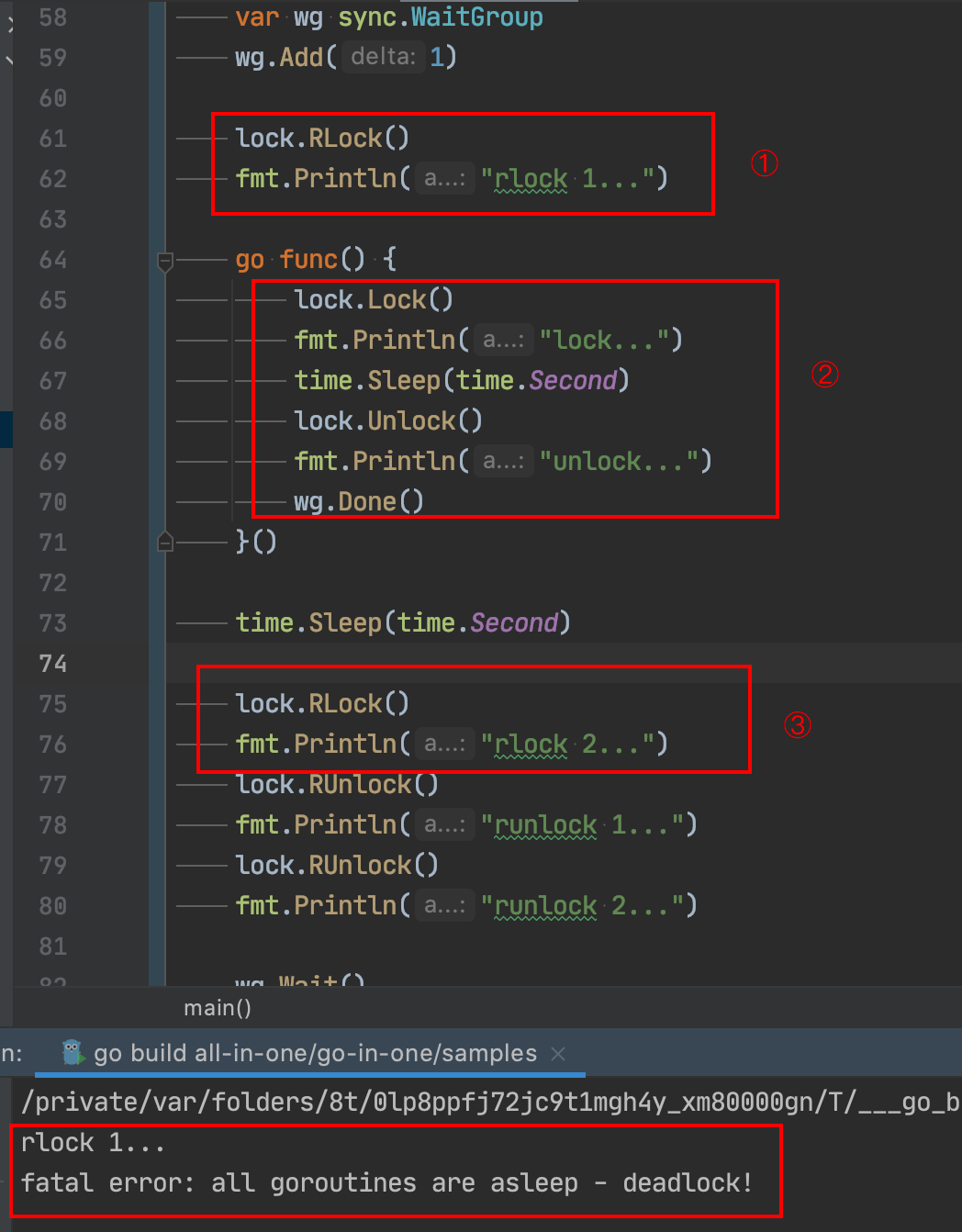
This code is pressed ①、②、③ Sequential execution , The first ② The segment write lock needs to be equal ① A read lock is released , The first ③ Segment read lock needs to wait ② Segment write lock release , Finally, it is a deadlock logic .
