当前位置:网站首页>ServerSocket and socket connection
ServerSocket and socket connection
2022-06-25 00:21:00 【BY-91】
List of articles
summary :
ServerSocket class TCP agreement , Server side , adopt serveSocket.accept(); Method to get socket example
Socket class TCP agreement adopt new Socket() Get instance , establish Socket Object, you need to declare a IP Address and ServerSocket Port number of the object , Only in this way can a connection request be sent to the server
serverSocket.accept() Accept connection requests from clients , And return a socket . If you are not connected to the client , Thread is blocked , The program can't go on
A server can accept connection requests from multiple clients , But only for the first connected socket , Only communicate with the first client , No communication with other clients
If you want to serve multiple clients , Client requests that the server receives (Socket socket=serverSocket.accept()) In a cycle , In fact, it's equivalent to having N Servers , Of course, it can be with n Client communications
1.getInputStream Method can get an input stream , Client's Socket On the object getInputStream Method is actually the data sent back from the server .
2.getOutputStream Method gets an output stream , Client's Socket On the object getOutputStream The output stream obtained by the method is actually the data sent to the server .
Usage on server side
1.getInputStream Method gets an input stream , Server side Socket On the object getInputStream The input stream obtained by the method is actually the data stream sent from the client to the server .
2.getOutputStream Method gets an output stream , Server side Socket On the object getOutputStream The output stream obtained by the method is actually the data sent to the client .
Socket Communicate with the browser
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketTest {
//ServerSocket Do the service side
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*5];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);// Read data from client
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
// Read the file
// FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\img\\binder.jpg");
outputStream.write(" From the server ".getBytes());
// while ((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
// outputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
// }
outputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
outputStream.flush();// Send data to client
// fileInputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
// socket.close();
} catch (IOException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

Connection and communication
Server side ServerSocket:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);// Read data from client
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
outputStream.write(" I am the server ".getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
client Socket
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket = new Socket("192.168.1.43",8080);
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(" Message from client ".getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
// Read server messages
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}


Socket Keep connected communication
client
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Client {
public static final int port = 8080;
public static final String host = "localhost";
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Client Start...");
while (true){
Socket socket = null;
try{
// Creates a stream socket and connects it to the specified port number on the specified host
socket = new Socket(host,port);
// Read server-side data
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
// Send data to the server
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(outputStream);
System.out.println(" Send to server :\t");
String str = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)).readLine();
printStream.println(str);
String ret = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println(" Server return :"+ret);
// If received "OK" Then disconnect
if ("OK".equals(ret)) {
System.out.println(" The client will close the connection ");
Thread.sleep(500);
break;
}
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(" Client exception "+e.toString());
}finally {
if(null != socket){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException exception) {
socket = null;
System.out.println(" client finally abnormal :"+exception.toString());
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
Server side
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static final int port = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) {
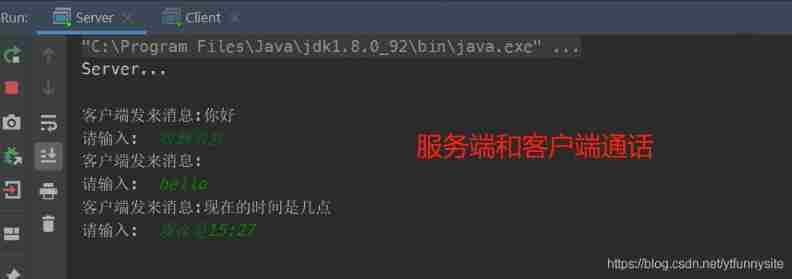
System.out.println("Server...\n");
Server server = new Server();
server.init();
}
private void init() {
try {
// Create a ServerSocket, Here you can specify the queue length of the connection request
//new ServerSocket(port,100); Means when there is... In the queue 100 The first connection request is , If Client Re request connection , Will be Server Refuse
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port,100);
while (true){
// Take a connection from the request queue
Socket socketClient = serverSocket.accept();
// Deal with connection
new HandlerThread(socketClient);
}
} catch (IOException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
private class HandlerThread implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public HandlerThread(Socket client) {
this.socket = client;
new Thread(this::run).start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
// Read client data , The reading and sending methods should be the same as those of the server , Otherwise, it will be thrown EOFException
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String clientMsg = bufferedReader.readLine();
// Processing client data
System.out.println(" The client sends a message :" + clientMsg);
// Reply to the client
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(outputStream);
System.out.print(" Please enter :\t");
String serverMsg = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)).readLine();
printStream.println(serverMsg);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException exception) {
System.out.println(" Server exception : " + exception.getMessage());
exception.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (null != socket){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException exception) {
socket =null;
System.out.println(" Server side finally abnormal :"+exception.toString());
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}

边栏推荐
- 颜色渐变梯度颜色集合
- 5G dtu无线通信模块的电力应用
- Ten commandments of self-learning in machine learning
- canvas线条的动态效果
- Reservoir dam safety monitoring
- Intensive reading of thinking about markdown
- Transition from digitalization to intelligent manufacturing
- [leaderboard] Carla leaderboard leaderboard leaderboard operation and participation in hands-on teaching
- Svg line animation background JS effect
- WordPress add photo album function [advanced custom fields Pro custom fields plug-in series tutorial]
猜你喜欢
![[leaderboard] Carla leaderboard leaderboard leaderboard operation and participation in hands-on teaching](/img/bd/b176e93ee6fa2125f021bcad3025c2.png)
[leaderboard] Carla leaderboard leaderboard leaderboard operation and participation in hands-on teaching

Color gradient gradient color collection
第三代电力电子半导体:SiC MOSFET学习笔记(五)驱动电源调研

【排行榜】Carla leaderboard 排行榜 运行与参与手把手教学

OTT营销之风正盛,商家到底该怎么投?

融合模型权限管理设计方案

C# Winform 最大化遮挡任务栏和全屏显示问题
How to use promise Race() and promise any() ?

为什么生命科学企业都在陆续上云?

Meta&伯克利基于池化自注意力机制提出通用多尺度视觉Transformer,在ImageNet分类准确率达88.8%!开源...
随机推荐
Svg+js keyboard control path
Analysis report on operation trend and investment strategy of global and Chinese tetrahydrofurfuryl propionate industry from 2022 to 2028
U.S. House of Representatives: digital dollar will support the U.S. dollar as the global reserve currency
人体改造 VS 数字化身
svg+js键盘控制路径
∞ symbol line animation canvasjs special effect
Design and practice of vivo server monitoring architecture
Microsoft won the title of "leader" in the magic quadrant of Gartner industrial Internet of things platform again!
After 5 years of software testing in didi and ByteDance, it's too real
为什么生命科学企业都在陆续上云?
Time unified system
December 6, 2019 what happens after the browser enters a URL
D manual destruction may violate memory security
Analysis report on operation pattern and supply and demand situation of global and Chinese cyano ketoprofen industry from 2022 to 2028
[leaderboard] Carla leaderboard leaderboard leaderboard operation and participation in hands-on teaching
The drawableleft of the custom textview in kotlin is displayed in the center together with the text
Difficult and miscellaneous problems: A Study on the phenomenon of text fuzziness caused by transform
Related operations of ansible and Playbook
Technology sharing | wvp+zlmediakit realizes streaming playback of camera gb28181
What is the difference between one way and two way ANOVA analysis, and how to use SPSS or prism for statistical analysis