Think about it , The most controversial of these is Once the read lock has been obtained, you need to wait for the write lock to enter the read lock again This logic .
Java Is this the case in ? Write a demo try :
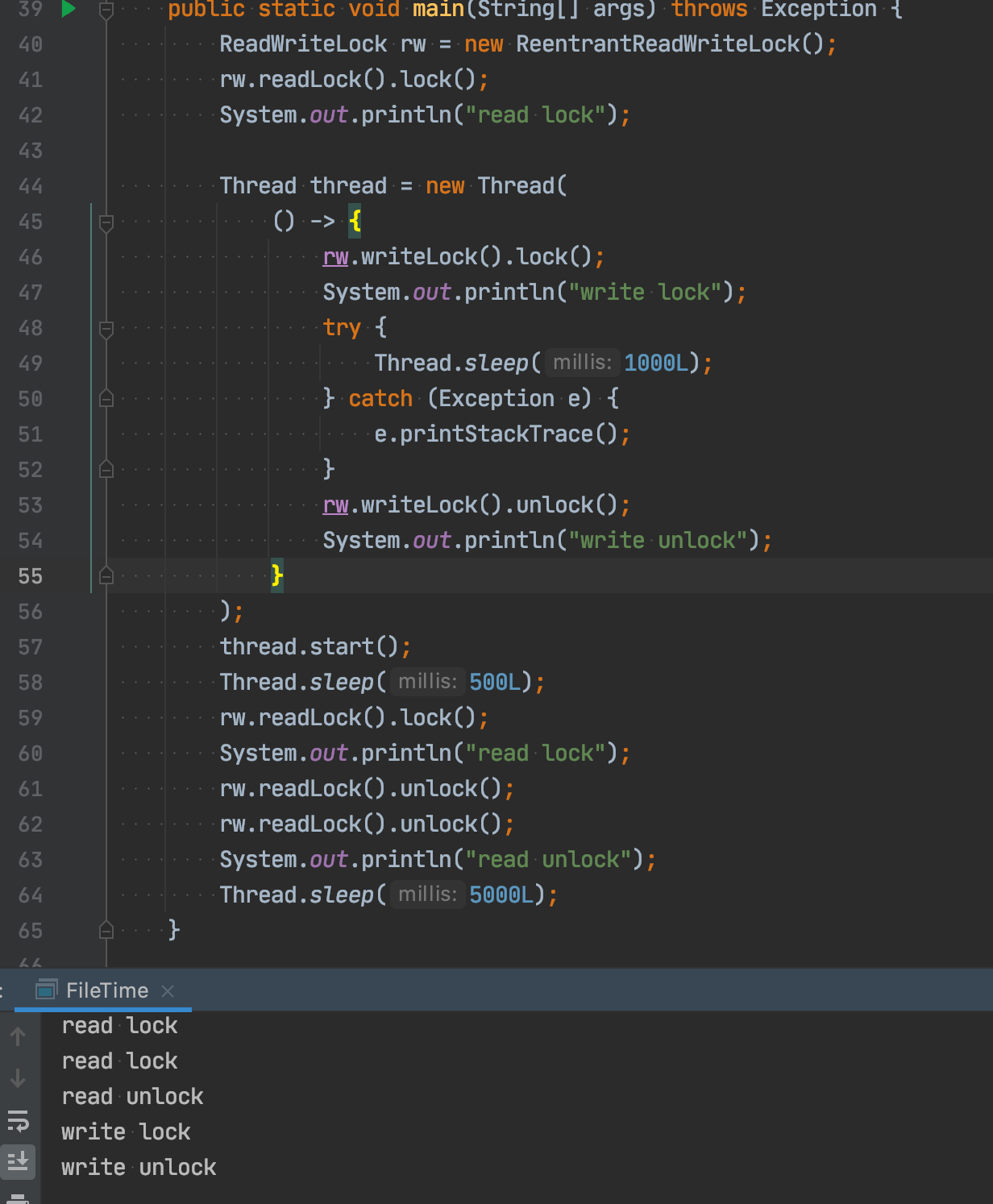
Java There is nothing , Why is this ? Never decide , Look at the source code ! but Java The source code is too long , It is not the focus of this article , So just a few important conclusions :
- Java Of ReentrantReadWriteLock Support lock
Downgrade, But notupgrade, That is, the thread that has obtained the write lock , Can continue to get read lock , But the thread that obtains the read lock can no longer obtain the write lock ; - ReentrantReadWriteLock It realizes fair and unfair locks , In the case of fair lock , Get read lock 、 Before writing a lock, you need to check whether the threads in the synchronization queue are queued before me ; In case of unfair lock : Write locks can directly preempt locks , But read lock acquisition has a concession condition , If the current synchronization queue head.next Is a write lock waiting , And they are not re - entrants , You have to give in and wait .
stay Java Under the realization of , If a thread holds a read lock , Writing locks naturally requires waiting , But the thread holding the read lock can also re-enter the read lock again .
We found that Java and Go The read-write lock implementation of is inconsistent , This inconsistency leads us to write BUG Why .
Is that reasonable?
Put aside implementation , Let's think about whether this is reasonable ?
- An agreement ( Or thread ) The read lock has been obtained , Other processes ( Threads ) When acquiring a write lock, you must wait for the release of the read lock
- Since this process ( Or thread ) You already have this read lock , So why do I need to wait for another write lock when I get a read lock again ?
Imagine patients queuing up to see doctors , The patient in front asked the doctor , Close the door when you go in , No matter how long you ask inside ( Theoretically ) It's his right , The patient in the back can't open the door until he comes out .
but Go The implementation of is , The former patient had to look at whether there was someone waiting outside the door after each sentence , If someone is waiting , Then he has to wait until the people outside the door have finished asking , But people outside the door are waiting for him to ask , So everyone is locked , Nobody wants to finish seeing a doctor .
Think it over , Feel if this is Go One of the BUG?
Go Why is this achieved
I try to github Did a search on , Found this issue:
https://github.com/golang/go/issues/30657
It can be seen from the title that he has the same problem as me :
Read-locking shouldn’t hang if thread has already a write-lock? #30657
Let's see what someone inside said :
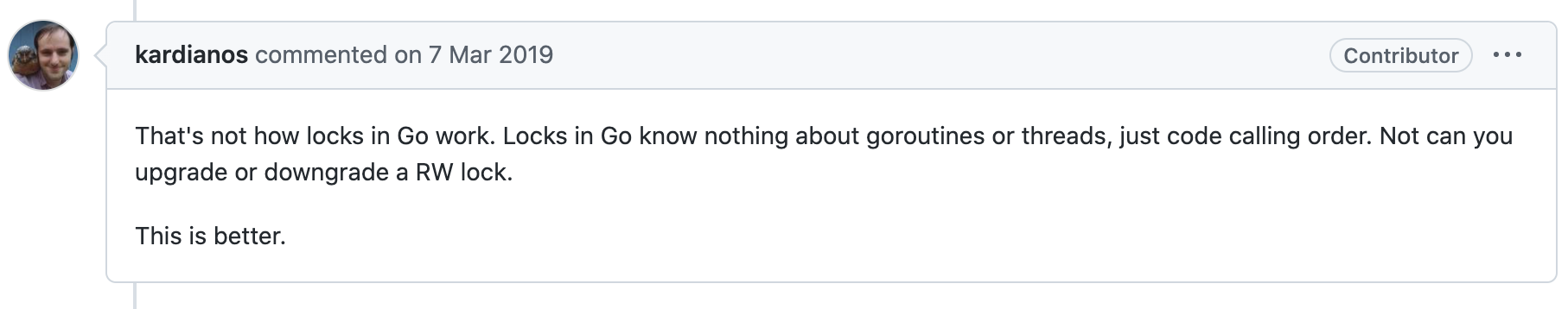
The big man said , This is not true. Go Principle of lock ,Go The lock of does not know the information of the process or thread , Only know the sequence of code calls , That is, the read-write lock cannot be upgraded or degraded .
Java The lock in records the holder ( Threads id), but Go I don't know who the holder is , Therefore, after obtaining the read lock, obtain the read lock again , The logic here does not distinguish between the holder and other processes , So we will deal with it in a unified way .
This is actually Go The comments of the source code reflect , It was only later that I noticed :

Translated as :
If a coroutine holds a read lock , Another coroutine may call Lock Add write lock , Then no one can get a read lock anymore , Until the previous read lock is released , This is to prohibit read lock recursion . It also ensures that the lock is finally available , A blocked write lock call will exclude new read locks .
But this warning is really too inconspicuous , This is probably the effect :

This scene is very much like products and programmers :
- The product manager : I want to implement this function , I don't care how to achieve it
- Go: This undermines my design principles , This function is not accepted
- The product manager : Everybody step back , You can solve it in a less expensive way
therefore , The programmer wrote a comment on the read-write lock :

Last
This deadlock pit is really easy to step on , In especial Java Programmers write Go, So we write Go The code still needs to be written more Go Just a little .
Go The designers of 「 paranoid 」, Think 「 Not good. 」 We will never realize the design of , Just as the implementation of locks should not depend on threads 、 Process information ; Reentrant ( recursive ) A lock is a bad design . So this seems to have BUG The design of the , There is also a certain truth .
Of course, everyone has his own ideas , You feel Go Is it reasonable to implement the read-write lock in this way ?
If you feel something after reading it , Give me one Fabulous 、 Looking at Well , Your support is the driving force of my continuous creation ~
WeChat official account " Master bug catcher ", Back end technology sharing , Architecture design 、 performance optimization 、 Source code reading 、 Troubleshoot problems 、 Step on the pit practice .
边栏推荐
- Real time computing framework: Flink cluster construction and operation mechanism
- What are the two types of digital factories
- Vulnerability recurrence - redis vulnerability summary
- 分别用SVM、贝叶斯分类、二叉树、CNN实现手写数字识别
- Alibaba interview question: multi thread related
- 抓取开机logcat
- Jeecgboot old version 2 x 3. X how to integrate building block reports?
- [iccv workshop 2021] small target detection based on density map: coarse-grained density map guided object detection in aerial images
- Andorid development art exploration notes (2), cross platform applet development framework
- Building a digital software factory -- panoramic interpretation of one-stop Devops platform
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Shutter control layout
解决base64压缩文件,经过post请求解压出来是空格的问题
version `ZLIB_ 1.2.9‘ not found (required by /lib64/libpng16.so.16)
[CVPR 2022] high resolution small object detection: cascaded sparse query for accelerating high resolution smal object detection
牛学长周年庆活动:软件大促限时抢,注册码免费送!
CVPR2022 | 可精简域适应
Interview notes for Android outsourcing workers for 3 years. I still need to go to a large factory to learn and improve. As an Android programmer
C language: sorting with custom functions
Real time computing framework: Flink cluster construction and operation mechanism
应用配置管理,基础原理分析
Skywalking installation and deployment practice
【CVPR 2020 Oral】极低光去噪论文:A Physics-based Noise Formation Model for Extreme Low-light Raw Denoising
Android App bundle exploration, client development interview questions
Vulnerability recurrence - redis vulnerability summary
C语言:递归实现N的阶乘
【ICCV Workshop 2021】基于密度图的小目标检测:Coarse-grained Density Map Guided Object Detection in Aerial Images
CVPR2022 | 可精简域适应
社招面试必不可少——《1000 道互联网大厂 Android工程师面试题》
C语言:百马百担问题求驮法
Superscalar processor design yaoyongbin Chapter 3 virtual memory -- Excerpt from subsection 3.1~3.2